Professional Documents
Culture Documents
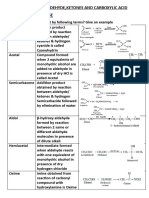
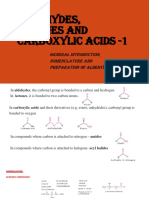
Aldehyde Ketone and Carboxylic
Uploaded by
Saransh Kumar0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
19 views2 pagesOriginal Title
Aldehyde ketone and Carboxylic
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
19 views2 pagesAldehyde Ketone and Carboxylic
Uploaded by
Saransh KumarCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
ASTER PUBLIC SCHOOL, (GNW)
CLASS: XII, ASSIGNMENT: 1
CH: ALDEHYDE KETONE AND CARBOXYLIC
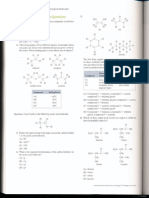
1.Write the IUPAC name of the following:
a) CH3-CH2-CHO
b) CH3-CH(OH)-CH2-CO-CH3
c) (CH3)2-CH-CHO
d) CH3-CH2-CH=CH-CHO
e) CH3-CO-CH=C(CH3)2
f) CH3-CH2-CO-Ph
g) CH3-CH(OH)-CH2-COOH
h) CH3-CH(OH)-CH2-COOH
2. Draw the structure of following:
a) 3-Methylpentanal
b) P-Methylbenzaldehyde
c) 3-Methylbutanal
d) 4-Chloropentan-2-one
e) 4-Methylpent-3-en-2-one
f) 3-Oxopentanal
g) 1-Phenylpropane-1-one
h) 3-Methylbutanal
i) P-Nitropropiophenone.
j) Semicarbazone of CH3CHO
3. Convert the following:
a) Ethanol to acetone
b) Propene to propanol
c) Ethyl chloride to ethanal
d) Propanone to propane
e) Benzoyl chloride to Benzaldehyde
f) Ethanal to but-2-enal
g) Ethanal to 3-Hydroxybutanal
h) Benzaldehyde to benzophenone
i) Ethyl cyanide to ethanoic acid
j) Butanol to butanoic acid
k) Benzoic acid to m-bromobenzoic acid
l) Ethyne to ethanal
m) Acetic acid to methane
4. Give sample test to distinguish between the following pair of compounds:
a) Pentanone and pentan-3-one
b) Ethanal and propanal
c) Benzaldehyde and acetophenone
d) Propan-2-one and pentane-3-one
e) Phenol and benzoic acid
f) Benzoic acid and ethyl benzoate
5. Rearrange the following compounds in the increasing order of their indicated property:
a) Ethanal, propanal, propanone and butanone. (N.A.R)
b) Acetaldehyde, acetone, methyl tert-butyl ketone (reactivity towards HCN)
c) Benzoic acid, 3,4-dinitrobenzoic acid, 4-methoxybenzoic acid (acidic Strength)
d) 2-Bromobutanoic acid, 3-Bromobutanoic acid and 2-methhlpropanoic acid (acidic strength)
e) CH3COCH3, C6H5COCH3, CH3CHO (reactivity towards nucleophilic addition reaction)
f) Cl-CH2-COOH, F-CH2-COOH, CH3-COOH (acidic character)
g) C6H5-CO-CH3, CH3-CHO CH3-CO-CH3 (N.A.R)
6. Write the equation involved in the following reactions:
a) Wolff kishner reduction
b) Etard reaction
c) Clemmensen reduction
d) Stephen reaction
e) Benzoyl chloride to Benzaldehyde
f) Ethanal to but-2-enal
7. Give a possible explanation for each one of the following:
a) There are two -NH2 groups in semicarbazide. However, only one such group is involved in the
formation of semicarbazones.
b) Cyclohexanone forms cyanohydrins in good yield but 2,2,6-trimethyl cyclohexanone does not.
c) Although phenoxide ion has more number of resonating structures than carboxylate ion,
carboxylic acid is a stronger acid than phenol.
d) Aromatic carboxylic acids do not undergo friedel- Crafts reaction.
e) PKa value of 4-nitrobenzoic acid is lower than that of benzoic acid.
f) Chloroacetic acid is a stronger than acetic acid.
g) pH of reaction should be carefully controlled while preparing ammonia derivatives of carbonyl
compounds.
8. A ketone A (C4H8O) which undergo haloform reaction give compound B on reduction. B on heating
with sulphuric acid give compound C which forms mono-ozonide D. D on hydrolysis with zinc dust give
only E. Identify A, B, C, D and E. Write the reaction involved.
9. Although phenoxide ion has more number of resonating structures than carboxylate ion, carboxylic
acid is a stronger acid than phenol. Give two reasons.
10. An organic compound A (C8H16O2) was hydrolysed with dilute sulphuric acid to give a carboxylic
acid B and an alcohol C. Oxidation of C with chromic acid also produced B. On dehydration C gives but-
1-ene. Write the equations for the reactions involved.
10. An aromatic organic compound ‘A’ with molecular formula C8H8O to give positive DNP and
iodoform tests. It neither reduce tollens reagent nor does it decolorise bromine water. Write the structure
of A.
11. A, B and C are three non-cyclic functional isomers of a carbonyl compound with molecular formula
C4H8O. Isomers A and C give positive tollens test whereas isomer B does not give tollens test, but gives
positive iodoform test. Isomers A and B on reduction with Zn(Hg)/conc. HCl give the same product D.
a) Write the structure of A, B, C and D.
b) Out of A, B and C isomers, which one is least reactive towards addition of HCN?
12. A and B are two functional isomers of compound C3H6O. On heating with NaOH and I2, isomer B
forms yellow precipitate of iodoform whereas isomer A does not form any precipitate. Write the formula
of A and B.
You might also like
- Aldehydes Ketones and Carboxylic Acid Final RevisionDocument3 pagesAldehydes Ketones and Carboxylic Acid Final RevisionROWA new year CelebrationNo ratings yet
- Aldehydes-Ketons and Carboxylic AcidsDocument11 pagesAldehydes-Ketons and Carboxylic AcidsMohammed IliasNo ratings yet
- Model Questions On U-12, 13 & 14Document12 pagesModel Questions On U-12, 13 & 14kadedoxNo ratings yet
- QB - Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic AcidsDocument5 pagesQB - Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic AcidsAkshith ReddyNo ratings yet
- Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic AcidsDocument5 pagesAldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic AcidsShazia FarheenNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Important QuestionsDocument20 pagesChemistry Important QuestionsArjun Ramesh0% (1)
- Aldehyde, Ketone and Carboxylic AcidDocument10 pagesAldehyde, Ketone and Carboxylic Acidgoodgirlz946No ratings yet
- Wa0003 PDFDocument3 pagesWa0003 PDFaPP bOssNo ratings yet
- Chemistry CT 3 22-23Document6 pagesChemistry CT 3 22-23Sancia SamNo ratings yet
- Section II Q No. 2. Attempt Any Eight Parts Out of TwelveDocument4 pagesSection II Q No. 2. Attempt Any Eight Parts Out of TwelveUsama IjazNo ratings yet
- Hydrocarbons Dps AssignmentDocument6 pagesHydrocarbons Dps AssignmentharshillbhartiNo ratings yet
- Test Aldehydes and KetonesDocument3 pagesTest Aldehydes and Ketonestanmay.sachdeva123No ratings yet
- AldehydesDocument5 pagesAldehydeslove.mansijhaNo ratings yet
- Benzene Structure and Reactions QuizDocument65 pagesBenzene Structure and Reactions QuizMoaz AzabNo ratings yet
- Aldehydes Ncert-1Document27 pagesAldehydes Ncert-1Sukumar PaniNo ratings yet
- Org 2Document9 pagesOrg 2Chandan SahuNo ratings yet
- Practice - Organic Nomenclature: Directions: Write Your Answers To The Following Questions in The Space Provided. UseDocument8 pagesPractice - Organic Nomenclature: Directions: Write Your Answers To The Following Questions in The Space Provided. UseKeshav GuptaNo ratings yet
- 12 Pre Board 1 1222Document5 pages12 Pre Board 1 1222geyeyo9277No ratings yet
- Holidays HW Class XiiDocument3 pagesHolidays HW Class XiiPoorvKumarNo ratings yet
- Cet (Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids)Document3 pagesCet (Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids)Arnab Jana100% (1)
- AKC Assignment-1Document2 pagesAKC Assignment-1Shubhpreet SinghNo ratings yet
- Grade Xii (Chemistry) : Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids (Term - 2) : Most Expecting QuestionsDocument5 pagesGrade Xii (Chemistry) : Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids (Term - 2) : Most Expecting QuestionsSupreeta KhatiwadaNo ratings yet
- Unit 12 Aldehysdes Ketones and Carboxylic AcidsDocument4 pagesUnit 12 Aldehysdes Ketones and Carboxylic Acidspavankumar3905syNo ratings yet
- OchempractwrkshtDocument13 pagesOchempractwrkshtlabaileyNo ratings yet
- Monthly Test Xii Chemistry October 2023-24Document4 pagesMonthly Test Xii Chemistry October 2023-24soumityachaudharyNo ratings yet
- ARRANGE THE FOLLOWING ORGANIC finalDocument2 pagesARRANGE THE FOLLOWING ORGANIC finalmunsifmohammed501No ratings yet
- Chemistry_Question-HydrocarbonDocument4 pagesChemistry_Question-Hydrocarbonpogboi2342No ratings yet
- Alcohols, Phenols and EthersDocument3 pagesAlcohols, Phenols and EthersCJ's Music GalleryNo ratings yet
- Sample Questions - HydrocarbonsDocument3 pagesSample Questions - Hydrocarbonsaisha.horizon16No ratings yet
- Pretest Orchem M5Document2 pagesPretest Orchem M5Panuphong KnottNo ratings yet
- Alcohols Phenols and Ethers RevsionDocument4 pagesAlcohols Phenols and Ethers RevsionAryan GuptaNo ratings yet
- Acetylene and Aromatic Hydrocarbons: Properties, Reactions and UsesDocument3 pagesAcetylene and Aromatic Hydrocarbons: Properties, Reactions and UsesJayanth KNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Theory Sample Paper (2022-23) on Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic AcidsDocument8 pagesChemistry Theory Sample Paper (2022-23) on Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic AcidsJems Chaudhary100% (1)
- Chemistry Su Aalo Iyo JawaaboDocument38 pagesChemistry Su Aalo Iyo Jawaabocazmi AndirahmanNo ratings yet
- ORGANIC CHEMISTRY TESTDocument4 pagesORGANIC CHEMISTRY TESTpritam neogiNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Revision: Alcohols, Phenols and EthersDocument4 pagesChemistry Revision: Alcohols, Phenols and Etherskalika parasharNo ratings yet
- Class-XII - Chemistry Worksheet-1 Aldehyde, Ketone and Carboxylic AcidsDocument3 pagesClass-XII - Chemistry Worksheet-1 Aldehyde, Ketone and Carboxylic AcidsSameer DahiyaNo ratings yet
- Aldehyde Ketones and Carboxylic AcidsDocument8 pagesAldehyde Ketones and Carboxylic AcidsSheetal KoriNo ratings yet
- Amines Final On Print WITH StampDocument8 pagesAmines Final On Print WITH StampAhmedAdelIbrahimNo ratings yet
- Alcohols, Phenols & Ethers QPDocument3 pagesAlcohols, Phenols & Ethers QPIniya RajasekharNo ratings yet
- ExerciseDocument16 pagesExercisecse.220840131017No ratings yet
- Quiz 3-Practice questions (1) نسخةDocument8 pagesQuiz 3-Practice questions (1) نسخةSabaa AbuzaidNo ratings yet
- CHM 102Document4 pagesCHM 102Fumzy AdelakunNo ratings yet
- Aldehydes and Ketones - 1-MergedDocument94 pagesAldehydes and Ketones - 1-MergedseNo ratings yet
- CH 8 S Eng. IDocument13 pagesCH 8 S Eng. Isomyayadav0192No ratings yet
- Org Nitro Cpds TutorialDocument4 pagesOrg Nitro Cpds TutorialDomNo ratings yet
- Revision Test-1, 12th ChemistryDocument4 pagesRevision Test-1, 12th ChemistryVasanthakumar shanmugamNo ratings yet
- Zumdahl Biology Tie inDocument2 pagesZumdahl Biology Tie injimmy615615No ratings yet
- CH7 Alcoholsphenols and Ethers HHW WorksheetDocument4 pagesCH7 Alcoholsphenols and Ethers HHW WorksheetAaditya SharmaNo ratings yet
- Lecture on aromatic hydrocarbons and their reactionsDocument46 pagesLecture on aromatic hydrocarbons and their reactionsAbdullah AmjadNo ratings yet
- XII -Second Unit Test -CHEMISTRYDocument3 pagesXII -Second Unit Test -CHEMISTRYrshobana78No ratings yet
- hydrocarbon 1Document6 pageshydrocarbon 1VK CREATIONNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Untuk Murid MHTDocument36 pagesOrganic Chemistry Untuk Murid MHTSuwandi Science13No ratings yet
- Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids: SolutionDocument9 pagesAldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids: SolutionPanchi palNo ratings yet
- 2013 Homework KimorDocument23 pages2013 Homework KimorDiamondNadinaNo ratings yet
- Assignment Haloalkanes and HaloarenesDocument2 pagesAssignment Haloalkanes and HaloarenesBasant KothariNo ratings yet
- Chem Class 12 WorksheetDocument8 pagesChem Class 12 WorksheetBHAVYA KUSHWAHANo ratings yet
- Alcohol ObjectivesDocument2 pagesAlcohol Objectivesfrost flowerNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Oo Kashqeysan Imtixaanka Dowlada 2022Document6 pagesChemistry Oo Kashqeysan Imtixaanka Dowlada 2022cazmi AndirahmanNo ratings yet
- Physical Organic Chemistry — 3: Plenary Lectures Presented at the Third IUPAC Conference on Physical Organic Chemistry, Montpellier, France, 6 - 10 September, 1976From EverandPhysical Organic Chemistry — 3: Plenary Lectures Presented at the Third IUPAC Conference on Physical Organic Chemistry, Montpellier, France, 6 - 10 September, 1976A. FruchierNo ratings yet
- Saransh Bio Project 999Document7 pagesSaransh Bio Project 999Saransh KumarNo ratings yet
- Structure of AtomDocument3 pagesStructure of AtomSaransh KumarNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics AssignmentDocument1 pageThermodynamics AssignmentSaransh KumarNo ratings yet
- DPP-3 ElectrostaticsDocument1 pageDPP-3 ElectrostaticsSaransh KumarNo ratings yet
- CH-8 Gravitation Worksheet-1Document2 pagesCH-8 Gravitation Worksheet-1Saransh KumarNo ratings yet
- Saransh TulsiDocument7 pagesSaransh TulsiSaransh KumarNo ratings yet
- Saransh Tulsi FinallDocument7 pagesSaransh Tulsi FinallSaransh KumarNo ratings yet
- Saransh Tulsi FinallDocument7 pagesSaransh Tulsi FinallSaransh KumarNo ratings yet
- Pete - S Plugs Product Guide PDFDocument21 pagesPete - S Plugs Product Guide PDFJuan Enrique Vergel MarinNo ratings yet
- Biosynthesis of FlavoursDocument9 pagesBiosynthesis of FlavoursDatta JoshiNo ratings yet
- Dampak Rokok Bagi Anak SekolahDocument51 pagesDampak Rokok Bagi Anak Sekolahsyakira renatia.officialNo ratings yet
- Avantor Product Price List 2022Document251 pagesAvantor Product Price List 2022Sudhir KumarNo ratings yet
- Unit 11 Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids: Points To RememberDocument27 pagesUnit 11 Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids: Points To Rememberchandan mallikNo ratings yet
- L-Pac ProductionlDocument10 pagesL-Pac ProductionlSonia Patel100% (1)
- Car Bani OnDocument29 pagesCar Bani OnPrashant Munnolli100% (1)
- Benzo Chem Industries Expansion Project Form I DetailsDocument359 pagesBenzo Chem Industries Expansion Project Form I Detailsप्रियदर्शन गोंधळेकरNo ratings yet
- 11 Aldehyde Ketone and C-Acids 19-02-2022 MCQ With SolutionsDocument26 pages11 Aldehyde Ketone and C-Acids 19-02-2022 MCQ With SolutionsANIKET BATTINWARNo ratings yet
- The Synthetic Use of Metals in Organic ChemistryDocument177 pagesThe Synthetic Use of Metals in Organic ChemistryWhiteOak ComenziNo ratings yet
- Silica Sulfuric Acid An Efficient and Reusable Catalyst For The One-Pot Synthesis of 3,4-Dihydropyrimidin-2 (1H) - OnesDocument3 pagesSilica Sulfuric Acid An Efficient and Reusable Catalyst For The One-Pot Synthesis of 3,4-Dihydropyrimidin-2 (1H) - OnesDuy Phuc LeNo ratings yet
- 12.Mcq - Aldehydes Ketones Carboxylic AcidsDocument23 pages12.Mcq - Aldehydes Ketones Carboxylic AcidsBedosi Bidita PandaNo ratings yet
- Plumeria Rubra L, Apocynaceae or DogbaneDocument7 pagesPlumeria Rubra L, Apocynaceae or DogbaneSiti Jari HandayaniNo ratings yet
- Biochemical Reac-NEW Colour Test For Glyoxylic AcidDocument17 pagesBiochemical Reac-NEW Colour Test For Glyoxylic AcidNuril Mega MusfitaNo ratings yet
- A One-Pot Synthesis of 3-Amino-3-Arylpropionic AcidsDocument13 pagesA One-Pot Synthesis of 3-Amino-3-Arylpropionic AcidsTuyenHHCNo ratings yet
- Functional Group Analysis 1Document17 pagesFunctional Group Analysis 1حسين أحمد حسينNo ratings yet
- The FEMA GRAS Assessment of Hydroxy - and Alkoxy-Substituted Benzyl Derivatives Used As Flavor IngredientsDocument31 pagesThe FEMA GRAS Assessment of Hydroxy - and Alkoxy-Substituted Benzyl Derivatives Used As Flavor IngredientskwangbokahnNo ratings yet
- K5Pw11Nio39-Catalyzed Oxidation of Benzyl Alcohol With Hydrogen PeroxideDocument9 pagesK5Pw11Nio39-Catalyzed Oxidation of Benzyl Alcohol With Hydrogen PeroxideValentina Vargas VargasNo ratings yet
- Oxidations With Nickel Peroxide (NICL2 + NAOCL)Document5 pagesOxidations With Nickel Peroxide (NICL2 + NAOCL)mladen lakicNo ratings yet
- PID Response Factors UK V1.10 1Document18 pagesPID Response Factors UK V1.10 1MeesanNo ratings yet
- Organic Syntheses Collective Volume 2Document813 pagesOrganic Syntheses Collective Volume 2caltexas88% (8)
- NF Monographs Benzalkonium Chloride SolutionDocument3 pagesNF Monographs Benzalkonium Chloride Solutionsergio910113No ratings yet
- Benzoin Exp7Document4 pagesBenzoin Exp7Liz Hackett0% (1)
- 12th Chemistry Second Revision Answer KeyDocument10 pages12th Chemistry Second Revision Answer KeySubbu RajaNo ratings yet
- Carbonyl Compounds 13thDocument21 pagesCarbonyl Compounds 13thRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 Aldehyde & KetonesDocument10 pagesChapter 12 Aldehyde & KetonesForzen flamesNo ratings yet
- Liquid Phase Oxidation of Toluene To Benzaldehyde by Air - PDF 1984Document4 pagesLiquid Phase Oxidation of Toluene To Benzaldehyde by Air - PDF 1984Oana VasileNo ratings yet
- Fragrance Industry GuideDocument25 pagesFragrance Industry GuideMimitotteNo ratings yet
- Chemical Resistance List2Document8 pagesChemical Resistance List2Jean Paul Pamo ValdiviaNo ratings yet
- TFA BreakdownDocument28 pagesTFA BreakdownRafli MuhamadNo ratings yet