Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 7 - Theory and Estimation of Cost - Farrukh Wazir Khan - Fall22
Uploaded by
IFRA AFZALOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 7 - Theory and Estimation of Cost - Farrukh Wazir Khan - Fall22
Uploaded by
IFRA AFZALCopyright:
Available Formats
The Theory and Estimation of Cost
Farrukh Wazir Khan
Chapter 7
The Theory and
Estimation of Cost
• Definition of Cost
• The Short Run Relationship Between Production and Cost
– The Short Run Cost Function
• The Long Run Relationship Between Production and Cost
– The Long Run Cost Function
• The Learning Curve
Farrukh Wazir Khan
Chapter 7
Definition of Cost
• A cost is relevant if it is affected by a management decision.
– Historical cost is incurred at the time of procurement
– Replacement cost is necessary to replace inventory
• Are historical costs relevant?
Farrukh Wazir Khan
Chapter 7
Definition of Cost
• There are two types of cost associated with economic analysis
– Opportunity cost is the value that is forgone in choosing one
activity over the next best alternative
– Out-of-pocket cost is actual transfer of value that occur
• Which cost is relevant?
Farrukh Wazir Khan
Chapter 7
Definition of Cost
• There are two types of cost associated with time
– Incremental cost varies with the range of options
available in the decision making process.
– Sunk cost does not vary with decision options.
• Is sunk cost relevant?
Farrukh Wazir Khan
Chapter 7
SR Relationship Between
Production and Cost
• A firm’s cost structure is related to its production process.
– Costs are determined by the production technology and
input prices.
• Assuming that the firm is a “price taker” in the input
market.
Farrukh Wazir Khan
Table 7.1 : Relationship between Production and Cost
Example 1 -
Total
Input TVC
SR Relationship Between (L) Q (TP) MP (wL)
Production and Cost 0 0 0
1 1,000 1,000 500
2 3,000 2,000 1,000
• Total variable cost (TVC) is 3 6,000 3,000 1,500
associated with the variable input 4 8,000 2,000 2,000
– Assume w=$500 per unit (price-taker) 5 9,000 1,000 ?
2,500
6 9,500 500 3,000
7 9,850 350 3,500
8 10,000 150 4,000
9 9,850 -150 4,500
Farrukh Wazir Khan
SR Relationship Between
Production and Cost
• Total cost (TC) is the cost associated with all of the
inputs. It is the sum of TVC and TFC.
• Marginal Costs
• Average Costs
Farrukh Wazir Khan
SR Relationship Between
Production and Cost
• Marginal cost (MC) is the change in total cost
associated a change in output.
TC
MC
Q
TC (TFC TVC ) TFC TVC TVC
MC 0
Q Q Q Q Q
Farrukh Wazir Khan
Table 7.1 : Relationship between Production and Cost
Example 1.2 -
Total
Input TVC
SR Relationship (L) Q MP (wL) MC
Between 0 0 0
Production and Cost 1 1,000 1,000 500 0.50
2 3,000 2,000 1,000 0.25
• Observe : 3 6,000 3,000 1,500 0.17
– When MP is increasing, MC 4 8,000 2,000 2,000 0.25
is decreasing or increasing? 5 9,000 1,000 2,500 ?
0.50
6 9,500 500 3,000 1.00
– When MP is decreasing, MC
7 9,850 350 3,500 1.43
is decreasing or increasing?
8 10,000 150 4,000 3.33
9 9,850 -150 4,500
Farrukh Wazir Khan
Fig 7.1 : SR Relationship Between Production and Cost
SR Relationship Between Production and Cost
• TP and TVC are mirror images of each other
Farrukh Wazir Khan
SR Relationship Between
Production and Cost
• The relationship between MP and MC is
TVC w L L 1 w
MC w w
Q Q Q MP MP
Law of diminishing returns implies that MC will eventually
increase! Why?
Farrukh Wazir Khan
The Short Run Cost Function
• Average total cost (ATC) is the average per-unit cost of
using all of the firm’s inputs (TC/Q)
– Average variable cost (AVC) is the average per-unit
cost of using the firm’s variable inputs (TVC/Q)
– Average fixed cost (AFC) is the average per-unit cost
of using the firm’s fixed inputs (TFC/Q)
Farrukh Wazir Khan
Table 7.2 : The Short Run Cost Function
Example 2 - ATC = AFC + AVC
Farrukh Wazir Khan
The Short Run Cost Function
• Production cost graph or map is
Farrukh Wazir Khan
The Short Run Cost Function
• Important Map Observations
– AFC declines steadily over the range of production. Why?
– In general, ATC is u-shaped. Why?
– MC intersects the minimum point (q*) on ATC. Why?
Farrukh Wazir Khan
The Short Run Cost Function
• Important Map Observations
– What is the economic significance of q*?
Farrukh Wazir Khan
The Cost Curves
Shifts in the Cost curves:
The location of the firms short run cost curves will change only
when things other than the output level changes especially
- the state of technology and
- the price of variable inputs.
Farrukh Wazir Khan
Example : Input Price Effect
Example 3 -
The Short Run Cost Function
• A change in input prices
will shift the cost curves.
– If fixed input costs are
reduced then ATC will
shift downward.
AVC and MC will remain
unaffected.
Farrukh Wazir Khan
Example : Input Price Effect:
The Short Run Cost Function
• A change in input prices
will shift the cost curves.
– If variable input costs
are reduced then MC,
AVC, and AC will all s
hift downward.
Farrukh Wazir Khan
The Long-Run Cost Function
• LRAC is made up for SRACs
– SRAC curves represent
various plant sizes
– Once a plant size is
chosen, per-unit
production costs are
found by moving
along that particular
SRAC curve
Farrukh Wazir Khan
The Long-Run Cost Function
• The LRAC is the lower envelope of all of the SRAC
curves.
– Minimum efficient scale is the lowest output level
for which LRAC is minimized
Is LRAC a function of market size?
What are implications?
Farrukh Wazir Khan
The Long-Run Cost Function
• Reasons for Economies of Scale…
Increasing returns to scale
Specialization in the use of labor and capital
• Economies in maintaining inventory
• Discounts from bulk purchases
• Lower cost of raising capital funds
• Spreading promotional and R&D costs
Management efficiencies
Farrukh Wazir Khan
The Long-Run Cost Function
• Reasons for Diseconomies of Scale…
Decreasing returns to scale
Input market imperfections
Management coordination and control
problems
Farrukh Wazir Khan
The Learning Curve
• Measures the percentage decrease
in additional labor cost each time
output doubles.
– An “80 percent” learning curve
implies that the labor costs
associated with the incremental
output will decrease to 80% of
their previous level.
Farrukh Wazir Khan
The Learning Curve
• A downward slope in the learning curve indicates the
presence of the learning curve effect
– Why? Workers improve their productivity with
practice
• The learning curve effect shifts the SRAC downward
Farrukh Wazir Khan
Appendix 7A
Appendix - Production Cost : Calculus
The general form of the short run production cost function is: TC = F (Q)
There are three specific forms of this function are used in economic
analysis: the cubic, the quadratic, and the linear.
Cubic function: TC = 100 +60Q – 3Q2 + 0.1Q3
Quadratic relationship: TC = 100 +60Q + 3Q2
Linear relationship: TC = 100 +60Q
Farrukh Wazir Khan
Appendix 7A
Example 4 - Production Cost : Calculus
This is a short run cost function with a TFC = $100, when Q = 0
Calculate - TVC, AFC, AVC, ATC and MC
Farrukh Wazir Khan
Reference:
Managerial Economics: Economic Tools for Today’s Decision Makers
By Paul G. Keat, Philip K. Y. Young, Stephen E. Erfle
Chapter 7
Farrukh Wazir Khan
You might also like
- Theory of Cost & RevenueDocument93 pagesTheory of Cost & Revenuenisa82% (11)
- The Theory and Estimation of CostDocument23 pagesThe Theory and Estimation of CostFadi ChouNo ratings yet
- Chap.13 Guerrero Job Order CostingDocument40 pagesChap.13 Guerrero Job Order CostingGeoff MacarateNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Cost and RevenueDocument59 pagesUnit 4 Cost and RevenueSangam KarkiNo ratings yet
- Theory of Production and CostDocument24 pagesTheory of Production and CostSharmila ZackieNo ratings yet
- Theory of Production CostDocument17 pagesTheory of Production CostDherya AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Cost Vs Production in Short and Long RunDocument32 pagesCost Vs Production in Short and Long Runmayura patilNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Cost Theory: Topics To Be DiscussedDocument8 pagesChapter 7 Cost Theory: Topics To Be DiscussedMadhunikaNo ratings yet
- Cost Analysis PDFDocument9 pagesCost Analysis PDFAnkit KagraNo ratings yet
- Cost Function - MEDocument27 pagesCost Function - MEDARSHANA SNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Economics (Econ. 101)Document27 pagesIntroduction To Economics (Econ. 101)Ali HassenNo ratings yet
- GRP PPT Cost CurvesDocument49 pagesGRP PPT Cost Curvesparulmathur85No ratings yet
- 2.4.theory of CostDocument28 pages2.4.theory of CostMotuma AdugnaNo ratings yet
- PRCH 7 NewDocument119 pagesPRCH 7 NewMicha Alexa HernandezNo ratings yet
- Cost Analysis: Dr. Mohsina HayatDocument36 pagesCost Analysis: Dr. Mohsina HayatFaizan QudsiNo ratings yet
- The Cost of ProductionDocument75 pagesThe Cost of Productionmuhammadtaimoorkhan100% (4)
- The Theory and Estimation of Cost: Unit-IVDocument26 pagesThe Theory and Estimation of Cost: Unit-IVSurya NarayanaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Economics (Econ. 101)Document31 pagesIntroduction To Economics (Econ. 101)Nahom MasreshaNo ratings yet
- Theory of CostDocument42 pagesTheory of CostSujan BhattaraiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document17 pagesChapter 4yafethdessalegn43No ratings yet
- Lecture 6-2Document13 pagesLecture 6-2Крістіна ДобромільськаNo ratings yet
- CostDocument23 pagesCostManish GuptaNo ratings yet
- The Theory of Production and CostDocument23 pagesThe Theory of Production and CostKareem Dad MaharNo ratings yet
- Chapter Five Theory of CostDocument18 pagesChapter Five Theory of CostGidisa LachisaNo ratings yet
- 7 Costs of ProductionDocument24 pages7 Costs of Productionakshat guptaNo ratings yet
- Business EcnomicsDocument17 pagesBusiness EcnomicsjyotsnaNo ratings yet
- 16793theory of CostDocument55 pages16793theory of CostAnonymous 1ClGHbiT0JNo ratings yet
- TopicThree-Theory of Costs-ECO 401Document18 pagesTopicThree-Theory of Costs-ECO 401Mister PhilipsNo ratings yet
- Analysis of CostsDocument26 pagesAnalysis of CostsTanvi ThakurNo ratings yet
- ECON 100A Midterm 2 Review SessionDocument64 pagesECON 100A Midterm 2 Review SessionJason WuNo ratings yet
- Current NewsDocument24 pagesCurrent NewsShivam YadavNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 & 6: Theory of CostsDocument14 pagesLecture 5 & 6: Theory of CoststagashiiNo ratings yet
- Module-6 Cost and Revenue AnalysisDocument46 pagesModule-6 Cost and Revenue Analysiskarthik21488No ratings yet
- Lecture 7Document30 pagesLecture 7kchen010907No ratings yet
- 11 SlidesDocument27 pages11 SlidesHameed MNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Costs and ProductionDocument27 pagesChapter 5 Costs and ProductionChen Yee KhooNo ratings yet
- Presented By-Trilok, Jaswant, Girish, Lalit, MohitDocument36 pagesPresented By-Trilok, Jaswant, Girish, Lalit, MohitŤŕiļöķ BákøļįâNo ratings yet
- 3.production CostDocument30 pages3.production CostroberaakNo ratings yet
- COSTDocument12 pagesCOSTsatya narayanaNo ratings yet
- Microeconomics P8Document15 pagesMicroeconomics P8Lee Wei ChuenNo ratings yet
- Cost AnalysisDocument30 pagesCost AnalysisPooja SheoranNo ratings yet
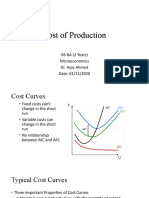
- Cost of Production: BS-BA (2 Years) Microeconomics Dr. Ayaz Ahmed Date: 01/12/2020Document13 pagesCost of Production: BS-BA (2 Years) Microeconomics Dr. Ayaz Ahmed Date: 01/12/2020Muhammad HassanNo ratings yet
- Presented By: Athulya V Panicker Lekha R Devi Priya K R Shija Vijayakumar SureshDocument24 pagesPresented By: Athulya V Panicker Lekha R Devi Priya K R Shija Vijayakumar SureshprankynNo ratings yet
- Econ - Unit - 5 - Cost TheoryDocument39 pagesEcon - Unit - 5 - Cost TheorySampurnaa DasNo ratings yet
- Short Run Average Costs - Marginal Cost, AFC, AVC, Formulas, EtcDocument10 pagesShort Run Average Costs - Marginal Cost, AFC, AVC, Formulas, EtcsakhawatNo ratings yet
- CH 09 Economic CostDocument28 pagesCH 09 Economic Costbitf22m535No ratings yet
- Module 2 PDFDocument61 pagesModule 2 PDFAa AaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 (Cost Theory)Document20 pagesChapter 6 (Cost Theory)AldrinNyandangNo ratings yet
- 2 - Chapter 5 - Supply Decision - Short & Long Run CostDocument38 pages2 - Chapter 5 - Supply Decision - Short & Long Run CostHadilNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Cost and RevenueDocument28 pagesAnalysis of Cost and RevenueSaurav SubediNo ratings yet
- Cost FunctionDocument58 pagesCost FunctionAishwarya ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Ch-3-2-Theory of CostDocument33 pagesCh-3-2-Theory of Costyonatan gizawNo ratings yet
- The Analysis of Costs: Managerial EconomicsDocument32 pagesThe Analysis of Costs: Managerial EconomicsalauoniNo ratings yet
- Average & Marginal Cost SchedulesDocument18 pagesAverage & Marginal Cost SchedulesnehaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Cost ConceptsDocument28 pagesChapter 8 Cost ConceptsRajveer SinghNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 Costs ,: RK FCDocument10 pagesChapter 10 Costs ,: RK FCsoumssflatNo ratings yet
- Unit Vi: The Theory and Estimation of CostDocument69 pagesUnit Vi: The Theory and Estimation of CostIshan PalNo ratings yet
- Cost FunctionDocument28 pagesCost FunctionYajata VermaNo ratings yet
- Power System Economics - Unilag Lecture NotesDocument43 pagesPower System Economics - Unilag Lecture Noteseresuyi100% (3)
- The Theory and Estimation of CostDocument38 pagesThe Theory and Estimation of Costde essensioNo ratings yet
- Introduction To CFA AnalysisDocument15 pagesIntroduction To CFA AnalysisIFRA AFZALNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 - Pricing Output Decisions - 1. Perfect Competition - Farrukh Wazir Khan - Fall22Document26 pagesChapter 8 - Pricing Output Decisions - 1. Perfect Competition - Farrukh Wazir Khan - Fall22IFRA AFZALNo ratings yet
- PricingandOutput MonopolisticCompetition - Farrukh Wazir Khan - Fall22Document12 pagesPricingandOutput MonopolisticCompetition - Farrukh Wazir Khan - Fall22IFRA AFZALNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - Demand Forecasting - Farrukh Wazir Khan Fall22Document25 pagesChapter 5 - Demand Forecasting - Farrukh Wazir Khan Fall22IFRA AFZALNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - Theory and Estimation of Production - Farrukh Wazir Khan - Fall22Document42 pagesChapter 6 - Theory and Estimation of Production - Farrukh Wazir Khan - Fall22IFRA AFZALNo ratings yet
- Chapter4A MathsofElasticity - FarrukhWazirKhan - Fall22Document24 pagesChapter4A MathsofElasticity - FarrukhWazirKhan - Fall22IFRA AFZALNo ratings yet
- Chapter4 Elasticity - FarrukhWazirKhan - Fall22Document42 pagesChapter4 Elasticity - FarrukhWazirKhan - Fall22IFRA AFZALNo ratings yet
- Assignment1 ManagerialEconomics - Farrukh Wazir Khan - Fall22Document2 pagesAssignment1 ManagerialEconomics - Farrukh Wazir Khan - Fall22IFRA AFZALNo ratings yet
- Unit 8 - BudgetingDocument8 pagesUnit 8 - Budgetingkevin75108No ratings yet
- W5. Ex2 - Inventories. Periodic - FIFO, LIFO, and Average-Cost With AnalysisDocument6 pagesW5. Ex2 - Inventories. Periodic - FIFO, LIFO, and Average-Cost With AnalysisJulian Lukman Simbolon0% (1)
- Baye Chap005Document29 pagesBaye Chap005Sagita SimanjuntakNo ratings yet
- Managerial Accounting Absorption and Variable Costing 081712Document14 pagesManagerial Accounting Absorption and Variable Costing 081712Mary Ann Jacolbe BaguioNo ratings yet
- Music Today 1Document42 pagesMusic Today 1dian indrianiNo ratings yet
- Cost of ProductionDocument57 pagesCost of Productionrabia liaqatNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Cost 2020Document20 pagesChapter 8 Cost 2020abcNo ratings yet
- Principles of Microeconomics - Costs of ProductionDocument45 pagesPrinciples of Microeconomics - Costs of ProductionKatherine SauerNo ratings yet
- EOQ ProblemsDocument6 pagesEOQ ProblemsDaneen GastarNo ratings yet
- Economics 20th Edition McConnell Test Bank 1Document151 pagesEconomics 20th Edition McConnell Test Bank 1betty100% (35)
- Colander ch09 Production&CostsIDocument71 pagesColander ch09 Production&CostsIRajatC111No ratings yet
- Technology, Production, and Costs: Chapter Summary and Learning ObjectivesDocument35 pagesTechnology, Production, and Costs: Chapter Summary and Learning ObjectivesseriosulyawksomNo ratings yet
- Activity Name Normal Time Normal Cost Crash Time Crash CostDocument3 pagesActivity Name Normal Time Normal Cost Crash Time Crash CostIbraheem DwikatNo ratings yet
- Manajemen Proyek Tik It-44-Gab (CDF) : Started OnDocument9 pagesManajemen Proyek Tik It-44-Gab (CDF) : Started OnAgung AlthaafNo ratings yet
- Why Average Cost Curve IsDocument2 pagesWhy Average Cost Curve IsHasinaImamNo ratings yet
- De Leon Solman 2014 2 CostDocument95 pagesDe Leon Solman 2014 2 CostgabrielleNo ratings yet
- 3Document4 pages3Beth Rachel Mae M. MilloraNo ratings yet
- Solman Cost Accounting 1 Guerrero 2015 Chapters 1-16 PDFDocument46 pagesSolman Cost Accounting 1 Guerrero 2015 Chapters 1-16 PDFMarylorieanne CorpuzNo ratings yet
- Analysis of CostsDocument26 pagesAnalysis of CostsTanvi ThakurNo ratings yet
- 3.3 Exam Practice QuestionsDocument2 pages3.3 Exam Practice QuestionsJavi MartinezNo ratings yet
- Absorption and Variable Costing - Illustrative Example - PagaddutDocument4 pagesAbsorption and Variable Costing - Illustrative Example - PagaddutLovely Rose GuinilingNo ratings yet
- Cost & Cost CurvesDocument46 pagesCost & Cost CurvesManoj Kumar SunuwarNo ratings yet
- 13 Costs ProductionDocument54 pages13 Costs ProductionAtif RaoNo ratings yet
- 1Document8 pages1Absolute ZeroNo ratings yet
- Different Types of Costs With ExamplesDocument6 pagesDifferent Types of Costs With ExamplesShyra SerencioNo ratings yet
- MAS Reviewer - Cost Behavior & CVP AnalysisDocument4 pagesMAS Reviewer - Cost Behavior & CVP AnalysisJohn Carlo PeruNo ratings yet
- Absorption and Marginal Costing Worked ExamplesDocument5 pagesAbsorption and Marginal Costing Worked ExamplesSymon MwenexNo ratings yet
- Yes 3Document1 pageYes 3yes yesnoNo ratings yet
- Quiz 2Document2 pagesQuiz 2hrshtkatwala100% (1)