Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Causes of Increasing Temperature - Understanding Climate Change
Causes of Increasing Temperature - Understanding Climate Change
Uploaded by
Muhammad MoeedOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Causes of Increasing Temperature - Understanding Climate Change
Causes of Increasing Temperature - Understanding Climate Change
Uploaded by
Muhammad MoeedCopyright:
Available Formats
Causes of
Increasing
Temperature:
Understanding
Climate Change
Introduction:
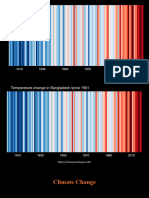
The rising global temperatures observed in recent decades have brought climate change to the
forefront of environmental concerns. This section delves into the causes of increasing
temperatures and their impact on Earth's climate system. By examining both natural and
human-induced factors, we can gain a comprehensive understanding of the mechanisms driving
global warming.
I. Natural Factors:
1. Solar Activity: Explore the influence of variations in solar radiation and sunspot cycles on
Earth's climate, including the role of solar output and its long-term impact on temperature
fluctuations.
2. Volcanic Activity: Discuss the impact of volcanic eruptions on global temperatures, examining
the release of greenhouse gases, aerosols, and their cooling effect in the short term.
II. Human-Induced Factors:
1. Greenhouse Effect: Explain the greenhouse effect and its role in regulating Earth's
temperature, including the natural greenhouse gases present in the atmosphere.
2. Carbon Dioxide (CO2) Emissions: Investigate the primary driver of anthropogenic climate
change, focusing on the burning of fossil fuels, deforestation, and land-use changes as
significant sources of CO2 emissions.
3. Methane and Other Greenhouse Gases: Highlight the contribution of methane, nitrous oxide,
and other greenhouse gases to global warming, exploring their sources and potency as drivers
of climate change.
4. Industrial Activities: Analyze the impact of industrial processes, including manufacturing,
energy production, and transportation, on greenhouse gas emissions and subsequent
temperature increases.
5. Land Use Changes: Discuss the conversion of forests to agricultural land, urbanization, and
deforestation as activities that alter land surfaces and influence local and regional temperatures.
6. Feedback Mechanisms: Examine positive feedback loops, such as the release of additional
greenhouse gases due to thawing permafrost, and their amplifying effect on global warming.
III. Climate Models and Scientific Consensus:
1. Climate Modeling: Provide an overview of climate models and their ability to simulate
historical climate patterns and project future temperature scenarios.
2. Scientific Consensus: Discuss the overwhelming consensus among the scientific community
regarding the role of human activities as the dominant cause of global temperature increases,
highlighting major international assessments and reports.
IV. Impacts of Increasing Temperatures:
1. Extreme Weather Events: Explore the connection between rising temperatures and the
frequency and intensity of heat waves, hurricanes, droughts, and other extreme weather
phenomena.
2. Sea-Level Rise: Explain the consequences of melting ice caps and glaciers, thermal
expansion of seawater, and their contribution to rising sea levels.
3. Ecosystem Disruption: Analyze the impact of temperature increases on ecosystems, including
shifts in species' distribution, changes in phenology, and threats to biodiversity.
Conclusion:
The causes of increasing temperatures are multifaceted, involving both natural and
human-induced factors. However, it is the human activities that have become the primary driver
of global warming. Understanding the complex interplay of these factors is crucial for
implementing effective mitigation and adaptation strategies. By acknowledging the causes of
increasing temperatures, we can work toward sustainable solutions and strive to mitigate the
adverse effects of climate change on our planet and future generations.
You might also like
- Climate and Climate ChangeDocument367 pagesClimate and Climate ChangeMarisela Fuentes100% (1)
- Climate Change: Group 6Document31 pagesClimate Change: Group 6Owen VelascoNo ratings yet
- The Night MailDocument3 pagesThe Night MailDamian Fernandes50% (2)
- Lesson Plan About Global WarmingDocument4 pagesLesson Plan About Global WarmingToni Gutz50% (4)
- Climate and Climate Change (John P. Rafferty) PDFDocument367 pagesClimate and Climate Change (John P. Rafferty) PDFDavid Bernardo Altamirano Arevalo100% (3)
- Climate Change Powerpoint PresentationDocument26 pagesClimate Change Powerpoint PresentationAdelita Morales Gomba100% (1)
- Air and Water Grade 5Document44 pagesAir and Water Grade 5shamshadNo ratings yet
- ENSC 1113 The Science of Global Challenges NotesDocument21 pagesENSC 1113 The Science of Global Challenges Notestalhahassanalvi786100% (2)
- Captive Power PlantDocument26 pagesCaptive Power PlantAshish Thakur100% (1)
- 12.STS Climate ChangeDocument16 pages12.STS Climate ChangeLannie Mae Samayang100% (1)
- NCA3 Full Report Appendix 3 Climate Science Supplement LowResDocument55 pagesNCA3 Full Report Appendix 3 Climate Science Supplement LowResJan DashNo ratings yet
- Module FiveDocument15 pagesModule FiveJohn Lloyd Artuz EnriquezNo ratings yet
- HDFHDFDocument3 pagesHDFHDFArushiNo ratings yet
- SerikkaliRaiymbek Global Warming ProblemDocument12 pagesSerikkaliRaiymbek Global Warming ProblemraiserikkaliNo ratings yet
- Climate Change Impact in The USADocument55 pagesClimate Change Impact in The USAAndres LinaresNo ratings yet
- Research Topic Ni LouisDocument2 pagesResearch Topic Ni LouisJ. RaphNo ratings yet
- Example of An 8-Mark Assessment ForDocument1 pageExample of An 8-Mark Assessment For20balarkNo ratings yet
- Climate ChangeDocument2 pagesClimate Changelkjhg ghjklNo ratings yet
- Consolidated Envi Science LectureDocument34 pagesConsolidated Envi Science LectureJoanna Angela GeralinNo ratings yet
- Module 5-Converted (3) ScienceDocument18 pagesModule 5-Converted (3) ScienceHarvey Rulloda Asis100% (1)
- Studyguide GlobalwarmDocument15 pagesStudyguide Globalwarmsunny_suNo ratings yet
- Assignment No: "01" Assignment Title: Submitted To: Date: Submitted byDocument18 pagesAssignment No: "01" Assignment Title: Submitted To: Date: Submitted byMuhammad AhmedNo ratings yet
- W6D5 - HomeworkDocument4 pagesW6D5 - HomeworkLe Van Nhat (K16 HCM)No ratings yet
- Module: Environmental Protection: Topic: Global WarmingDocument11 pagesModule: Environmental Protection: Topic: Global WarmingJam CamaligNo ratings yet
- U TA Ing The I PA Limat Hange E Ucati P N O R UD: Nders ND M Ctsofc E C: An D Onal Rese Tati NFO ST EntsDocument22 pagesU TA Ing The I PA Limat Hange E Ucati P N O R UD: Nders ND M Ctsofc E C: An D Onal Rese Tati NFO ST EntsAyushmaan MaithaniNo ratings yet
- Literature Review 2Document10 pagesLiterature Review 2api-334798873No ratings yet
- Global Warming 2Document2 pagesGlobal Warming 2testtest1234No ratings yet
- Greenhouse EffectDocument24 pagesGreenhouse EffecthaileyNo ratings yet
- Global Warming: An IntroductionDocument13 pagesGlobal Warming: An IntroductionSunit SahuNo ratings yet
- Weather Evolution Tracing The Dynamic Changes Over TimeDocument1 pageWeather Evolution Tracing The Dynamic Changes Over TimerockNo ratings yet
- Bono, Leo Joselito E. EH406Document4 pagesBono, Leo Joselito E. EH406Rash Ibno PundingNo ratings yet
- Science Technology and Society ModuleDocument20 pagesScience Technology and Society ModuleZachary Yassir GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Cliamte Change & SustainabilityDocument29 pagesCliamte Change & SustainabilityPiyush SinghNo ratings yet
- Climate Change: Navigation SearchDocument13 pagesClimate Change: Navigation SearchRovina Narayan DiasNo ratings yet
- Climate ChangeDocument79 pagesClimate ChangeitzmeabeerNo ratings yet
- Climate ChangeDocument12 pagesClimate ChangeEno-obong Okwara EkongNo ratings yet
- ctc502 The Climate Change Challenge Scientific Evidence and ImplicationsDocument24 pagesctc502 The Climate Change Challenge Scientific Evidence and Implicationsmariusz.podgorskiNo ratings yet
- Climate Change: An Najah National University Faculty of Graduate StudiesDocument7 pagesClimate Change: An Najah National University Faculty of Graduate StudiesMajedaNo ratings yet
- Climate ChangeDocument2 pagesClimate ChangeovoNo ratings yet
- C. ChangeDocument86 pagesC. ChangeAngel Lu CabaelNo ratings yet
- Global WarmingDocument10 pagesGlobal WarmingNidhi MistryNo ratings yet
- Science Reviewer 1Document2 pagesScience Reviewer 1Jescel Kristine MosqueteNo ratings yet
- Climate Change Occurs When Changes in Earth's Climate System Result inDocument20 pagesClimate Change Occurs When Changes in Earth's Climate System Result inEllaAdayaMendiolaNo ratings yet
- Greenhouse Effect and Climate ChangeDocument45 pagesGreenhouse Effect and Climate ChangeGalal NadimNo ratings yet
- Activity 3Document3 pagesActivity 3mervie loberianoNo ratings yet
- 1Document2 pages1Aybern BawtistaNo ratings yet
- Global Warming: Temperature ChangesDocument4 pagesGlobal Warming: Temperature ChangesTharaneeswaran ThanigaiveluNo ratings yet
- Task #9 - Climate Change and Energy CrisisDocument8 pagesTask #9 - Climate Change and Energy CrisisKristoff Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- TNT 12 Q1 0402 SG Climate-Change-FDocument12 pagesTNT 12 Q1 0402 SG Climate-Change-FSophia BompatNo ratings yet
- Uldana ZHunisbekDocument13 pagesUldana ZHunisbekUldana ZhunisbekNo ratings yet
- DocumentDocument1 pageDocumentMa. Elaine L. AlfonsoNo ratings yet
- Warming and Climate Change: An Earth Science Perspective" University Digital MagazineDocument3 pagesWarming and Climate Change: An Earth Science Perspective" University Digital MagazineCarolina CastiblancoNo ratings yet
- Geoglogy Activity 9Document4 pagesGeoglogy Activity 9Cejay SarzNo ratings yet
- Green House Effect & Global WarmingDocument5 pagesGreen House Effect & Global WarmingAnanya SharmaNo ratings yet
- Climate-Change FinishDocument22 pagesClimate-Change FinishRodcooje Dagui RiosNo ratings yet
- University of Duhok College of Engineering Surveying DepartmentDocument34 pagesUniversity of Duhok College of Engineering Surveying DepartmentAlan ArifNo ratings yet
- Climate Change: Criedy@uts - Edu.auDocument15 pagesClimate Change: Criedy@uts - Edu.auAfter PartyNo ratings yet
- STS Module 3Document8 pagesSTS Module 3Delia TadiaqueNo ratings yet
- Daniels ReportDocument2 pagesDaniels ReportLouie SantosNo ratings yet
- FOUN1201 WS S2M1 Thurs Group9Document18 pagesFOUN1201 WS S2M1 Thurs Group9Kenroy WilsonNo ratings yet
- Causas Del Cambio ClimaticoDocument3 pagesCausas Del Cambio ClimaticoDiego González FerradaNo ratings yet
- BBA AssignmentDocument2 pagesBBA Assignmentarchana agarwalNo ratings yet
- Structure 6005Document3 pagesStructure 6005Giang Nguyễn HươngNo ratings yet
- Geological Historyof Natuna IslandDocument6 pagesGeological Historyof Natuna IslandUntuk FacebookNo ratings yet
- IEC Workshop Report-FinalDocument53 pagesIEC Workshop Report-FinalRakesh PatleNo ratings yet
- Revision: 00 Date: 12.02.2020: Material Safety Data SheetDocument8 pagesRevision: 00 Date: 12.02.2020: Material Safety Data SheetERIKO DARMAWANNo ratings yet
- Ch6 Hydro Power PlantDocument23 pagesCh6 Hydro Power PlantAzraqul IlmiNo ratings yet
- GENE Publication Award2019 Final WebDocument28 pagesGENE Publication Award2019 Final WebAna LarcherNo ratings yet
- Claymont Riverfront Oct 2021 - FinalDocument60 pagesClaymont Riverfront Oct 2021 - FinalDelaware Public MediaNo ratings yet
- 2021 Multi V Catalogue (Commercial Air Solutions)Document170 pages2021 Multi V Catalogue (Commercial Air Solutions)Paulo AlvesNo ratings yet
- Mater. Sci. Eng-3Document6 pagesMater. Sci. Eng-3gopierode4No ratings yet
- Commercial Intellichlor: Salt Chlorine GeneratorDocument1 pageCommercial Intellichlor: Salt Chlorine GeneratorHéctor RomeroNo ratings yet
- June 2017 (v3) QP - Paper 3 CIE Geography A-LevelDocument4 pagesJune 2017 (v3) QP - Paper 3 CIE Geography A-LevelMarvin IconsNo ratings yet
- Sanatery ProjectDocument31 pagesSanatery ProjectOkNo ratings yet
- SDG GOAL 9: Industry, Innovation and Infrastructure: Mec600 - Engineer in SocietyDocument9 pagesSDG GOAL 9: Industry, Innovation and Infrastructure: Mec600 - Engineer in SocietydasdasdNo ratings yet
- Outgoing - MenroDocument5 pagesOutgoing - MenroMhen M. SudaraNo ratings yet
- I Am Sharing 'Jsjabahvdnfb' With YouDocument2 pagesI Am Sharing 'Jsjabahvdnfb' With Youlady magpantayNo ratings yet
- BUS320 Task 1 NotesDocument1 pageBUS320 Task 1 NotesCalNo ratings yet
- BlankDocument20 pagesBlankJan Eric LansangNo ratings yet
- Pros and Cons of Living in FranceDocument2 pagesPros and Cons of Living in FranceRaluca Maria BobuNo ratings yet
- 9-2 SentDocument6 pages9-2 SentCông ThếNo ratings yet
- Bottled Water Should Be BannedDocument8 pagesBottled Water Should Be BannedSafayet AzizNo ratings yet
- Urban Design and CommunityDocument6 pagesUrban Design and CommunityMark Russell DimayugaNo ratings yet
- K-8188 Spec US-CA Kohler enDocument2 pagesK-8188 Spec US-CA Kohler enC.A. BravoNo ratings yet
- Safety Data Sheet: (S) - Lactic Acid About 85% EMPROVE® EXPERT PH Eur, BP, E 270Document10 pagesSafety Data Sheet: (S) - Lactic Acid About 85% EMPROVE® EXPERT PH Eur, BP, E 270Saifur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Cat Litter CatalogueDocument6 pagesCat Litter Cataloguelegecoj868No ratings yet
- Essay IsmailDocument8 pagesEssay IsmailSyed Aamir AhmedNo ratings yet
- Community Planning Facilitation Presentation GroupDocument29 pagesCommunity Planning Facilitation Presentation GroupAela SalipuranNo ratings yet