0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2K views10 pagesClass 8 Science: Microorganisms Solutions
This document provides solutions to multiple choice and short answer questions from NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 2 on Microorganisms Friend and Foe. The questions cover topics like types of microorganisms that cause diseases like influenza, malaria and tuberculosis in humans; the use of antibiotics, vaccines and other medicines to treat pathogenic microbes; microorganisms involved in industrial processes like fermentation and their role as symbionts in lichens; and the work of scientists like Pasteur, Koch, Jenner and Fleming.
Uploaded by
Pradipti VermaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2K views10 pagesClass 8 Science: Microorganisms Solutions
This document provides solutions to multiple choice and short answer questions from NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 2 on Microorganisms Friend and Foe. The questions cover topics like types of microorganisms that cause diseases like influenza, malaria and tuberculosis in humans; the use of antibiotics, vaccines and other medicines to treat pathogenic microbes; microorganisms involved in industrial processes like fermentation and their role as symbionts in lichens; and the work of scientists like Pasteur, Koch, Jenner and Fleming.
Uploaded by
Pradipti VermaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
- Multiple-Choice Questions: Contains questions in a multiple-choice format to test basic understanding of microorganisms and their functions.
- Very Short Answer Questions: Provides very short answer questions to reinforce understanding of key concepts regarding microorganisms.
- Short Answer Questions: Features questions requiring short, descriptive answers about various microorganisms and their classification.
- Long Answer Questions: Includes questions that require detailed and explanatory answers, covering broader topics.
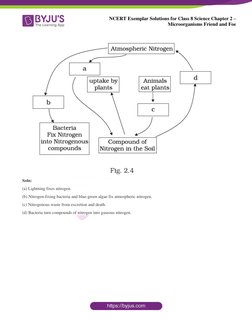
- Diagrams and Exercises: Presents diagrams followed by questions to assess visual comprehension and application of concepts.