Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Class 11 Biology Chapter 11 - Revision Notes
Uploaded by
Gopal NaikCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Class 11 Biology Chapter 11 - Revision Notes
Uploaded by
Gopal NaikCopyright:
Available Formats
Revision Notes
Class 11 Biology
Chapter 11 – Transport in Plants
Translocation refers to the process of transport in plants via xylem and phloem. It
includes the transport of water, minerals, and solutes.
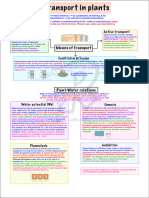
Means of transport
Plants have three primary modes of transportation:
• Diffusion is the most common mode of plant transport. It is defined as the
movement of molecules from a high concentration region to a low concentration
region without the use of energy. As a result, diffusion is a passive process. The rate
of diffusion is affected by the concentration gradient, temperature, and pressure.
• Facilitated diffusion is a transport process facilitated by proteins known as
permeases. It is a passive process as well. Transport reaches its maximum when all
of the protein available for transport is saturated. It is a specific process that only
allows certain molecules to pass through. Porins and aquaporins are proteins that aid
in the process of facilitated diffusion. Porins are pores found in cell organelles such
as mitochondria and plastids, as well as in some bacteria. Aquaporins are water
channels that transport molecules of water.
Class XI Biology www.vedantu.com 1
The following process can result in facilitated diffusion:
• Symport: The transport of multiple molecules in the same direction.
• Antiport: The movement of molecules in the opposite direction.
• Uniport: The movement of single molecules in any direction.
Note: Recreated above diagram
Active transport in plants
The transport of molecules necessitates the expenditure of energy. It can transport
solutes from a low concentration region to a high concentration region and vice
versa. Active transport is facilitated by membrane proteins. It is a specific mode of
solute transport.
Class XI Biology www.vedantu.com 2
Note: Recreated above diagram
Plant water relations
Water is required for the growth of plants. However, too much or too little water is
harmful to the plants. The process by which terrestrial plants lose some of their water
from their aerial parts in the form of water vapor is known as transpiration.
Water potential
Water potential is a measure of water's potential energy. The water potential of the
cell is determined by solute potential and pressure potential. The highest water
potential is found in pure water. Water always moves from a higher to a lower water
potential. The potential of water is denoted by the symbol psi or ψ. Pascals are the
unit of measurement for water potential.
Class XI Biology www.vedantu.com 3
When a solute is added to pure water, the water potential falls to a negative value.
This is referred to as solute potential. It is denoted by the symbol ψs . Water potential
increases when pressure exceeds atmospheric pressure in the case of pure water.
Water moves from a region of high water potential to a region of low water potential,
or from a dilute solution to a concentrated solution, as shown in the diagram above.
When water enters the plant cell, pressure builds up against the cell wall, making it
more turgid. This increases the potential for pressure. As a result, the following is
the relationship between water potential ψ , solute potential ψs , and pressure
potential ψp :
ψ = ψp ψs
Osmosis
It is defined as the process of water molecules moving across a semi-permeable
membrane. The movement of water is influenced by the concentration gradient and
the pressure gradient.
Water molecules move until an equilibrium is reached between the two solutions.
Osmotic pressure is the pressure applied to prevent the net movement of solute
molecules across the membrane. Osmosis is required for the movement of molecules
across membranes such as ions, proteins, and polysaccharides.
Class XI Biology www.vedantu.com 4
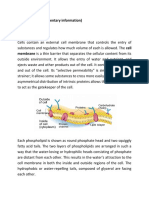
Plasmolysis
The behavior of plant cells in relation to the external medium is subject to change.
If the osmotic potential of the plant cell matches that of the external medium, the
solution is said to be isotonic. The solution is said to be hypertonic if the osmotic
potential is greater outside the cell than inside the cell. When the solute potential
inside the cell is greater than the solute potential outside the cell, the solution is said
to be hypotonic.
A hypertonic solution causes water molecules to move outside the cell. The cell is
now referred to as flaccid. When a cell is immersed in hypotonic solution, water
moves within the cell. The cell is described as turgid. Plasmolysis is the process by
which protoplasm shrinks away from the cell wall when a plant cell is kept in
hypertonic solution. Water moves out of the cell as a result of being immersed in a
hypertonic solution. This is referred to as plasmolysis.
Class XI Biology www.vedantu.com 5
Imbibition
Imbibition refers to the absorption of water by solids, which causes them to expand
in size. The most common example of imbibition is the swelling of raisins when kept
in water. This is regarded as diffusion because water moves from high concentration
to low concentration, i.e. along the concentration gradient.
Long distance transport of water
Long-distance water transport is the quickest mode of water transport. Water, food,
and minerals are typically moved by bulk flow or mass flow. Mass flow occurs
between two pressure-differentiated solutions.
Translocation refers to the movement of substances through the vascular tissues of
plants. Xylem and phloem are vascular tissues. Xylem aids in the movement of water
molecules from the roots to various parts of the plant. Phloem facilitates the
movement of food from the leaves to other parts of the plant.
Different pathways of water absorption
Water is absorbed by plants through their roots. Root hairs are responsible for the
absorption of water and minerals from the soil. Water moves from the roots to
various parts of the plant via two different pathways. These routes are as follows:
• Apoplast pathway
It is concerned with the movement of water in non-living plant parts such as
intercellular spaces and cell walls. This pathway is disrupted by the endodermis.
Endodermis is protected from water movement by casparian strips. It does not entail
the movement of water across the cell membrane.
Class XI Biology www.vedantu.com 6
• Symplast pathway
It is the movement of water through protoplasts via cell-to-cell connections known
as plasmodesmata. It aids in direct cytoplasm-to-cytoplasm movement. This process
is slower than the apoplastic pathway of water movement.
Some plants, such as Pinus, have different structures for water absorption called
Mycorrhiza. Mycorrhiza are fungal associations that occur between fungi and the
roots of higher plants. It is a symbiotic relationship between the fungus and the plant
roots. The fungal hyphae aid in the absorption of mineral ions and water from the
soil, whereas the roots supply sugars and N-containing compounds to plant roots.
Water movement up the plant
• Root pressure occurs when ions present in the soil are actively transported into the
vascular tissues of the roots, resulting in positive pressure inside the roots.
• Transpiration pull occurs when ions present in the soil are actively transported into
the vascular tissues of the roots, resulting in positive pressure inside the roots. This
pressure is referred to as the root pressure, and it is responsible for the upward
movement of water. When a stem is cut horizontally from the base, root pressure is
measured. From the cut stem, a liquid will ooze out. The effect of root pressure can
Class XI Biology www.vedantu.com 7
also be seen at night. Excess water in the form of water droplets is observed near the
tips of the leaves when the rate of evaporation is low. This is referred to as guttation.
• The driving force for water's upward movement is transpiration pull. Dixon and
Jolly proposed the cohesion-tension theory to explain the upward movement of
water in plants. The attraction between water molecules is referred to as cohesion.
The attraction between water molecules and other polar molecules is referred to as
adhesion. Surface tension is another property that promotes transpiration pull. The
attraction between water molecules in liquid phase is referred to as surface tension.
Water is lost during transpiration, causing a negative pressure in the xylem vessels.
This is referred to as transpiration pull.
Transpiration
Transpiration is the loss of water from leaves in the form of water vapor through
stomata. Stomata are small openings in the leaves that open during the day and close
at night.
Factors influencing transpiration
• Elevated temperatures increase the rate of transpiration.
• A larger surface area increases the rate of evaporation; high humidity decreases the
rate of evaporation; and wind speed increases the rate of evaporation.
Mineral nutrient absorption and transport
Minerals are absorbed by plants both passively and actively. The majority of the
transport occurs actively because ions are charged and cannot cross the membrane
without expending energy. ATP is used to provide energy. Sucrose, the end product
of photosynthesis, is transported from the source (where synthesis occurs, such as
leaves) to the sink (organs that store food). Food or sucrose transport is bidirectional,
as opposed to water transport, which is unidirectional.
For sugar translocation from source to sink, the pressure flow hypothesis, mass flow
hypothesis, or Munch hypothesis was proposed. This happens through the phloem.
Sieve tubes, companion cells, and phloem parenchyma make up phloem. Food is
actively moved from source to sink via sieve tubes and companion cells. Sugars
Class XI Biology www.vedantu.com 8
move through the phloem starting at the source, where they are loaded into a sieve
tube. The loading in sieve tubes produces a hypertonic environment, which allows
water to enter the phloem. Because of the high osmotic pressure at the source, the
food/sucrose moves towards the sink (with low osmotic pressure). As a result, it is
possible to conclude that osmotic pressure drives the movement of food from the
source to the sink.
Class XI Biology www.vedantu.com 9
You might also like
- BIO 205 - Transport in PlantsDocument10 pagesBIO 205 - Transport in PlantsadebolaabdulghalibNo ratings yet
- Transport in Plants PDFDocument10 pagesTransport in Plants PDFAlhiza JoaquinNo ratings yet
- 11 Biology Notes ch11 Transport in PlantDocument6 pages11 Biology Notes ch11 Transport in PlantMuskan VarlaniNo ratings yet
- Transport in Plants: K C Meena PGT Biology KV Vikaspuri Ii ShiftDocument24 pagesTransport in Plants: K C Meena PGT Biology KV Vikaspuri Ii ShiftKaviyaNo ratings yet
- CBSE Quick Revision Notes CBSE Class-11 Biology Chapter-11 Transport in PlantsDocument10 pagesCBSE Quick Revision Notes CBSE Class-11 Biology Chapter-11 Transport in PlantsPriyanshu BhadanaNo ratings yet
- Transportation in PlantsDocument5 pagesTransportation in PlantsMitali PatelNo ratings yet
- Inter 2nd Year Botany 1.transport - Plants Study Material PDFDocument8 pagesInter 2nd Year Botany 1.transport - Plants Study Material PDFsingoj.bhargava chary100% (10)
- 10TH PPT - 2Document22 pages10TH PPT - 2Anshika BhattNo ratings yet
- NotesDocument5 pagesNoteskavitaruby1980No ratings yet
- Transport Mind MapDocument49 pagesTransport Mind MapMiryaNo ratings yet
- Transport in Plant-NCERTDocument7 pagesTransport in Plant-NCERTketakeeNo ratings yet
- Bios - Transport of MaterialDocument46 pagesBios - Transport of MaterialNeseriani AndersonNo ratings yet
- TRANSPORT in PLANTSDocument27 pagesTRANSPORT in PLANTSRish HeeNo ratings yet
- Absorption by Roots - Summary NotesDocument5 pagesAbsorption by Roots - Summary NotesSanjayNo ratings yet
- Transport in PlantsDocument12 pagesTransport in PlantsNisa ShaqiriNo ratings yet
- Biology Form 6-1Document200 pagesBiology Form 6-1Justine MakolokaNo ratings yet
- ch11 170122071310Document25 pagesch11 170122071310Honleth Jheney MamarilNo ratings yet
- BOTANY ApDocument168 pagesBOTANY ApRobba Vinay KumarNo ratings yet
- Ch-11 Transport in PlantsDocument17 pagesCh-11 Transport in PlantsSam RNo ratings yet
- 1CHAPTER V.Plant Nutritional RequirementsDocument15 pages1CHAPTER V.Plant Nutritional RequirementsLei Jenevive UmbayNo ratings yet
- Transport in Plants - IDocument28 pagesTransport in Plants - IPukazhvanthen ParamanandhanNo ratings yet
- Lec02-Role and Significance of WaterDocument11 pagesLec02-Role and Significance of Waterkhmaj9792No ratings yet
- Means of TransportDocument2 pagesMeans of Transportsridevikamaraj16No ratings yet
- Xylem and PhloemDocument35 pagesXylem and PhloemAvanish PratapNo ratings yet
- Crop PhysiologyDocument136 pagesCrop PhysiologySwikarKarkiNo ratings yet
- Transport in Plants Part 1Document12 pagesTransport in Plants Part 1Andre MorrisonNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument3 pagesUntitledKate Loren BacarroNo ratings yet
- Cells and Its Environment Ss1 NoteDocument14 pagesCells and Its Environment Ss1 NoteEllaNo ratings yet
- Gr9 - Movement of SubstancesDocument40 pagesGr9 - Movement of SubstancesKara NewmanNo ratings yet
- MF009 5C Transportation James L2Document19 pagesMF009 5C Transportation James L2PikuNo ratings yet
- Gene103Lab DiffusionandOsmosisDocument5 pagesGene103Lab DiffusionandOsmosisbodurr571No ratings yet
- Lecture 3 Osmosis and Togor PressureDocument12 pagesLecture 3 Osmosis and Togor Pressuremichael328wanjiruNo ratings yet
- Movement in and Out of CellsDocument40 pagesMovement in and Out of CellslubaajamesNo ratings yet
- Movement - S-Cool, The Revision WebsiteDocument8 pagesMovement - S-Cool, The Revision WebsiteThilini BadugeNo ratings yet
- Absorption by Roots - The Processes InvolvedDocument6 pagesAbsorption by Roots - The Processes InvolvedRahulNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 - Diffusion and OsmosisDocument11 pagesLecture 2 - Diffusion and Osmosiskinza yasirNo ratings yet
- TRANSPORT IN PLANTS Updated ZimsecDocument24 pagesTRANSPORT IN PLANTS Updated ZimsecnatashamautsiNo ratings yet
- Absorption of WaterDocument13 pagesAbsorption of WaterDr.Krishnan VijayaraghavanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3.1 - Transportation in PlantsDocument13 pagesChapter 3.1 - Transportation in Plantsbabylen bahalaNo ratings yet
- Diffusion and OsmosisDocument6 pagesDiffusion and OsmosisCharlesNo ratings yet
- Theory: 1 Plant Water RelationsDocument11 pagesTheory: 1 Plant Water RelationsalekhyaNo ratings yet
- Transport MechanismDocument19 pagesTransport MechanismAaron Roxas100% (2)
- Movement Into and Out of Cells Objectives:3.1Document12 pagesMovement Into and Out of Cells Objectives:3.1Army ForeverNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Doc 4Document4 pagesChapter 1 Doc 4Enju ChipepeNo ratings yet
- 3.3. Transport in PlantsDocument5 pages3.3. Transport in PlantsFatima NissaNo ratings yet
- Cell MembranesDocument5 pagesCell MembranesTiaraHadiAshariNo ratings yet
- Transport in Vascular PlantsDocument21 pagesTransport in Vascular PlantsFahami WahidNo ratings yet
- Transport in Phloem Lesson 3Document13 pagesTransport in Phloem Lesson 3Kajana Sivarasa ShenthanNo ratings yet
- CELL PHYSIOLOGY@starDocument6 pagesCELL PHYSIOLOGY@starDENIS KIPKOSGEINo ratings yet
- Biological ProcessesDocument2 pagesBiological ProcessesIsra OmerNo ratings yet
- BS 1Document12 pagesBS 1JAHANZEB NAZIRNo ratings yet
- Transportation in PlantsDocument31 pagesTransportation in PlantssamskruthamanabroluNo ratings yet
- Water Movement Between CellsDocument26 pagesWater Movement Between CellsEdwin AlejoNo ratings yet
- Bio Notes FinalsDocument4 pagesBio Notes FinalsJoaquine ArateaNo ratings yet
- Finals NotesDocument21 pagesFinals NotesJoaquine ArateaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10: Transport in Multicellular Plants: SummaryDocument6 pagesChapter 10: Transport in Multicellular Plants: SummaryMerimaNo ratings yet
- Diffusion and OsmosisDocument1 pageDiffusion and OsmosisNoisy KenNo ratings yet
- GRADE 11 (Supplementary Information)Document3 pagesGRADE 11 (Supplementary Information)EleinaNo ratings yet
- Movement in and Out of Cells NotesDocument9 pagesMovement in and Out of Cells Notesmanarehab35No ratings yet
- Mental Health Psychiatric Nursing PracticeDocument14 pagesMental Health Psychiatric Nursing PracticeShara SampangNo ratings yet
- Data Alkes 2020 TerbaruDocument23 pagesData Alkes 2020 TerbaruRoyliNo ratings yet
- CropSci101 Module 3Document11 pagesCropSci101 Module 3Jetro Neil GapasinNo ratings yet
- Types of Burns ArticleDocument7 pagesTypes of Burns ArticleSeltri 'ceti' SeptianiNo ratings yet
- BrodmannDocument2 pagesBrodmannEdelleMojicaDafilmotoNo ratings yet
- Gangguan Dan Keseimbangan Cairan Dan ElektrolitDocument37 pagesGangguan Dan Keseimbangan Cairan Dan ElektrolitFyana PutriNo ratings yet
- Desolation - RL CaulderDocument308 pagesDesolation - RL CaulderInes LagarrigueNo ratings yet
- Guide To AMA Manual of StyleDocument5 pagesGuide To AMA Manual of StyleAbo Ahmed TarekNo ratings yet
- Lea Joy Jugo Exercise 23Document6 pagesLea Joy Jugo Exercise 23Joan Aclo SerencioNo ratings yet
- Assignment Module 3Document14 pagesAssignment Module 3Asshi Sha50% (4)
- Botulinum Toxins in Clinical Aesthetic Practice 3rd Edition Volume Two - Functional Anatomy and Injection Techniques 2018Document237 pagesBotulinum Toxins in Clinical Aesthetic Practice 3rd Edition Volume Two - Functional Anatomy and Injection Techniques 2018Dogukan Demir75% (4)
- Transfer To Definitive Care EcaDocument40 pagesTransfer To Definitive Care EcaFahrurido Kusbari100% (1)
- Cell Membrane Structure and FunctionDocument10 pagesCell Membrane Structure and FunctionkyleeebooggNo ratings yet
- Co2 PDFDocument4 pagesCo2 PDFSITI SARAH BTE NOOR MEAHNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 Innate ImmunityDocument26 pagesLecture 3 Innate ImmunitytimcarasNo ratings yet
- Prinsip Penyusunan Gigi Artifisial Kelompok 7Document53 pagesPrinsip Penyusunan Gigi Artifisial Kelompok 7gilangNo ratings yet
- Seeley's Chapter 8 Nervous SystemDocument100 pagesSeeley's Chapter 8 Nervous SystemChristine Tapawan88% (8)
- Dr. Lakshmi Kiruba N Assistant Professor Department of Anatomy SmbtimsrcDocument25 pagesDr. Lakshmi Kiruba N Assistant Professor Department of Anatomy Smbtimsrclakshmi kirubaNo ratings yet
- 24 Cerebral Blood FlowDocument31 pages24 Cerebral Blood FlowZuhaib Ahmed100% (1)
- Blg1502 Exam Prep Doc - Part 1&2Document18 pagesBlg1502 Exam Prep Doc - Part 1&2Pasipanodya MuzendaNo ratings yet
- Voicedisordersinthe Elderly: Karen M. Kost,, Robert T. SataloffDocument13 pagesVoicedisordersinthe Elderly: Karen M. Kost,, Robert T. SataloffFernanda MerichesNo ratings yet
- TranslationDocument1 pageTranslationGianne AbcedeNo ratings yet
- Science 8 Q4M1 Digestive System 2021 2022Document5 pagesScience 8 Q4M1 Digestive System 2021 2022carl helloNo ratings yet
- 6.1 Digestion BNDocument24 pages6.1 Digestion BNHana ElattarNo ratings yet
- From Li ZhongziDocument4 pagesFrom Li ZhongziRadhakrishnan KasthuriNo ratings yet
- VEALDocument8 pagesVEALcutiepattotieNo ratings yet
- Nutrisi Cedera KepalaDocument46 pagesNutrisi Cedera Kepalatsunami555No ratings yet
- PhysioEx Exercise 9 Activity 5Document3 pagesPhysioEx Exercise 9 Activity 5Gonzeilo11No ratings yet
- Reviewer 18 4 BPPK MCQDocument5 pagesReviewer 18 4 BPPK MCQBio Data50% (2)
- Forensic 5Document19 pagesForensic 5rochelle posadasNo ratings yet