Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Solar Inverter
Uploaded by
Mutaz M Banat0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views10 pagesThe document discusses solar PV inverters and their efficiency. It notes that inverters convert DC electricity from PV arrays into AC electricity for the grid by latching onto the grid's frequency and voltage. The efficiency of inverters depends on input voltage and power levels and is not constant. Weighted efficiencies that combine performance over a range of conditions provide a single representative value. Models like the Sandia National Laboratories model provide curves describing instantaneous efficiency as a function of input parameters.
Original Description:
Original Title
solar inverter (1)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses solar PV inverters and their efficiency. It notes that inverters convert DC electricity from PV arrays into AC electricity for the grid by latching onto the grid's frequency and voltage. The efficiency of inverters depends on input voltage and power levels and is not constant. Weighted efficiencies that combine performance over a range of conditions provide a single representative value. Models like the Sandia National Laboratories model provide curves describing instantaneous efficiency as a function of input parameters.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views10 pagesSolar Inverter
Uploaded by
Mutaz M BanatThe document discusses solar PV inverters and their efficiency. It notes that inverters convert DC electricity from PV arrays into AC electricity for the grid by latching onto the grid's frequency and voltage. The efficiency of inverters depends on input voltage and power levels and is not constant. Weighted efficiencies that combine performance over a range of conditions provide a single representative value. Models like the Sandia National Laboratories model provide curves describing instantaneous efficiency as a function of input parameters.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 10
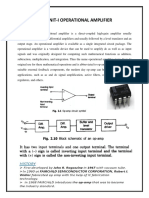
Solar PV Inverters
In grid-connected systems, the inverter is connected directly
to the PV array and converts the DC electricity coming from
the PV array into AC electricity
– The inverter latches on to the grid’s frequency and voltage
– It contains an MPP tracker, a DC-DC converter, and a DC-AC
inverter
© 2020 S. Alnaser - The University of Jordan 1
Solar PV Implementation Topologies
© 2020 S. Alnaser - The University of Jordan 2
Efficiency of the inverter - Definition
This definition comprises the complete inverter unit
– Since the real inverter has many components and due to the lack
of detailed data from inverters manufacturers, some models have
been developed to describe the efficiency These models are
based on empirical formulas
– It is important to note that the efficiency here reported is an
instantaneous value, which means that it is time-dependent
© 2020 S. Alnaser - The University of Jordan 3
Efficiency of the inverter - Definition
The inverter efficiency is not constant, but strongly depends on
the DC input voltage and the total DC input power
– It should be noted that every inverter and every manufacturer
show a different behaviour when it comes to efficiencies
© 2020 S. Alnaser - The University of Jordan 4
Weighted Efficiencies
A reliable way of expressing the inverter efficiency with a
single number is to use weighted efficiencies
– This method combines the inverter efficiencies over a wide range
of solar expositions
– Eta values like the one in the red circle denote the efficiency at a
certain percentage of nominal power of the inverter.
– Two different weighted efficiencies are commonly used
• First, the European efficiency, which represents a low
insolation climate such as in Central Europe
• second, the California Energy Commission (CEC) efficiency,
which represents the PV system performance in high insolation
regions such as in the southwest of the United Sta
© 2020 S. Alnaser - The University of Jordan 5
Instantaneous Efficiencies Estimation - SNL model
Weighted coefficients approach is a better approach compared
to the peak efficiency, it still provides an average efficiency
More accurate representation of the instantaneous inverter
performance at every level of input power and voltage must be
developed
Many research institutes around the world have published
extended data
– These data present efficiency curves for a large range of inverters
as a function of several characteristic parameters
– One useful database is the one provided by Sandia National
Laboratories (SNL model)
© 2020 S. Alnaser - The University of Jordan 6
SNL model - Parameters
Non-linearity between DC input and AC output
A device working at nominal voltage Vdc zero
– The pattern changes with a lower or a higher voltage
The AC power limit for which the inverter is designed is Pac0
and provides the nominal dc power Pdc0 when it crosses the
nominal voltage line
Ps zero, which is the self consumption of the inverter
C zero used to describe the non-linear nature of the inverter
© 2020 S. Alnaser - The University of Jordan 7
SNL model - Inverter Efficiency with DC input
voltage
For a different type of inverter, a higher voltage can lead to
higher efficiencies or vice versa
© 2020 S. Alnaser - The University of Jordan 8
SNL model
The SNL model provides also some empirical formulas for the
AC power output as function of different parameters
© 2020 S. Alnaser - The University of Jordan 9
Pac = ac-power output from inverter based on input power and voltage, (W)
Pdc = dc-power input to inverter, typically assumed to be equal to the PV array
maximum power, (W)
Vd = dc-voltage input, typically assumed to be equal to the PV array maximum power
voltage, (V)
Paco = maximum ac-power “rating” for inverter at reference or nominal operating
condition, assumed to be an upper limit value, (W)
Pdco = dc-power level at which the ac-power rating is achieved at the reference
operating condition, (W)
Vdco = dc-voltage level at which the ac-power rating is achieved at the reference
operating condition, (V)
Pso = dc-power required to start the inversion process, or self-consumption by inverter,
strongly influences inverter efficiency at low power levels, (W)
Pnt = ac-power consumed by inverter at night (night tare) to maintain circuitry required
to sense PV array voltage, (W) Co = parameter defining the curvature (parabolic) of the
relationship between ac-power and dc-power at the reference operating condition, default
value of zero gives a linear relationship, (1/W)
C1 = empirical coefficient allowing Pdco to vary linearly with dc-voltage input, default
value is zero, (1/V)
C2 = empirical coefficient allowing Pso to vary linearly with dc-voltage input, default
value is zero, (1/V)
C3 = empirical coefficient allowing Co to vary linearly with dc-voltage input, default value
is zero, (1/V)
© 2020 S. Alnaser - The University of Jordan 10
You might also like
- A Tuned Rectifier For RF Energy Harvesting From Ambient RadiationsDocument6 pagesA Tuned Rectifier For RF Energy Harvesting From Ambient RadiationsAppu ManiNo ratings yet
- Seal Kit Seal KitDocument61 pagesSeal Kit Seal KitМаксим Стратила0% (1)
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- PW160-7K S 0411Document890 pagesPW160-7K S 0411ado_22100% (3)
- Vallorbs Guide Cut Vs Rolled ThreadsDocument3 pagesVallorbs Guide Cut Vs Rolled ThreadsOrlando AriasNo ratings yet
- GED 7 Life and Works of Jose RizalDocument104 pagesGED 7 Life and Works of Jose RizalRheamie Fuyonan100% (1)
- Business Ethics Case StudiesDocument25 pagesBusiness Ethics Case Studiesswaggerbox100% (2)
- Pereira 2021Document9 pagesPereira 2021Serapio TrabucoNo ratings yet
- Single-Phase Seven-Level Grid-Connected Inverter For Photovoltaic SystemDocument7 pagesSingle-Phase Seven-Level Grid-Connected Inverter For Photovoltaic Systemanil kasotNo ratings yet
- To Simulate, Design & Implementation of Maximum Power Harvesting of Solar Energy by Using DC-DC ConverterDocument6 pagesTo Simulate, Design & Implementation of Maximum Power Harvesting of Solar Energy by Using DC-DC Convertershrawani rajputNo ratings yet
- Maximum Power Point Tracking of Coupled Interleaved Boost Converter Supplied SystemDocument10 pagesMaximum Power Point Tracking of Coupled Interleaved Boost Converter Supplied SystemRaveendhra IitrNo ratings yet
- Interleaved 08846718Document14 pagesInterleaved 08846718Marcelo Flavio GuepfrihNo ratings yet
- Full TextDocument9 pagesFull TextManoj GuptaNo ratings yet
- FinalDocument53 pagesFinalKishore GvNo ratings yet
- Design, Modeling, Analysis and Simulation of A SEPIC ConverterDocument7 pagesDesign, Modeling, Analysis and Simulation of A SEPIC ConverterLovely LianaNo ratings yet
- A Buck-Boost Based DC AC Converter For Residential PV ApplicationsDocument6 pagesA Buck-Boost Based DC AC Converter For Residential PV ApplicationsFrancesco AcunzoNo ratings yet
- Unipolar and Bipolar SPWM Voltage Modula PDFDocument5 pagesUnipolar and Bipolar SPWM Voltage Modula PDFĐorđe ĐurđićNo ratings yet
- A Seven Level Inverter Using A Solar Power Generation SystemDocument7 pagesA Seven Level Inverter Using A Solar Power Generation Systemsasitharan33No ratings yet
- The Kavery Engineering College, MecheriDocument21 pagesThe Kavery Engineering College, MecheriperumalNo ratings yet
- Solar PDFDocument5 pagesSolar PDFjhony7373No ratings yet
- Genetic Algorithm Based Maximum Power Tracking in Solar Power GenerationDocument6 pagesGenetic Algorithm Based Maximum Power Tracking in Solar Power GenerationzedibNo ratings yet
- Design of Transformer Less Single Phase InverterDocument9 pagesDesign of Transformer Less Single Phase InverterEditor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- Design and Implementation of PV Fed Two Stage DC/DC Converter For Home ApplicationsDocument6 pagesDesign and Implementation of PV Fed Two Stage DC/DC Converter For Home ApplicationsVishal KevatNo ratings yet
- Simulation of VSC Based HVDC Transmission System For The IntegratDocument5 pagesSimulation of VSC Based HVDC Transmission System For The IntegratManideep AdepuNo ratings yet
- Modelling, Simulation of MPPT Using Perturb and Observe and Incremental Conductance Techniques For Stand-Alone PV Systems PDFDocument7 pagesModelling, Simulation of MPPT Using Perturb and Observe and Incremental Conductance Techniques For Stand-Alone PV Systems PDFEberton SantosNo ratings yet
- Controller Design and Implementation of Solar Panel Companion InvertersDocument11 pagesController Design and Implementation of Solar Panel Companion InvertersroyNo ratings yet
- Implementation of SVPWM Technique in Four Wire Inverter For Uninterruptible Power Supply (Ups) ApplicationsDocument10 pagesImplementation of SVPWM Technique in Four Wire Inverter For Uninterruptible Power Supply (Ups) ApplicationsMani Vannan SoundarapandiyanNo ratings yet
- Based Power Tracking For Nonlinear PV SourcesDocument8 pagesBased Power Tracking For Nonlinear PV SourcesRaveendhra IitrNo ratings yet
- BATCH 4-Power QualityDocument22 pagesBATCH 4-Power QualityVasanthNo ratings yet
- (Project) INTEGRATION OF SOLAR PV INTO GRIDDocument13 pages(Project) INTEGRATION OF SOLAR PV INTO GRIDMadhavan. M /013No ratings yet
- Budiman 2018 IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 288 012031Document7 pagesBudiman 2018 IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 288 012031Rasool Bakhsh RajarNo ratings yet
- Implementation of Dual Control MPPT-based DC-DC Converter Fed Solar PV Power ApplicationDocument8 pagesImplementation of Dual Control MPPT-based DC-DC Converter Fed Solar PV Power ApplicationArun raj DharamsuthNo ratings yet
- Presentation On Single Phase Grid Connected Rooftop IntegratedDocument42 pagesPresentation On Single Phase Grid Connected Rooftop IntegratedmonaNo ratings yet
- Transformerless InverterDocument4 pagesTransformerless InverterPunitNo ratings yet
- A Review of The Main Methods To Trace The I-V Characteristic Curve of PV SourcesDocument7 pagesA Review of The Main Methods To Trace The I-V Characteristic Curve of PV SourcesShubham KumarNo ratings yet
- Review of DC-DC Converters in Photovoltaic Systems For MPPT SystemsDocument5 pagesReview of DC-DC Converters in Photovoltaic Systems For MPPT SystemsLuis Angel Garcia ReyesNo ratings yet
- 14sepicconferencepaper PDFDocument6 pages14sepicconferencepaper PDFSherrinNo ratings yet
- Back-Stepping Control of Off-Grid PV InverterDocument6 pagesBack-Stepping Control of Off-Grid PV InverterMartino Ojwok AjangnayNo ratings yet
- Final PDFDocument43 pagesFinal PDFحسن كميت hassankomeit lNo ratings yet
- 2014 Divya Prasanna-RajuDocument7 pages2014 Divya Prasanna-RajuRaju KuruvaNo ratings yet
- Literature Review of PV Panel EmulatorDocument12 pagesLiterature Review of PV Panel EmulatorEsala Hirumal SenevirathneNo ratings yet
- Comparative Study of MLI and Dual Inverter Using Space Vector Modulation TechniquesDocument8 pagesComparative Study of MLI and Dual Inverter Using Space Vector Modulation Techniquesshiva256No ratings yet
- A Solar Power Generation System With A Seven-Level Inverter: Jinn-Chang Wu, Member, IEEE, Chia-Wei ChouDocument9 pagesA Solar Power Generation System With A Seven-Level Inverter: Jinn-Chang Wu, Member, IEEE, Chia-Wei Chouckrishna625No ratings yet
- Anand2019 Article ADynamicLoadControllerForAStanDocument10 pagesAnand2019 Article ADynamicLoadControllerForAStanMoahmmed AlharbiNo ratings yet
- Experiment 5 PDFDocument1 pageExperiment 5 PDFAstuNo ratings yet
- Incremental Conductance MPPT Algorithm For PV System Implemented Using DC-DC Buck and Boost ConverterDocument10 pagesIncremental Conductance MPPT Algorithm For PV System Implemented Using DC-DC Buck and Boost ConverterSkp FANo ratings yet
- Malaysia Z SourceInverterWithImprovedPerformanceforPhotovoltaicApplicationsDocument6 pagesMalaysia Z SourceInverterWithImprovedPerformanceforPhotovoltaicApplicationsJayanth Kumar M HNo ratings yet
- Back-Stepping Control of Off-Grid PV InverterDocument6 pagesBack-Stepping Control of Off-Grid PV InverterMartino Ojwok AjangnayNo ratings yet
- MPPT P&oDocument7 pagesMPPT P&onoumsi briceNo ratings yet
- Soft-Switching Current-Fed Push-Pull Converter For 250-W AC Module ApplicationsDocument10 pagesSoft-Switching Current-Fed Push-Pull Converter For 250-W AC Module ApplicationsTaubat NasukhaNo ratings yet
- An Efficient Wireless Charger For Electric Vehicle Battery ChargingDocument5 pagesAn Efficient Wireless Charger For Electric Vehicle Battery ChargingPrasadNooluNo ratings yet
- Paper 5Document9 pagesPaper 5Mustansar KhosaNo ratings yet
- A Single-Stage Multi-Port Buck-Boost InverterDocument14 pagesA Single-Stage Multi-Port Buck-Boost Invertertengfei.sunNo ratings yet
- Iccicct - 122 PDFDocument6 pagesIccicct - 122 PDFGlan DevadhasNo ratings yet
- Comparison of Different DC-DC ConverterDocument6 pagesComparison of Different DC-DC ConverterabdelbassetNo ratings yet
- A Controlled Full-Bridge Rectifier As AC-DC Converter For On-Board EV ChargersDocument5 pagesA Controlled Full-Bridge Rectifier As AC-DC Converter For On-Board EV ChargersAlice LiewNo ratings yet
- Sundar 2016Document5 pagesSundar 2016rajapandiyaNo ratings yet
- Photovoltaic Powered DC-DC Boost Converter Based oDocument12 pagesPhotovoltaic Powered DC-DC Boost Converter Based oMeryouma LarbNo ratings yet
- Base Paper 7Document13 pagesBase Paper 7Prince RohithNo ratings yet
- Inverter Distributed: Controller Generation SystemsDocument7 pagesInverter Distributed: Controller Generation SystemsJohnNo ratings yet
- Multiple Output Smps Using A Single Cuk Converter: Jbvreddy@nic - in Bhuvan@ee - Iitd.ernet - inDocument6 pagesMultiple Output Smps Using A Single Cuk Converter: Jbvreddy@nic - in Bhuvan@ee - Iitd.ernet - indan1007No ratings yet
- ELDADocument4 pagesELDAarurizaNo ratings yet
- Single Switch AC DC Cuk Converter For Power Factor and Efficiency EnhancementDocument5 pagesSingle Switch AC DC Cuk Converter For Power Factor and Efficiency EnhancementInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Paper 1Document17 pagesPaper 1Shambhu SharanNo ratings yet
- Rao 2021Document17 pagesRao 2021NiamatasifNo ratings yet
- 02 Samss 009Document13 pages02 Samss 009barouniamineNo ratings yet
- BAEnglish Language Linguistics PDFDocument93 pagesBAEnglish Language Linguistics PDFAnonymous p5BEJzvqrkNo ratings yet
- Quiz 1 Distribusi Plus JawabanDocument6 pagesQuiz 1 Distribusi Plus JawabandimasfupNo ratings yet
- Ic NotesDocument67 pagesIc NotesVijaya Kumar VadladiNo ratings yet
- CDI1Document40 pagesCDI1Leonino Angelica Aiko S.No ratings yet
- Gb590 Report - SpangaroDocument137 pagesGb590 Report - Spangarotome44No ratings yet
- Circuflow 5200 Operating InstructionsDocument24 pagesCircuflow 5200 Operating InstructionsalexNo ratings yet
- Entire Environmental Quality - DesignDocument374 pagesEntire Environmental Quality - DesignLTE002No ratings yet
- ECN 301 - Lecture 3Document36 pagesECN 301 - Lecture 3Parvez Bin KamalNo ratings yet
- Competitiveness Huawei Casestudy WebDocument40 pagesCompetitiveness Huawei Casestudy Webjameslee27No ratings yet
- DAA NotesDocument97 pagesDAA Notesanish.t.pNo ratings yet
- Karma: "Dove La Legge Della Grazia È Attiva, Finisce La Legge Del Karma"Document37 pagesKarma: "Dove La Legge Della Grazia È Attiva, Finisce La Legge Del Karma"Lars JensenNo ratings yet
- Revo Uninstaller Pro HelpDocument61 pagesRevo Uninstaller Pro HelpGuy Sinclaire OmbeNo ratings yet
- Edi WowDocument11 pagesEdi WowfantasighNo ratings yet
- Public Servants and Government ServantsDocument10 pagesPublic Servants and Government Servantsalexandra angelinaNo ratings yet
- 제8차 전력수급기본계획Document51 pages제8차 전력수급기본계획김명근No ratings yet
- Sınıf 2. Yazılı A-B RelearnDocument5 pagesSınıf 2. Yazılı A-B RelearncanerNo ratings yet
- Canon Ir8070 Error Codes List PDFDocument18 pagesCanon Ir8070 Error Codes List PDFGirish KumarNo ratings yet
- Pte Apeuni 20240408 Global Monthly en Kd54Document321 pagesPte Apeuni 20240408 Global Monthly en Kd54Boyes WorldNo ratings yet
- ElectrogravimetryDocument5 pagesElectrogravimetryMELISSA VERONICA TUDELANO OSPINANo ratings yet
- 5 Ijcms-V3i2-2012-02Document6 pages5 Ijcms-V3i2-2012-02saiNo ratings yet
- Image Processing (Rry025)Document22 pagesImage Processing (Rry025)Babasrinivas GuduruNo ratings yet
- SPHE8281DDocument35 pagesSPHE8281Ddiego-tNo ratings yet
- Omb ValvesDocument52 pagesOmb ValvesCesar SotoNo ratings yet
- Model Rocketry Safety CodeDocument2 pagesModel Rocketry Safety CodeAviation/Space History LibraryNo ratings yet