Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Amines All Sheet
Uploaded by
Mahendra ShahCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Amines All Sheet
Uploaded by
Mahendra ShahCopyright:
Available Formats
TG: @Chalnaayaaar
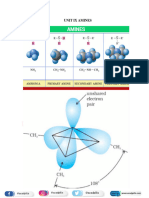
Amines
Part-01
Amines can be considered as derivatives of ammonia obtained by replacement of one, two or all the three
hydrogen atoms by alkyl/aryl groups.
Classification of Amines
Amines are classified according to the number of carbon atoms bonded directly to the nitrogen atom.
Methods of Preparation of amines
1. Reduction of nitro compounds
Nitro compounds are reduced to amines by passing hydrogen gas in the presence of finely divided nickel,
palladium or platinum and also by reduction with metals in acidic medium.
2. Reduction of nitriles(cyanides) and isonitriles (isocyanides)
Nitriles on reduction with lithium aluminium hydride (LiAlH4) or catalytic hydrogenation produce primary amines
but isonitriles produce secondary amines.
Digital Pvt. Ltd. [1]
TG: @Chalnaayaaar
Amines Part-01
3. Reduction of amides
Amides on reduction with lithium aluminium hydride (LiAlH4) produce amines.
4. Ammonolysis of alkyl halides
Alkyl halide on reaction with ethanolic solution of ammonia undergoes nucleophilic substitution in which the
halogen atom is replaced by amino (-NH2) group. The process of cleavage of C-X bond by ammonia is known
as Ammonolysis.
NH3 + R—X ⎯→ R—NH2
Ammonolysis reaction yields a mixture of primary, secondary, tertiary amines and also quaternary ammonium
salt. However primary amine can be obtained as major product taking large excess of ammonia and quaternary
ammonium salt will be major product if alkyl halide is taken in excess.
5. Gabriel phthalimide synthesis
Gabriel synthesis is used for the preparation of 1° aliphatic amines.
Phthalimide on treatment with ethanolic potassium hydroxide forms potassium salt of phthalimide which on
reaction with alkyl halide followed by alkaline or acidic hydrolysis produces the corresponding primary amine.
Mechanism
Digital Pvt. Ltd. [2]
TG: @Chalnaayaaar
Amines
Part-02
Methods of Preparation of amines
6. Hoffmann bromamide degradation reaction
Reagents that may be used for this reaction
1. X2 + alkaline medium
Br2 + NaOH
Br2 + KOH
2. NaOX (NaOCl, NaOBr etc.)
KOX (KOCl, KOBr etc.)
Physical Properties of Amines
Solubility
1. Lower aliphatic amines are soluble in water because they can form hydrogen bonds with water molecules.
2. Solubility decreases with increase in molar mass of amines due to increase in size of the hydrophobic alkyl part.
3. Higher amines are essentially insoluble in water.
Boiling point
Primary and secondary amines are engaged in intermolecular association due to hydrogen bonding between
nitrogen of one and hydrogen of another molecule.
This intermolecular association is more in primary amines than in secondary amines as there are two hydrogen
atoms available for hydrogen bond formation in it.
Tertiary amines do not have intermolecular association due to the absence of hydrogen atom required for
hydrogen bond formation.
The order of boiling points of isomeric amines is as follows:
Primary > Secondary > Tertiary
Digital Pvt. Ltd. [1]
TG: @Chalnaayaaar
Amines Part-02
Chemical reactions of Amines
(1) Reaction showing basic nature
Amines being basic in nature react with acids to form salts.
Amine salts on treatment with a base like NaOH, regenerate the parent amine.
(2) Acylation reaction
Aliphatic and aromatic primary and secondary amines react with acid chlorides, anhydrides and esters by
nucleophilic substitution reaction.
(3) Hoffmann's carbylamine reaction or isocyanide test
Aliphatic and aromatic primary amines on heating with chloroform and ethanolic potassium hydroxide form
isocyanides or carbylamines which are foul smelling substances.
Note: Dichlorocarbene is formed in this reaction.
Digital Pvt. Ltd. [2]
TG: @Chalnaayaaar
Amines
Part-03
Chemical reactions of Amines
(4) Reaction with Benzenesulphonyl chloride (Hinsberg’s reagent)
Note:
Hinsberg test is used to distinguish between primary, secondary and tertiary amines.
These days benzenesulphonyl choride is replaced by p-toluenesulphonyl chloride (TsCl)
(5) Reaction with nitrous acid (HNO2)
Digital Pvt. Ltd. [1]
TG: @Chalnaayaaar
Amines Part-03
(a) 1° Aliphatic amine
Mechanism
(b) 1° Aromatic amine
If the temperature of the diazonium salt solution is allowed to rise upto 283K, the salt gets hydrolysed to phenol.
(c) 2° Aromatic amine
(d) 3° Aromatic amine
Digital Pvt. Ltd. [2]
TG: @Chalnaayaaar
Amines Part-03
Chemical reaction of Diazonium salts
A. Reactions involving displacement of nitrogen
B. Reactions involving retention of diazo group
Coupling reaction of benzene diazonium chloride (ESR)
Benzene diazonium chloride reacts with aromatic compounds containing strongly activating groups like
–OH, –NH2, –NHR, –NR2
Digital Pvt. Ltd. [3]
TG: @Chalnaayaaar
Amines
Part-04
Chemical reactions of Amines
(6) Electrophilic Substitution Reaction (ESR)
Halogenation of Aniline
Nitration of Aniline
Illustration
Sulphonation of Aniline
Note:
Aniline does not show Friedel Crafts reaction (alkylation and acylation)
Digital Pvt. Ltd. [1]
TG: @Chalnaayaaar
Amines Part-04
Reduction of Nitrobenzene
Digital Pvt. Ltd. [2]
You might also like
- 12 Chemistry Notes ch13 AminesDocument11 pages12 Chemistry Notes ch13 AminesAkNo ratings yet
- Notes For Chemistry Class 12 Chapter 13 AminesDocument22 pagesNotes For Chemistry Class 12 Chapter 13 AminesVanshika JainNo ratings yet
- 5.surface Chemistry Final 4-3-2014 PDFDocument16 pages5.surface Chemistry Final 4-3-2014 PDFArinjayNo ratings yet
- ORM-II Theory+exercise+ Answer PDFDocument58 pagesORM-II Theory+exercise+ Answer PDFGOURISH AGRAWALNo ratings yet
- Tricks of Isomerism in Coordination Compounds Chemistry For NEET & JEE 2019Document5 pagesTricks of Isomerism in Coordination Compounds Chemistry For NEET & JEE 2019misostudy0% (1)
- 28 Salt Analysis Revision Notes QuizrrDocument46 pages28 Salt Analysis Revision Notes Quizrrprince thakur100% (2)
- Nomenclature SheetDocument24 pagesNomenclature SheetEkta MishraNo ratings yet
- Reaction IntermediatesDocument20 pagesReaction IntermediatesSacchitDShethNo ratings yet
- CLS Aipmt-19-20 XIII Che Study-Package-3 Level-1 Chapter-15 PDFDocument40 pagesCLS Aipmt-19-20 XIII Che Study-Package-3 Level-1 Chapter-15 PDFThavasimariselvam N100% (1)
- Sample Question Paper Class XII Chemistry 2023-24Document100 pagesSample Question Paper Class XII Chemistry 2023-24MRIGANKO DeyNo ratings yet
- Quantitative and QualitativeDocument15 pagesQuantitative and QualitativesquadralsupremeNo ratings yet
- Pre-Medical: Chemistry Allen: Carbonyl Compounds, Acids and It'S Derivatives Carbonyl CompoundsDocument18 pagesPre-Medical: Chemistry Allen: Carbonyl Compounds, Acids and It'S Derivatives Carbonyl CompoundsJK JHANo ratings yet
- Assignment Periodic Table JH Sir-3575Document30 pagesAssignment Periodic Table JH Sir-3575aachuNo ratings yet
- Aromaticity DPP 4Document4 pagesAromaticity DPP 4SubhadeepNo ratings yet
- VMC Salt AnalysisDocument53 pagesVMC Salt AnalysisAkash Mukherjee100% (3)
- Coordination Chemistry JEE AdvancedDocument44 pagesCoordination Chemistry JEE AdvancedKartikey SharmaNo ratings yet
- OC - Halogen Derivatives - EDocument100 pagesOC - Halogen Derivatives - EJohn DoeNo ratings yet
- DPP (31 To) IcDocument41 pagesDPP (31 To) IcRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- DPP Haloalkanes and Haloarenes 1631899722769Document32 pagesDPP Haloalkanes and Haloarenes 1631899722769Mohit KumarNo ratings yet
- OC - Electronic Displacement Effect - EDocument80 pagesOC - Electronic Displacement Effect - EJohn Doe100% (1)
- DPP GoccccDocument10 pagesDPP GoccccMayur Khichi0% (1)
- Chemical Bonding (Leader)Document93 pagesChemical Bonding (Leader)Hero Perfect100% (2)
- PRACTICE SHEET - 03 (Chemistry) : CH - CH - CH CN CN CNDocument3 pagesPRACTICE SHEET - 03 (Chemistry) : CH - CH - CH CN CN CNABD 17No ratings yet
- Alcohol, Phenol and EtherDocument35 pagesAlcohol, Phenol and EtherSubhrota PradhanNo ratings yet
- Alkyl and Aryl Halides - DPP-05 - Alkyl and Aryl halides-DPP-05 - (NEET) Lakshay BatchDocument4 pagesAlkyl and Aryl Halides - DPP-05 - Alkyl and Aryl halides-DPP-05 - (NEET) Lakshay BatchAryan SinghNo ratings yet
- CBSE Chemistry Question Bank 2023Document496 pagesCBSE Chemistry Question Bank 2023NafeesNo ratings yet
- Goc and Isomerism Notes - PMD - 1 PDFDocument46 pagesGoc and Isomerism Notes - PMD - 1 PDFrutvik bhoraniyaNo ratings yet
- Hydrocarbon DPPDocument24 pagesHydrocarbon DPPDhruv Jyot SinghNo ratings yet
- Prince Singh: Physical & Inorganic ChemistryDocument5 pagesPrince Singh: Physical & Inorganic ChemistryJatin SinglaNo ratings yet
- CH13 Hydrocarbons Shobhit NirwanDocument58 pagesCH13 Hydrocarbons Shobhit NirwanpujaNo ratings yet
- 26 Amines: SolutionsDocument32 pages26 Amines: SolutionsDrNaresh SahuNo ratings yet
- 01 D and F Block Elements Theory Final EDocument17 pages01 D and F Block Elements Theory Final Etech 2 life100% (1)
- Stereoisomerism VKP SirDocument49 pagesStereoisomerism VKP SirSandeep ReddyNo ratings yet
- 12 Salt Analysics EMDocument20 pages12 Salt Analysics EMUma SaravananNo ratings yet
- Part - I: Objective Questions: Section A: Geometrical IsomerismDocument10 pagesPart - I: Objective Questions: Section A: Geometrical IsomerismTejas pawarNo ratings yet
- The D and F Block ElementsDocument48 pagesThe D and F Block ElementsRocking vevo100% (1)
- Alkene DPPDocument20 pagesAlkene DPPKalyan ReddtNo ratings yet
- Nic Compunds Containing Nitrogen KCET PYQsDocument2 pagesNic Compunds Containing Nitrogen KCET PYQsPunith kumar50% (2)
- Name ReactionsDocument10 pagesName ReactionsParam SoniNo ratings yet
- DPP (1 - ) For (A) 12th IcDocument29 pagesDPP (1 - ) For (A) 12th IcRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- DPP 1 Acidic Basic Strength VKP Sir-3688Document1 pageDPP 1 Acidic Basic Strength VKP Sir-3688pNo ratings yet
- DPP 01 Gaseous State JH Sir-3583Document11 pagesDPP 01 Gaseous State JH Sir-3583Shivam Kumar75% (4)
- UmpolungDocument28 pagesUmpolungmeauna100% (1)
- Acid Bases and Salts - Shobhit NirwanDocument21 pagesAcid Bases and Salts - Shobhit NirwanBhaskar 8287100% (1)
- Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids NotesDocument74 pagesAldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids Notessamay gujratiNo ratings yet
- Carbonyl CompoundsDocument10 pagesCarbonyl CompoundsMahendra ChouhanNo ratings yet
- Haloalkanes and HaloarenesDocument26 pagesHaloalkanes and Haloarenesrajputrishi1982No ratings yet
- 12 Chemistry Notes Ch12 Aldehydes Ketones and CarboxylicacidDocument11 pages12 Chemistry Notes Ch12 Aldehydes Ketones and Carboxylicacidankajkumar100% (1)
- CLS Aipmt 19 20 XII Che Study Package 4 Level 1 Chapter 10Document36 pagesCLS Aipmt 19 20 XII Che Study Package 4 Level 1 Chapter 10Utkarsh KumarNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure IITDocument16 pagesAtomic Structure IITAdiChemAdi69% (13)
- Co Ordination Compounds MHT CET Synopsis PDFDocument11 pagesCo Ordination Compounds MHT CET Synopsis PDFAbhishek MandlikNo ratings yet
- DPP 04 Ionic Equilibrium JH Sir-4295Document4 pagesDPP 04 Ionic Equilibrium JH Sir-4295T sidharth100% (1)
- General Organic Chemistry Exercise 1 and 2Document33 pagesGeneral Organic Chemistry Exercise 1 and 2Vedant JNo ratings yet
- S BlockDocument84 pagesS BlockPrakhar ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure Short Notes 7 PageDocument7 pagesAtomic Structure Short Notes 7 PageSubhajit GoraiNo ratings yet
- Reduction, Oxidation - Hydrolysis APSP PDFDocument24 pagesReduction, Oxidation - Hydrolysis APSP PDFGOURISH AGRAWALNo ratings yet
- AminesDocument13 pagesAminesSohamNo ratings yet
- Amines Class 12 Notes NEET Chemistry (PDF)Document19 pagesAmines Class 12 Notes NEET Chemistry (PDF)Scar LNo ratings yet
- 12 Notes Ammines and AcidsDocument11 pages12 Notes Ammines and AcidsXyzdevuNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Chemistry - Amines Chapter NotesDocument12 pagesCBSE Class 12 Chemistry - Amines Chapter NotesGayathiriNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding Part-01Document40 pagesChemical Bonding Part-01Mahendra ShahNo ratings yet
- Cbse 11 Chap 1,2,3 MathstDocument2 pagesCbse 11 Chap 1,2,3 MathstMahendra ShahNo ratings yet
- Board Question Paper: July 2018: BiologyDocument3 pagesBoard Question Paper: July 2018: BiologyMahendra ShahNo ratings yet
- Atoms NuclearDocument39 pagesAtoms NuclearMahendra ShahNo ratings yet
- Atoms StructureDocument47 pagesAtoms StructureMahendra ShahNo ratings yet
- Biomolecules SheetDocument21 pagesBiomolecules SheetMahendra Shah100% (1)
- EXERCISEDocument24 pagesEXERCISEMahendra ShahNo ratings yet
- Acknowledgement Slip - Document UpdateDocument1 pageAcknowledgement Slip - Document Updateগ্রাহক সেবা কেন্দ্রNo ratings yet
- Board Question Paper: July 2019: PhysicsDocument3 pagesBoard Question Paper: July 2019: PhysicsMahendra ShahNo ratings yet
- HwstatetrignoandpairstlineDocument2 pagesHwstatetrignoandpairstlineMahendra ShahNo ratings yet
- Kendriya Vidyalaya Gachibowli, Hyderabad: Sample Paper 03: Periodic Test - 1 (2019 - 20) Class - Xi MathematicsDocument2 pagesKendriya Vidyalaya Gachibowli, Hyderabad: Sample Paper 03: Periodic Test - 1 (2019 - 20) Class - Xi MathematicsMahendra ShahNo ratings yet
- Hotel Booking Ref-2409210054733Document3 pagesHotel Booking Ref-2409210054733Mahendra ShahNo ratings yet
- Maths 11 SecondunitDocument1 pageMaths 11 SecondunitMahendra ShahNo ratings yet
- Maths 2 NdunitDocument1 pageMaths 2 NdunitMahendra ShahNo ratings yet
- Toaz - Info CH 11 Three Dimentional Geometry Multiple Choice Questions With Answers PRDocument5 pagesToaz - Info CH 11 Three Dimentional Geometry Multiple Choice Questions With Answers PRMahendra ShahNo ratings yet
- Hwstate 11 Lines 2Document1 pageHwstate 11 Lines 2Mahendra ShahNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 (Electric Charges and Field) UnsolvedDocument6 pagesChapter 1 (Electric Charges and Field) UnsolvedMahendra ShahNo ratings yet
- 9702 Capacitors All Completed Upto May June 2011Document0 pages9702 Capacitors All Completed Upto May June 2011Ritwik KumarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 (Atoms) UnsolvedDocument4 pagesChapter 12 (Atoms) UnsolvedMahendra ShahNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 (Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter) Unsolved-1Document4 pagesChapter 11 (Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter) Unsolved-1Mahendra ShahNo ratings yet
- Class 10th Syllabus and Marking SchemeDocument5 pagesClass 10th Syllabus and Marking SchemeSagar ChhabraNo ratings yet
- 9702 Capacitors All Completed Upto May June 2011Document0 pages9702 Capacitors All Completed Upto May June 2011Ritwik KumarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 (Wave Optics) UnsolvedDocument5 pagesChapter 10 (Wave Optics) UnsolvedMahendra ShahNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 (Wave Optics) UnsolvedDocument5 pagesChapter 10 (Wave Optics) UnsolvedMahendra ShahNo ratings yet
- Board Question Paper: July 2018: PhysicsDocument3 pagesBoard Question Paper: July 2018: PhysicsMahendra ShahNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 (Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter) Unsolved-1Document4 pagesChapter 11 (Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter) Unsolved-1Mahendra ShahNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 (Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance) UnsolvedDocument8 pagesChapter 2 (Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance) UnsolvedMahendra ShahNo ratings yet
- H WCB Se 12 Electric ChargeDocument2 pagesH WCB Se 12 Electric ChargeMahendra ShahNo ratings yet
- 9702 Capacitors All Completed Upto May June 2011Document0 pages9702 Capacitors All Completed Upto May June 2011Ritwik KumarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 (Electric Charges and Field) UnsolvedDocument6 pagesChapter 1 (Electric Charges and Field) UnsolvedMahendra ShahNo ratings yet
- SMM200 Derivatives and Risk Management 2021 QuestionsDocument5 pagesSMM200 Derivatives and Risk Management 2021 Questionsminh daoNo ratings yet
- Rate LawsDocument20 pagesRate LawsReginal MoralesNo ratings yet
- Biochem Laboratory ReviewerDocument6 pagesBiochem Laboratory Reviewer202370092No ratings yet
- Pfe ReportDocument87 pagesPfe ReportAzmi AbrougNo ratings yet
- ASTM B 280-20 STD Spec For Seamless Copper Tubing For Air Conditioning and Refrigeration Field ServiceDocument9 pagesASTM B 280-20 STD Spec For Seamless Copper Tubing For Air Conditioning and Refrigeration Field Servicetomhansen935No ratings yet
- 2.4 GHZ 14 Dbi 90 Degree Vertical Polarized Sector Panel Wireless Lan Antenna - Model: Hg2414Sp-090Document2 pages2.4 GHZ 14 Dbi 90 Degree Vertical Polarized Sector Panel Wireless Lan Antenna - Model: Hg2414Sp-090Giovanni José Huacasi SupoNo ratings yet
- CHM170L Exp6 Heat of CombustionDocument5 pagesCHM170L Exp6 Heat of CombustionKaiser SaltoNo ratings yet
- Mathematics: Applications & Interpretation: Unit Planner: Part 2: Representing Space: Non Right Angled Trig and VolumesDocument7 pagesMathematics: Applications & Interpretation: Unit Planner: Part 2: Representing Space: Non Right Angled Trig and VolumesLorraine SabbaghNo ratings yet
- Parker Comoso P16 Series Aluminium Bushing Gear Pump.55b98395d96e7Document4 pagesParker Comoso P16 Series Aluminium Bushing Gear Pump.55b98395d96e7Jas SumNo ratings yet
- Surpac IntroductionDocument207 pagesSurpac IntroductionKrist Jan Jimenez Separa0% (1)
- Iso 10724 1 1998Document11 pagesIso 10724 1 1998rtsultanNo ratings yet
- Substance Chemistry Lesson 1Document28 pagesSubstance Chemistry Lesson 1samsonNo ratings yet
- Parts of An Automobile and The FunctionDocument11 pagesParts of An Automobile and The Functionrajronson6938100% (8)
- TechnicalInformationNewProducts PDFDocument32 pagesTechnicalInformationNewProducts PDFsmartel01No ratings yet
- MTBFDocument4 pagesMTBFJulio CRNo ratings yet
- DC80D MK3 Genset Controller User Manual V1.1Document37 pagesDC80D MK3 Genset Controller User Manual V1.1nathalie gonzelez100% (1)
- Rfid Ic List: Brand U H F Part Number Frequency Description RemarkDocument1 pageRfid Ic List: Brand U H F Part Number Frequency Description RemarkRamzi BenameurNo ratings yet
- 11th Maths Vol2 EM WWW - Tntextbooks.inDocument288 pages11th Maths Vol2 EM WWW - Tntextbooks.inGv HarishNo ratings yet
- Manuale PJ6KPS-CA Rev 1.4 EngDocument89 pagesManuale PJ6KPS-CA Rev 1.4 EngTerver Fred KumadenNo ratings yet
- Example Paper CC270 SpontaneousGenDocument14 pagesExample Paper CC270 SpontaneousGenLaert VeliaNo ratings yet
- Chapter2 - 3 - 3D Stiffness and Compliance MatricesDocument43 pagesChapter2 - 3 - 3D Stiffness and Compliance MatricesRobby GunadiNo ratings yet
- The Mathematical Gazette Volume 86 Issue 507 2002 (Doi 10.2307 - 3621155) Nick Lord - 86.76 Maths Bite - Sides of Regular PolygonsDocument3 pagesThe Mathematical Gazette Volume 86 Issue 507 2002 (Doi 10.2307 - 3621155) Nick Lord - 86.76 Maths Bite - Sides of Regular PolygonsEduardo CostaNo ratings yet
- The Performance and Service Life of Wire Ropes Under Deep Koepe and Drum Winders Conditions - Laboratory SimulationDocument9 pagesThe Performance and Service Life of Wire Ropes Under Deep Koepe and Drum Winders Conditions - Laboratory SimulationRicardo Ignacio Moreno MendezNo ratings yet
- 2155 13572 1 PBDocument8 pages2155 13572 1 PBIliace ArbaouiNo ratings yet
- MANUAL For IONIZING AIR BARDocument11 pagesMANUAL For IONIZING AIR BARGerardo BoisNo ratings yet
- Manual Sitrans Fup1010Document46 pagesManual Sitrans Fup1010cchung147554No ratings yet
- Deep Learning (R20A6610)Document46 pagesDeep Learning (R20A6610)barakNo ratings yet
- Introduction To IoT With Machine Learning and Image Processing Using Raspberry Pi (Shrirang Ambaji Kulkarni, Varadrah P. Gurupur Etc.) (Z-Library)Document167 pagesIntroduction To IoT With Machine Learning and Image Processing Using Raspberry Pi (Shrirang Ambaji Kulkarni, Varadrah P. Gurupur Etc.) (Z-Library)Siddhant RawatNo ratings yet
- Goldscmidt AlgoDocument4 pagesGoldscmidt AlgochayanpathakNo ratings yet
- New Plan Ai TS 2022-2023 - Revised As On 17.08.2022Document2 pagesNew Plan Ai TS 2022-2023 - Revised As On 17.08.2022VANo ratings yet