Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Photosynthesis #1
Uploaded by
Wally WestCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Photosynthesis #1
Uploaded by
Wally WestCopyright:
Available Formats
All life on earth depends on photosynthesis, either directly or, as in the case of animals, indirectly.
Photosynthesis makes both carbon and energy available to living organisms and produces the
oxygen in the atmosphere which is vital for all aerobic forms of life. During photosynthesis plants
take in carbon dioxide and give off oxygen as a by-product. Without green plants performing
photosynthesis there would be no way for nature to replace all the oxygen being consumed in
processes such as respiration and combustion. Furthermore the levels of carbon dioxide in the
atmosphere would increase. Thus, the balance of atmospheric gases is kept stable by
photosynthesis. Green plants are called producers because they produce all their own food from the
raw materials around them via photosynthesis. Animals and humans on the other hand are
consumers and all the food they eat comes directly or indirectly from plants. Thus photosynthesis is
the ultimate source of almost all of our food.
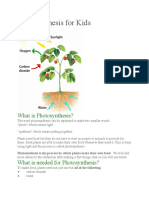
Sugar is made during photosynthesis from carbon dioxide and water. The energy for the reaction
comes from light and is stored within sugar which is an energy-rich molecule. The overall equation
for this reaction is: 6CO2 + 6H20 ------> C6H1206 + 6O2. The xylem tissues of roots, stems and leaf
vascular bundles bring water to the photosynthesising cells of the leaf. The carbon dioxide diffuses
into the leaf through stomata. It then diffuses air spaces and into mesophyll cells and finally into
chloroplasts.
In eukaryotes, photosynthesis takes place in organelles called chloroplasts. They are found in the
cytoplasm. Chloroplasts are surrounded by two membranes, which form the chloroplast envelope.
They always contain chlorophyll and other photosynthetic pigments located on a system of
membranes, the membranes run through a ground substance, or stroma. The membrane system is
the site of the light dependent reactions in photosynthesis. The membranes are covered with
chlorophyll and other pigments, enzymes and electron carriers. The system consists of many
flattened, fluid-filled sacs called thylakoids which forms stacks called grana at intervals, with lamellae
between the grana. The stroma is the site of the light independent reactions of photosynthesis. The
structure is gel-like, containing soluble enzymes, such as sugars and organic acids. Excess
carbohydrate from photosynthesis is sometimes seen stored as grains of starch Lipid droplets are
often associated with the membranes. They become larger as membranes break down during ageing
presumably accumulating lipids from the membrane.
Photosynthesis uses light energy to cause carbon dioxide and water to react to produce
carbohydrates and oxygen. The light energy is transformed to chemical energy in the carbohydrates.
Most photosynthesis takes place inside chloroplasts in palisade cells in leaves. Inside the chloroplast
are stacks of thylakoids, called grana, as well as stroma, the dense fluid inside of the chloroplast.
These thylakoids contain the chlorophyll that is necessary for the plant to go through
photosynthesis.
You might also like
- Photosynthesis and RespirationDocument46 pagesPhotosynthesis and RespirationCarmsNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis Converts Light Energy to Chemical EnergyDocument13 pagesPhotosynthesis Converts Light Energy to Chemical EnergyMina IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Biology Project KBDocument35 pagesBiology Project KBHarshita ThakkarNo ratings yet
- PHOTOSYNTHESISDocument4 pagesPHOTOSYNTHESISsuwethajNo ratings yet
- Introduction To PhotosynthesisDocument11 pagesIntroduction To PhotosynthesisSohmNo ratings yet
- PhotosynthesisDocument2 pagesPhotosynthesisHans ZacariasNo ratings yet
- Essay On PhotosynthesisDocument1 pageEssay On PhotosynthesisRameesha MalikNo ratings yet
- Kreb's Cycle ExplainedDocument7 pagesKreb's Cycle ExplainedEdelaine V. SayconNo ratings yet
- What Is PhotosynthesisDocument4 pagesWhat Is PhotosynthesisJohn Dulay MendozaNo ratings yet
- Photosyntheis and RespirationDocument37 pagesPhotosyntheis and Respirationfelisilda.136571140273No ratings yet
- What Is Photosynthesis?: Cellular Respiration FermentationDocument8 pagesWhat Is Photosynthesis?: Cellular Respiration FermentationDiana Jean Alo-adNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis: How Plants Use Sunlight to Produce FoodDocument21 pagesPhotosynthesis: How Plants Use Sunlight to Produce FoodEpoyNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis Notes and LectureDocument18 pagesPhotosynthesis Notes and LectureDexter JamesNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in ElsDocument4 pagesReviewer in ElsJane VelascoNo ratings yet
- SUMMARY NOTES On Biodiversity & PhotosynthesisDocument4 pagesSUMMARY NOTES On Biodiversity & PhotosynthesisBonachita YamNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis - Part I: The Sun and LightDocument3 pagesPhotosynthesis - Part I: The Sun and LightKc0911100% (1)
- Presentaion On NutritionDocument33 pagesPresentaion On NutritionAarushi PatidarNo ratings yet
- Practical 3: Photosynthesis & Transpiration: Student Name: Lê Hà Phương Ly ID: BTBTIU21220Document2 pagesPractical 3: Photosynthesis & Transpiration: Student Name: Lê Hà Phương Ly ID: BTBTIU21220Le Phuong LyNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3. Crop ScienceDocument57 pagesLesson 3. Crop ScienceKa Hilie Escote MiguelNo ratings yet
- biolab2Document3 pagesbiolab2diemtruc414No ratings yet
- Understanding Photosynthesis and Plant ProcessesDocument3 pagesUnderstanding Photosynthesis and Plant ProcessesQuynh Dang PhuongNo ratings yet
- Pre-Labs 3: 1. What Are Autotrophs and Heterotrophs? Give Each One ExampleDocument4 pagesPre-Labs 3: 1. What Are Autotrophs and Heterotrophs? Give Each One ExampleGiao TranNo ratings yet
- How Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Work TogetherDocument5 pagesHow Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Work TogetherKhyla Grace DijenoNo ratings yet
- ECOSYSTEMDocument39 pagesECOSYSTEMJessica Manawes NavorNo ratings yet
- BIOL111 1st Sem, Final TermDocument40 pagesBIOL111 1st Sem, Final TermJasmine CatanaNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis: 6CO2+6H2O+light Energy C6H12O6 + 6O2Document3 pagesPhotosynthesis: 6CO2+6H2O+light Energy C6H12O6 + 6O2louNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 OutlineDocument13 pagesChapter 10 OutlineJosephinemwNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis (Reviewer) - JMDPDocument2 pagesPhotosynthesis (Reviewer) - JMDPJhianne Mylz ParañalNo ratings yet
- Ppt Chapter 7Document77 pagesPpt Chapter 7Joel CabañasNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Earth SystemsDocument6 pagesChapter 2 - Earth SystemsTwix ChweNo ratings yet
- Concept 10Document2 pagesConcept 10dewi amalinaNo ratings yet
- Letter For RenewalDocument5 pagesLetter For RenewalBobby Arguilles PaboresNo ratings yet
- Formation of Pharmacologically - Active Compounds in Plants - BiosynthesisDocument68 pagesFormation of Pharmacologically - Active Compounds in Plants - BiosynthesisMichi OnozaNo ratings yet
- Week 7-8 Science 9Document42 pagesWeek 7-8 Science 9Eden Rey ParoanNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis: Light-Dependent and Light-Independent ReactionsDocument12 pagesPhotosynthesis: Light-Dependent and Light-Independent ReactionsMalinda GreeneNo ratings yet
- Bioenergetics Photosynthesis and Energy FlowDocument4 pagesBioenergetics Photosynthesis and Energy Flowvin ocangNo ratings yet
- ECOSYSTEMDocument10 pagesECOSYSTEMRyanKingjimDiezUyNo ratings yet
- CPTIIDocument23 pagesCPTIIkenfack sergeNo ratings yet
- Biology Notes - Module 2 Part 2Document19 pagesBiology Notes - Module 2 Part 2belindaNo ratings yet
- Plants and Other Autotrophs Are The Producers of The BiosphereDocument12 pagesPlants and Other Autotrophs Are The Producers of The Biosphereюрий локтионовNo ratings yet
- Eals 11abma1 MangosingDocument34 pagesEals 11abma1 MangosingAndrea Mae V. MangosingNo ratings yet
- Nutrition in Plants 1 PDFDocument6 pagesNutrition in Plants 1 PDFNakshatra PaliwalNo ratings yet
- Nutrition in PlantsDocument2 pagesNutrition in PlantsAhmed OmarNo ratings yet
- What Is Photosynthesis And Where Does It OccurDocument11 pagesWhat Is Photosynthesis And Where Does It OccurAllisa KhedarooNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis ReadingDocument11 pagesPhotosynthesis ReadingLogan ParkisonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 ChloroplastDocument43 pagesChapter 5 Chloroplastapi-302118206No ratings yet
- What Is PhotosynthesisDocument4 pagesWhat Is Photosynthesisasif shawNo ratings yet
- Algal Bead Lab IntroductionDocument1 pageAlgal Bead Lab IntroductionMahini DabhiNo ratings yet
- Written Report Topic: Introduction of Photosynthesis Sub. To: Prof. Ruthela Payawal Sub. By: Platero, Emily SDocument4 pagesWritten Report Topic: Introduction of Photosynthesis Sub. To: Prof. Ruthela Payawal Sub. By: Platero, Emily Sgtalite100% (1)
- Differences Between Mitochondria and ChloroplastDocument10 pagesDifferences Between Mitochondria and ChloroplastAsma Adawiyah Idris100% (1)
- Unit 1 L-1.1 1.2 1.3 Science Grade 8Document24 pagesUnit 1 L-1.1 1.2 1.3 Science Grade 8andeepthiNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis 1Document14 pagesPhotosynthesis 1Kithmini100% (1)
- PHOTOSYNTHESIS (Explanation Text)Document4 pagesPHOTOSYNTHESIS (Explanation Text)khairun nisa'No ratings yet
- PhotsynthesisDocument2 pagesPhotsynthesisLady RedNo ratings yet
- PhotosynthesisDocument1 pagePhotosynthesisPRINTDESK by DanNo ratings yet
- ZumdahlDocument17 pagesZumdahlmohammedraafat1977No ratings yet
- Photosynthesis NcellularrespirationDocument18 pagesPhotosynthesis NcellularrespirationBobby Arguilles PaboresNo ratings yet
- PHOTOSYNTHESIS (Explanation Text)Document4 pagesPHOTOSYNTHESIS (Explanation Text)khairun nisa'No ratings yet
- Photosynthesis #2Document1 pagePhotosynthesis #2Wally WestNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis: 7.1 Photosynthetic OrganismsDocument5 pagesPhotosynthesis: 7.1 Photosynthetic OrganismsSiti Amirah ShalihinNo ratings yet
- Philippine Science 9 Summative Exam ReviewDocument3 pagesPhilippine Science 9 Summative Exam ReviewMARY ROSE D. BORINAGANo ratings yet
- Principles of Horticultural PhysiologyDocument401 pagesPrinciples of Horticultural Physiologyamorio75No ratings yet
- Mock 2 IRDocument3 pagesMock 2 IRWendell Kim LlanetaNo ratings yet
- Plant Nanobionics A Novel Approach To Overcome The Environmental ChallengesDocument11 pagesPlant Nanobionics A Novel Approach To Overcome The Environmental ChallengesCuriousNo ratings yet
- MCQ Exemplar - Cell StructureDocument6 pagesMCQ Exemplar - Cell StructurenitikaNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis Presentation NXPowerLiteDocument23 pagesPhotosynthesis Presentation NXPowerLite3DSツTRĪCKSHØTNo ratings yet
- Mitochondria and ChloroplastDocument3 pagesMitochondria and ChloroplastMark Lorenz LorillaNo ratings yet
- The Cell ActivitiesDocument3 pagesThe Cell Activitiestiareximena0308No ratings yet
- Complex I to IV and ATP Synthase: Unlocking the Energy from PhotosynthesisDocument22 pagesComplex I to IV and ATP Synthase: Unlocking the Energy from PhotosynthesisArgus SavageNo ratings yet
- NAQT You Gotta KnowDocument42 pagesNAQT You Gotta Knowluigiram1No ratings yet
- PhotosynthesisDocument6 pagesPhotosynthesisFuturephd3000No ratings yet
- Thematic Unit Lesson Plan FinalDocument30 pagesThematic Unit Lesson Plan Finalapi-398862244No ratings yet
- Kendriya Vidyalaya Science Practice TestDocument19 pagesKendriya Vidyalaya Science Practice TestSaipragati AravindNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Cell Structure & Organization - Lecture NotesDocument4 pagesChapter 2 Cell Structure & Organization - Lecture Notesapi-372850888% (8)
- Biology Chapter 8 (Due Jan. 18, Test Jan. 22)Document9 pagesBiology Chapter 8 (Due Jan. 18, Test Jan. 22)عبدالرحمن شحاتهNo ratings yet
- Fifth Edition Answers To End-Of-Chapter Questions: GCSE Biology For YouDocument1 pageFifth Edition Answers To End-Of-Chapter Questions: GCSE Biology For YouclydeNo ratings yet
- Algae (1ST)Document5 pagesAlgae (1ST)bemiebooNo ratings yet
- Biological Science Canadian 2Nd Edition Freeman Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument38 pagesBiological Science Canadian 2Nd Edition Freeman Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFkieranthang03m100% (14)
- Plant Cell 2Document12 pagesPlant Cell 2Icy MendozaNo ratings yet
- Cell WorksheetDocument12 pagesCell WorksheetNahed SafiNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure (Grade 6) - Free Printable Tests and Worksheets PDFDocument2 pagesCell Structure (Grade 6) - Free Printable Tests and Worksheets PDF234iagia75% (4)
- IBO 2008 Theoretical Test Part A Questions and AnswersDocument49 pagesIBO 2008 Theoretical Test Part A Questions and AnswersHanifah Ainun AryanaNo ratings yet
- Grade 12 Cell Structure and FunctionsDocument21 pagesGrade 12 Cell Structure and FunctionsNoemi DenostaNo ratings yet
- Microbiology MCQS: BacteriaDocument13 pagesMicrobiology MCQS: BacteriaIqbal HussainNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 Study Guide (Campbell & Reece)Document4 pagesChapter 10 Study Guide (Campbell & Reece)grantg2008No ratings yet
- Science 7 Quarter 2 Plant and AnimalDocument6 pagesScience 7 Quarter 2 Plant and AnimalMelerose Dela SernaNo ratings yet
- DSE Bio Check PointDocument253 pagesDSE Bio Check PointLeo DaiNo ratings yet
- Code-A: Regd. Office: Aakash Tower, 8, Pusa Road, New Delhi-110005 PH.: 011-47623456Document15 pagesCode-A: Regd. Office: Aakash Tower, 8, Pusa Road, New Delhi-110005 PH.: 011-47623456rhevaNo ratings yet
- The Fundamental Unit of LifeDocument11 pagesThe Fundamental Unit of LifeRaghav AggarwalNo ratings yet