Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Global Health Explaination
Uploaded by
Blessy Biju0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views2 pagesInfectious diseases are caused by foreign agents like viruses, bacteria, parasites or fungi. They cause symptoms like fever, nausea, vomiting, skin rashes, coughing and diarrhea depending on the type of disease. Some common infectious diseases include the flu, UTIs, pneumonia, tuberculosis, the common cold, HPV, and malaria. HIV/AIDS is caused by the HIV virus and can be transmitted sexually or from mother to child. It attacks white blood cells and weakens the immune system. Tuberculosis is caused by the Mycobacterium tuberculosis bacteria, usually affects the lungs, and can be transmitted through the air from those with an active infection.
Original Description:
Original Title
GLOBAL HEALTH EXPLAINATION
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentInfectious diseases are caused by foreign agents like viruses, bacteria, parasites or fungi. They cause symptoms like fever, nausea, vomiting, skin rashes, coughing and diarrhea depending on the type of disease. Some common infectious diseases include the flu, UTIs, pneumonia, tuberculosis, the common cold, HPV, and malaria. HIV/AIDS is caused by the HIV virus and can be transmitted sexually or from mother to child. It attacks white blood cells and weakens the immune system. Tuberculosis is caused by the Mycobacterium tuberculosis bacteria, usually affects the lungs, and can be transmitted through the air from those with an active infection.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views2 pagesGlobal Health Explaination
Uploaded by
Blessy BijuInfectious diseases are caused by foreign agents like viruses, bacteria, parasites or fungi. They cause symptoms like fever, nausea, vomiting, skin rashes, coughing and diarrhea depending on the type of disease. Some common infectious diseases include the flu, UTIs, pneumonia, tuberculosis, the common cold, HPV, and malaria. HIV/AIDS is caused by the HIV virus and can be transmitted sexually or from mother to child. It attacks white blood cells and weakens the immune system. Tuberculosis is caused by the Mycobacterium tuberculosis bacteria, usually affects the lungs, and can be transmitted through the air from those with an active infection.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
DEFINITION
So infectious disease means that the disease is caused by any causative
agent, such as a virus, bacteria, parasite, or fungus, and it basically
means that any foreign body entered our body and released toxins later
on to fight the host cells or that body's cells wherever they are in the
body depending on where they are. It has different symptoms
depending on the kind, but it usually causes fever, nausea, vomiting,
skin rashes, itching, coughing, sneezing, and diarrhea.
TYPES OF DISEASES
So when we talk about those types of diseases, we have to include
diseases like flu, UTI or urinary tract infection, pneumonia, TB or
tuberculosis, common cold which is very common everywhere, human
papillomavirus which causes warts which are not cancerous but are an
abnormal skin growth, Malaria which is caused by mosquitos and
causes high fever, HIV/AIDS or acquired immunodeficiency syndrome
which is an STD (sexually transmitted disease).
HIV/AIDS
So one of the most well-known is HIV/AIDS, which is caused by a virus
called lentivirus that, as previously said, is spread through sexual
contact, Mother-to-child contact during pregnancy and nursing,
contaminated blood, sharing needles, and drug use. So it can be
transmitted in a variety of ways, and because it attacks the body's
immune system, specifically white blood cells, and reduces their
number, the body becomes more vulnerable and susceptible to a
variety of other diseases such as cytomegalovirus, some cancers, or
infections from other types of viruses, fungi, and protozoa. So these
patients are also at risk if they have other sexually transmitted illnesses
such as herpes type 2, gonorrhea, or syphilis.
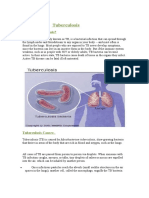
TUBERCULOSIS -TB
Another common infectious disease is tuberculosis (TB), which mostly
affects the lungs and is caused by the bacteria Mycobacterium
tuberculosis. Most of the time, there are no symptoms, which is known
as latent infection. About 10% of those latent infections become active,
and if not treated properly, it can kill nearly half of those infected. If it is
persistent, it will induce a bloody cough with mucus, fever, cold sweats,
and weight loss. It is communicated through the air from one person to
another by persons who do not have a latent infection but an active
form of tuberculosis.
You might also like
- Grade 9 Why Do We Fall IllDocument43 pagesGrade 9 Why Do We Fall IllMehala Sri AurobindoNo ratings yet
- TP 1Document8 pagesTP 1nitesh tirkeyNo ratings yet
- Infectious DiseasesDocument4 pagesInfectious DiseasesBlessy BijuNo ratings yet
- Infectious or Communicable DiseasesDocument2 pagesInfectious or Communicable DiseasesДария КоваленкоNo ratings yet
- Cours tuberculosediabetEBOAHIVDocument18 pagesCours tuberculosediabetEBOAHIVhamedpourlesmeufsNo ratings yet
- Topic: - Disease: Dr. Homi Bhabha Competition Test SeriesDocument10 pagesTopic: - Disease: Dr. Homi Bhabha Competition Test SeriesHarshaWakodkarNo ratings yet
- Symptoms: by Mayo Clinic StaffDocument32 pagesSymptoms: by Mayo Clinic StaffLourghem Libut FerrerNo ratings yet
- Why Do We Fall Ill 2Document3 pagesWhy Do We Fall Ill 2Shreyashkar JhaNo ratings yet
- Why Do We Fall Ill Class 9Document7 pagesWhy Do We Fall Ill Class 9Madhav Lohchab100% (1)
- What Is Tuberculosis?Document10 pagesWhat Is Tuberculosis?samira_666No ratings yet
- Chronic Inflammation of The Thin Tissue Lining Each Air Sac Causes Scarring and Makes The Sacs Less FlexibleDocument8 pagesChronic Inflammation of The Thin Tissue Lining Each Air Sac Causes Scarring and Makes The Sacs Less FlexibleRosalina MarilaoNo ratings yet
- The Big Book of Infectious Disease Trivia: Everything You Ever Wanted to Know about the World's Worst Pandemics, Epidemics and DiseasesFrom EverandThe Big Book of Infectious Disease Trivia: Everything You Ever Wanted to Know about the World's Worst Pandemics, Epidemics and DiseasesNo ratings yet
- HEALTH 8: Communicable DiseaseDocument31 pagesHEALTH 8: Communicable DiseaseElissah S PabilonaNo ratings yet
- TuberculosisDocument8 pagesTuberculosisArathi KarshNo ratings yet
- TUBERCULOSISDocument6 pagesTUBERCULOSISByzid ByzidNo ratings yet
- Poppy Tia AndriaDocument2 pagesPoppy Tia AndriaT. RAHMADANINo ratings yet
- Why Do We Fall IllDocument11 pagesWhy Do We Fall IllSara SultanaNo ratings yet
- Writing Techniques: DescriptionDocument7 pagesWriting Techniques: DescriptionGlenda B AjilaNo ratings yet
- What Is TuberculosisDocument6 pagesWhat Is Tuberculosissachin002kypNo ratings yet
- Form 2 Chap 4 DiseasesDocument15 pagesForm 2 Chap 4 Diseasesscribble_55No ratings yet
- Basic Health Care Series: Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STD)From EverandBasic Health Care Series: Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STD)Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Bio Board Project-1Document22 pagesBio Board Project-1Nikita LotlikarNo ratings yet
- By Mayo Clinic Staff: When To See A DoctorDocument5 pagesBy Mayo Clinic Staff: When To See A DoctorKimberly SolisNo ratings yet
- TUBERCULOSISDocument4 pagesTUBERCULOSISamirNo ratings yet
- Mode of Infection of DiseaseDocument14 pagesMode of Infection of Diseasekhalid100% (1)
- Pharmacotherapeutics PDFDocument30 pagesPharmacotherapeutics PDFprazol shresthaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2Document53 pagesLecture 2Amar Wadood KhanNo ratings yet
- Article Tuberculosis (Module)Document1 pageArticle Tuberculosis (Module)The FigureNo ratings yet
- Classification of Communicable DiseasesDocument40 pagesClassification of Communicable Diseasesvarshasharma0575% (8)
- Communicable Diseases: Upgrade To Access Full EssayDocument2 pagesCommunicable Diseases: Upgrade To Access Full EssayBrendan B. MastayNo ratings yet
- Viral Vistas: Insights into Infectious Diseases: The Invisible War: Decoding the Game of Hide and Seek with PathogensFrom EverandViral Vistas: Insights into Infectious Diseases: The Invisible War: Decoding the Game of Hide and Seek with PathogensNo ratings yet
- DengueDocument2 pagesDengueJonavia Jumaylab MahumasNo ratings yet
- CH 14 EpidemiologyDocument33 pagesCH 14 EpidemiologyCangelkween Krixen BautistaNo ratings yet
- A. PandemicsDocument21 pagesA. Pandemicsakarshverma01No ratings yet
- Sexually Transmitted DiseasesDocument64 pagesSexually Transmitted DiseasesClinton BradleyNo ratings yet
- Bacterial InfectionsDocument20 pagesBacterial InfectionsFahad RasheedNo ratings yet
- Communicable Disease: List of Communicable DiseasesDocument13 pagesCommunicable Disease: List of Communicable DiseasesjasmineNo ratings yet
- Hivebolatuberculiosis DiabetesDocument18 pagesHivebolatuberculiosis DiabetesImDaniella DelBirutNo ratings yet
- Communicable Disease 2Document15 pagesCommunicable Disease 2jasmineNo ratings yet
- Chickenpox or Chicken Pox Is A Highly: Contagious Infection Varicella Zoster Virus Vesicular Rash PockmarksDocument3 pagesChickenpox or Chicken Pox Is A Highly: Contagious Infection Varicella Zoster Virus Vesicular Rash PockmarksBryan MayoralgoNo ratings yet
- Biology Project On TBDocument20 pagesBiology Project On TBAdnan Fazeel73% (15)
- Common Tropical DiseasesDocument19 pagesCommon Tropical DiseasesMarko TomicNo ratings yet
- Final Hand in 1Document14 pagesFinal Hand in 1lauraNo ratings yet
- COMMUNITY HEALTH NSC 322 LectureDocument52 pagesCOMMUNITY HEALTH NSC 322 LectureChinenye LovethNo ratings yet
- Communicable DiseasesDocument10 pagesCommunicable DiseasesHelloPepsNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14 Principles of Disease and Epidemiology1926Document33 pagesChapter 14 Principles of Disease and Epidemiology1926Liezel CauilanNo ratings yet
- Prevention and Control of Diseases and DisordersDocument45 pagesPrevention and Control of Diseases and DisordersBhel San Pedro MarzanNo ratings yet
- Dhananjay Bokade Practice School 1Document16 pagesDhananjay Bokade Practice School 1Gayatri BokadeNo ratings yet
- Session ONE-Concepts of HIV - AIDS - STIs-STDs - Public Health HygieneDocument7 pagesSession ONE-Concepts of HIV - AIDS - STIs-STDs - Public Health Hygienenzainga lukasNo ratings yet
- Infectious Tuberculosis-18 (Muhadharaty)Document11 pagesInfectious Tuberculosis-18 (Muhadharaty)dr.salam.hassaniNo ratings yet
- CWTS NewDocument32 pagesCWTS NewnerlynNo ratings yet
- Bacterial Disease 1. Pulmonary TuberculosisDocument7 pagesBacterial Disease 1. Pulmonary TuberculosiskanishqcNo ratings yet
- Tubercolosis Part 6Document1 pageTubercolosis Part 6Tân NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Mantoux test-TSTDocument13 pagesMantoux test-TSTNektarios TsakalosNo ratings yet
- Tuberculosis OrginalDocument11 pagesTuberculosis Orginalthanuja mathew100% (1)
- TUBERCULOSISDocument47 pagesTUBERCULOSISIfeoluwa Deborah Olopade100% (1)
- ENGLISHDocument5 pagesENGLISHआरोहण बस्नेतNo ratings yet
- Epidemic, Pandemic, Should I Call the Medic? Biology Books for Kids | Children's Biology BooksFrom EverandEpidemic, Pandemic, Should I Call the Medic? Biology Books for Kids | Children's Biology BooksNo ratings yet
- DiseaseDocument6 pagesDiseasebioenvironNo ratings yet
- Biology Summer Homework, Diseases and Infections: Disease Pathogen Linked Type of OrganismDocument3 pagesBiology Summer Homework, Diseases and Infections: Disease Pathogen Linked Type of OrganismPedro Gomez GuevaraNo ratings yet