Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Osmosis and Diffusion
Uploaded by
Christine Kylene AycardoOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Osmosis and Diffusion
Uploaded by
Christine Kylene AycardoCopyright:
Available Formats
OSMOSIS AND DIFFUSION
PROCESSES BY WHICH SUBSTANCES ARE TRANSFERRED ACROSS CELL MEMBRANES:
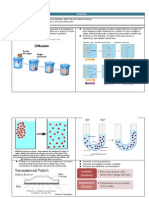
Diffusion – the movement of any substance from an area where it is more concentrated to an
area where it is less concentrated.
Osmosis – is a type of diffusion that involves only the movement of water across a membrane
and therefore proceeds from the more dilute to the more concentrated solution.
Facilitated diffusion – moves substances in and out of cells from higher to lower concentrations
of a particular solutes
Active transport – moves substances across the cell membrane against the concentration
gradient, - from lower to higher concentration. This results in the accumulation of substances on
one side of the cell membrane. ATP is required. AA movement from the SI to the blood is an
example of active transport. The Na-K pump is another example.
Phagocytosis – is the term used when solid particles are ingested. It is the process by which a
cell engulfs a foreign substance or body.
Pinocytosis – the pumping of water across the membrane. It is similar to phagocytosis, except
the smaller vesicles containing liquids are formed.
The exchange of materials occurs between cells and their environment, across the cell
membrane. To make this exchange as efficient as possible, some organisms have evolved
specialized exchange surfaces like the alveoli in the lungs, root hairs in plants, or the nephrons in
the kidneys. Depending upon what is being exchanged and which direction along the
concentration gradient things are traveling will determine whether diffusion, osmosis or active
transport will be used. Diffusion is the process in which particles spread out from each other.
They move from high concentration to an area of low concentration, down the concentration
gradient until they are evenly distributed. Osmosis is remarkably similar to diffusion but just for
water. It is the movement of water into or out of a cell. Again, it is the movement from a dilute
solution (so high concentration of water molecules) down the concentration gradient to a more
concentrated solution - so low concentration of water molecules. The water molecules move
across a partially permeable membrane.
You might also like
- Transport in Plants PDFDocument10 pagesTransport in Plants PDFAlhiza JoaquinNo ratings yet
- Transport MechanismDocument19 pagesTransport MechanismAaron Roxas100% (2)
- Osmosis, Diffusion, Active TransportDocument21 pagesOsmosis, Diffusion, Active TransportPrince SanjiNo ratings yet
- Personal NotesDocument7 pagesPersonal NoteslayshengNo ratings yet
- Diffusion and OsmosisDocument6 pagesDiffusion and OsmosisCharlesNo ratings yet
- Movement in and Out of Cells NotesDocument9 pagesMovement in and Out of Cells Notesmanarehab35No ratings yet
- Diffusion Vs OsmosisDocument3 pagesDiffusion Vs OsmosisK TanNo ratings yet
- BS 1Document12 pagesBS 1JAHANZEB NAZIRNo ratings yet
- Movement in and Out of CellsDocument4 pagesMovement in and Out of Cellshillskimberly24No ratings yet
- Diffusion and OsmosisDocument3 pagesDiffusion and OsmosisRenee Dwi Permata MessakaraengNo ratings yet
- Movement - S-Cool, The Revision WebsiteDocument8 pagesMovement - S-Cool, The Revision WebsiteThilini BadugeNo ratings yet
- Gene103Lab DiffusionandOsmosisDocument5 pagesGene103Lab DiffusionandOsmosisbodurr571No ratings yet
- Transport in Plants - IDocument28 pagesTransport in Plants - IPukazhvanthen ParamanandhanNo ratings yet
- Transport Across The Cell MembraneDocument16 pagesTransport Across The Cell MembraneJagruti MaratheNo ratings yet
- Cell MembranesDocument5 pagesCell MembranesTiaraHadiAshariNo ratings yet
- Cell Transport: by Felipe Hoffmann, Juan Felipe Canal, Juan Sebastian Lopez, Nicolas Castrillon and Simon KnudsenDocument6 pagesCell Transport: by Felipe Hoffmann, Juan Felipe Canal, Juan Sebastian Lopez, Nicolas Castrillon and Simon KnudsenSimon KnudsenNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Doc 4Document4 pagesChapter 1 Doc 4Enju ChipepeNo ratings yet
- BioCLab Mod3Document11 pagesBioCLab Mod3Samantha BolanteNo ratings yet
- DiffusionDocument2 pagesDiffusionchrisgal21No ratings yet
- Diffusion, Osmosis AND Active TransportDocument18 pagesDiffusion, Osmosis AND Active TransportScience,Physical Education And Sports VideosNo ratings yet
- Bio Diffusion OsmosisDocument9 pagesBio Diffusion OsmosisRodge BuereNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGY SUMMARY TOPIC 3 IgcseDocument5 pagesBIOLOGY SUMMARY TOPIC 3 IgcsesameehaNo ratings yet
- BiologyDocument2 pagesBiologyChaca LurpheChachos XiaraNo ratings yet
- SiglerDocument2 pagesSigleri kmnwNo ratings yet
- 03 BIO X ICSE AbsorbtionDocument8 pages03 BIO X ICSE Absorbtionrkjoseph1410No ratings yet
- Movement in and OutDocument35 pagesMovement in and OutzefanyaNo ratings yet
- Document 8Document8 pagesDocument 8Tiana PolackNo ratings yet
- 11 Biology Notes ch11 Transport in PlantDocument6 pages11 Biology Notes ch11 Transport in PlantMuskan VarlaniNo ratings yet
- Movement Into and Out of Cells Objectives:3.1Document12 pagesMovement Into and Out of Cells Objectives:3.1Army ForeverNo ratings yet
- Diffusion and OsmosisDocument3 pagesDiffusion and Osmosisshaniah100% (1)
- Transport in PlantsDocument22 pagesTransport in PlantsShantanu GhoshNo ratings yet
- 4.transport MechanismsDocument94 pages4.transport MechanismsHyacinth RaeNo ratings yet
- Diffusion and OsmosisDocument2 pagesDiffusion and OsmosisMera FunportalNo ratings yet
- 2 General Classification of Cellular Transport SystemDocument5 pages2 General Classification of Cellular Transport Systemangela mamauagNo ratings yet
- Membrane Structure & PermiabilityDocument21 pagesMembrane Structure & Permiabilitydinakempho3No ratings yet
- Gr9 - Movement of SubstancesDocument40 pagesGr9 - Movement of SubstancesKara NewmanNo ratings yet
- Osmosis and Semipermeable MembranesDocument4 pagesOsmosis and Semipermeable MembranesAarhan KhanNo ratings yet
- Cellular Transport - The Cellular Traffic: Kimberly Matas Angel TrinidadDocument23 pagesCellular Transport - The Cellular Traffic: Kimberly Matas Angel TrinidadangelNo ratings yet
- Cell Physiology: Membrane Transport: Prepared By: Mr. Charlie C. Falguera, RN, MANDocument15 pagesCell Physiology: Membrane Transport: Prepared By: Mr. Charlie C. Falguera, RN, MANchfalgueraNo ratings yet
- Class 11 Biology Chapter 11 - Revision NotesDocument9 pagesClass 11 Biology Chapter 11 - Revision NotesGopal NaikNo ratings yet
- MF009 3A Transportation Across Cell Membrane James L2Document33 pagesMF009 3A Transportation Across Cell Membrane James L2PikuNo ratings yet
- By: Tiffany M. AustriaDocument10 pagesBy: Tiffany M. Austrianyzgirl17No ratings yet
- Movement in and Out of CellsDocument40 pagesMovement in and Out of CellslubaajamesNo ratings yet
- Movement of Particles NoteDocument2 pagesMovement of Particles NoteSabita SinghNo ratings yet
- By: Tiffany M. AustriaDocument10 pagesBy: Tiffany M. Austrianyzgirl17No ratings yet
- Osmosis and Diffusion - 2nd YearDocument13 pagesOsmosis and Diffusion - 2nd YearFrancisco Samarco100% (1)
- OsmosisDocument19 pagesOsmosisdamyangdcsNo ratings yet
- Diffusion Diffusion in Living Organisms: Diffusion Across The Cell MembraneDocument11 pagesDiffusion Diffusion in Living Organisms: Diffusion Across The Cell MembraneRahil BhavanNo ratings yet
- BIO 205 - Transport in PlantsDocument10 pagesBIO 205 - Transport in PlantsadebolaabdulghalibNo ratings yet
- Laporan Physio ExDocument13 pagesLaporan Physio ExsolideoNo ratings yet
- Bios - Transport of MaterialDocument46 pagesBios - Transport of MaterialNeseriani AndersonNo ratings yet
- Osmosis, Diffusion, Active TransportDocument21 pagesOsmosis, Diffusion, Active TransportDine MaglanqueNo ratings yet
- Transport in Plants: K C Meena PGT Biology KV Vikaspuri Ii ShiftDocument24 pagesTransport in Plants: K C Meena PGT Biology KV Vikaspuri Ii ShiftKaviyaNo ratings yet
- Movement Into and Out of The CellDocument17 pagesMovement Into and Out of The CellsamskruthamanabroluNo ratings yet
- Bio Lab IntroDocument2 pagesBio Lab Introapi-327731714No ratings yet
- Cell Transport Powerpoint NotesDocument33 pagesCell Transport Powerpoint Notesapi-644325383No ratings yet
- Movement Into and Out of CellsDocument12 pagesMovement Into and Out of Cellsf8sdh6xvzyNo ratings yet
- Cell Transport NotesDocument10 pagesCell Transport NotesReyad BarbarNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology Lecture: Cells That Connect Body PartsDocument4 pagesAnatomy and Physiology Lecture: Cells That Connect Body PartsGabriel EmperioNo ratings yet