Professional Documents
Culture Documents
DR SK Haldarx27s Lectures On Industrial Health For Afih Students Cobalt PDF Free
Uploaded by
Ashan San0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
24 views2 pagesCobalt is a silvery grey magnetic metal that is recovered as a byproduct from copper and silver mining. It has several important industrial uses, including in producing super alloys for jet engines, cutting steel and rock, magnets, paints, and batteries. Exposure to cobalt can occur through inhalation or ingestion, with a portion being absorbed in the lungs and gut and stored mainly in organs like the liver, spleen, and kidneys. Excessive exposure to cobalt powder can cause respiratory issues like lung fibrosis or asthma as well as effects on the thyroid, blood, and heart when combined with alcohol. Monitoring workers involves regular health exams, pulmonary function tests, and chest x-rays to check for early signs
Original Description:
Original Title
pdfcoffee.com_dr-sk-haldarx27s-lectures-on-industrial-health-for-afih-students-cobalt-pdf-free
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCobalt is a silvery grey magnetic metal that is recovered as a byproduct from copper and silver mining. It has several important industrial uses, including in producing super alloys for jet engines, cutting steel and rock, magnets, paints, and batteries. Exposure to cobalt can occur through inhalation or ingestion, with a portion being absorbed in the lungs and gut and stored mainly in organs like the liver, spleen, and kidneys. Excessive exposure to cobalt powder can cause respiratory issues like lung fibrosis or asthma as well as effects on the thyroid, blood, and heart when combined with alcohol. Monitoring workers involves regular health exams, pulmonary function tests, and chest x-rays to check for early signs
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
24 views2 pagesDR SK Haldarx27s Lectures On Industrial Health For Afih Students Cobalt PDF Free
Uploaded by
Ashan SanCobalt is a silvery grey magnetic metal that is recovered as a byproduct from copper and silver mining. It has several important industrial uses, including in producing super alloys for jet engines, cutting steel and rock, magnets, paints, and batteries. Exposure to cobalt can occur through inhalation or ingestion, with a portion being absorbed in the lungs and gut and stored mainly in organs like the liver, spleen, and kidneys. Excessive exposure to cobalt powder can cause respiratory issues like lung fibrosis or asthma as well as effects on the thyroid, blood, and heart when combined with alcohol. Monitoring workers involves regular health exams, pulmonary function tests, and chest x-rays to check for early signs
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
Cobalt
It is a Silvery Grey Magnetic Metal, which is recovered as a by product from Copper & Silver
mining.
Uses:- 1) To manufacture High Temperature Resistant Alloy known as Super Alloy;
principally used in Jet Engine.
2) Cutting of Steel & Rock
3) Used in Magnet
4) Paint Industry
5) In Nickel Cadmium Batteries as a Catalyst
6) Radioactive Cobalt CO60 is used as a source of High Energy Gamma Radiation in
Radio Therapy & Industrial Radio Graphy.
Absorption:- 1) Gut:- 5 to 40% is absorbed through Gut
2) Lungs:- 30% is absorbed through lungs
Storage:- Mainly stored in Liver, Spleen, Kidneys, Muscles & Fat
Excretion:- 80% through Urine, remaining in the faeces.
Toxicity:- Inhalation of Cobalt powder may cause
1) Hard Metal Fibrosis (Interstitial lung Fibrosis) Characterised by:-
i) Wheezing ii) Dyspnoea iii) Chest Tightness iv) Lung
Functions show Restrictive Defects with Decreased FVC &
Decreased Diffusion Capacity.
2) Corpulmonale
3) Death
4) Bronchial Asthma:- Occupational Asthma. A specific TgE is detected. It
is Type I reaction.
It was being used as a Foam Stabilizing Agent to reduce the
foam in the beer. If Cobalt is mixed in the Alcohol, it is very
very dangerous mixture, causing a) Abrupt Onset of LVF
b) Pericardial Effusion c) Polycythemia
Mechanism:- Cobalt has Synergistic Effect with Alcohol in
Myocardial Functions. If patient is Malnourished and
consuming Beer suffers most.
5) Thyroid Hyperplasia:- Cobalt inhibits Tyrosine, & thus prevents
Synthesis of Thyroxine, leading to over secretion of TSH
6) Polycythemia:- Mechanism:- Due to increased release of
erythropoietin by kidneys resulting from Tissue Hypoxia.
Tissue Hypoxia may be caused by the inactivation of 2,3 –
Diphospho Glycerate (2,3 DPG) by the impaired release of
oxygen from RBCs. Release of Oxygen from RBCs depleted of
2,3 DPG or by formation of Cobalt Haemoglobin with a
sequence shift of Oxygen Dissociation Curve to the Left ( Shift
to left means Oxygene Release is less).
Medical Surveillance:- 1) Periodic Health Examination with special attention to lung
& Skin
2) Pulmonary Function Tests
3) Periodic X-Ray Chest
Biological Monitoring:- Normal Value in Urine is Less than 3 Micro Mole / Mol of Cretinine
You might also like
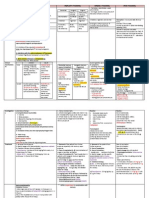
- Dr. S.K. Haldar's Lectures On Industrial Health For AFIH Students - Chemical AsphyxiantsDocument3 pagesDr. S.K. Haldar's Lectures On Industrial Health For AFIH Students - Chemical AsphyxiantsDr. Prakash KulkarniNo ratings yet
- Macrocytic Anemia - Megaloblastic AnemiaDocument42 pagesMacrocytic Anemia - Megaloblastic AnemiaDarien LiewNo ratings yet
- Endocrine 1.2 CushingDocument7 pagesEndocrine 1.2 CushingJem QuintoNo ratings yet
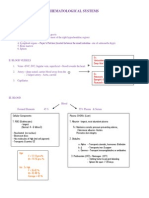
- Hematological Systems - Lecture NotesDocument15 pagesHematological Systems - Lecture NotesAmiel Francisco ReyesNo ratings yet
- Respiration Physiology SEQs With KeyDocument12 pagesRespiration Physiology SEQs With KeyMudassar Roomi100% (1)
- MRCS Osce Sample-2 PDFDocument25 pagesMRCS Osce Sample-2 PDFAmmarNo ratings yet
- Cell InjuryDocument30 pagesCell InjuryLucia Ruiz MenachoNo ratings yet
- Republic of The Philippines Puerto Princesa City: Palawan State UniversityDocument3 pagesRepublic of The Philippines Puerto Princesa City: Palawan State UniversityRosemarie EustaquioNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For HyperthyroidismDocument13 pagesNursing Care Plan For Hyperthyroidismjhonroks92% (13)
- 3 Biomedical Sciences 2020 JUNE 1720Document204 pages3 Biomedical Sciences 2020 JUNE 1720almohandNo ratings yet
- Microbial AssayDocument67 pagesMicrobial AssayBilal AbbasNo ratings yet
- Cellular Injury & DeathDocument72 pagesCellular Injury & Deathnithin nair100% (4)
- Non Respi O2 CO2 TransportDocument13 pagesNon Respi O2 CO2 TransportRicky JalecoNo ratings yet
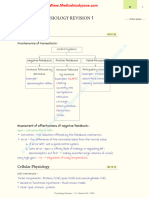
- General Physiology: APEC Exam Study NotesDocument9 pagesGeneral Physiology: APEC Exam Study NotesKC PalattaoNo ratings yet
- 1 - Goljan - Cell InjuryDocument10 pages1 - Goljan - Cell Injuryjhk451No ratings yet
- LECTURE 1 General Physiology!-1-1Document9 pagesLECTURE 1 General Physiology!-1-1Dr Haris AwanNo ratings yet
- Physiology I Blood & ImmunityDocument13 pagesPhysiology I Blood & Immunitynadine azmyNo ratings yet
- 8 Hormones of Adrenal GlandDocument27 pages8 Hormones of Adrenal GlandRana AbdullahNo ratings yet
- #Heavy MetalsDocument2 pages#Heavy MetalsameerabestNo ratings yet
- Selective B2-Adrenergic Agonists:: Mode of ActionDocument9 pagesSelective B2-Adrenergic Agonists:: Mode of ActionAda JoraimiNo ratings yet
- Poisoning 4804Document39 pagesPoisoning 4804Hasan Al MasudNo ratings yet
- 2018, Braud Et Al, JCI InsightDocument15 pages2018, Braud Et Al, JCI Insightlbraud01No ratings yet
- BloodDocument25 pagesBloodAbdul KhadirNo ratings yet
- 2016 Short Answer Semester 1Document8 pages2016 Short Answer Semester 1Shiv SookunNo ratings yet
- Document 1Document8 pagesDocument 1sejalNo ratings yet
- 1 Blood: Composition of Blood (Viva)Document21 pages1 Blood: Composition of Blood (Viva)Priyanka MhNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Physiology:: Human Lung ModelsDocument50 pagesRespiratory Physiology:: Human Lung ModelsBad BunnyNo ratings yet
- general systemic states د.عزيزةDocument75 pagesgeneral systemic states د.عزيزةAhmed Hamdy NaDa100% (2)
- Q1 Science 9 (Biology)Document3 pagesQ1 Science 9 (Biology)Łuci MattiasNo ratings yet
- Quick ReviewDocument63 pagesQuick ReviewAvi BhavsarNo ratings yet
- Medical Test Consolidation DocumentDocument6 pagesMedical Test Consolidation Documenthayat yimerNo ratings yet
- Trace Element: Written By: Hamed FouladiDocument10 pagesTrace Element: Written By: Hamed Fouladimatch.amirNo ratings yet
- 2020 Pathology Compilation Questions by TopicsDocument7 pages2020 Pathology Compilation Questions by Topicsrupertgrint2000No ratings yet
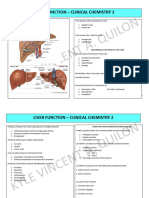
- Liver Function Reviewer Cc2Document7 pagesLiver Function Reviewer Cc2Leo NoquilNo ratings yet
- Liver Function Reviewer Cc2Document7 pagesLiver Function Reviewer Cc2Leo NoquilNo ratings yet
- Copd - Midterm NotesDocument2 pagesCopd - Midterm NotesInday BertaNo ratings yet
- Dr. Ligia Eliya Matti: College of Health Sciences Clinical Biochemistry Department Theoretical Toxicology 24-4-2019Document7 pagesDr. Ligia Eliya Matti: College of Health Sciences Clinical Biochemistry Department Theoretical Toxicology 24-4-2019aveen rasulNo ratings yet
- The Adrenal GlandesDocument19 pagesThe Adrenal GlandesamrsameerNo ratings yet
- 2020 Lec2Document7 pages2020 Lec2م.م.زينة عبد الحسينNo ratings yet
- CO FinalDocument31 pagesCO FinalAhmed SalahNo ratings yet
- 1 CopdDocument37 pages1 CopdnaturehalwestNo ratings yet
- لقطة شاشة ٢٠٢٤-٠٣-٢٠ في ٣.٢٩.٣٤ صDocument23 pagesلقطة شاشة ٢٠٢٤-٠٣-٢٠ في ٣.٢٩.٣٤ ص5rdqfr98ngNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System V4Document25 pagesRespiratory System V4Mohammed EljackNo ratings yet
- Aplications of Colchicine As An Article in Medicine: by Babak NamiDocument29 pagesAplications of Colchicine As An Article in Medicine: by Babak NamiBabak NamiNo ratings yet
- 6-Adrenocortical Hormones PancreaseDocument47 pages6-Adrenocortical Hormones Pancreasetmqt2fbnzgNo ratings yet
- Cell InjuryDocument22 pagesCell Injuryridin007No ratings yet
- Part Vii. Hypoxia: Table 7-1. Classification of The HypoxiaDocument7 pagesPart Vii. Hypoxia: Table 7-1. Classification of The HypoxiaAlex HirschNo ratings yet
- Section 2 Tissue and Cellular DamageDocument49 pagesSection 2 Tissue and Cellular DamageAnjuli MarieNo ratings yet
- Electrolyte Summary NotesDocument9 pagesElectrolyte Summary Notesnurhana faudziNo ratings yet
- Group 9 (Module 23)Document26 pagesGroup 9 (Module 23)maba.zuniga.sjcNo ratings yet
- Plasma Physiology (1-2020) by DR Khaled A AbulfadleDocument9 pagesPlasma Physiology (1-2020) by DR Khaled A AbulfadleUzama Binu AliNo ratings yet
- WEEK 9 Calcification & Pigmentation PDFDocument17 pagesWEEK 9 Calcification & Pigmentation PDFotaibynaifNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Ii 3 Stage Conversion of Amino Acids To Specialized ProductsDocument32 pagesBiochemistry Ii 3 Stage Conversion of Amino Acids To Specialized Productsسلام شاكر حميد جميل 6506No ratings yet
- Toxic GasesDocument44 pagesToxic Gasesasmaa100% (1)
- HermonesDocument21 pagesHermonesmohamed abu mughaisibNo ratings yet
- TG Ol XIlq Fe Yac TLxisDocument83 pagesTG Ol XIlq Fe Yac TLxisepic sound everNo ratings yet
- Anaesthesia and Thyroid DiseaseDocument9 pagesAnaesthesia and Thyroid DiseasedrrksNo ratings yet
- Overview of Respiratory SystemDocument10 pagesOverview of Respiratory SystemDioyceNo ratings yet
- Vitamin B12:: A Water Soluble Hematopoietic VitaminDocument25 pagesVitamin B12:: A Water Soluble Hematopoietic Vitamindr. SheryarOrakzaiNo ratings yet
- Dr. MD - Serajul Islam ChowdhuryDocument64 pagesDr. MD - Serajul Islam ChowdhuryPyronNo ratings yet
- Enr Saqs 2Document5 pagesEnr Saqs 2Mahnoor KhanNo ratings yet
- Iii ParcijalaDocument5 pagesIii ParcijalaKemo MokeNo ratings yet
- Adrenal HormonesDocument2 pagesAdrenal Hormonesffa15r.phNo ratings yet
- HDL Cholesterol - Precipitant PDFDocument2 pagesHDL Cholesterol - Precipitant PDFHamed AlsalhyNo ratings yet
- Herbal Medicine in The Treatment of Patients With Type 2Document8 pagesHerbal Medicine in The Treatment of Patients With Type 2Abdul Laura CondulaNo ratings yet
- DiscorsoDocument9 pagesDiscorsodughi95No ratings yet
- GalactosemiaDocument6 pagesGalactosemiaakbar alituNo ratings yet
- Department of Laboratory Medicine: Haematology Test Result Unit Biological Reference Interval Complete Blood Count (CBC)Document3 pagesDepartment of Laboratory Medicine: Haematology Test Result Unit Biological Reference Interval Complete Blood Count (CBC)abhilash eNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates 1Document26 pagesCarbohydrates 1buena carillaNo ratings yet
- Melatonin Gummies: Body Requirement and Effects of MelatoninDocument13 pagesMelatonin Gummies: Body Requirement and Effects of MelatoninmelatoningummiesNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Unfolding Case StudyDocument4 pagesPediatric Unfolding Case StudyJessica100% (1)
- CarnitineDocument3 pagesCarnitineOlescu VladNo ratings yet
- Molecular Docking of Flavonoids From Rumex Vesicarius With FOXO1 Target Related To Diabetes MellitusDocument7 pagesMolecular Docking of Flavonoids From Rumex Vesicarius With FOXO1 Target Related To Diabetes MellitusRakesh DavellaNo ratings yet
- PBL Endocrine Week 1 Jason Leonard Wijaya 01071180063Document8 pagesPBL Endocrine Week 1 Jason Leonard Wijaya 01071180063Jason LeonardNo ratings yet
- What Is Newborn ScreeningDocument2 pagesWhat Is Newborn ScreeningroksanmiNo ratings yet
- Pyloric StenosisDocument14 pagesPyloric Stenosisgangguan hepatobilierNo ratings yet
- Nutrition in DiabetesDocument3 pagesNutrition in DiabetesJyoti KushwahaNo ratings yet
- Vitamin B6 Deficiency As A Cause of Polyneuropathy in POEMS Syndrome Rapid Recovery With Supplementation in Two CasesDocument7 pagesVitamin B6 Deficiency As A Cause of Polyneuropathy in POEMS Syndrome Rapid Recovery With Supplementation in Two CasesYaseen MohamnadNo ratings yet
- Coverage Plan and TrackerDocument91 pagesCoverage Plan and TrackerAi RaNo ratings yet
- Metabolism: Lipid Metabolism: Inge HolsbeeksDocument35 pagesMetabolism: Lipid Metabolism: Inge Holsbeekssabasaktir4142No ratings yet
- AU Instructions For Use Creatine Kinase (CK NAC)Document8 pagesAU Instructions For Use Creatine Kinase (CK NAC)Anas TjNo ratings yet
- FIA Meter Plus: Fluorescence Immunoassay Rapid Quantitative TestDocument4 pagesFIA Meter Plus: Fluorescence Immunoassay Rapid Quantitative Testأياام زمانNo ratings yet
- Correlation Between Neonatal Hyperbilirubinemia and Vitamin D Levels: A Meta-AnalysisDocument12 pagesCorrelation Between Neonatal Hyperbilirubinemia and Vitamin D Levels: A Meta-AnalysisAbdurrahman HasanuddinNo ratings yet
- Increased Male Fertility Using FertilityDocument11 pagesIncreased Male Fertility Using FertilityUmme HaniNo ratings yet
- Department of Biochemistry Campaign Diabetic Check (With PP)Document2 pagesDepartment of Biochemistry Campaign Diabetic Check (With PP)gsm2008No ratings yet
- Metformina y Estrés Oxidativo en Pacientes DiabéticosDocument14 pagesMetformina y Estrés Oxidativo en Pacientes DiabéticosJesus D. Hernandez GuitianNo ratings yet
- Manish Narayan Dhar Shivalika Singh: Luiza GharibyanDocument42 pagesManish Narayan Dhar Shivalika Singh: Luiza GharibyanSachi LakhyaniNo ratings yet
- 11 ProdrugDocument26 pages11 ProdrugMiranda MetriaNo ratings yet
- Quarter 3: WORKSHEET NO. 1 Name: Score: Section: Date Submitted The Endocrine SystemDocument4 pagesQuarter 3: WORKSHEET NO. 1 Name: Score: Section: Date Submitted The Endocrine SystemPrincess RamoleteNo ratings yet