Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Research 5
Research 5
Uploaded by
ALI-A ALI0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views4 pagesThis study examined the relationship between empathy, well-being, and patient care among emergency room nurses. A survey was administered to 37 nurses working in the ER of a hospital in Quebec, Canada. The survey collected data on empathy levels using a validated scale, as well as demographic information. The results were analyzed using descriptive statistics to understand the association between empathy, well-being, and quality of patient care provided by ER nurses. The study aimed to provide insights into how promoting empathy and well-being among nurses could enhance patient care outcomes. However, the small sample size limited the generalizability of the findings.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
ODT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis study examined the relationship between empathy, well-being, and patient care among emergency room nurses. A survey was administered to 37 nurses working in the ER of a hospital in Quebec, Canada. The survey collected data on empathy levels using a validated scale, as well as demographic information. The results were analyzed using descriptive statistics to understand the association between empathy, well-being, and quality of patient care provided by ER nurses. The study aimed to provide insights into how promoting empathy and well-being among nurses could enhance patient care outcomes. However, the small sample size limited the generalizability of the findings.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as ODT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views4 pagesResearch 5
Research 5
Uploaded by
ALI-A ALIThis study examined the relationship between empathy, well-being, and patient care among emergency room nurses. A survey was administered to 37 nurses working in the ER of a hospital in Quebec, Canada. The survey collected data on empathy levels using a validated scale, as well as demographic information. The results were analyzed using descriptive statistics to understand the association between empathy, well-being, and quality of patient care provided by ER nurses. The study aimed to provide insights into how promoting empathy and well-being among nurses could enhance patient care outcomes. However, the small sample size limited the generalizability of the findings.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as ODT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
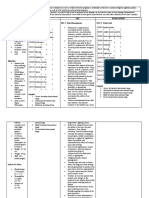
Title : Effect Of Empathy And Well-Being On Health Care Among
Emergency Nurses
Introduction : Pain alleviation of many patients who are
admitted at emergency department, pose an inspectional quest
about its effectiveness when they are discharged (Bourgault
et al., 2015)1. This study suggests some explanations about the
relationship of pain management to nurses’ level of empathy
and their well-being in which may potentially affect the
patient care negatively as correspondingly as nurses’
competency (Shanafelt et al., 2005)2.
Problem statement : Alleviation of pain after discharge of
significant number of patients from emergency department is
managed ineffectively upon their initial visit (Bourgault et
al., 2015)1.
Gap / Limitations : Due to the low sample size and narrow
environmental study context, it is challenging to generalize the
findings. Additionally, since empathy exhibits both a cognitive
and behavioral component, relying solely on self-reported
surveys may be insufficient to measure it accurately.
Consequently, a comprehensive evaluation should incorporate
multiple assessment techniques(Bourgault et al., 2015)1.
Significance : The study is enforcing the positive clinical
benefits of empathy, such as better patient compliance and
greater patient satisfaction to promote well-being and empathy
in clinical practice (Bourgault et al., 2015)1.
Purpose : This study is attended to understand the
shortcomings of pain control provided by emergency nurses
with regards to their characteristics (Bourgault et al., 2015)1.
Research questions :
What is the association between empathy and wellbeing
among emergency nurses ?
How does promoting empathy and wellbeing enhance
patient care in clinical practice .
Methodology :
Design : cross-sectional descriptive correlational design
(Bourgault et al., 2015)1.
Sampling technique : Recruiting emergency nurses was
conducted through convenience sampling to meet inclusion
criteria of study (Bourgault et al., 2015)1.
Sample size : The sample size is 37 of the 40 emergency
nurses who volunteered to be present during all three work
shifts and estimated to examine the relationship between two
continuous variables (empathy and well-being) (Bourgault et
al., 2015)1.
Sample characteristics : The study is conducted on nurses in
emergency departments at all their three work shifts.90% of
the participants were female, and the sample was primarily
young (80% were between the ages of 20 and 25; 23.3% were
between the ages of 26 and 30; 23.3% were between the ages
of 31 and 35; and 33.3 % were older than 36 ). A small
majority ( 53.3% ) worked the day shift, while 33.3% worked
the evening shift, 10% worked the night shift, and 3.3%
rotated across all three shifts. A college diploma was the
greatest degree of education completed for 43.3% of
participants, while university was the highest level for the
remaining 56.7%. A general nurse may practice with a college
nursing diploma (3-year program). The majority of the
nurses had experience in the emergency department for one to
five years (44.8%), six to ten years (34.5%), and more than
ten years (20.7%). 65.5% of the participants had received
ongoing training (credited or accredited) on pain management
as a requirement of their jobs, while 34.6% had chosen to do
so (Bourgault et al., 2015)1.
Setting : Emergency departments of University hospital center
located in the Province of Québec, Canada (Bourgault et al.,
2015)1.
Recruitment procedures : The initial step in the recruitment
process was gaining the ethical committee permission from
the local hospital. Then, emergency nurses signed a consent
form after being informed of the study's variables and
confidentiality guidelines (Bourgault et al., 2015)1.
Data collection : for data collection, a Self-administered
questionnaire conducted by two researchers ( PB & SL ) and
returned during work hours with manager permission. The
questionnaire contains sociodemographic data as well as a
scale ( JSPE ) was used to measure the empathy of emergency
nurses participants on a 7-point Likert scale (Bourgault et al.,
2015)1.
Statistical analysis : The study is statistically analyzed in a
Descriptive manner regarding the characteristics of the
sample , expressed in percentages, averages, and standard
deviations (Bourgault et al., 2015)1.
Ethical considerations : The research conduction consent is
approved from the ethical committee of the local hospital.
Emergency nurses signed a consent form of participation after
informing and explaining for them study variables and
confidentiality rules (Bourgault et al., 2015)1.
You might also like
- Leuzinger J Lilr ResearchDocument19 pagesLeuzinger J Lilr Researchapi-399228109No ratings yet
- Neurology, Psychiratry and ResearchDocument6 pagesNeurology, Psychiratry and Researchhmyzone55No ratings yet
- Intensive & Critical Care Nursing: Research ArticleDocument9 pagesIntensive & Critical Care Nursing: Research ArticleNur MiladiyahNo ratings yet
- The Evaluation of Outpatient Quality Services in Physiotherapy in The Teaching Health Centers of Shahid Beheshti University Based On Servqual ToolsDocument8 pagesThe Evaluation of Outpatient Quality Services in Physiotherapy in The Teaching Health Centers of Shahid Beheshti University Based On Servqual Toolspt.mahmoudNo ratings yet
- Tammy Tarner Journal Club EntryDocument1 pageTammy Tarner Journal Club Entryapi-357707616No ratings yet
- Burnout Among Healthcare ProfessionalsDocument2 pagesBurnout Among Healthcare ProfessionalsrohqayantiNo ratings yet
- Leadership Strategy Analysis FinalDocument8 pagesLeadership Strategy Analysis Finalapi-242603823No ratings yet
- Manuscript KHandyDocument23 pagesManuscript KHandySanjeev Sampang RaiNo ratings yet
- Nurses ' Perceptions of A Pressure Ulcer Prevention Care Bundle: A Qualitative Descriptive StudyDocument10 pagesNurses ' Perceptions of A Pressure Ulcer Prevention Care Bundle: A Qualitative Descriptive StudyBrekhna SaharNo ratings yet
- Negar and Eh 2014Document4 pagesNegar and Eh 2014vindhiNo ratings yet
- Annotated Bibliography Unit IIIDocument13 pagesAnnotated Bibliography Unit IIIRonalyne Cervantes GloriaNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Assessment: Literature ReviewDocument5 pagesUnit 4 Assessment: Literature Reviewyetunde badruNo ratings yet
- EBP Shift Length Affects Patient SafetyDocument5 pagesEBP Shift Length Affects Patient SafetyTuTitNo ratings yet
- JournalDocument9 pagesJournalJonathan LiscanoNo ratings yet
- Scale Comfort Touch Scale 2015Document15 pagesScale Comfort Touch Scale 2015Johana CifuentesNo ratings yet
- 1.pdf JsessionidDocument39 pages1.pdf JsessionidAlvin Josh CalingayanNo ratings yet
- ProQuestDocuments 2014-11-18Document14 pagesProQuestDocuments 2014-11-18Anonymous nEC4alrPjGNo ratings yet
- International Journal of Management (Ijm) : ©iaemeDocument9 pagesInternational Journal of Management (Ijm) : ©iaemeIAEME PublicationNo ratings yet
- Ambulatory Ortho PtsDocument8 pagesAmbulatory Ortho PtsRio BarriosNo ratings yet
- Post-Seclusion And/or Restraint Review in Psychiatry: A Scoping Review Article OutlineDocument27 pagesPost-Seclusion And/or Restraint Review in Psychiatry: A Scoping Review Article OutlineStudentnurseMjNo ratings yet
- Nurse Education Today: Joelle Yan Xin Chua, Shefaly ShoreyDocument9 pagesNurse Education Today: Joelle Yan Xin Chua, Shefaly ShoreyflorenceNo ratings yet
- Quality Improvement ProjectDocument7 pagesQuality Improvement Projectapi-272534722100% (1)
- Jnu.12274 Sistematik ReviewDocument10 pagesJnu.12274 Sistematik ReviewMastifa HanasitaNo ratings yet
- A Study To Assess The Patient's Satisfaction On Nursing Care in Emergency DepartmentDocument3 pagesA Study To Assess The Patient's Satisfaction On Nursing Care in Emergency DepartmentIOSRjournalNo ratings yet
- NUR 340 - Nursing Reasearch Problem-Based Research PaperDocument7 pagesNUR 340 - Nursing Reasearch Problem-Based Research Papercharlene doverNo ratings yet
- Irl FinalDocument17 pagesIrl Finalapi-663098440No ratings yet
- European Journal of Oncology Nursing: A B C D A B e F G A B H FDocument10 pagesEuropean Journal of Oncology Nursing: A B C D A B e F G A B H FBety RindaNo ratings yet
- Final Revised!!!!!!Document44 pagesFinal Revised!!!!!!Far Daurong100% (1)
- Nurs 350 Pico Paper, Spring 2014Document12 pagesNurs 350 Pico Paper, Spring 2014api-253664398No ratings yet
- Penelitian Cross-Sectional 3 PDFDocument29 pagesPenelitian Cross-Sectional 3 PDFSherin AlindaNo ratings yet
- Health AssessmentDocument25 pagesHealth AssessmentGovindaraju Subramani100% (1)
- Running Head: Nurse BurnoutDocument11 pagesRunning Head: Nurse BurnoutPaul MumoNo ratings yet
- The Development of Nursing Care Model in Patients With Total Knee Replacement Reconstructive SurgeryDocument17 pagesThe Development of Nursing Care Model in Patients With Total Knee Replacement Reconstructive SurgeryGlobal Research and Development ServicesNo ratings yet
- Artikel Ebsco 3Document7 pagesArtikel Ebsco 3bakena bajentaNo ratings yet
- A Study To Evaluate The Level of Satisfaction Perceived by PostnatalDocument12 pagesA Study To Evaluate The Level of Satisfaction Perceived by PostnatalAlexander DeckerNo ratings yet
- Managing Change Towards Bedside Shift ReportDocument12 pagesManaging Change Towards Bedside Shift Reportapi-438607141No ratings yet
- Nursing AssessmentDocument28 pagesNursing AssessmentKierstine Joy YamatNo ratings yet
- TransitionDocument13 pagesTransitionDonna NituraNo ratings yet
- Wong Et Al-2015-Health & Social Care in The CommunityDocument13 pagesWong Et Al-2015-Health & Social Care in The CommunityJoNo ratings yet
- Gardner 2010Document5 pagesGardner 2010Denis MirandaNo ratings yet
- Fitzpatrick OriginalDocument6 pagesFitzpatrick OriginalKristianus S PulongNo ratings yet
- Content ServerDocument9 pagesContent ServerSatriya PranataNo ratings yet
- Does Clinical Supervision Lead To Better Patient Outcomes in Mental Health NursingDocument8 pagesDoes Clinical Supervision Lead To Better Patient Outcomes in Mental Health Nursingml305No ratings yet
- Primary Care 5e Dunphy PDFDocument530 pagesPrimary Care 5e Dunphy PDFKim85% (13)
- Job SatisfactionDocument38 pagesJob SatisfactionBishwajitMazumderNo ratings yet
- Change InitiativeDocument7 pagesChange InitiativeWajiha ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Hubungan Penerapan Metode Tim Dengan Rencana Asuhan Keperawatan Pasien Diruang Rawat Inap Sari Madonni 1Document9 pagesHubungan Penerapan Metode Tim Dengan Rencana Asuhan Keperawatan Pasien Diruang Rawat Inap Sari Madonni 1rogerNo ratings yet
- 908 FullDocument4 pages908 FullJorgecelyNo ratings yet
- Study PDFDocument68 pagesStudy PDFNuri SongNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S2214139120301165 MainDocument6 pages1 s2.0 S2214139120301165 MainsarvitaNo ratings yet
- Implications in Practice and Conclusions - EditedDocument11 pagesImplications in Practice and Conclusions - EditedAtanas WamukoyaNo ratings yet
- Running Head: Nurse BurnoutDocument10 pagesRunning Head: Nurse BurnoutPaul MumoNo ratings yet
- Nurse To Nurse Bedside Shift Report LB 5th WeekDocument12 pagesNurse To Nurse Bedside Shift Report LB 5th Weekapi-527286440No ratings yet
- Quantitative Article Critique and SummaryDocument8 pagesQuantitative Article Critique and SummaryEmmanuelNo ratings yet
- The Role of Nurse Practitioners in Care Coordination and TransitionDocument10 pagesThe Role of Nurse Practitioners in Care Coordination and Transitionapi-312364579No ratings yet
- Analysis of Factors Related To The Level of Patient Satisfaction in Hospital Care ServicesDocument5 pagesAnalysis of Factors Related To The Level of Patient Satisfaction in Hospital Care ServicesInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Perception and Use of The Results of Patient Satisfaction Surveys by Care Providers in A French Teaching HospitalDocument6 pagesPerception and Use of The Results of Patient Satisfaction Surveys by Care Providers in A French Teaching HospitalSagor AhmedNo ratings yet
- Vpa+2022 1Document20 pagesVpa+2022 1Thomas BudimanNo ratings yet
- Nurse Turnover Rate RuaDocument14 pagesNurse Turnover Rate RuaDaniel WambuaNo ratings yet
- Metadona-Expert Consensus White Paper 2019Document15 pagesMetadona-Expert Consensus White Paper 2019carito88No ratings yet
- Pain Management For Patients With Chronic Kidney.4Document9 pagesPain Management For Patients With Chronic Kidney.4hadiatussalamahNo ratings yet
- Culture, Pain Perceptions and BehaviorsDocument5 pagesCulture, Pain Perceptions and BehaviorsJennifer LongNo ratings yet
- Purdue Liste PDFDocument2 pagesPurdue Liste PDFSebasNo ratings yet
- Buy Codeine..........Document5 pagesBuy Codeine..........Shakilur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Sowerby Closing LetterDocument2 pagesSowerby Closing Letterapi-524946388No ratings yet
- Advil - PLUS - FA - For - Download - ENGLISHDocument2 pagesAdvil - PLUS - FA - For - Download - ENGLISHShuvroNo ratings yet
- The Effectiveness of Deep Breathing Relaxation Technique and Guided Imagery To Decrease Pain Intensity On Postoperative Fracture Patients in Bougenvile Ward of DR Soegiri Hospital LamonganDocument7 pagesThe Effectiveness of Deep Breathing Relaxation Technique and Guided Imagery To Decrease Pain Intensity On Postoperative Fracture Patients in Bougenvile Ward of DR Soegiri Hospital LamonganFaki D'pasnizerNo ratings yet
- MEDICAMENTOSDocument8 pagesMEDICAMENTOSPakinn ShadoowNo ratings yet
- Cholecystitis NCPDocument4 pagesCholecystitis NCPdark-canales50% (4)
- Test Bank For Nursing A Concept Based Approach To Learning Volume II 3rd Edition 3rd EditionDocument93 pagesTest Bank For Nursing A Concept Based Approach To Learning Volume II 3rd Edition 3rd EditionLarry Cessor100% (31)
- Yoga TeachersDocument1 pageYoga TeachersleslieNo ratings yet
- 08 Malignant WoundsDocument67 pages08 Malignant WoundsmasleleNo ratings yet
- Multiple-Choice QuestionsDocument38 pagesMultiple-Choice QuestionsVjs Mrunalini50% (6)
- Pain Management and Unani MedicineDocument1 pagePain Management and Unani MedicineMSKCNo ratings yet
- Oligoanalgesia in Adult Colles Fracture Patients Admitted To The Emergency DepartmentDocument18 pagesOligoanalgesia in Adult Colles Fracture Patients Admitted To The Emergency DepartmentTeja Laksana NukanaNo ratings yet
- 13-00188-EN-FR-ES-DE-NL - Rev - A - Cefar - TENS - IFU - Digital - User - Manual - (DIGITAL) - (2) 2Document244 pages13-00188-EN-FR-ES-DE-NL - Rev - A - Cefar - TENS - IFU - Digital - User - Manual - (DIGITAL) - (2) 2RUSNETNo ratings yet
- Narcotics ClassificationDocument23 pagesNarcotics Classificationzohaib hassan100% (2)
- Current Anaesthesia & Critical Care: Michelle HayesDocument1 pageCurrent Anaesthesia & Critical Care: Michelle HayesDani Toledo ArrauNo ratings yet
- The Control of PainDocument17 pagesThe Control of PainalifafnanNo ratings yet
- NEW GUIDELINES - CDC Softens Opioid Prescribing Guidelines For DoctorsDocument100 pagesNEW GUIDELINES - CDC Softens Opioid Prescribing Guidelines For DoctorsDan LehrNo ratings yet
- IASP-PainManagementCenter ToolkitDocument89 pagesIASP-PainManagementCenter ToolkitAlejandra Molina BarradasNo ratings yet
- Sickle Cell Disease ED Vasocclusive Crises Pain Management GuidelineDocument1 pageSickle Cell Disease ED Vasocclusive Crises Pain Management GuidelineLakshmanan KrishnamurtiNo ratings yet
- 9 Anak (Manajemen Nyeri)Document7 pages9 Anak (Manajemen Nyeri)dewiNo ratings yet
- 9 Laporan Pasien UmumDocument222 pages9 Laporan Pasien UmumANDRES PULANA 521201018No ratings yet
- Pain Management in Palliative Care: Ns. Dwi Yunita Haryanti, S.Kep., M.KesDocument17 pagesPain Management in Palliative Care: Ns. Dwi Yunita Haryanti, S.Kep., M.Kesiqbal yudo5No ratings yet
- Thesis Topics in Emergency MedicineDocument6 pagesThesis Topics in Emergency Medicineamandabarbergilbert100% (2)
- Chronic Low Back Pain ThesisDocument6 pagesChronic Low Back Pain Thesiskatrinabankswashington100% (1)
- Nursing Diagnosis Acute PainDocument5 pagesNursing Diagnosis Acute Painlovelove DayoNo ratings yet
- Patient Satisfaction and Benefts of Music Therapy Services To Manage Stress and Pain in The Hospital Emergency DepartmentDocument25 pagesPatient Satisfaction and Benefts of Music Therapy Services To Manage Stress and Pain in The Hospital Emergency DepartmentBapak Sunaryo SPBU100% (1)