Professional Documents
Culture Documents
EXP#10
EXP#10
Uploaded by
Stephen Joel Sevilla0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views2 pagesThe document summarizes subnetting a Class C IP address of 200.156.109.0 into 4 subnets with 55 hosts on each subnet. It determines that the required subnet mask is 255.255.255.192 and calculates the valid IP address ranges and broadcast addresses for each of the 4 subnets. It finds that each subnet can support a maximum of 64 hosts.
Original Description:
VLSM EXPERIMENT 10
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document summarizes subnetting a Class C IP address of 200.156.109.0 into 4 subnets with 55 hosts on each subnet. It determines that the required subnet mask is 255.255.255.192 and calculates the valid IP address ranges and broadcast addresses for each of the 4 subnets. It finds that each subnet can support a maximum of 64 hosts.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views2 pagesEXP#10
EXP#10
Uploaded by
Stephen Joel SevillaThe document summarizes subnetting a Class C IP address of 200.156.109.0 into 4 subnets with 55 hosts on each subnet. It determines that the required subnet mask is 255.255.255.192 and calculates the valid IP address ranges and broadcast addresses for each of the 4 subnets. It finds that each subnet can support a maximum of 64 hosts.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
SEVILLA, STEPHEN JOEL G.
GERRY,BAUTISTA Jr.
Experiment #10
Title: Class C IP Address Subnetting
Objective:
• Learn how to subnet
• Subnet a class B IP address
Scenario:
Your company has one Class C address; 200.156.109.0. Recently the company has been
experiencing extremely heavy network traffic. As the network administrator, you decide to subnet
the LAN into two physical networks. There will 55 hosts on each network.
• How many subnets are required for this configuration?
• What is the subnet mask for all hosts on all subnets?
• What are the subnet ID’s for all subnets?
• What are the valid addresses for each subnet?
• How many hosts can each subnet host at maximum?
Step 1 – Determining the # of subnets and the subnet mask
A unique network id is required for each physical network. If you must take WAN links into
consideration on your network, you also require a unique id for the WAN connection.
Calculate the number of subnets required for this scenario, and from the chart, determine the
subnet mask.
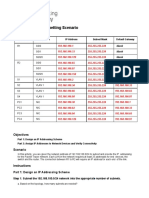
Number of Subnets: 4
Subnet Mask: 255.255.255.
# Network Address Useable Addresses Network Broadcast
From 200 156 109 0
0 200 156 109 0 200.156.109.63
To 200 156 109 62
From 200 156 109 64
1 200 156 109 64 200.156.109.127
To 200 156 109 126
From 200 156 109 128
2 200 156 109 128 200.156.109.191
To 200 156 109 190
From 200 156 109 192
3 200 156 109 192 200.156.109.255
To 200 156 109 194
We do not use the first subnet (according to Microsoft – even though it is used in the real world)
and we do not use the subnet id with the subnet mask in it either. You cannot have a subnet id
equal to your subnet mask. Therefore we must cross out the first subnet id and the last subnet id.
Step 3 – Calculating valid IP addresses for each subnet
Addresses for each subnet are calculated by beginning with an address that is, one after the
subnet id, to one before the next subnet id. Fill in the right hand side of the chart above.
Step 4 – Determine the number of hosts each subnet can support
Use the formula 2n – 2 where n= the number of host bits remaining. Remember to include host
bits from all octets. If 8 bits were used subnetting a Class B address, there would be 8 host bits
remaining. Therefore, using the formula above:
28–2
= 256 –2
=254
hosts per subnet Use the formula to determine the number of hosts supported on each subnet of
the network in this exercise.
# host bits used: 6
# host bits remaining: 2
# hosts per subnet: 64
Use the calculator in scientific mode to complete the calculation.
(Start >Programs >Accessories >Calculator. View pulldown menu, select Scientific.)
You might also like
- Cisco CCNA Command Guide: An Introductory Guide for CCNA & Computer Networking Beginners: Computer Networking, #3From EverandCisco CCNA Command Guide: An Introductory Guide for CCNA & Computer Networking Beginners: Computer Networking, #3No ratings yet
- VLSM Workbook Instructors Edition - V1 - 0Document27 pagesVLSM Workbook Instructors Edition - V1 - 0genny91100% (4)
- Network with Practical Labs Configuration: Step by Step configuration of Router and Switch configurationFrom EverandNetwork with Practical Labs Configuration: Step by Step configuration of Router and Switch configurationNo ratings yet
- Subnetting ItexampracticeDocument12 pagesSubnetting ItexampracticeMohammad Tayyab KhusroNo ratings yet
- 5G Non Terrestrial Networks 2022 WP IdDocument35 pages5G Non Terrestrial Networks 2022 WP IdSouvik ChoudhuriNo ratings yet
- Ethernet Networks: Design, Implementation, Operation, ManagementFrom EverandEthernet Networks: Design, Implementation, Operation, ManagementRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- IP AddressingDocument8 pagesIP AddressingtombekinNo ratings yet
- Subnetting Examples1Document3 pagesSubnetting Examples1hammad choudharyNo ratings yet
- XG Firewall Overview v17.5Document7 pagesXG Firewall Overview v17.5Mahmoud AbdallahNo ratings yet
- Subnetting ExercisesDocument57 pagesSubnetting Exercisesعمار الفلاحيNo ratings yet
- Ccna Day 1 Assignment: WWW - Ironlink.asiaDocument5 pagesCcna Day 1 Assignment: WWW - Ironlink.asiaReal Espinosa50% (2)
- 11.7.5 Packet Tracer - Subnetting ScenarioDocument5 pages11.7.5 Packet Tracer - Subnetting ScenarioCathleen Rose GadianeNo ratings yet
- How To Install Hyperion Planning / Workspace / Essbase Part 1b - SQL Server Setup For Hyperion PlanningDocument17 pagesHow To Install Hyperion Planning / Workspace / Essbase Part 1b - SQL Server Setup For Hyperion PlanningdreamscapeukNo ratings yet
- Subnetting EasyDocument15 pagesSubnetting EasyOM Mahindra RaebareliNo ratings yet
- Semi DanjeffDocument4 pagesSemi DanjeffChristophe SumalinogNo ratings yet
- Laborator 7 - Disciplina Retele de CalculatoareDocument5 pagesLaborator 7 - Disciplina Retele de CalculatoaresorinproiecteNo ratings yet
- Packet Tracer - Subnetting Scenario: Nombre: Cesar Jesus Rios Morales Addressing TableDocument4 pagesPacket Tracer - Subnetting Scenario: Nombre: Cesar Jesus Rios Morales Addressing TableL HammeRNo ratings yet
- Ipv4 Subnetting: Khawar Butt Ccie # 12353 (R/S, Security, SP, DC, Voice, Storage & Ccde)Document16 pagesIpv4 Subnetting: Khawar Butt Ccie # 12353 (R/S, Security, SP, DC, Voice, Storage & Ccde)madanmohan22100% (1)
- Ip-Subnetting-Workbook - Part CDocument14 pagesIp-Subnetting-Workbook - Part CYazenNo ratings yet
- 09-Subnetting IP NetworkDocument30 pages09-Subnetting IP Networkksav yadavNo ratings yet
- Ipv4 AddressingDocument9 pagesIpv4 AddressingMohan Krishna SuggunaNo ratings yet
- Subnettingnn2 1464ff863377435Document50 pagesSubnettingnn2 1464ff863377435Monica Sabogal ArevaloNo ratings yet
- Homework 1Document5 pagesHomework 1Jennifer Tomalá GonzalézNo ratings yet
- IP DIRECCION Y SUBNETING IPV4 - Ent 2Document88 pagesIP DIRECCION Y SUBNETING IPV4 - Ent 2MARIA PAULA GOMEZ CEBALLOSNo ratings yet
- 3 Easy Subnetting PDFDocument25 pages3 Easy Subnetting PDFmrkamikhiNo ratings yet
- CCNA Sesion OnLine IPV4Document57 pagesCCNA Sesion OnLine IPV4FrankFrankNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 LABDocument10 pagesLecture 3 LABSerin AskecNo ratings yet
- 11.7.5-Packet-Tracer - Subnetting-ScenarioDocument5 pages11.7.5-Packet-Tracer - Subnetting-Scenariostudy timeNo ratings yet
- Computer Communication and Networking: Assignment (Ip Addressing and Subnetting)Document6 pagesComputer Communication and Networking: Assignment (Ip Addressing and Subnetting)Abdul HafeezNo ratings yet
- VLSM Tutorial With ExamplesDocument8 pagesVLSM Tutorial With ExamplesMark BrownNo ratings yet
- IP Address Sub Netting TutorialDocument9 pagesIP Address Sub Netting Tutorialapi-3699863No ratings yet
- Subnetting 140104012952 Phpapp01Document49 pagesSubnetting 140104012952 Phpapp01सुजन कार्कीNo ratings yet
- 9.1.4.6 Packet Tracer - Subnetting Scenario 1 Instructions IGDocument4 pages9.1.4.6 Packet Tracer - Subnetting Scenario 1 Instructions IGsalin zambranoNo ratings yet
- 8.1.4.7 Packet Tracer Subnetting Scenario 1Document5 pages8.1.4.7 Packet Tracer Subnetting Scenario 1Alex VolkovNo ratings yet
- 4.understanding Internet Protocol: It Equals 11110000Document7 pages4.understanding Internet Protocol: It Equals 11110000Afif MananNo ratings yet
- Acn FeDocument18 pagesAcn FeBizuayehu DesalegnNo ratings yet
- Assignment # 1 Internet Architecture and Protocols: IP Addressing and SubnettingDocument4 pagesAssignment # 1 Internet Architecture and Protocols: IP Addressing and SubnettingZeeshan AjmalNo ratings yet
- Addressing Network v1Document47 pagesAddressing Network v1سلمان شكيبNo ratings yet
- Sub NettingDocument8 pagesSub Nettingapi-3747051No ratings yet
- Device Interface Ip Address Subnet Mask Default-GatewayDocument3 pagesDevice Interface Ip Address Subnet Mask Default-GatewayJr de GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Address Classes: N BlueDocument12 pagesAddress Classes: N BlueJonathan DelbreyNo ratings yet
- IP Address Sub Netting TutorialDocument9 pagesIP Address Sub Netting TutorialTaukettNo ratings yet
- Computer Networks: Innovative ExaminationDocument7 pagesComputer Networks: Innovative ExaminationNanditaNo ratings yet
- Topology: - : Asad Malik Lab File 2018-CE-123Document58 pagesTopology: - : Asad Malik Lab File 2018-CE-123fasihNo ratings yet
- Subnet An IPv4 NetworkDocument6 pagesSubnet An IPv4 NetworkTriba TribaNo ratings yet
- Lab 1: Basic Cisco Device Configuration: Topology DiagramDocument17 pagesLab 1: Basic Cisco Device Configuration: Topology DiagramnhiNo ratings yet
- Question Sub NettingDocument7 pagesQuestion Sub NettingjosephchagasNo ratings yet
- Class Range Example Number of Networks Number of Hosts in Each Subnet ADocument8 pagesClass Range Example Number of Networks Number of Hosts in Each Subnet Akerya ibrahimNo ratings yet
- 11.5.5 Group5Document8 pages11.5.5 Group5Sum SoVathNo ratings yet
- Computer Networks Practical: S.Y.B.Sc. I.T. - SEM IIIDocument16 pagesComputer Networks Practical: S.Y.B.Sc. I.T. - SEM IIIManav ParmarNo ratings yet
- 8.1.4.7 Packet Tracer - Subnetting Scenario 1Document4 pages8.1.4.7 Packet Tracer - Subnetting Scenario 1Rubén Darío Saa MontañoNo ratings yet
- CAMEL: Intelligent Networks for the GSM, GPRS and UMTS NetworkFrom EverandCAMEL: Intelligent Networks for the GSM, GPRS and UMTS NetworkRating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (1)
- Using C-Kermit: Communication Software for OS/2, Atari ST, UNIX, OS-9, VMS, AOS/VS, AMIGAFrom EverandUsing C-Kermit: Communication Software for OS/2, Atari ST, UNIX, OS-9, VMS, AOS/VS, AMIGANo ratings yet
- Token Ring Technology ReportFrom EverandToken Ring Technology ReportNo ratings yet
- BBC micro:bit Recipes: Learn Programming with Microsoft MakeCode BlocksFrom EverandBBC micro:bit Recipes: Learn Programming with Microsoft MakeCode BlocksNo ratings yet
- Next Generation IPTV Services and TechnologiesFrom EverandNext Generation IPTV Services and TechnologiesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- TK Series HMI ModbusRTU Communication InstructionDocument10 pagesTK Series HMI ModbusRTU Communication InstructionTech HausNo ratings yet
- A Low Power Asynchronous Viterbi Decoder Using LEDR EncodingDocument6 pagesA Low Power Asynchronous Viterbi Decoder Using LEDR EncodingRahul SharmaNo ratings yet
- MC Lag QFX SeriesDocument34 pagesMC Lag QFX SeriesBon Tran HongNo ratings yet
- Wireless Applications: Become A Wireless ResellerDocument20 pagesWireless Applications: Become A Wireless ResellerarabsailNo ratings yet
- Eagle Pro Mesh Router M32 REVA MANUAL v1.00 WWDocument159 pagesEagle Pro Mesh Router M32 REVA MANUAL v1.00 WWJai Sri HariNo ratings yet
- User Guide: Smart Access Web ManagementDocument26 pagesUser Guide: Smart Access Web ManagementDan FelixNo ratings yet
- ASA Part OneDocument9 pagesASA Part OneRatnesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Docu79370 - ECS 3.0 Security Configuration Guide PDFDocument26 pagesDocu79370 - ECS 3.0 Security Configuration Guide PDFvenkatcms7637No ratings yet
- Huewai 4G Router HelpDocument49 pagesHuewai 4G Router HelpShrinivas DasariNo ratings yet
- Completed DOC 4.1.2.9 Documenting The NetworkDocument1 pageCompleted DOC 4.1.2.9 Documenting The NetworkCristian GarciaNo ratings yet
- Lumel KS5 Service ManualDocument36 pagesLumel KS5 Service ManualBreabăn MarianNo ratings yet
- 11-Igmp Principle Issue1.01Document32 pages11-Igmp Principle Issue1.01thato69100% (1)
- 01 Introduction To Networking November 5, 2018Document29 pages01 Introduction To Networking November 5, 2018princeyahweNo ratings yet
- Actuador Limitorque MX y QXDocument6 pagesActuador Limitorque MX y QXManuel FernizaNo ratings yet
- Cisco Meeting Server 2 9 Single Combined Server DeploymentDocument194 pagesCisco Meeting Server 2 9 Single Combined Server DeploymentCTO Green IT HubNo ratings yet
- Prelim Examination NET 1 Lec and LabDocument9 pagesPrelim Examination NET 1 Lec and LabCj AntonioNo ratings yet
- Week 10: - UTRAN Architecture - UTRA Air Interface - Enhancements To UMTSDocument35 pagesWeek 10: - UTRAN Architecture - UTRA Air Interface - Enhancements To UMTSConor O 'ReganNo ratings yet
- ManhathanDocument9 pagesManhathanPancho LuzónNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Communicating Over The Network: CCNA Exploration 4.0Document43 pagesChapter 2 - Communicating Over The Network: CCNA Exploration 4.0Nguyen AnhNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Osi and Tcp/Ip Network ModelsDocument56 pagesIntroduction To Osi and Tcp/Ip Network ModelsRohitha6lasanthaNo ratings yet
- PEXAM Network Security - Attempt Review25-30Document6 pagesPEXAM Network Security - Attempt Review25-30mark gonzalesNo ratings yet
- Packet ClassificationDocument28 pagesPacket ClassificationVăn Thịnh NgôNo ratings yet
- WIresharkDocument11 pagesWIresharkTogrul AsgerliNo ratings yet
- Installation Guide Above-Deck-and Below-Deck-UnitsDocument30 pagesInstallation Guide Above-Deck-and Below-Deck-UnitsstavrosgrNo ratings yet
- Solusi Internet Smartfren - SMB V.1 PDFDocument15 pagesSolusi Internet Smartfren - SMB V.1 PDFEdo KrismaNo ratings yet
- Keyword ReportDocument4 pagesKeyword ReportMuhammad rehan baigNo ratings yet
- stm32 stm8 Embedded Software SolutionsDocument68 pagesstm32 stm8 Embedded Software Solutionsdanielc_007No ratings yet