Professional Documents
Culture Documents
11.7.5 Packet Tracer - Subnetting Scenario
Uploaded by
Cathleen Rose GadianeOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
11.7.5 Packet Tracer - Subnetting Scenario
Uploaded by
Cathleen Rose GadianeCopyright:
Available Formats
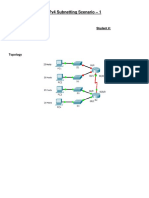
Packet Tracer - Subnetting Scenario
Addressing Table
Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway
R1 G0/0 192.168.100.1 255.255.255.224 blank
G0/1 192.168.100.33 255.255.255.224 blank
R1
R1
S0/0/0 192.168.100.129 255.255.255.224 blank
R2 G0/0 192.168.100.65 255.255.255.224 blank
R2 G0/1 192.168.100.97 255.255.255.224 blank
R2
S0/0/0 192.168.100.158 255.255.255.224 blank
S1 VLAN 1 192.168.100.2 255.255.255.224 192.168.100.1
S2 VLAN 1 192.168.100.34 255.255.255.224 192.168.100.33
S3 VLAN 1 192.168.100.66 255.255.255.224 192.168.100.65
S4 VLAN 1 192.168.100.98 255.255.255.224 192.168.100.97
PC1 NIC 192.168.100.30 255.255.255.224 192.168.100.1
PC2 NIC 192.168.100.62 255.255.255.224 192.168.100.33
PC3 NIC 192.168.100.94 255.255.255.224 192.168.100.65
PC4 NIC 192.168.100.126 255.255.255.224 192.168.100.97
Blank Line, No additional information
Objectives
Part 1: Design an IP Addressing Scheme
Part 2: Assign IP Addresses to Network Devices and Verify Connectivity
Scenario
In this activity, you are given the network address of 192.168.100.0/24 to subnet and provide the IP addressing
for the Packet Tracer network. Each LAN in the network requires at least 25 addresses for end devices, the
switch and the router. The connection between R1 to R2 will require an IP address for each end of the link.
Instructions
Part 1: Design an IP Addressing Scheme
Step 1: Subnet the 192.168.100.0/24 network into the appropriate number of subnets.
Questions:
a. Based on the topology, how many subnets are needed?
5
♥ 2014 - 2021 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Cisco Public Page 1 of 4 www.netacad.com
Packet Tracer - Subnetting Scenario
b. How many bits must be borrowed to support the number of subnets in the topology table? 3
c. How many subnets does this create?
8
d. How many usable hosts does this create per subnet?
30
Note: If your answer is less than the 25 hosts required, then you borrowed too many bits. e. Calculate the
binary value for the first five subnets. The first two subnets have been done for you.
Subnet Network Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
Address
0 192.168.100. 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
1 192.168.100. 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0
2 192.168.100. 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0
3 192.168.100. 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 0
4 192.168.100. 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Blank Line, No additional information
f. Calculate the binary and decimal value of the new subnet mask.
First Octet Second Third Mask Mask Mask Mask Mask Mask Mask Mask
Octet Octet Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
11111111 11111111 11111111 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0
First Second Third Fourth Decimal Octet
Decimal Decimal Decimal
Octet Octet Octet
255. 255. 255. 224
Blank Line, No additional information
g. Fill in the Subnet Table, listing the decimal value of all available subnets, the first and last usable host
address, and the broadcast address. Repeat until all addresses are listed.
Note: You may not need to use all rows.
Subnet Table
Subnet Subnet Address First Usable Last Usable Broadcast Address
Number Host Address Host Address
0 192.168.100.0 192.168.100.1 192.168.100.30 192.168.100.31
1 192.168.100.32 192.168.100.33 192.168.100.62 192.168.100.63
2 192.168.100.64 192.168.100.65 192.168.100.94 192.168.100.95
3 192.168.100.128 192.168.100.97 192.168.100.126 192.168.100.127
4 192.168.100.160 192.168.100.129 192.168.100.158 192.168.100.159
♥ 2014 - 2021 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Cisco Public Page 2 of 4 www.netacad.com
Packet Tracer - Subnetting Scenario
Subnet Subnet Address First Usable Last Usable Broadcast Address
Number Host Address Host Address
5 192.168.100.160 192.168.100.161 192.168.100.190 192.168.100.191
6 192.168.100.192 192.168.100.193 192.168.100.222 192.168.100.223
7 192.168.100.224 192.168.100.225 192.168.100.254 192.168.100.255
8 blank blank blank blank
9 blank blank blank blank
10 blank blank blank blank
Blank Line, No additional information
Step 2: Assign the subnets to the network shown in the topology.
a. Assign Subnet 0 to the LAN connected to the GigabitEthernet 0/0 interface of R1:
192.168.100.0 /27
b. Assign Subnet 1 to the LAN connected to the GigabitEthernet 0/1 interface of R1:
192.168.100.32 /27
c. Assign Subnet 2 to the LAN connected to the GigabitEthernet 0/0 interface of R2:
192.168.100.64 /27
d. Assign Subnet 3 to the LAN connected to the GigabitEthernet 0/1 interface of R2:
192.168.100.96 /27
e. Assign Subnet 4 to the WAN link between R1 to R2:
192.168.100.128 /27
Step 3: Document t192.168.100.0 /27he addressing scheme.
Fill in the Addressing Table using the following guidelines:
a. Assign the first usable IP addresses in each subnet to R1 for the two LAN links and the WAN link.
b. Assign the first usable IP addresses in each subnet to R2 for the LAN links. Assign the last usable IP
address for the WAN link.
c. Assign the second usable IP address in the attached subnets to the switches.
d. Assign the last usable IP addresses to the PCs in each subnet.
Part 2: Assign IP Addresses to Network Devices and Verify Connectivity
Most of the IP addressing is already configured on this network. Implement the following steps to complete the
addressing configuration. EIGRP dynamic routing is already configured between R1 and R2.
Step 1: Configure R1 LAN interfaces.
a. Configure both LAN interfaces with the addresses from the Addressing Table.
b. Configure the interfaces so that the hosts on the LANs have connectivity to the default gateway.
Step 2: Configure IP addressing on S3.
a. Configure the switch VLAN1 interface with addressing.
♥ 2014 - 2021 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Cisco Public Page 3 of 4 www.netacad.com
Packet Tracer - Subnetting Scenario
b. Configure the switch with the default gateway address.
Step 3: Configure PC4.
Configure PC4 with host and default gateway addresses.
Step 4: Verify connectivity.
You can only verify connectivity from R1, S3, and PC4. However, you should be able to ping every IP address
listed in the Addressing Table.
End of Document
♥ 2014 - 2021 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Cisco Public Page 4 of 4 www.netacad.com
You might also like
- Cyber Security Internship ReportDocument70 pagesCyber Security Internship Reportvicky75% (8)
- 4.5.2 Lab - Implement Inter-VLAN RoutingDocument5 pages4.5.2 Lab - Implement Inter-VLAN RoutingCarlos RiveraNo ratings yet
- Lab 1.4.1: Challenge Review: (Instructor Version)Document26 pagesLab 1.4.1: Challenge Review: (Instructor Version)AnilNo ratings yet
- 1.3.2.5 Packet Tracer - Investigating Directly Connected Routes InstructionsDocument4 pages1.3.2.5 Packet Tracer - Investigating Directly Connected Routes InstructionsVictor CardosoNo ratings yet
- BACnet IP Architecture OverviewDocument2 pagesBACnet IP Architecture OverviewGopal KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Đề chuẩn S1-Openlab-ver16062013Document3 pagesĐề chuẩn S1-Openlab-ver16062013Ngọc Hiếu100% (1)
- 19.4.4 Packet Tracer - Build A Switch and Router Network - ILMDocument8 pages19.4.4 Packet Tracer - Build A Switch and Router Network - ILMjohannachicaNo ratings yet
- Lab 3.4.3 Part A: Configuring Inter-VLAN Routing: CCNA Discovery Introducing Routing and Switching in The EnterpriseDocument5 pagesLab 3.4.3 Part A: Configuring Inter-VLAN Routing: CCNA Discovery Introducing Routing and Switching in The EnterpriseRano RenoNo ratings yet
- Lab 5 - Implement Inter-VLAN RoutingDocument15 pagesLab 5 - Implement Inter-VLAN RoutingShara MerinNo ratings yet
- 8.1.2.7 LabDocument7 pages8.1.2.7 LabbreakdoenNo ratings yet
- 8.1.4.7 Packet Tracer - Subnetting Scenario 1Document4 pages8.1.4.7 Packet Tracer - Subnetting Scenario 1Rubén Darío Saa MontañoNo ratings yet
- IP RAN ConfigurationDocument39 pagesIP RAN ConfigurationSenthilathiban Thevarasa100% (2)
- 5.3.2.3 Lab - Implement Local SPANDocument7 pages5.3.2.3 Lab - Implement Local SPANcrisNo ratings yet
- 9.2.1.11 Packet Tracer - Configuring Named Standard ACLs Luis SanchezDocument4 pages9.2.1.11 Packet Tracer - Configuring Named Standard ACLs Luis Sanchezrafael8214No ratings yet
- Experiment 8 OspfDocument10 pagesExperiment 8 OspfMoa AnwarNo ratings yet
- 11.5.5 Packet Tracer - Subnet An IPv4 NetworkDocument7 pages11.5.5 Packet Tracer - Subnet An IPv4 NetworkKrystelle Ungria TimtimNo ratings yet
- Hasil Lab 17.7.7 - AHMAD THORIQ OSHAMA SIAGIAN - Packet Tracer - Troubleshoot Connectivity IssuesDocument17 pagesHasil Lab 17.7.7 - AHMAD THORIQ OSHAMA SIAGIAN - Packet Tracer - Troubleshoot Connectivity IssuesThoriq oshamaNo ratings yet
- ACL Interview Questions and Answers - Networker InterviewDocument3 pagesACL Interview Questions and Answers - Networker InterviewBhupendar Singh100% (1)
- Lab 9.1: Basic VLSM Calculation and Addressing Design: Topology DiagramDocument6 pagesLab 9.1: Basic VLSM Calculation and Addressing Design: Topology DiagramRecky JimmyNo ratings yet
- Design and Implement a VLSM Addressing SchemeDocument18 pagesDesign and Implement a VLSM Addressing SchemeJBK programNo ratings yet
- BGP ROUTING POLICY GUIDEDocument2 pagesBGP ROUTING POLICY GUIDEMauricio LeivaNo ratings yet
- IP addressing questions answeredDocument2 pagesIP addressing questions answeredDavidBravo30No ratings yet
- Cisco IOS XR Advanced System Command Reference For The Cisco CRS Router, Release 4.2.xDocument604 pagesCisco IOS XR Advanced System Command Reference For The Cisco CRS Router, Release 4.2.xHamam IsmailNo ratings yet
- CNE191 Assignments PDFDocument25 pagesCNE191 Assignments PDFbabaroga007No ratings yet
- Nexus FP PDFDocument48 pagesNexus FP PDFPeter MkamaNo ratings yet
- 7.4.1-Packet-Tracer - Implement-Dhcpv4Document2 pages7.4.1-Packet-Tracer - Implement-Dhcpv4study timeNo ratings yet
- 4 Ways Reset MikrotikDocument3 pages4 Ways Reset MikrotikYukito YukazaNo ratings yet
- VLSM ExercisesDocument17 pagesVLSM ExercisesAishwary AgrahariNo ratings yet
- Router-on-a-StickDocument5 pagesRouter-on-a-StickGabriel Julio Navarro PianetaNo ratings yet
- 4.5.1-Packet-Tracer - Inter-Vlan-Routing-ChallengeDocument7 pages4.5.1-Packet-Tracer - Inter-Vlan-Routing-Challengestudy timeNo ratings yet
- (Variable Length Subnet MasksDocument49 pages(Variable Length Subnet MasksAnonymous GvIT4n41GNo ratings yet
- Yeastar Certified Technician TrainingDocument152 pagesYeastar Certified Technician TrainingEnectteh ZimbabweNo ratings yet
- 8.3.3.3 Lab - Collecting and Analyzing NetFlow Data PDFDocument7 pages8.3.3.3 Lab - Collecting and Analyzing NetFlow Data PDFbeef22No ratings yet
- Last Phase NETW204 Class ProjectDocument21 pagesLast Phase NETW204 Class ProjectShivani100% (4)
- MSS LogDocument69 pagesMSS LogNikhil ShahNo ratings yet
- EzeePay DistributorDocument19 pagesEzeePay Distributorpavan bNo ratings yet
- Class Format Default Subnet Mask A B C: Power of 2'S TableDocument4 pagesClass Format Default Subnet Mask A B C: Power of 2'S TableselooeNo ratings yet
- AfterlockDocument33 pagesAfterlockMaina Mathenge100% (1)
- Troubleshooting Cisco IOS and PIX Firewall-Based IPSec ImplementationsDocument54 pagesTroubleshooting Cisco IOS and PIX Firewall-Based IPSec ImplementationsdanilofantinatoNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 Networking Today, Basic Switch and End Device ConfigurationDocument96 pagesTopic 1 Networking Today, Basic Switch and End Device ConfigurationZam SkemaNo ratings yet
- S1 OpenLab Ver16062013Document2 pagesS1 OpenLab Ver16062013Trương Tùng Dương100% (1)
- 11.5.5 Packet Tracer - Subnet An IPv4 NetworkDocument6 pages11.5.5 Packet Tracer - Subnet An IPv4 NetworkFerdy Layuk AlloNo ratings yet
- ITN Skills Assess - Student TRNG - ExamDocument9 pagesITN Skills Assess - Student TRNG - ExamYary QuirosNo ratings yet
- جافا عملي qDocument22 pagesجافا عملي qكيمو تيكNo ratings yet
- SSH, Telnet Sitch s5700Document3 pagesSSH, Telnet Sitch s5700manuNo ratings yet
- Ltrcol 2250 SlidesDocument34 pagesLtrcol 2250 SlidestedykoweNo ratings yet
- 6.4.3.3 Packet Tracer - Connect A Router To A LANDocument5 pages6.4.3.3 Packet Tracer - Connect A Router To A LANSergio MonteNo ratings yet
- 6500 Part 4Document57 pages6500 Part 4Ratnesh KumarNo ratings yet
- ASA 5506 10.2.1.9 Lab B - Configure A Site-to-Site IPsec VPN Using ISR CLI and ASA ASDMDocument23 pagesASA 5506 10.2.1.9 Lab B - Configure A Site-to-Site IPsec VPN Using ISR CLI and ASA ASDMOsmany Escobedo100% (1)
- Citrix Education Learning JourneyDocument16 pagesCitrix Education Learning JourneyRudrali HitechNo ratings yet
- Session1e PTActA ACLDocument4 pagesSession1e PTActA ACLKhông TrânNo ratings yet
- 3.6.1.2 Packet Tracer - Configure AAA Authentication On Cisco RoutersDocument4 pages3.6.1.2 Packet Tracer - Configure AAA Authentication On Cisco RoutersSandoval El MonoNo ratings yet
- Cisco FabricPath Technology OverviewDocument97 pagesCisco FabricPath Technology OverviewĐức Mạnh PhùngNo ratings yet
- Ipv4 AddressesDocument30 pagesIpv4 AddressesAnjali BhatiaNo ratings yet
- Packet Tracer - Subnetting Scenario: Nombre: Cesar Jesus Rios Morales Addressing TableDocument4 pagesPacket Tracer - Subnetting Scenario: Nombre: Cesar Jesus Rios Morales Addressing TableL HammeRNo ratings yet
- Packet Tracer - Subnetting Scenario: Addressing TableDocument4 pagesPacket Tracer - Subnetting Scenario: Addressing TableJonathanCampoverdeNo ratings yet
- 11.7.5-Packet-Tracer - Subnetting-ScenarioDocument5 pages11.7.5-Packet-Tracer - Subnetting-Scenariostudy timeNo ratings yet
- Packet Tracer - Subnetting Scenario: Addressing TableDocument4 pagesPacket Tracer - Subnetting Scenario: Addressing TableBenj MendozaNo ratings yet
- Packet Tracer - Subnetting Scenario: Addressing TableDocument7 pagesPacket Tracer - Subnetting Scenario: Addressing TableYanaNo ratings yet
- 8.1.4.7 Packet Tracer Subnetting Scenario 1Document5 pages8.1.4.7 Packet Tracer Subnetting Scenario 1Alex VolkovNo ratings yet
- 9.1.4.6 Packet Tracer - Subnetting Scenario 1 Instructions IGDocument4 pages9.1.4.6 Packet Tracer - Subnetting Scenario 1 Instructions IGsalin zambranoNo ratings yet
- Device Interface Ip Address Subnet Mask Default-GatewayDocument3 pagesDevice Interface Ip Address Subnet Mask Default-GatewayJr de GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Semi DanjeffDocument4 pagesSemi DanjeffChristophe SumalinogNo ratings yet
- IPv4 Subnetting Scenario 1Document4 pagesIPv4 Subnetting Scenario 1mehrdad arabiNo ratings yet
- 8.1.4.7 Packet Tracer - Subnetting Scenario 1 - ILMDocument5 pages8.1.4.7 Packet Tracer - Subnetting Scenario 1 - ILMHanif AwalludinNo ratings yet
- TCW Chapter 3 Markt IntegrationDocument6 pagesTCW Chapter 3 Markt IntegrationCathleen Rose GadianeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 STRUCTURE OF GLOBALIZATIONDocument3 pagesChapter 2 STRUCTURE OF GLOBALIZATIONCathleen Rose GadianeNo ratings yet
- TCW Chapter 5 Contemporary Global GovernanceDocument13 pagesTCW Chapter 5 Contemporary Global GovernanceCathleen Rose GadianeNo ratings yet
- 1.1.2.4 Lab - Mapping The InternetDocument13 pages1.1.2.4 Lab - Mapping The InternetCathleen Rose GadianeNo ratings yet
- TCW Chapter 2 STRUCTURE OF GLOBALIZATION The Global EconomyDocument2 pagesTCW Chapter 2 STRUCTURE OF GLOBALIZATION The Global EconomyCathleen Rose GadianeNo ratings yet
- MAHABHARATADocument33 pagesMAHABHARATACathleen Rose GadianeNo ratings yet
- Lab - How Connected Are You?Document1 pageLab - How Connected Are You?Cathleen Rose GadianeNo ratings yet
- TCW Chapter 4. Global Interstate SystemDocument11 pagesTCW Chapter 4. Global Interstate SystemCathleen Rose GadianeNo ratings yet
- Welte Mutual Fund OptimizationDocument2 pagesWelte Mutual Fund OptimizationCathleen Rose GadianeNo ratings yet
- 9.3.3 Packet Tracer - HSRP Configuration GuideDocument5 pages9.3.3 Packet Tracer - HSRP Configuration GuideCathleen Rose GadianeNo ratings yet
- Generate Python code from Webex API using PostmanDocument3 pagesGenerate Python code from Webex API using PostmanCathleen Rose GadianeNo ratings yet
- 1 Creating A Network Topology Using Virtual Machines in VirtualBoxDocument3 pages1 Creating A Network Topology Using Virtual Machines in VirtualBoxCathleen Rose GadianeNo ratings yet
- PHILO 101 LESSON 3 RELIGION CIVIL LAWS HUMAN VALUESDocument3 pagesPHILO 101 LESSON 3 RELIGION CIVIL LAWS HUMAN VALUESCathleen Rose GadianeNo ratings yet
- Use Ansible to Back Up and Configure a CSR1000vDocument24 pagesUse Ansible to Back Up and Configure a CSR1000vCathleen Rose GadianeNo ratings yet
- L2 - A Moral BeingDocument2 pagesL2 - A Moral BeingCathleen Rose GadianeNo ratings yet
- 1.9.3 Lab - Research It and Networking Job OpportunitiesDocument3 pages1.9.3 Lab - Research It and Networking Job OpportunitiesCathleen Rose GadianeNo ratings yet
- 1.0.5 Packet Tracer Logical and Physical Mode ExplorationDocument4 pages1.0.5 Packet Tracer Logical and Physical Mode ExplorationJimbo Baby GamingNo ratings yet
- 2 Authenticating With Cisco DNA and Retrieving Network Devices With PostmanDocument3 pages2 Authenticating With Cisco DNA and Retrieving Network Devices With PostmanCathleen Rose GadianeNo ratings yet
- 1.1.1.2 Lab - How Connected Are YouDocument1 page1.1.1.2 Lab - How Connected Are YouCathleen Rose GadianeNo ratings yet
- 1.6.2 Packet Tracer - Configure Basic Router Settings - Physical ModeDocument5 pages1.6.2 Packet Tracer - Configure Basic Router Settings - Physical ModeCathleen Rose GadianeNo ratings yet
- PCI ChecklistDocument3 pagesPCI Checklistfuckaccount1No ratings yet
- Wireless bridge installation guideDocument2 pagesWireless bridge installation guideTokioNo ratings yet
- A Network Ready Device Is Directly Connected To A Mikrotik Routerboard 750 With A Correct U.T.PDocument6 pagesA Network Ready Device Is Directly Connected To A Mikrotik Routerboard 750 With A Correct U.T.Ppomade storeNo ratings yet
- Asus X751LK ManualDocument104 pagesAsus X751LK ManualmentoriaNo ratings yet
- Crestron-Cisco Touch 10 Routing and Control: Deployment GuideDocument20 pagesCrestron-Cisco Touch 10 Routing and Control: Deployment GuidepicoboNo ratings yet
- CIS Controls Mobile Companion Guide Mapping Applicability-1Document83 pagesCIS Controls Mobile Companion Guide Mapping Applicability-1JoNo ratings yet
- TC1890 - Keyyo Configuration Guideline R910 PDFDocument28 pagesTC1890 - Keyyo Configuration Guideline R910 PDFKlenti ÇukariNo ratings yet
- My Technical ReportDocument71 pagesMy Technical ReportGloryNo ratings yet
- Fronius Datamanager UmDocument88 pagesFronius Datamanager UmSalin ShakyaNo ratings yet
- Cisco Unified Communications Manager Express ReferenceDocument1,138 pagesCisco Unified Communications Manager Express ReferenceElvis SorensenNo ratings yet
- CX200 QSG v2.0 20200316Document16 pagesCX200 QSG v2.0 20200316yusril.integraNo ratings yet
- Learn Training Textbook S7-1200 EN PDFDocument672 pagesLearn Training Textbook S7-1200 EN PDFRafaelNo ratings yet
- S1104309GC10 AA Lab09Document18 pagesS1104309GC10 AA Lab09nicholas ombajoNo ratings yet
- Emotron Option Fieldbus 2 0 01 3698 01 R4 EnglishDocument98 pagesEmotron Option Fieldbus 2 0 01 3698 01 R4 EnglishRafael InacioNo ratings yet
- How To Install PfSense, Configure and Block Spicific WebsiteDocument38 pagesHow To Install PfSense, Configure and Block Spicific WebsiteAlbert100% (2)
- NetworkingDocument111 pagesNetworkingNuri MisbahNo ratings yet
- Cisco QuizDocument2 pagesCisco QuizJatinder SinghNo ratings yet
- NKSTPP WiFi Access System DocsDocument6 pagesNKSTPP WiFi Access System DocsPawan VaskarNo ratings yet
- VlanDocument46 pagesVlanchitrang_11No ratings yet
- IETF: Internet Engineering Task Force What Does The IETF Do?Document2 pagesIETF: Internet Engineering Task Force What Does The IETF Do?barone_28No ratings yet
- Pharos Control V1 UserGuide CPE210Document77 pagesPharos Control V1 UserGuide CPE210ssa_joeNo ratings yet
- Cisco - Assingment 1Document9 pagesCisco - Assingment 1Amirul AidilNo ratings yet
- MPCDocument17 pagesMPCBoova RagavanNo ratings yet
- Ethernet Instrument Control TutorialDocument9 pagesEthernet Instrument Control TutorialChatty LuvwhkhaaNo ratings yet
- Comtech/EFData FX Series 7.x WAN Optimization DatasheetDocument5 pagesComtech/EFData FX Series 7.x WAN Optimization DatasheetarzeszutNo ratings yet
- Lab Guide Training v2.0 PDFDocument36 pagesLab Guide Training v2.0 PDFabijith13No ratings yet