Professional Documents
Culture Documents
BioChem Lecture 2
Uploaded by
Feben grace MaglasangOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
BioChem Lecture 2
Uploaded by
Feben grace MaglasangCopyright:
Available Formats
BIOCHEMISTRY MC3112
Biochem Lecture 2.docx FOR CON 1A(NON-STEM)
Open with Google Docs
MTH 7:30-9:00 (LECTURE); MTH 5:00-8:00 (LABORATORY)
Page 1 of 5
Announcement
Maria Teresa Pangilinan • Yesterday (Edited Yesterday)
Biochem Lecture Notes 2
LECTURE CARBOHYDRATES
A. INTRODUCTION
Biochem Lecture 1.docx
- commonlyWord
known as SUGARS (polar and water-soluble); hydrate of carbon
Polar - a covalent bond between two atoms where the electrons forming the bond
are unequally distributed; one is negative and one is positive
Biochem Lecture 2.docx
Word
- are the most abundant class of bioorganic molecules on planet earth. Although their abundance in the
human body is relatively low.
- Carbohydrates constitute about 75% by mass of dry plants.
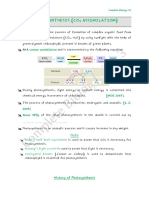
- Green(chlorophyll-containing) plants produce carbohydrates via photosynthesis. In this process, carbon
Biochem
dioxide from the air and water fromLecture
the soil are 3.docx
the reactants, and sunlight absorbed by the chlorophyll is
the energy source. Word
chlorophyll
CO 2 + H 2 O + solar energy -------------------- carbohydrates + O 2
Plant enzymes
Biochem Lecture 4.docx
Plants have two mainWorduses for the carbohydrates they produce. In the form of cellulose (chief part of the
cell walls of plants; usually fibrous), carbohydrates serve as structural elements, and in the form of starch,
they provide energy reserves for the plants.
Dietary intake of plant materials is the major carbohydrate source for humans and animals. The
average
Classhuman diet should ideally be about 2/3 carbohydrates by mass.
comments
Carbohydrates have the following functions in humans:
Add class comment…
1. Carbohydrate oxidation provides energy.
2. Carbohydrate storage in the form of glycogen, provides a short-term energy reserve.
3. Carbohydrates supply carbon atoms for the synthesis of other biochemical substances
(proteins, lipids and nucleic acids)
4. Carbohydrates form part of the structural framework of DNA and RNA molecules
Page 1 / 5
You might also like
- BIOL 307 Biochemistr Y: by Çağdaş D. SonDocument101 pagesBIOL 307 Biochemistr Y: by Çağdaş D. SonMetehan KaraNo ratings yet
- Microbiology MCQS: BacteriaDocument13 pagesMicrobiology MCQS: BacteriaIqbal HussainNo ratings yet
- Activate 2 Biology Chapter2 AnswersDocument8 pagesActivate 2 Biology Chapter2 AnswersJohn Lebiz100% (1)
- S7 End-Of-unit Test 1Document2 pagesS7 End-Of-unit Test 1Dr Ahmed Reyad83% (6)
- Unit 2 - Envi Sci HandoutsDocument2 pagesUnit 2 - Envi Sci HandoutsRuby SamarNo ratings yet
- Module in Carbohydrates PDFDocument19 pagesModule in Carbohydrates PDFAndreiNo ratings yet
- Kami Export - Cycles ActivityDocument9 pagesKami Export - Cycles ActivityEthan BompartNo ratings yet
- Plant Nutrition: Biology Study Guide: Term AnalysisDocument7 pagesPlant Nutrition: Biology Study Guide: Term Analysisapi-356944076No ratings yet
- Modes of NutritionDocument14 pagesModes of NutritionastakuneruNo ratings yet
- c6 ClimatechangeDocument35 pagesc6 ClimatechangeJohn Michael SomorostroNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document70 pagesChapter 1nidNo ratings yet
- Ecology Revision ListDocument6 pagesEcology Revision ListFULYA YALDIZNo ratings yet
- ES202L-Part 1 - (GPRoy)Document60 pagesES202L-Part 1 - (GPRoy)Adnan RizviNo ratings yet
- BioenergeticsDocument3 pagesBioenergeticsGabrielle VaporNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis 1Document14 pagesPhotosynthesis 1Kithmini100% (1)
- Nabila Tisa Lathifah - Week 2Document11 pagesNabila Tisa Lathifah - Week 2Nabila LathifahNo ratings yet
- Session - 7 Unit - III Material Cycles: Dr. H.S. RameshDocument48 pagesSession - 7 Unit - III Material Cycles: Dr. H.S. Rameshadithya700No ratings yet
- ÇM Book 6Document20 pagesÇM Book 6Eğitim ParaylaNo ratings yet
- Cultivation of BacteriaDocument16 pagesCultivation of Bacteriakauser banuNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Physiology and Disease For The Health Professions 3rd Edition Booth Solutions ManualDocument25 pagesAnatomy Physiology and Disease For The Health Professions 3rd Edition Booth Solutions ManualCathyHowardokqm100% (64)
- Effect of Light/dark Cycles On Wastewater Treatments by MicroalgaeDocument2 pagesEffect of Light/dark Cycles On Wastewater Treatments by MicroalgaeGregorius BudiantoNo ratings yet
- UNIT - 02 Food & Nutrition Introduction To The ChapterDocument10 pagesUNIT - 02 Food & Nutrition Introduction To The ChapterNeha HenstridgeNo ratings yet
- Role of MicrobesDocument7 pagesRole of MicrobesPreetiSinghNo ratings yet
- What Ecological Systems Can You Think Of?Document23 pagesWhat Ecological Systems Can You Think Of?abioticbiotic666No ratings yet
- Natsci 02Document2 pagesNatsci 02Sofia Coleen Naluaran TemplonuevoNo ratings yet
- Microbio Unit 2-2 - MergedDocument39 pagesMicrobio Unit 2-2 - MergedVaibhavNo ratings yet
- Integrated Principles of Zoology 16th Edition Hickman Solutions ManualDocument7 pagesIntegrated Principles of Zoology 16th Edition Hickman Solutions ManualMichaelBrewerpfexa100% (16)
- Biological MoleculesDocument38 pagesBiological MoleculesmuzammalNo ratings yet
- Biotechnology Basics and ApplicationsDocument12 pagesBiotechnology Basics and ApplicationsHabiba AmrNo ratings yet
- PHOTOSYNTHESISDocument4 pagesPHOTOSYNTHESISNANDITA NAYAK BNo ratings yet
- Chapter II - The EcosystemDocument7 pagesChapter II - The EcosystemJhon Lloyd Zarco BantigueNo ratings yet
- Written Report On MicrophyDocument13 pagesWritten Report On MicrophyAustin Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- 12.metabolism of MicrobesDocument46 pages12.metabolism of MicrobesSubhi MishraNo ratings yet
- Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering Subject Code: Cy1201 Environmental Science & EnggDocument20 pagesDepartment of Electronics and Communication Engineering Subject Code: Cy1201 Environmental Science & EnggJohn BerkmansNo ratings yet
- Carbon Cycle PDFDocument9 pagesCarbon Cycle PDFheyitsmemuahNo ratings yet
- Bio 20 Unit C Topic 3 - Biogeochemical CyclesDocument18 pagesBio 20 Unit C Topic 3 - Biogeochemical CyclesUnzal FatehullahNo ratings yet
- Biology Presentation From Havish - Chapter 01Document12 pagesBiology Presentation From Havish - Chapter 01devprasad472010No ratings yet
- ECOSYSTEM: Life Energy: What I Need To KnowDocument16 pagesECOSYSTEM: Life Energy: What I Need To KnowJunriel Arig BonachitaNo ratings yet
- AECC-I Env - Science - Question and Answers 2022-23Document23 pagesAECC-I Env - Science - Question and Answers 2022-23Eshwar PasulaNo ratings yet
- How To Be A PlantDocument12 pagesHow To Be A PlantsextansNo ratings yet
- Effluent Treatment2Document14 pagesEffluent Treatment2Mirza Md. Nazmus SakibNo ratings yet
- Ecology G 12Document209 pagesEcology G 12Samuel LegissaNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual For Integrated Principles of Zoology 16th Edition Hickman Keen Larson Eisenhour Anson Roberts 0073524212 9780073524214Document35 pagesSolution Manual For Integrated Principles of Zoology 16th Edition Hickman Keen Larson Eisenhour Anson Roberts 0073524212 9780073524214daniel.mercer243100% (11)
- Solution Manual For Integrated Principles of Zoology 16th Edition Hickman Keen Larson Eisenhour Anson Roberts 0073524212 9780073524214Document36 pagesSolution Manual For Integrated Principles of Zoology 16th Edition Hickman Keen Larson Eisenhour Anson Roberts 0073524212 9780073524214coleclarkgsqodbprfz100% (29)
- Integrated Principles of Zoology 16th Edition Hickman Keen Larson Eisenhour Anson Roberts Solution ManualDocument7 pagesIntegrated Principles of Zoology 16th Edition Hickman Keen Larson Eisenhour Anson Roberts Solution Manualtiffany100% (27)
- Photoautotrophic Lithotrophs Photoheterotrophic Organotrophs Chemoautotrophic Lithotrophs Chemoheterotrophic OrganotrophsDocument2 pagesPhotoautotrophic Lithotrophs Photoheterotrophic Organotrophs Chemoautotrophic Lithotrophs Chemoheterotrophic OrganotrophsHitesh MoreNo ratings yet
- Bio Final Exam 1Document13 pagesBio Final Exam 1kabinskiNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 ReviewDocument10 pagesUnit 4 Reviewapi-259727482No ratings yet
- Science and Technology - II Energy Flow in An Ecosystem: NandnDocument6 pagesScience and Technology - II Energy Flow in An Ecosystem: NandnAnushka RajputNo ratings yet
- Lecture 29 - Metabolism Part 1Document17 pagesLecture 29 - Metabolism Part 1Loago SeropolaNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE-8-Q4-M-6-cycle of MaterialsDocument3 pagesSCIENCE-8-Q4-M-6-cycle of MaterialsDesiree de GuzmanNo ratings yet
- UNIT I Gen Bio ReviewerDocument4 pagesUNIT I Gen Bio ReviewerKym DacudaoNo ratings yet
- Adenosine Triphosphate ATP ATP Currency Used Throughout The Cell. Energy Carrier For Cells Mechanical Work To Move Cilia and Vesicles Transport Substances Across The Membrane and Perform Variou 1Document4 pagesAdenosine Triphosphate ATP ATP Currency Used Throughout The Cell. Energy Carrier For Cells Mechanical Work To Move Cilia and Vesicles Transport Substances Across The Membrane and Perform Variou 1Kurt IgotNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis: Photosynthesis Is A Process Used by Plants and OtherDocument19 pagesPhotosynthesis: Photosynthesis Is A Process Used by Plants and OtherJay RonssonNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis CO AssimilationDocument30 pagesPhotosynthesis CO AssimilationUttam GurungNo ratings yet
- Lesson 11 BPPDocument20 pagesLesson 11 BPPMa LeslynneNo ratings yet
- Plants and Environment Factors - The PlantDocument33 pagesPlants and Environment Factors - The PlantRania PrastiwiNo ratings yet
- Dwnload Full Integrated Principles of Zoology 16th Edition Hickman Solutions Manual PDFDocument26 pagesDwnload Full Integrated Principles of Zoology 16th Edition Hickman Solutions Manual PDFrasbimzorij100% (8)
- Full Download Integrated Principles of Zoology 16th Edition Hickman Solutions ManualDocument35 pagesFull Download Integrated Principles of Zoology 16th Edition Hickman Solutions Manualniekamperrodc100% (33)
- CH2501 Atmospheric Chemistry Course NotesDocument23 pagesCH2501 Atmospheric Chemistry Course NotesElle WoodsNo ratings yet
- Two Marks Questions With Answers - WWW - Eeenotes.InDocument23 pagesTwo Marks Questions With Answers - WWW - Eeenotes.InsmikedaneNo ratings yet
- Unit 7 Structure and Function of Living ThingsDocument82 pagesUnit 7 Structure and Function of Living ThingsSUMMER JORDAN CARLUENNo ratings yet
- Algowhite BrochureDocument11 pagesAlgowhite BrochureSham SajaNo ratings yet
- Worksheet - I: Biology XDocument7 pagesWorksheet - I: Biology XDharmendra SinghNo ratings yet
- ID Kesembuhan Skin Flap H Plasty Dan Linear PDFDocument7 pagesID Kesembuhan Skin Flap H Plasty Dan Linear PDFAndhika GilangNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 - PerceptionDocument5 pagesLecture 4 - PerceptionCynthia WhelehanNo ratings yet
- Vestigial Organs 1Document3 pagesVestigial Organs 1api-711119679No ratings yet
- Energy HealingDocument22 pagesEnergy HealingSwami AbhayanandNo ratings yet
- Class11 Biology Biology - 2019 Set - 1Document11 pagesClass11 Biology Biology - 2019 Set - 1priyaNo ratings yet
- Muscle Fiber Type Transitions With Exercise Training: Shifting PerspectivesDocument11 pagesMuscle Fiber Type Transitions With Exercise Training: Shifting PerspectivesEnzoNo ratings yet
- Wa0006.Document12 pagesWa0006.Jose VillasmilNo ratings yet
- USPDocument2 pagesUSPheocon857351No ratings yet
- Animal Kingdom - Practice Sheet - Aarambh NEET 2024Document9 pagesAnimal Kingdom - Practice Sheet - Aarambh NEET 2024gotisk2000No ratings yet
- Cellulalar and Tissue ChangesDocument11 pagesCellulalar and Tissue ChangesKiranNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Human Physiology 16th Edition Stuart Fox Krista RompolskiDocument36 pagesTest Bank For Human Physiology 16th Edition Stuart Fox Krista Rompolskidualinvair.kriub398% (46)
- Lehninger - 7e - PPT - ch05 - Final (Autosaved)Document53 pagesLehninger - 7e - PPT - ch05 - Final (Autosaved)Chance SwansonNo ratings yet
- Brochure PHYSICON 2019Document2 pagesBrochure PHYSICON 2019Amit SinghNo ratings yet
- SR Elite (Set - 2), SR Aiims S60 & Neet MPL Neet Module Test - 3 Paper (01-04-2024)Document26 pagesSR Elite (Set - 2), SR Aiims S60 & Neet MPL Neet Module Test - 3 Paper (01-04-2024)prabha bandaruNo ratings yet
- ANA101 Respiratory System DR GIEDocument44 pagesANA101 Respiratory System DR GIEMarian Kyla MarianoNo ratings yet
- Biology Presentation of Group 2Document45 pagesBiology Presentation of Group 2Ummi Robbania MushthofaNo ratings yet
- 106生物Document16 pages106生物德瑞克No ratings yet
- Physiological Psychology Lecture 3 MidtermDocument2 pagesPhysiological Psychology Lecture 3 MidtermAngelo SumaoyNo ratings yet
- National Grade Six Assessment ScienceDocument11 pagesNational Grade Six Assessment ScienceGrace EtwaruNo ratings yet
- Small Animal Massage TherapyDocument7 pagesSmall Animal Massage TherapyShayne ShotNo ratings yet
- Buenasher Learning Academy IncDocument4 pagesBuenasher Learning Academy IncEl CruzNo ratings yet
- Psychology: History & PerspectivesDocument32 pagesPsychology: History & PerspectivesTreblig Dominiko MartinezNo ratings yet
- The Cell Membrane: Homeostasis & Cellular TransportDocument23 pagesThe Cell Membrane: Homeostasis & Cellular TransportMarifer DapatNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiolgyDocument12 pagesAnatomy and PhysiolgyIvy cencie AgawinNo ratings yet
- DLL - Science 6 - Q2 - W4Document6 pagesDLL - Science 6 - Q2 - W4AnatasukiNo ratings yet