Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Apocrypha Timeline of Inclusion & Exclusion
Uploaded by
Thomas Lorenz (Fit For Faith Ministries)Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Apocrypha Timeline of Inclusion & Exclusion
Uploaded by
Thomas Lorenz (Fit For Faith Ministries)Copyright:
Available Formats
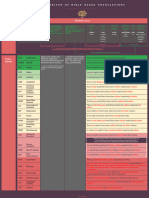
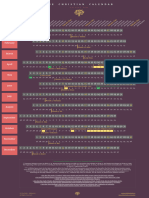
- BC - AD - Timeline of Inclusion and Exclusion
Profitable 'only'
Profitable 'only'
100%
Books
Same weight as
Heb, Jam, Jud & Rev
either 15
Profitable 'only', but pushed hard
Published 75% Written
14 14 14 14
in Bibles 13 13 13 13 13 13 13
or 12 12 12 12 12 12 12 12 12
Not written on special Bible parchment
11 11 11 11 11 11 11 11 11 11 11
Profitable 'only'
Considered 10 10 10 10 10 10 10 10 10 10 10 10 10 10
Canonical 9 9 9 9 9 9 9 9 9 9 9 9 9 9
Profitable 'only'
Treated as Scripture
by Individuals
8 8 8 8 8 8 8 8 8 8 8 8 8 8
33% Written
7 7 7 7 7 7 7 7 7 7 7 7 7 7 7 7 7 7 7 7 7 7 7 7 7 7
6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6
5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5
4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4 4
3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3
2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2
1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Apocrypha Read in Churches / ≤ 95% Inclusion in Bibles
No / Minor Influence ~ 50% Inclusion in Bibles Exclusion
Pushed by Scholars (Time of Reformation)
║ ║ ║ ║ ║ ║ ║ ║ ║ ║ ║ ║ ║ ║ ║ ║ ║ ║ ║ ║ ║ ║ ║ ║ ║ ║ ║ ║ ║ ║ ║ ║ ║ ║ ║ ║ ║ ║ ║ ║ ║ ║ ║ ║ ║ ║ ║ ║ ║ ║ ║ ║ ║ ║ ║ ║ ║ ║ ║ ║
) D D ) . D ) D D . D . D D D D D
BC BC BC D D D D D
BC . AD 0 A . A 0 A 0 AD 0 AD0 AD0 AD AD . A 0 A 0 AD 0 A 4 A 5 AD0 AD0 AD0 AD 0 AD0 AD AD 7 AD0 AD0 AD0 AD 5 A
D
AD th C 2 A non 7 A 5 A th C 5 A th C 0 A 0 A c. A 0 A 2 A AD AD D D D D D D D D D D D D D AD
5 0 4 0 4 0 1 1 c 4 1 c 7 8 9 0 5 c . 2 c 6 7 4 2 2 5 6 6 6 6 0 6 7 8 8 8 0 4 8 a 9 0 5 0 5 3 3 3 4 5 5 17 24 A 34 A 37 A 38 A 46 A 60 A 61 A 68 A 71 A 69 A 92 A 11 A 7 A 85
- 5 2
-2 - -11 , ,
50 RS BC- ct) fter s, ~ nia, C- 0- 2-4 rly , - to,
1 1 1 1 , 2 ~3 ), 3 ~3 ~3 ~3 ~3 ~3 35 ~3 ~3 ~3 ~3 ~3 3 ), , 3 C , 3 , 4 4- , 4 ), ~7 11 , 1 13 14 14 15 15 15 15 15 15 15 15 15 15 15 15 1 6
64 18
82 300 250 , ~1 E e a u B 0 d ( ea yr li en ea, ed m, m, rs, ri, us, a, ~ ria, at, ns, us, us, ) , ~ s (B on) ant age t I n), ate s (A s, r, ~ ria a, ~ l), l e, ble, le, le, le, le, c), le, ts), le, s), le, te, ble, , 1 ble,
2 T 0 S , h m 1 g s a h t n u o a r a b i b b b b
i Bi Bi Bi ol i is i ca ib lg B i b b n a i F
, ~ ), ~ , ~ n) RI , 2 s ( ra ep Ja 00 t, ~ u st, art Me Ori sar or sale nha itie gli anz dice nd Gre no chi ani lep anu Can tes rth oce itio ulg rinu asc ict din Ly nic Bi B o Bi
-5 ks -39 itte W dria roll f Ez Jos l of , ~2 ex alm s Li M a e nd u te Po Ca zi o xa e Ca ilo ph A i c ic ro Ca nn os s V d m t V Or of e r g lot ch B er 's le ath va B lvin 's B gli ra B Vu es e r C es
1 r ( t e i h w a p
s oo 6 r NT an Sc o ci n) c T / T io tin C e e el f f a
a L le t ic h h i s a l P f I p e' n a n
of ith' of J Ch y o er o f N of f A sil tol mp Ep icu V tho ist / cil o pe nal om lexa of D Sai ssa ola Ecu ten Poly Zü Lu tth ver an Gen n-C ish s (A -Va ntin g Ja
s m b g r t e d C e a o n l e e m st m
o ok t B oks
s s W ES, lex ea pse o un etio reti kh enn Jus s l r f o l o a s t a o o r f l o h ( s a o m a e n in g Ja
k u d a i
il uci ory nc ius t. B po A i C n n P rs Je A u ' B l a e i m n
X , B Fir , Bo oo IPL of A ad cal
S y C pl so na ry
a a B e bi 'Ju yri H S A i na a n alvi ou e o hn h o G Nic nce G ian gli
s
M s C Ro
e ( t in
i
r tic ein lem K e st Ki
5 B e m T s t C L g u s S C p J g e i n l t s A R C
LX a ( OT her ISC ilo D Apo Co M Eu , bu e o a m C e( u or n
te Zw y
M ren
u W
ek ph eek t D Ph s, n Gr (C han ( Ro ic & m
H Fl lu ug 39
e r S k o t l o f p T ( A
y
Gr ocr Gr 6 F , HI
u o n A us o Je
r lo om of n
p + Bo ca as ath n ci C c il s io
( T 4 o m C
A a IS + (n a o(
Co
u un es
ph CHR h a( ea e Dipp Co o nf
y a p C
oc
r yp Ni
c Po f H ic
cr lg
Ap o o f e o e
Ap il in B
u nc u st
Co g
Au
see next page
A P O C R Y P H A / E C C L E S I A S T I C A L B O O K S
2 · T i m e l i n e O f I n c l u s i o n & E x c l u s i o n
Timeline Bible / Actor Count Survey
Old Testament Apocrypha, only counted if part of the 15 deuterocanonical books
Old Testament Canon (22, modern count 39 books) 22 + 15 (Psalm 151 and additions to Esther not counted as book; 1&2 Clement added).
BC It is not always clear if Nehemiah & Ezra are counted as 1 or 2 books called Esdras.
~282-250 BC · Greek Pentateuch 5 + 0 Apocrypha not yet written. The 70 elders translated only Source
(Septuagint, 70, LXX) the Pentateuch (five books of the Torah / Law).
~300-140 BC · Apocrypha (Part I / III) - 5 5 Books written during the completion of the Greek OT: Source
(Letter of Jeremiah ~300 BC, Psalm 151 ~300-200 BC,
Sirach ~180-175 BC, Tobit ~225-164 BC, Wisdom of
Solomon ~150 BC, 1 Esdras ~200-140 BC)
~250-140 BC · Greek Old Testament 22 + 0 Further, unknown translators amongst the Alexandrian Source
Jews translated the remaining 17 books of the OT. What
some coined 'Septuagintal Plus' (=Apocrypha) and many
still erroneously consider integral part of the Septuagint, Source
would not even be finished until 240 years after (!) the
Greek OT had been fully translated in 140 BC.
1c. BC · Jews of Alexandria - 0 All groups except the Samaritans (and naturally certain Source
and of Palestine sects) had the same canon, although not specified as
such.
150-1 BC · Apocrypha (Part II / III) - 11 6 Books written after the completion of the Greek OT: Source
(2 Maccabees ~150-120 BC, 1 Maccabees ~135-103 BC,
Judith ~150-100 BC, Additions to Daniel ~100 BC,
3 Maccabees ~ 100-50 BC, Esther-Additions ~100-1 BC)
1c. AD · Christ, His disciples and - 0 Christ and His disciples read and quoted from one Source
AD NT writers canon, from the Greek and Aramaic / Hebrew OT. Jesus
and the NT writers not even once quoted the Apocrypha,
Source
although there are hundreds of quotes and references
to almost all of the canonical books of the OT.
20 BC-40 AD · Philo of Alexandria - 0 He quoted the OT extensively, but he never quoted Source
(Hellenistic Jewish Phil.) from the Apocrypha as being inspired.
No / Minor Influence
1c. AD · Dead Sea Scrolls 21 + 3 Apocrypha included in the collection of biblical and Source
(Written 3c. BC - 1c. AD) extra biblical books (3 books), but not written on
Source
the special parchment reserved for the Bible.
after 70 AD · Apocalypse of Ezra 24 + 0 Considered dozens of other books, but excluded those Source
upon a 'special revelation' from God to consider only
the 24 books (22 books + ?).
~80 AD · Josephus 22 + 0 Apocrypha thoroughly rejected. He frequently used Flavius
Josephus,
(Roman-Jewish historian) the Greek OT. He specifically mentioned 22 OT books Against
and also used the Septuagint 5500 BC timeline. Apion 1:8
~90 AD · Council of Jamnia - - Some sources state that they did not recognize the Source
Apocrypha, while others say that this council was
Source
not about the canon at all.
200 BC · Apocrypha (Part III / III) - 15 4 Books finished after Christ (completing 15 books): Source
- 100 AD (Prayer of Manasseh ~200 BC-50 AD, 4 Maccabees ~18-
55 AD, Baruch ~200 BC-100 AD, 2 Esdras ~90-100 AD)
~120-160 AD · Masoretic Text 24 + 0 Apocrypha not included. Rabbi Akiva (died 135 AD; Source
(Basic text for most modern (39) the mastermind behind the OT manipulation and the
translations such as AMP,
heretical Talmud; hater of the Gospel; he proclaimed
ESV, KJV, NASB, NIV, NLT ...
For centuries erroneously Bar Kochba as 'messiah') was instrumental in draw-
Source
thought to be the original ing up the canon of the Tanakh. He condemned the
Hebrew text, and now only public-, but favored a private reading of the Apo-
reluctantly being admitted by
crypha; he even made frequent use Sirach.
scholars).
2-4c. AD · Tanakh / Talmud 24 + 0 Wisdom of Sirach (Ben Sira) was now quoted several Source
(39) times in the Talmud and was closest to an inclusion
in the canon. Considered as 'historically valuable':
1-2 Maccabees and Judith. Considered 'heretical':
3-4 Maccabees, Susanna, plus Enoch and Jubilees.
(early 2c. AD) · Bryennios List 22 - Apocrypha not included. Source
- 160 AD · Justin Martyr - - Apocrypha never mentioned in any of his works. Source
(Apologist & Philosopher)
170 AD · Melito 21 - Apocrypha not mentioned in his OT canon list. Source
(Bishop of Sardis)
1-3c. AD · Christian Church - ? Many Christians accepted Apocrypha / Ecclesiastical The Canon
of Scripture,
Books as 'profitable for reading'. It also became a part by F.F. Bruce
of the liturgy in many churches. Jerome
240 AD · Origen Adamantius 22 + 0 He saw the Christian canon as consisting of '22 books Ernst Rede-
penning,
(Scholar, Ascetic, Theologian) (7) of the Hebrews' (he included the Epistle of Jeremiah), page 237-
plus the Ecclesiastical books. But he used those apo- 238
cryphal books indiscriminately with those of Scripture
as sources for dogmatic proof texts, and cited as in- ▶ see also
spired / Scripture: Baruch, Judith, Maccabees (plural), the study
'Canon'
Tobit, Wisdom (of Solomon). He also defended Bel and
the Dragon, Sirach and Susanna. He only discriminated Source
the Pseudepigrapha, which he called in fact 'Apo-
crypha' in the sense of being hidden / secret.
~324 AD · Eusebius of Caesarea - 2 Apocrypha considered as 'profitable for reading', ▶ see also
the study
(Historian, Exegete) and 2 books considered as canonical. 'Canon'
325 AD · Council of Nicaea - 1 No definition of the biblical canon, but the Source
(Ecumenical Council) book of Judith was considered inspired.
~350 AD · Cyril of Jerusalem 22 + 2 Apocrypha considered as 'profitable for reading',
(Theologian, Bishop) and 2 books considered as canonical.
Read in Churches
▶ see also the
~360 AD · Cheltenham 22 + 4 Apocrypha considered canonical (4 books). study
'Canon'
(37) The list specifically mentions 22 OT books.
~360 AD · Hilary of Poitiers 22 + 0 Apocrypha considered as 'profitable for reading'. Judith,
(Bishop, Catholic Doctor of (5) Tobith considered canonical by some. He quoted Baruch References
the Church, Philosopher)
in one breath with Moses and Isaiah, quoted Wisdom to Baruch,
Maccabees,
and called Susanna 'blessed'. Susanna
~360 AD · Lucifer of Cagliari - 5 5 books considered as canonical. Source
(Catholic Bishop)
~360 AD · Gregory of Nazianzus 22 + 0 Apocrypha rejected. He counted 22 OT books. But he Source
(Catholic)
(Archbishop, Theologian) (4) taught from Baruch, Judith, Sirach and from Wisdom
of Solomon, and treated it rather as Scripture.
~363 AD · Council of Laodicea 22 + 2 Apocrypha considered as 'profitable for reading',
and 2 books considered as canonical. 22 OT books. ▶ see also the
study
~367 AD · Athanasius of Alexan- 22 + 4 Apocrypha considered as 'profitable for reading', 'Canon'
dria (Pope of Coptic Church) and 4 books considered as canonical. 22 OT books.
~370 AD · Basil the Great - 4 He quoted 4 books as Scripture: Baruch, Judith, Sirach, Source
(Catholic)
(Catholic Doctor, Bishop, Wisdom of Solomon.
Theologian)
~380 AD · Apostolic Canons 22 + 4 Apocrypha considered as 'profitable for reading',
(Syrian Church Order) (39) and 4 books considered as canonical. 22 OT books.
▶ see also the
~380 AD · Amphilochius 21 + 0 Apocrypha thoroughly rejected. study
(Bishop) 'Canon'
~385 AD · Epiphanius 22 + 2 Apocrypha considered as 'profitable for reading',
(Bishop) (27) and 2 books considered as canonical.
~350 AD · Sinaiticus (Aleph) - 6 Apocrypha included (6 books), only part of Source
Greek Old Testament the manuscript survived.
(Alexandrian text-type)
4th C. · Vaticanus (B) 39 + 7 Apocrypha included (7 books). Source
Greek Old Testament
(Alexandrian text-type)
382 AD · Pope Damasus / 39 + 6 Apocrypha partly legalized as canonical, through Source
Council of Rome his Council of Rome. Fully merged with biblical texts.
(Catholic Canon) Damasus then commissioned in 383 AD the Latin Vulgate
Source
edition of the Bible, which would prove instrumental in
the fixation of the canon in the West.
393 AD · Augustine of Hippo 39 + 7 The decisive link to legalize the Apocrypha as canonical Source
(3rd Catholic Doctor & for both 'Christians' and Roman Catholics, through his Source
Patriarch of Calvinism =
Council of Hippo. Most studies on the Canon intention- Source
significant conflict of
interest) ally conceal his role based on the significant conflict of
interest. Augustine frequently drew from the apocryphal
books in his writings. (He was also a former Manicha- ▶ see also
ean, Amillennialist, followed the 7 Catholic sacraments, the detailed
discernment
Genesis only myth, Infant Baptism, Purgatory, Ransom-
Theorist, et al.).
397 AD · Council of Carthage 39 + 7 Summary of the Council of Hippo, reconfirmed 419 AD, Source
(and 419 AD) therefore Apocrypha formalized as canonical. Source
405 AD · Pope Innocent I 39 + 7 Re-confirmation of the council of Hippo & Carthage, Source
therefore Apocrypha formalized as canonical.
4-5th C. · Jerome (of Stridon) 0 Apocrypha rejected (personal position). But he called Source
(Confessor, Historian, (7) Baruch a prophet, quoted from Bel and the Dragon,
Priest, Theologian)
2 Maccabees, Sirach, Susannah, Tobit and Wisdom. Source
He encouraged churches to read Wisdom of Solomon
and Eccesiasticus for their edification.
405 AD · Jerome's Vulgate 39 + 7 Jerome had now submitted to the decree of Rome of Source
Latin Old Testament / Maso- Pope St Damasus who had commissioned the Vulgate.
retic Text (Western text-type) Source
He included 7 books as canonical.
5th C. · Alexandrinus (A) 39 + 10 Apocrypha included (10 books), merged. The Canon
of Scripture,
Greek Old Testament
by F.F. Bruce
(Alexandrian text-type)
~590 AD · Pope Gregory the Great 39 + 3-7 Considered Sirach, Tobit and Wisdom explicitly as Source
Scripture. He probably accepted 7 books, with reser- 'Macc.'
vations on 1 Maccabees. He refers to the Apocrypha
'Tobit'
~37-40 times in the same way as to Scripture. He did
clearly -NOT- remove it from the codices. 'Wisdom'
Inclusion in Majority of Bibles
~730 AD · John of Damascus 22 + 7 Apocrypha considered as canonical (7 books; Source
(Apologist, Monk, Priest) disguised as content of the 'Apostolic Canons').
⋮ ⋮ ⋮
⋮
~1130 AD · Hugh of Saint Victor 22 + 0 Apocrypha considered as 'profitable for reading'.
(Mystic, Theologian) Source
(limited
12c. AD · Glossa Ordinaria 22 + 0 Apocrypha considered as 'profitable for reading'. credibility,
(Medieval Scholarly Bible) numerous
errors)
~1330 AD · Nicholas of Lyra 39 + 0 Apocrypha thoroughly rejected.
(Franciscan, former Jew)
⋮ ⋮ ⋮
⋮
1442 AD · Council of Florence 39 + 7 Apocrypha included (7 books), merged. Source
(Ecumenical Council)
~1450 AD · Antoninus of Florence 22 + 0 Apocrypha thoroughly rejected. Source
(Dominican Friar, Archbishop)
1455 AD · Gutenberg Bible 39 + 10 Apocrypha included (10 books), fully merged. Original
Bible
(First Mass-Produced Bible)
~1510 AD · Erasmus 22 ? Apocrypha considered as 'profitable for reading'. Source
(Catholic Theologian, (39) He indicated an acceptance of a wide Christian canon. Source
Philosopher)
1517 AD · Complutensian Polyglot - + 7 Apocrypha included (7 books), separate section. Source
(Franciscan)
1524 AD · Zwingli's Zürich Bible 39 + 10 Apocrypha included, fully merged (some say separate Original
Bible
(Reformed) section, but the original clearly shows it to be included
in between-, not at the end of the OT books)
1534 AD · Luther Bible 24 + 11 Apocrypha included (11 books), same weight as the Original
Bible
(Augustinian) (39) books of Hebrews, James, Jude and Revelation. He
badly disparaged the book of James. Also rejection Source
of Esther, while he regarded 1 Maccabees and Judith
as "not unworthy" to be reckoned among Holy Scrip-
Works of
ture. He cited Sirach (191x) and Wisdom of Solomon; Luther
in many quotes he treated those as 'Scripture'.
1537 AD · Matthew's Bible 39 + 14 Apocrypha included (14 books), separate section. Original
Source
1538 AD · Myles Coverdale Bible 39 + 12 Apocrypha included (12 books), separate section. Original
Bible
(Preacher, Theologian,
Augustinian > Puritan)
1546 AD · Council of Trent 39 + 7 Apocrypha included (7 books), merged. Source
(Roman Catholic) Formal confirmation of the Roman Catholic
canon set into practise some 1146 years earlier.
1560 AD · Geneva Bible 39 + 12 Apocrypha included (12 books), separate section. Original
Bible
(Presbyterian)
1561 AD · Belgic Confession 39 + 13 Rejected, but 13 books considered 'profitable for Source
(Augustinian-Calvinists) reading'.
1568 AD Bishop's Bible 39 + 13 Apocrypha included (13 books), separate section. Source
1569 AD · Reina-Valera Bible 39 + 14 Apocrypha included (14 books), merged. Separate sec- Source
(Spanish Bible) tion in second edition in 1602 AD, removed in 1862 AD.
1571 AD · 39 Articles 39 + 13 Rejected, but 13 books considered 'profitable for reading' Source
(Anglican) and read in their churches until today.
1592 AD · Clementine Vulgate 39 + 7 Apocrypha included (7 books), separate section. Source
1611 AD · King James Bible 39 + 14 Apocrypha included (14 books), separate section. Source
Source
1647 AD · Westminster CoF 39 + 0 Apocrypha thoroughly rejected. Source
(Augustinian)
Gradual Exclusion
1851 AD · Lancelot Brenton LXX 39 + 15 Apocrypha included (15 books), separate section. Source
1885 AD · King James Bible 39 + 0 Apocrypha excluded for reasons related to costs. The Source
National Bible Society of Scotland had successfully pe- Source
titioned in 1826 to not print anymore the Apocrypha.
If it would not have proven less costly to produce the
Bibles without it, we would most probably (!) still
have the Apocrypha in our common Bibles today.
1979 AD · Good News Bible 39 + 14 Apocrypha included (14 books), separate section. Original
Bible
(Reformed)
see next page
A P O C R Y P H A / E C C L E S I A S T I C A L B O O K S
3 · C o n c l u s i o n s
Summarizing now the studies 'Biblical Canon · Comparison of 28 Resources & Historians', 'Bible · Introduction to Non-Canon-
Conclusions ical Writings' and 'Septuagint · Biblical Proof for Superiority over Masoretic Texts', we can conclude the following facts:
1. The 'Apocrypha' should rather be designated 'Ecclesiastical Books', because most are neither hidden nor strictly Source
heretical books and had been openly used in Jewish Synagogues and Christian churches.
2. The 70 (72) elders exclusively translated the Pentateuch, while other Jews translated the remaining 17 books of Source
the Old Testament (Prophets and Writings) by about 140 BC, completing therefore 22 books (modern count 39).
At the time the translation of the Greek OT had been finalized in 140 BC, only 5 apocryphal books were written. 11
apocryphal books were completed until the time of Christ, while it took at least until 100 AD (2 Esdras possibly
until 300 AD) until the Apocrypha / Ecclesiastical Books were completed.
3. There is no evidence that the Alexandrian Jews ever promulgated a canon of Scripture. Source
4. It can be said with reasonable certainty that the Septuagint did not include the Apocrypha until the middle of see
previous
the second century AD. Christ and His disciples, the New Testament in itself, (the Apocalypse of Ezra), Josephus,
list
Bryennios List, Justin Martyr and Melito, all not mentioning or explicitly rejecting the Apocrypha, are sources of
too much of importance to be simply ignored. Even the authors of the Dead Sea Scrolls, who included Septuagint
texts, intentionally wrote the Apocrypha on normal parchment and not on parchment reserved for the Bible.
5. The oldest-surviving nearly-complete manuscripts of the Greek OT including parts of the Apocrypha are from Source
about 325-350 AD (about 600 years before the oldest Hebrew manuscript). We simply do not know at what
point between the middle of the second century AD and the creation of the mega codices the Apocrypha had
been included.
6. The complete Apocrypha is not found in any of the various codices that contain the Greek Old Testament. ▶ see also the
study 'Canon'
7. Although the Roman Catholic church can probably be blamed to have first formalized parts of the Apocrypha, it
has also to be said from a mature viewpoint, that their inclusion was preceded by the universal church having read -
those Ecclesiastical writings in their churches.
8. The first formal inclusion involved both the Roman Catholic church and Proto-Calvinism. Augustine, who was -
at the same time the third doctor of the RCC and the 'patriarch' of Calvinism quoted in Calvin's works 4,119 times
(Calvin: "Augustine is so wholly within me, that if I wished to write a confession of my faith, I could do so with all full-
ness and satisfaction to myself out of his writings."), were the responsible characters to canonize the Apocrypha.
This truth is also the main driver for the ongoing 'confusion' about the Apocrypha. Instead of taking responsi-
bility, the past is continually being left in the dark by both the RCC and Protestants. The vast majority of argu-
ments from both sides are biased and regularly leave uncomfortable details out.
9. As a matter of fairness, it must also be stated that the RCC and Augustine did 'only' include a fraction of the -
Apocrypha. The Reformation, although under the disguise of separating those books from the truly inspired
books, actually increased the quantity of books printed in Bibles, as clearly seen on page 1 of this study.
In nearly all discussions, we hear the unreflected argument that e.g. Luther separated those books, what usually
silences the listeners. But even the Roman Catholic Church made a distinction between the Apocrypha and the
other books of the Bible prior to the Protestant Reformation, a fact usually ignored.
Most importantly, we rarely reflect on what God actually thinks about the matter - if He would be impressed
by such arguments. The very probable reality is, that it is entirely irrelevant in God's eyes if those books are in
a separate section or merged. Everyone will be held responsible at the Great Judgment who added any word in
between the 2 covers of His Word. God will not be impressed by human reasoning and excuses.
Every Writing [is] God-breathed, and profitable for teaching, for conviction, for setting aright, for instruction that 2Tim
3:16-17
[is] in righteousness, that the man of God may be fitted - for every good work having been completed.
> The Reformed Church should take the lead and acknowledge their complicity before God and the universal church, namely to
have been responsible for having included up to 95% of the OT Apocrypha into nearly all our Bibles, from the time of Zwingli
(1524 AD) until the time the King James Version excluded it in 1885 AD. We as individual believers do not bear inter-genera-
tional guilt, but we have to take responsibility on an 'denominational' level, by openly reflecting and decidedly returning to
God's Word alone. By the appearance of the Apocrypha in the Good News Bible (1979, having involved at least 28 Reformed
translators), it should be apparent that we are far from Sola Scriptura. Many popular Bible softwares in our day now include
without any further orientation the Apocrypha and it is only a question of time until people become once again all too familiar
with the Apocrypha.
Fit For Faith - Ministries contact@fitforfaith.ca
All Rights Reserved. www.fitforfaith.ca/bible
You might also like
- Book of Enoch Refutation of The Prophecy of The 10 WeeksDocument1 pageBook of Enoch Refutation of The Prophecy of The 10 WeeksThomas Lorenz (Fit For Faith Ministries)No ratings yet
- Is The Apocrypha Inspired Scripture PDFDocument86 pagesIs The Apocrypha Inspired Scripture PDFRobert TuttleNo ratings yet
- Blindness in PartDocument82 pagesBlindness in PartKarina Bagdasarova0% (1)
- (WAM) A Study of The Book of Revelation - YashanetDocument13 pages(WAM) A Study of The Book of Revelation - YashanetAlejandro González TerrizaNo ratings yet
- Nsti Read Bible in A YearDocument3 pagesNsti Read Bible in A YearNicolas Martin BaylissNo ratings yet
- Topics AbortionDocument1 pageTopics AbortionThomas Lorenz (Fit For Faith Ministries)No ratings yet
- Spiritual and Human Beings (God, Christ, Morning Stars, Angels, Hosts of Heaven, Humans)Document2 pagesSpiritual and Human Beings (God, Christ, Morning Stars, Angels, Hosts of Heaven, Humans)Thomas Lorenz (Fit For Faith Ministries)100% (1)
- Spiritual Gifts Continuationism vs. CessationismDocument2 pagesSpiritual Gifts Continuationism vs. CessationismThomas Lorenz (Fit For Faith Ministries)No ratings yet
- Theophanies 187 Manifestations of GodDocument3 pagesTheophanies 187 Manifestations of GodThomas Lorenz (Fit For Faith Ministries)No ratings yet
- Topics Marriage & DivorceDocument6 pagesTopics Marriage & DivorceThomas Lorenz (Fit For Faith Ministries)No ratings yet
- Women Pastors / Preachers? Can A Woman Be A Pastor or Preacher?Document3 pagesWomen Pastors / Preachers? Can A Woman Be A Pastor or Preacher?ManuelNo ratings yet
- Words ReligionDocument2 pagesWords ReligionThomas Lorenz (Fit For Faith Ministries)No ratings yet
- Words DisciplineDocument2 pagesWords DisciplineThomas Lorenz (Fit For Faith Ministries)No ratings yet
- Topics FoodDocument1 pageTopics FoodThomas Lorenz (Fit For Faith Ministries)No ratings yet
- Book of Jubilees Refutation of The TimelineDocument7 pagesBook of Jubilees Refutation of The TimelineThomas Lorenz (Fit For Faith Ministries)No ratings yet
- Virtues and Vices (Fruits of The Spirit & Works of The Flesh)Document2 pagesVirtues and Vices (Fruits of The Spirit & Works of The Flesh)Thomas Lorenz (Fit For Faith Ministries)No ratings yet
- Discernment Comparison of Bible-Based TranslationsDocument2 pagesDiscernment Comparison of Bible-Based TranslationsThomas Lorenz (Fit For Faith Ministries)No ratings yet
- Christophanies Angel of The LordDocument2 pagesChristophanies Angel of The LordThomas Lorenz (Fit For Faith Ministries)No ratings yet
- Words GospelDocument2 pagesWords GospelThomas Lorenz (Fit For Faith Ministries)No ratings yet
- Ruth Handout CPDocument5 pagesRuth Handout CPanton_428No ratings yet
- Covenants in The Bible-1Document1 pageCovenants in The Bible-1Hatfulloftricks700No ratings yet
- Bible Non-Canonical WritingsDocument5 pagesBible Non-Canonical WritingsThomas Lorenz (Fit For Faith Ministries)No ratings yet
- Topics CommunionDocument1 pageTopics CommunionThomas Lorenz (Fit For Faith Ministries)No ratings yet
- Yisraelite Basic PreceptsDocument53 pagesYisraelite Basic Preceptsapi-329036268100% (1)
- Psalm 82 The Divine Council Worldview - Reimagining AuthorityDocument21 pagesPsalm 82 The Divine Council Worldview - Reimagining AuthorityDeepak M. BabuNo ratings yet
- Mephibosheth and The King: A Story of Covenant Chesed II Samuel 9Document6 pagesMephibosheth and The King: A Story of Covenant Chesed II Samuel 9CotedivoireFreedomNo ratings yet
- Topics Sexual DisciplineDocument6 pagesTopics Sexual DisciplineThomas Lorenz (Fit For Faith Ministries)No ratings yet
- Church Structure Elders / Deacons / SaintsDocument3 pagesChurch Structure Elders / Deacons / SaintsThomas Lorenz (Fit For Faith Ministries)No ratings yet
- Geisler Norman & Saleeb Abdul Answering Islam 14Document46 pagesGeisler Norman & Saleeb Abdul Answering Islam 14Daniel PawlowiczNo ratings yet
- One AnotheringDocument3 pagesOne AnotheringThomas Lorenz (Fit For Faith Ministries)No ratings yet
- History of Joseph The CarpenterDocument4 pagesHistory of Joseph The CarpenterChristine MbinyaNo ratings yet
- What Is Saving Faith?Document5 pagesWhat Is Saving Faith?Grace Church ModestoNo ratings yet
- Sabbaths, Weekly vs. Ceremonial Differentiation & ApplicationDocument7 pagesSabbaths, Weekly vs. Ceremonial Differentiation & ApplicationThomas Lorenz (Fit For Faith Ministries)No ratings yet
- Chapter Twenty-Four: The Seed of The WomanDocument2 pagesChapter Twenty-Four: The Seed of The WomanAyeah GodloveNo ratings yet
- 101 Acts Alternative 1Document196 pages101 Acts Alternative 1Ojie Oteda SolitarioNo ratings yet
- What Does The Phrase "My Name" Mean in The Bible?Document4 pagesWhat Does The Phrase "My Name" Mean in The Bible?dlee7067No ratings yet
- Numbers in The Bible Numerical PatternsDocument8 pagesNumbers in The Bible Numerical PatternsThomas Lorenz (Fit For Faith Ministries)No ratings yet
- Daughters of ZelophehadDocument6 pagesDaughters of ZelophehadalwinalexanderNo ratings yet
- Baruch HaShem - The Pronunciation of YHVHDocument7 pagesBaruch HaShem - The Pronunciation of YHVHPiet Janse van RensburgNo ratings yet
- Words Works of Faith vs. Works of The LawDocument2 pagesWords Works of Faith vs. Works of The LawThomas Lorenz (Fit For Faith Ministries)50% (2)
- Topics BaptismDocument3 pagesTopics BaptismThomas Lorenz (Fit For Faith Ministries)No ratings yet
- 508 AD by Doug MitchellDocument4 pages508 AD by Doug MitchellTrent Riffin WildeNo ratings yet
- These 2 Conditions Have Been Met - : - (On This)Document1 pageThese 2 Conditions Have Been Met - : - (On This)Marc BoyerNo ratings yet
- What Is A Non-Trinitarian Nader Mansour PDFDocument1 pageWhat Is A Non-Trinitarian Nader Mansour PDFDajiedlangki LyngdohNo ratings yet
- The Gospel of The Kingdom of God, Form #17.003Document423 pagesThe Gospel of The Kingdom of God, Form #17.003Sovereignty Education and Defense Ministry (SEDM)100% (2)
- The MysteryDocument30 pagesThe MysteryperixmindNo ratings yet
- 3.UYIQARA (Full Color) - B.R ScripturesDocument144 pages3.UYIQARA (Full Color) - B.R ScripturesMark DavidsonNo ratings yet
- Örnek - Aşama 3Document4 pagesÖrnek - Aşama 3Mert SarıNo ratings yet
- Heartaches by The NumberDocument6 pagesHeartaches by The NumberDavid FerraraNo ratings yet
- Exotic Guitar Sound: Ichika NitoDocument2 pagesExotic Guitar Sound: Ichika NitoMinecraftNo ratings yet
- Daily Blues Lick 407Document2 pagesDaily Blues Lick 407Ruben Del VillarNo ratings yet
- Your SongDocument4 pagesYour SongIago NeivaNo ratings yet
- CompleteDocument1 pageCompleteapi-384831789No ratings yet
- BluesRock Solo in EDocument2 pagesBluesRock Solo in ERandy SeriosaNo ratings yet
- Timeout Shohoku 主音Document1 pageTimeout Shohoku 主音Yichen ZhanNo ratings yet
- MundoDocument2 pagesMundoMarc Jeffrey BesinanNo ratings yet
- Shine-On-You-Crazy-Diamond 2Document8 pagesShine-On-You-Crazy-Diamond 2Francisco Antonio PalmaNo ratings yet
- G Major Cello Suite BachDocument2 pagesG Major Cello Suite BachMarius Andrei NegrescuNo ratings yet
- Carcass - Buried Dreams DrumDocument3 pagesCarcass - Buried Dreams DrumChris TangNo ratings yet
- Planet Fantastic Tab PDFDocument8 pagesPlanet Fantastic Tab PDFSlushyNo ratings yet
- JOSIASDocument1 pageJOSIASfernandoeduardo615No ratings yet
- Church Structure Elders / Deacons / SaintsDocument3 pagesChurch Structure Elders / Deacons / SaintsThomas Lorenz (Fit For Faith Ministries)No ratings yet
- In The Beginning, Ages, Generations & Last DaysDocument1 pageIn The Beginning, Ages, Generations & Last DaysThomas Lorenz (Fit For Faith Ministries)No ratings yet
- Christophanies Angel of The LordDocument2 pagesChristophanies Angel of The LordThomas Lorenz (Fit For Faith Ministries)No ratings yet
- Discernment Comparison of Bible-Based TranslationsDocument2 pagesDiscernment Comparison of Bible-Based TranslationsThomas Lorenz (Fit For Faith Ministries)No ratings yet
- The Christian CalendarDocument3 pagesThe Christian CalendarThomas Lorenz (Fit For Faith Ministries)No ratings yet
- Discernment Identification of False TeachersDocument1 pageDiscernment Identification of False TeachersThomas Lorenz (Fit For Faith Ministries)No ratings yet
- Discernment Types of False TeachersDocument1 pageDiscernment Types of False TeachersThomas Lorenz (Fit For Faith Ministries)No ratings yet
- End Times The Book of DanielDocument2 pagesEnd Times The Book of DanielThomas Lorenz (Fit For Faith Ministries)100% (1)
- Promises of The New TestamentDocument1 pagePromises of The New TestamentThomas Lorenz (Fit For Faith Ministries)No ratings yet
- The Historical Adams Adam and ChristDocument1 pageThe Historical Adams Adam and ChristThomas Lorenz (Fit For Faith Ministries)No ratings yet
- God's Communication 11 Ways He (Might) Communicate With UsDocument3 pagesGod's Communication 11 Ways He (Might) Communicate With UsThomas Lorenz (Fit For Faith Ministries)No ratings yet
- Book of Jubilees Refutation of The TimelineDocument7 pagesBook of Jubilees Refutation of The TimelineThomas Lorenz (Fit For Faith Ministries)No ratings yet
- Salvation Eternal Security vs. Conditional SecurityDocument5 pagesSalvation Eternal Security vs. Conditional SecurityThomas Lorenz (Fit For Faith Ministries)100% (1)
- Salvation Past, Present & Future SalvationDocument6 pagesSalvation Past, Present & Future SalvationThomas Lorenz (Fit For Faith Ministries)No ratings yet
- Trinity The Father, The Son and The Holy SpiritDocument3 pagesTrinity The Father, The Son and The Holy SpiritThomas Lorenz (Fit For Faith Ministries)100% (1)
- Spiritual GiftsDocument3 pagesSpiritual GiftsThomas Lorenz (Fit For Faith Ministries)100% (2)
- Symbolism & TypologyDocument2 pagesSymbolism & TypologyThomas Lorenz (Fit For Faith Ministries)No ratings yet
- Virtues and Vices (Fruits of The Spirit & Works of The Flesh)Document2 pagesVirtues and Vices (Fruits of The Spirit & Works of The Flesh)Thomas Lorenz (Fit For Faith Ministries)No ratings yet
- Words LoveDocument2 pagesWords LoveThomas Lorenz (Fit For Faith Ministries)No ratings yet
- Words Works of Faith vs. Works of The LawDocument2 pagesWords Works of Faith vs. Works of The LawThomas Lorenz (Fit For Faith Ministries)50% (2)
- Words TongueDocument2 pagesWords TongueThomas Lorenz (Fit For Faith Ministries)100% (1)
- Words ReligionDocument2 pagesWords ReligionThomas Lorenz (Fit For Faith Ministries)No ratings yet
- Words HeavensDocument3 pagesWords HeavensThomas Lorenz (Fit For Faith Ministries)No ratings yet
- Words Kingdom of GodDocument1 pageWords Kingdom of GodThomas Lorenz (Fit For Faith Ministries)No ratings yet
- Words GospelDocument2 pagesWords GospelThomas Lorenz (Fit For Faith Ministries)No ratings yet
- Esther: and Memucan, The Seven Princes of Persia andDocument8 pagesEsther: and Memucan, The Seven Princes of Persia andaverbisNo ratings yet
- The Bible Timeline Reading Plan: Early WorldDocument1 pageThe Bible Timeline Reading Plan: Early WorldJeffrey VelascoNo ratings yet
- Old Testament 180 Day Reading Plan: AY OOK Hapters AY OOK HaptersDocument2 pagesOld Testament 180 Day Reading Plan: AY OOK Hapters AY OOK HaptersMariolivrosNo ratings yet
- Bible Book AbbreviationsDocument3 pagesBible Book AbbreviationsDavid Lisboa NetoNo ratings yet
- Apocrypha Timeline of Inclusion & ExclusionDocument3 pagesApocrypha Timeline of Inclusion & ExclusionThomas Lorenz (Fit For Faith Ministries)No ratings yet
- Program To Read The Bible Every DayDocument2 pagesProgram To Read The Bible Every DayFREDERIC ROSSIGNOLNo ratings yet
- Heb-Xn-Bibles ChartDocument2 pagesHeb-Xn-Bibles ChartJhada BainNo ratings yet
- Perjanjian Lama Perjanjian Baru: No B.Indonesia Batak English No B.Indonesia Batak EnglishDocument2 pagesPerjanjian Lama Perjanjian Baru: No B.Indonesia Batak English No B.Indonesia Batak EnglishNurma siagianNo ratings yet
- When Was The Bible WrittenDocument1 pageWhen Was The Bible WrittenjottingsNo ratings yet
- The Books of The Old Testament: History 12Document1 pageThe Books of The Old Testament: History 12Jeremy McDonaldNo ratings yet
- Merged Bible Books CrosswordDocument10 pagesMerged Bible Books CrosswordRexford AdjeiNo ratings yet
- 60 - DAY Bible ChallengeDocument2 pages60 - DAY Bible ChallengePromise AjijolaNo ratings yet
- Bible in A Year Reading Plan (OT+NT)Document6 pagesBible in A Year Reading Plan (OT+NT)MuanpuiaNo ratings yet
- Book of The Bible Periodic Table Print Able FBDocument7 pagesBook of The Bible Periodic Table Print Able FBAicelle Marie GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Bible TabsDocument8 pagesBible TabsAstrid TabordaNo ratings yet
- Ot LawDocument1 pageOt Lawjc3839No ratings yet
- Chronological Bible PlanDocument2 pagesChronological Bible PlanmcfmiNo ratings yet
- The Bible in A Year - FR Mike SchmitzDocument38 pagesThe Bible in A Year - FR Mike SchmitzaslopiNo ratings yet
- Book of EstherDocument9 pagesBook of EsthernsanyoNo ratings yet
- Questions Bible QuizDocument3 pagesQuestions Bible QuizninreyNo ratings yet
- 6 Month Bible Reading PlanDocument6 pages6 Month Bible Reading PlanAjith ANo ratings yet
- Theo 202 Canons of The BibleDocument1 pageTheo 202 Canons of The BibleShant DerohanessianNo ratings yet
- Chronological Bible Reading in One YearDocument6 pagesChronological Bible Reading in One YearJohnson ShodipoNo ratings yet
- 6 Month Ot Bible Reading PlanDocument1 page6 Month Ot Bible Reading Plana.amoskatoNo ratings yet
- Bible in A YearDocument4 pagesBible in A Yearcfi2834657No ratings yet
- Esther Chapter 6: 1 On That Night Could Not The KingDocument3 pagesEsther Chapter 6: 1 On That Night Could Not The Kingvendredi67No ratings yet
- The Old Testament Books Listed and Compared: Orthodox Old Testament Roman Catholic Old Testament Protestant Old TestamentDocument1 pageThe Old Testament Books Listed and Compared: Orthodox Old Testament Roman Catholic Old Testament Protestant Old TestamentBeavis JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Day Bible Reading Program: Week No. Date To ReadDocument2 pagesDay Bible Reading Program: Week No. Date To ReadGuido OrsiniNo ratings yet
- Blue Letter Bible: Historical PlanDocument2 pagesBlue Letter Bible: Historical PlanRenier van RooyenNo ratings yet