Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Shigella and Cholera
Uploaded by
mohamed mowafeyOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Shigella and Cholera
Uploaded by
mohamed mowafeyCopyright:
Available Formats
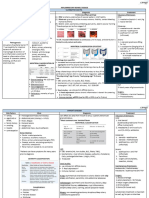
Shigellosis = Bacillary dysentry Cholera
Definition Bloody mucoid diarrhea with tenesmus (=cramping rectal pain) Severe perfuse excessive watery (secretory) diarrhea leading to dehydration
Causative 1. Shigella dysenteriae 2. Shigella flexneri
Vibrio cholera
agent 3. Shigella boydii 4. Shigella sonnei
IP 1-3 days 1-3 days
MOT Feco-oral, mainly water contaminated with cholera Feco-oral, mainly water contaminated with cholera
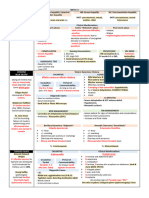
1. Ingestion of food contaminated by shigella dysenteriae 1. Ingested
2. Presence of bacteria in the lumen of the colon (causing irritation due to endotoxin secretion) 2. Present in lumen (non-invasive) and secrete:
3. Locally invasion of colon wall & secretion of 3 exotoxins: a. Endotoxin leading to irritation of intestinal mucosa
Pathogenesis a. Cytotoxin: cell death b. Enterotoxin: intestinal damage b. Exotoxin: has 2 subunits (A, B): B subunit facilitate wall invasion by A: Causing
c. Neurotoxin: convulsions in children activation of adenyl cyclase leading to increased ATP and opening of all channels
into lumen leading to loss of K+, Na+, water (20-30 L/day)
1. Vomiting: at first: food remnants, Then rice-water (off white).
1. Constitutional symptoms: fever, malaise, anorexia, nausea, vomiting. 2. Diarrhea: at first: fecal matter, Then rice-water.
2. Specific symptoms: dysentery (=bloody mucoid diarrhea with tenesmus), abdominal pain, 3. Dehydration:
colic. a. Hypotension, tachycardia with weak pulsation
C/P b. Hypothermia
c. Cold dry skin & extremities
d. Rapid shallow breathing leading to acidosis
e. Coma and death
1. Clinical in epidemic area (= Presented with the C\P)
1. Detection of organism in stool: by stool analysis and culture 2. Lab: stool analysis and isolation of organism by stool culture on TCBS (=Thiosulfate citrate
2. Effect: reduced electrolytes as K+ bile salts sucrose agar)
Investigations 3. Effect:
3. PCR, ELISA, Increased ESR
a. Decreased K+ & Na+ & Cl- & HCO3-
b. Increased urea and creatinine due to hypovolemia leading to prerenal failure
All are due to dehydration:
Dysentery, necrosis, ulcer, heal with a membrane (after membrane removing): 1. Corneal ulcer
1. Bleeding per rectum, anemia and hypotension. 2. Chest: pneumonia
Complications 2. Perforation leading to peritonitis and IBD. 3. Cholecystitis
3. Reiter’s syndrome leading to conjunctivitis, urethritis, arthritis. 4. Convulsions and coma
5. In females: Abortion
6. In males: scrotal gangrene
1. Symptomatic treatment Rehydration by: Ringer lactate > saline > ORS
Treatment 2. Antibiotic if complicated by ciprofloxacin 500mg oral twice daily (same as **Saline causes increased Cl- which exchange with H+ leading to acidosis
typhoid) Antibiotic (if needed): Tetracycline & doxycycline (used also for prevention)
>> DD: Anaerobic dysentery caused by entamoeba histolytica which also cause ulcer Vaccination : Koll’s vaccine (killed vaccine)
Note: Hepatic patient presents with renal impairment, how to differentiate between prerenal
and hepatorenal impairment? By: Urea / Creatinine ration:
1. If >100 = prerenal and need rehydration As: urea and creatinine are increased but
Note Typhoid treatment same as shigella treatment, and typhoid is isolated on MacConkey agar
urea is increased more due to its increased affinity of reabsorption.
2. If normal ration = hepatorenal
You might also like
- Kolaeva NotesfsdffDocument16 pagesKolaeva NotesfsdffsharenNo ratings yet
- Acidosis: Clinical Aspects and Treatment with Isotonic Sodium Bicarbonate SolutionFrom EverandAcidosis: Clinical Aspects and Treatment with Isotonic Sodium Bicarbonate SolutionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Express GI Notes 2012Document31 pagesExpress GI Notes 2012Zul Azim AnuarNo ratings yet
- The Principal Diseases of Lower VertebratesFrom EverandThe Principal Diseases of Lower VertebratesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Infectious Diseases Tabelle (Examen 6. Jahr)Document34 pagesInfectious Diseases Tabelle (Examen 6. Jahr)Aastha SethNo ratings yet
- Diverticulosis, A Simple Guide to the Condition, Treatment and Related DiseasesFrom EverandDiverticulosis, A Simple Guide to the Condition, Treatment and Related DiseasesRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- DiarrheaDocument10 pagesDiarrheaDwi putri PermatasariNo ratings yet
- Ncmb312 Lec FinalDocument63 pagesNcmb312 Lec FinalRose Ann CammagayNo ratings yet
- GU Blackboard OutlineDocument15 pagesGU Blackboard Outlinedlneisha61No ratings yet
- Gastrointestinal DisordersDocument9 pagesGastrointestinal Disordersgrazelantonette.calubNo ratings yet
- DiarrheaDocument6 pagesDiarrheaSara JosephNo ratings yet
- Lesson 7 8 9Document8 pagesLesson 7 8 9daryl jan komowangNo ratings yet
- Animal Proposal (Yojana)Document24 pagesAnimal Proposal (Yojana)Sreekanth reddyNo ratings yet
- Choler A: Prepared By: Angelou Mortos John Radley SantosDocument11 pagesCholer A: Prepared By: Angelou Mortos John Radley SantosAdhaNo ratings yet
- Diarrhea: Acute, Sub Acute, & Chronic: - ! DefinitionDocument7 pagesDiarrhea: Acute, Sub Acute, & Chronic: - ! DefinitionWen Jie LauNo ratings yet
- Parasitic - Toxic SummaryDocument9 pagesParasitic - Toxic Summaryakilesh hardowarNo ratings yet
- Week-13 Cd-Vid-Lec-1-3-Sir-GerryDocument10 pagesWeek-13 Cd-Vid-Lec-1-3-Sir-Gerryjmmacar19No ratings yet
- Structure and Classification of Bacteria: Morpho DifferencesDocument8 pagesStructure and Classification of Bacteria: Morpho DifferencesJaz CNo ratings yet
- UC & Crohn's DiseaseDocument3 pagesUC & Crohn's DiseaseYalin AbouhassiraNo ratings yet
- Week 13 - Vid Lec 1-3 Sir GerryDocument10 pagesWeek 13 - Vid Lec 1-3 Sir Gerryjmmacar19No ratings yet
- Week 13 NCMB 312 Lect NotesDocument18 pagesWeek 13 NCMB 312 Lect NotesAngie BaylonNo ratings yet
- NCMB 312 Finals!Document25 pagesNCMB 312 Finals!Justine Dinice MunozNo ratings yet
- Medsurg ElearningDocument46 pagesMedsurg ElearningNathaniel PulidoNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Disorders of Pediatric Clients-1Document10 pagesRespiratory Disorders of Pediatric Clients-1Genalyn PenuagaNo ratings yet
- Swine InfirmitiesDocument6 pagesSwine InfirmitiesNezuko CutieeeNo ratings yet
- Diarrhea PDFDocument7 pagesDiarrhea PDFLhie SamaNo ratings yet
- Pathology: One By: Bdulrahman Aljadoa & Anar AljebreenDocument7 pagesPathology: One By: Bdulrahman Aljadoa & Anar AljebreenRizki WahyuniNo ratings yet
- Sweat Chloride Test: 1. Splenic Rupture 2. Avoid Sports and Physical Activity 3. Atypical LymphocytesDocument7 pagesSweat Chloride Test: 1. Splenic Rupture 2. Avoid Sports and Physical Activity 3. Atypical LymphocytesAnonymous GfqHQ5SNwNo ratings yet
- SIMCLEX Renal and Genitourinary DisordersDocument7 pagesSIMCLEX Renal and Genitourinary DisorderssandraNo ratings yet
- AMOEBIASISDocument16 pagesAMOEBIASISAngeline TaghapNo ratings yet
- Nursing Lecture RespiratoryDocument13 pagesNursing Lecture RespiratoryAedge010100% (1)
- NCM 112 Lesson2Document5 pagesNCM 112 Lesson2Trisha LopezNo ratings yet
- CholeraDocument3 pagesCholeraKrista CabelloNo ratings yet
- Urinary System Large RuminantDocument103 pagesUrinary System Large RuminantAya HagagNo ratings yet
- By: Aseel Ali YousDocument7 pagesBy: Aseel Ali YousSharafaddin Ahmed Abbas SharafaddinNo ratings yet
- E Learning SamifinalDocument22 pagesE Learning SamifinalAhmad BaolayyanNo ratings yet
- Vibrio CholeraeDocument3 pagesVibrio CholeraeBrycelle AlleraNo ratings yet
- Report On Etiological Structure and Epidemiology of The Acute Intestinal Infections. Pa Tho Genesis of Diarrohea Caused by Infectious Agents.Document3 pagesReport On Etiological Structure and Epidemiology of The Acute Intestinal Infections. Pa Tho Genesis of Diarrohea Caused by Infectious Agents.Adnan Akram, MD (Latvia)No ratings yet
- 07 MCQ TropMed 1Document6 pages07 MCQ TropMed 1Dapot SianiparNo ratings yet
- Hemolytic Transfusion ReactionDocument3 pagesHemolytic Transfusion ReactionAinin SofiyaNo ratings yet
- Module 5Document31 pagesModule 5xtnreyesNo ratings yet
- PeritonitisDocument1 pagePeritonitisYalin AbouhassiraNo ratings yet
- Oncomelania Quadrasi (Tiny Snail)Document7 pagesOncomelania Quadrasi (Tiny Snail)JoshuaNo ratings yet
- Soil Transmitted HelminthiasesDocument6 pagesSoil Transmitted HelminthiasesJemimah MejiaNo ratings yet
- Vibrio VulnificusDocument2 pagesVibrio VulnificusDerek Miguel SmithNo ratings yet
- Gram Negative RodsDocument8 pagesGram Negative RodsRuel Maddawin100% (1)
- Arthur R. Cushny: Pharmacological Laboratory, University College, LondonDocument18 pagesArthur R. Cushny: Pharmacological Laboratory, University College, LondonAlexNo ratings yet
- Concept Map - F and EDocument1 pageConcept Map - F and EAbigail LonoganNo ratings yet
- Asthma PathophysiologyDocument4 pagesAsthma Pathophysiologysmitha lakkavallyNo ratings yet
- Laporan C IsiDocument97 pagesLaporan C Isi123 456No ratings yet
- GoutDocument4 pagesGoutapi-3822433100% (1)
- 1-5 BedahDocument9 pages1-5 BedahHalwia SiruaNo ratings yet
- PEDIATRICS DISORDER PART 2 LECTURE MergedDocument33 pagesPEDIATRICS DISORDER PART 2 LECTURE MergedErika CadawanNo ratings yet
- Fluid and ElectrolytesDocument21 pagesFluid and ElectrolytesKc Cabanilla LizardoNo ratings yet
- Pedia 2 3.04 Pediatric NephrologyDocument11 pagesPedia 2 3.04 Pediatric NephrologyJudith Dianne IgnacioNo ratings yet
- PDF DocumentDocument4 pagesPDF DocumentAnmol SinghNo ratings yet
- Report On Ethiology, Epidemiology, Pathogenesis, Clinical Features and The Treatment Principles of Cholera. Dehydration - Rehydration.Document2 pagesReport On Ethiology, Epidemiology, Pathogenesis, Clinical Features and The Treatment Principles of Cholera. Dehydration - Rehydration.Adnan Akram, MD (Latvia)No ratings yet
- BCH 376 (Urinalysis Lecture Notes)Document7 pagesBCH 376 (Urinalysis Lecture Notes)biddyusmc100% (1)
- 885 MCQs - IPCDocument181 pages885 MCQs - IPCmohamed mowafeyNo ratings yet
- 600 MCQs - CPC KAMKUSDocument102 pages600 MCQs - CPC KAMKUSmohamed mowafeyNo ratings yet
- MCQ HTNDocument18 pagesMCQ HTNmohamed mowafeyNo ratings yet
- 30 MCQs - Capital Market and SecuritiesDocument9 pages30 MCQs - Capital Market and Securitiesmohamed mowafeyNo ratings yet
- 50 MCQs - LAND LAWS MAHARASTRADocument20 pages50 MCQs - LAND LAWS MAHARASTRAmohamed mowafeyNo ratings yet
- 200 MCQs - FINANCIAL MARKETS AND OPERATIONSDocument22 pages200 MCQs - FINANCIAL MARKETS AND OPERATIONSmohamed mowafeyNo ratings yet
- 64 MCQs - SEBIDocument19 pages64 MCQs - SEBImohamed mowafeyNo ratings yet
- 2 - MCQ 2 DoneDocument9 pages2 - MCQ 2 Donemohamed mowafeyNo ratings yet
- Prelim Exam 22-23 DSBDADocument2 pagesPrelim Exam 22-23 DSBDAmohamed mowafeyNo ratings yet
- 1.3 - MCQ 1 DoneDocument7 pages1.3 - MCQ 1 Donemohamed mowafeyNo ratings yet
- JaundiceDocument5 pagesJaundicemohamed mowafeyNo ratings yet
- OSCE Internal MedicineDocument4 pagesOSCE Internal Medicinemohamed mowafeyNo ratings yet
- DiarrheaDocument5 pagesDiarrheamohamed mowafeyNo ratings yet
- MCQ Internal MedicineDocument16 pagesMCQ Internal Medicinemohamed mowafey100% (2)
- HypoglycemiaDocument3 pagesHypoglycemiamohamed mowafeyNo ratings yet
- Diabetic KetoacidosisDocument85 pagesDiabetic Ketoacidosismohamed mowafeyNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Questions Hip and ThighDocument11 pagesAnatomy Questions Hip and Thighmohamed mowafeyNo ratings yet
- HypoglycemiaDocument3 pagesHypoglycemiamohamed mowafeyNo ratings yet
- Peri-Arrest ArrythmiaDocument14 pagesPeri-Arrest Arrythmiamohamed mowafeyNo ratings yet
- Oa OsteoaethritisDocument30 pagesOa Osteoaethritismohamed mowafeyNo ratings yet
- NRPDocument15 pagesNRPmohamed mowafeyNo ratings yet
- NCM 116 W1 Reading HandoutDocument13 pagesNCM 116 W1 Reading Handoutriza sarmientoNo ratings yet
- Kode Kode DiagnosaDocument4 pagesKode Kode DiagnosaSibintang 123pagarNo ratings yet
- Approach To The Hypoglycemic PatientDocument13 pagesApproach To The Hypoglycemic PatientFiorella Peña Mora100% (2)
- Notice To Employer (Final 5.2.24)Document12 pagesNotice To Employer (Final 5.2.24)Khasyafsufi AdminNo ratings yet
- Module 7 - Meningitis and EncephalitisDocument35 pagesModule 7 - Meningitis and EncephalitisRick RanitNo ratings yet
- NCRB 2008 DataDocument2 pagesNCRB 2008 DatasilkboardNo ratings yet
- Health Science Reports - 2023 - Abbasi - Revitalizing Hope For Older Adults The Use of The Novel Arexvy For ImmunizationDocument3 pagesHealth Science Reports - 2023 - Abbasi - Revitalizing Hope For Older Adults The Use of The Novel Arexvy For Immunizationhalfani.solihNo ratings yet
- Biological Report - AS90926Document4 pagesBiological Report - AS90926Kyra ElderNo ratings yet
- Rheumatoid Arthritis in Cervical Spine NewDocument19 pagesRheumatoid Arthritis in Cervical Spine NewmarmerosNo ratings yet
- Programme: DementiaDocument20 pagesProgramme: DementiaNikolaj KaluđerovićNo ratings yet
- Types of Disability and Disorders-1Document49 pagesTypes of Disability and Disorders-1Digambar SahooNo ratings yet
- 8 Focus CrimesDocument2 pages8 Focus CrimesCIDMU NAGANo ratings yet
- Colon Spanish TranslationDocument200 pagesColon Spanish TranslationCaren Márquez100% (1)
- Skills Lab Ncmb317 Mental Status Examination FormDocument2 pagesSkills Lab Ncmb317 Mental Status Examination Formkpbalay5921pamNo ratings yet
- Patho OTDocument23 pagesPatho OTBea Y. Bas-ongNo ratings yet
- NP5 Recalls7Document11 pagesNP5 Recalls7AhrisJeannine EscuadroNo ratings yet
- 06 AQU347 Course Notes Chapter 1Document13 pages06 AQU347 Course Notes Chapter 1Nurul Syafiqah Binti ShaidanNo ratings yet
- Peoria County Booking Sheet 08/06/15Document8 pagesPeoria County Booking Sheet 08/06/15Journal Star police documentsNo ratings yet
- Iq2wjqjhfkkby1lyhkyd5z3iDocument2 pagesIq2wjqjhfkkby1lyhkyd5z3iSubham RajputNo ratings yet
- Essay 1Document4 pagesEssay 1Farahida IbrahimNo ratings yet
- IASP-PainManagementCenter ToolkitDocument89 pagesIASP-PainManagementCenter ToolkitAlejandra Molina BarradasNo ratings yet
- The World PandemicDocument3 pagesThe World PandemicMariel Niña ErasmoNo ratings yet
- Management Protocol in Medicine: ContentsDocument12 pagesManagement Protocol in Medicine: ContentsAMIT KAPOORNo ratings yet
- Rohit Budhiraja, MD Divisions of Sleep and Circadian DisordersDocument55 pagesRohit Budhiraja, MD Divisions of Sleep and Circadian DisordersAlonso Rodriguez EscobedoNo ratings yet
- Monthly Census of Chemotherapy Administration-Surgery-1Document13 pagesMonthly Census of Chemotherapy Administration-Surgery-1myvi317No ratings yet
- Younan Nowzaradan The Scale Does Not Lie - People Do. - Reversing Obesity Now. - 2019 - 1Document150 pagesYounan Nowzaradan The Scale Does Not Lie - People Do. - Reversing Obesity Now. - 2019 - 1edfred79100% (1)
- Glasgow Coma ScaleDocument3 pagesGlasgow Coma ScaleMuhamad RidloNo ratings yet
- Jardiance Us PiDocument50 pagesJardiance Us PiWertonNo ratings yet
- Infection Control GuidelinesDocument409 pagesInfection Control GuidelinesmopaselNo ratings yet
- Approach To A Patient With JaundiceDocument33 pagesApproach To A Patient With JaundiceRahul Kumar VermaNo ratings yet