Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Standard Penetration Test Procedure
Uploaded by
Raghavan AR0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
32 views4 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
32 views4 pagesStandard Penetration Test Procedure
Uploaded by
Raghavan ARCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
Standard Penetration Test (SPT)-
Procedure,Precautions, Advantages
Home/ Geotechnical Engineering
Reading time: 4 minutes
Contents: [hide]
• Standard Penetration Test (SPT)
• Tools for Standard Penetration Test
• Procedure for Standard Penetration Test
• Corrections in Standard Penetration Test
o 1. Dilatancy Correction
• Precautions taken for Standard Penetration Test
• Advantages of Standard Penetration Test
• Disadvantages of Standard Penetration Test
Standard Penetration Test (SPT)
The standard penetration test is an in-situ test that is coming under the category of penetrometer
tests. The standard penetration tests are carried out in borehole. The test will measure the
resistance of the soil strata to the penetration undergone. A penetration emphirical correlation is
derived between the soil properties and the penetration resistance. The test is extremely useful
for determining the relative density and the angle of shearing resistance of cohesionless soils. It
can also be used to determine the unconfined compressive strength of cohesive soils.
Tools for Standard Penetration Test
The requirements to conduct SPT are:
1. Standard Split Spoon Sampler
2. Drop Hammer weighing 63.5kg
3. Guiding rod
4. Drilling Rig.
5. Driving head (anvil).
Procedure for Standard Penetration Test
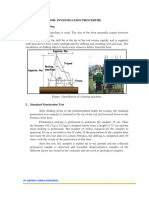
The test is conducted in a bore hole by means of a standard split spoon sampler.Once the drilling
is done to the desired depth, the drilling tool is removed and the sampler is placed inside the bore
hole. By means of a drop hammer of 63.5kg mass falling through a height of 750mm at the rate
of 30 blows per minute, the sampler is driven into the soil. This is as per IS -2131:1963. The
number of blows of hammer required to drive a depth of 150mm is counted. Further it is driven
by 150 mm and the blows are counted. Similarly, the sampler is once again further driven by
150mm and the number of blows recorded. The number of blows recorded for the first 150mm
not taken into consideration.. The number of blows recorded for last two 150mm intervals are
added to give the standard penetration number (N). In other words,
N = No: of blows required for 150mm penetration beyond seating drive of 150mm.
Fig.1: Standard penetration Test
If the number of blows for 150mm drive exceeds 50, it is taken as refusal and the test is
discontinued. The standard penetration number is corrected for dilatancy correction and
overburden correction.
Corrections in Standard Penetration Test
Before the SPT values are used in empirical correlations and in design charts, the field ‘N’ value
have to be corrected as per IS 2131 – 1981. The corrections are:
1. Dilatancy Correction
2. Overburden Pressure Correction
1. Dilatancy Correction
Silty fine sands and fine sands below the water table develop pore water pressure which is not
easily dissipated. The pore pressure increases the resistance of the soil and hence the penetration
number (N). Terzaghi and Peck (1967) recommend the following correction in the case of silty
fine sands when the observed value is N exceeds 15. The corrected penetration number,
NC = 15 + 0.5 (NR -15)
Where NR is the recorded value and NC is the corrected value. If NR less than or equal to 15, then
Nc = NR 2. Overburden Pressure Correction From several investigations, it is proven that the
penetration resistance or the value of N is dependent on the overburden pressure. If there are two
granular soils with relative density same, higher ‘N’ value will be shown by the soil with higher
confining pressure. With the increase in the depth of the soil, the confining pressure also
increases. So the value of ‘N’ at shallow depth and larger depths are underestimated and
overestimated respectively. Hence, to account this the value of ‘N’ obtained from the test are
corrected to a standard effective overburden pressure. The corrected value of ‘N’ is
Nc = CN N
Here CN is the correction factor for the overburden pressure.
Precautions taken for Standard Penetration Test
1. Split spoon sampler must be in good condition.
2. The cutting shoe must be free from wear and tear
3. The height of fall must be 750mm. Any change from this will affect the ‘N’ value.
4. The drill rods used must be in standard condition. Bent drill rods are not used.
5. Before conducting the test, the bottom of the borehole must be cleaned.
Advantages of Standard Penetration Test
The advantages of standard penetration test are:
1. The test is simple and economical
2. The test provides representative samples for visual inspection, classification tests and for
moisture content.
3. Actual soil behaviour is obtained through SPT values
4. The method helps to penetrate dense layers and fills
5. Test can be applied for variety of soil conditions
You might also like
- SOP - Standard Penetration TestDocument5 pagesSOP - Standard Penetration TestGajendra PandeyNo ratings yet
- Standard Penetration TestDocument21 pagesStandard Penetration TestVenkatesh ThumatiNo ratings yet
- Submitted By: Tem-244 Geotechnical Engineering-2Document4 pagesSubmitted By: Tem-244 Geotechnical Engineering-2Zulqarnain IshaqNo ratings yet
- In-Situ Tests (SPT) PDFDocument28 pagesIn-Situ Tests (SPT) PDFnikhilarora1988No ratings yet
- Methodology For SPT & UdsDocument7 pagesMethodology For SPT & UdsPravin SahuNo ratings yet
- SPT Test Fa18-Cve-000Document8 pagesSPT Test Fa18-Cve-000Hassan AhmedNo ratings yet
- Standard Penetration TestDocument7 pagesStandard Penetration TestAndres GranadosNo ratings yet
- Standard Penetration Test (SPT) - Procedure, Precautions, AdvantagesDocument5 pagesStandard Penetration Test (SPT) - Procedure, Precautions, Advantagesvenkateswara rao pothina100% (1)
- Foun Lect 6 - Penetration TestDocument32 pagesFoun Lect 6 - Penetration TestC63Kunal GattaniNo ratings yet
- Lecture - Field Tests and Instuments - 2022Document116 pagesLecture - Field Tests and Instuments - 2022Zanele MbathaNo ratings yet
- SPT Test Provides Insights Into Soil Properties For Foundation Engineering ProjectsDocument7 pagesSPT Test Provides Insights Into Soil Properties For Foundation Engineering ProjectsZahid Bashar100% (1)
- Soil Exploration Penetrometer Tests: Avinash Kumar Gupta Training Institute CCW Air New DelhiDocument30 pagesSoil Exploration Penetrometer Tests: Avinash Kumar Gupta Training Institute CCW Air New DelhiRaja SekharNo ratings yet
- Soil Exploration Part 2 and 3Document38 pagesSoil Exploration Part 2 and 3naman.h.cogniNo ratings yet
- Exp#5: Standard Penetration Test: ObjectiveDocument5 pagesExp#5: Standard Penetration Test: ObjectiveMuhammad Hussain AbbasNo ratings yet
- Standard Penetration Test: Assam Engineering College Department of Civil EngineeringDocument25 pagesStandard Penetration Test: Assam Engineering College Department of Civil EngineeringDipanjal DasNo ratings yet
- Soil InvestigationDocument3 pagesSoil Investigationwahyu maradonaNo ratings yet
- Acquisition of Design Soil Parameters From In-Situ TestingDocument7 pagesAcquisition of Design Soil Parameters From In-Situ TestingZaid AlsarayrehNo ratings yet
- Standard Penetration Test (SPT) - Procedure, Precautions, Advantages - The ConstructorDocument5 pagesStandard Penetration Test (SPT) - Procedure, Precautions, Advantages - The ConstructorLeticia Freitas da CostaNo ratings yet
- HTTP Nptel - Iitm.acDocument5 pagesHTTP Nptel - Iitm.acKetakee SagdeoNo ratings yet
- Standard Penetration TestDocument32 pagesStandard Penetration TestIndranil Banerjee100% (1)
- Disaster ManagementDocument272 pagesDisaster ManagementJoy lordNo ratings yet
- Ganesh Test DescriptionDocument8 pagesGanesh Test DescriptionTushar MankarNo ratings yet
- Unit IV - Part 2 - Plate Load Test and Standard Penetration TestDocument36 pagesUnit IV - Part 2 - Plate Load Test and Standard Penetration TestPinak RayNo ratings yet
- Standard Penetration Test (SPT) ExplainedDocument6 pagesStandard Penetration Test (SPT) ExplainedDanica Alejo100% (1)
- Altered soil samples should not be usedDocument4 pagesAltered soil samples should not be usedBertin BakariNo ratings yet
- Soil Exploration Methods & TechniquesDocument6 pagesSoil Exploration Methods & TechniquesA.k.MandalNo ratings yet
- Geotechnical Testign Methods II - ASDocument24 pagesGeotechnical Testign Methods II - ASelcivilengNo ratings yet
- Standard Penetration Test Procedure and CorrectionsDocument45 pagesStandard Penetration Test Procedure and CorrectionsVivek DhutNo ratings yet
- Soil Investigation - WPDocument4 pagesSoil Investigation - WPKanupriya JainNo ratings yet
- Foundation Design - Insitu TestingDocument22 pagesFoundation Design - Insitu TestingSnow YoshimaNo ratings yet
- Soil Exploration ReportDocument12 pagesSoil Exploration ReportAryamaan SinghNo ratings yet
- Bu I 4 - Part 2 Chapter 4Document26 pagesBu I 4 - Part 2 Chapter 4jerryleekgkgNo ratings yet
- Factors That Could Affect The Test Results. The Measured SPT N Value Can Be InfluencedDocument4 pagesFactors That Could Affect The Test Results. The Measured SPT N Value Can Be InfluencedlenanaNo ratings yet
- Subsoil Investigation 6Document34 pagesSubsoil Investigation 6insti postaNo ratings yet
- of Standard Penetration TestDocument19 pagesof Standard Penetration Testrishav baishyaNo ratings yet
- Geotechnical Investigation MethodsCV332Document20 pagesGeotechnical Investigation MethodsCV332Muhammad Umar TariqNo ratings yet
- Boring Log IntrepretationDocument8 pagesBoring Log IntrepretationiploguNo ratings yet
- SPT DCPT UDS Collection Lab ManualDocument34 pagesSPT DCPT UDS Collection Lab ManualshivaNo ratings yet
- SITE INVESTIGATION METHODSDocument51 pagesSITE INVESTIGATION METHODSSelah AbdulahiNo ratings yet
- GEOTECHNICAL EXPLORATION: Soil Testing Methods & ImportanceDocument36 pagesGEOTECHNICAL EXPLORATION: Soil Testing Methods & ImportanceAwais HameedNo ratings yet
- Assignment FoundationDocument4 pagesAssignment FoundationHuzaifah ZainuddinNo ratings yet
- Prepared By:: Geotechnical Engineering Sessional - IIDocument15 pagesPrepared By:: Geotechnical Engineering Sessional - IIShahidul IslamNo ratings yet
- SPT TestDocument41 pagesSPT Testronnie_syncinNo ratings yet
- Geotechnical Investigations For BridgesDocument45 pagesGeotechnical Investigations For BridgeskesharinareshNo ratings yet
- FOUNDATION DESIGN FUNDAMENTALSDocument40 pagesFOUNDATION DESIGN FUNDAMENTALSSAMANT RANANo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 v1Document26 pagesLecture 2 v1Anwar Hossain PolasNo ratings yet
- SPT and CPT Geotech DetailedDocument6 pagesSPT and CPT Geotech DetailedAmmad AsifNo ratings yet
- Geotechnical Engineering 2 1Document325 pagesGeotechnical Engineering 2 1Arpan NandyNo ratings yet
- SOFTCOPY FINAL REPORT (167-2021)Document62 pagesSOFTCOPY FINAL REPORT (167-2021)Sze Mian KuehNo ratings yet
- Subsoil Investigation 5Document27 pagesSubsoil Investigation 5insti postaNo ratings yet
- Table of Content: Annexes: Bore Hole Logs Laboratory Test Result Figures and PhotographsDocument19 pagesTable of Content: Annexes: Bore Hole Logs Laboratory Test Result Figures and PhotographsOm ConsultantNo ratings yet
- Geotechnical Engineering Standard Penetration Test (SPTDocument41 pagesGeotechnical Engineering Standard Penetration Test (SPTMohamedNo ratings yet
- Standard Penetration Test PDFDocument13 pagesStandard Penetration Test PDFMohamedRaahimNo ratings yet
- Penetrant Testing: Principles, Techniques, Applications and Interview Q&AFrom EverandPenetrant Testing: Principles, Techniques, Applications and Interview Q&ANo ratings yet
- Disaster Management Mechanism in OdishaDocument55 pagesDisaster Management Mechanism in Odishaguddu.diebackNo ratings yet
- 15 seismic-resilience-for-buried-pipelines-9c2c67cdDocument1 page15 seismic-resilience-for-buried-pipelines-9c2c67cdRaghavan ARNo ratings yet
- Strength of ConcreteDocument8 pagesStrength of ConcreteRaghavan ARNo ratings yet
- Six Sigma Methodology For Project ManagementDocument9 pagesSix Sigma Methodology For Project ManagementRaghavan ARNo ratings yet
- IS Codes For Public Health EngineeringDocument4 pagesIS Codes For Public Health EngineeringRaghavan ARNo ratings yet
- Sizing Building Water Supply AppendixDocument43 pagesSizing Building Water Supply AppendixMonica VergaraNo ratings yet
- MSc Thesis on VAW in PhilippinesDocument100 pagesMSc Thesis on VAW in Philippineselma cutamoraNo ratings yet
- Harsheen Kaur BhasinDocument20 pagesHarsheen Kaur Bhasincalvin kleinNo ratings yet
- Diagrama RSAG7.820.7977Document14 pagesDiagrama RSAG7.820.7977Manuel Medina100% (4)
- Communication Strategy Target AudienceDocument47 pagesCommunication Strategy Target Audienceguille simariNo ratings yet
- Holden Commodore Sedan VT To VZDocument6 pagesHolden Commodore Sedan VT To VZابو سعدNo ratings yet
- Edited General English Question Paper Part 1Document12 pagesEdited General English Question Paper Part 1Utkarsh R MishraNo ratings yet
- Postpaid Bill AugDocument2 pagesPostpaid Bill Augsiva vNo ratings yet
- Group Assgnmt 8 Rev080515Document9 pagesGroup Assgnmt 8 Rev080515Suhaila NamakuNo ratings yet
- Briefing Ai Trading BotDocument10 pagesBriefing Ai Trading BotMeaningful LifeNo ratings yet
- How to Launder Money in Real EstateDocument58 pagesHow to Launder Money in Real EstateSpeedyGonsalesNo ratings yet
- Anne Frank Halloween Costume 2Document5 pagesAnne Frank Halloween Costume 2ive14_No ratings yet
- SoalDocument4 pagesSoalkurikulum man2wonosoboNo ratings yet
- Bruce MoenDocument4 pagesBruce MoenGeorge Stefanakos100% (5)
- Proposal to Enhance Science InstructionDocument4 pagesProposal to Enhance Science InstructionAzzel ArietaNo ratings yet
- List of Registered Non Govt and Govt Secondary SchoolDocument200 pagesList of Registered Non Govt and Govt Secondary SchoolDennisEudes78% (9)
- TNPSC Vas: NEW SyllabusDocument12 pagesTNPSC Vas: NEW Syllabuskarthivisu2009No ratings yet
- Samsung C&T AuditDocument104 pagesSamsung C&T AuditkevalNo ratings yet
- Report On Foundations For Dynamic Equipment: Reported by ACI Committee 351Document14 pagesReport On Foundations For Dynamic Equipment: Reported by ACI Committee 351Erick Quan LunaNo ratings yet
- PRAGMATISMDocument22 pagesPRAGMATISMChristian Jay A MoralesNo ratings yet
- ENGLISH 7 FIRST QUARTER EXAMDocument2 pagesENGLISH 7 FIRST QUARTER EXAMAlleli Faith Leyritana100% (1)
- PH.D Scholars UGCDocument25 pagesPH.D Scholars UGCUsha MurthyNo ratings yet
- 100 Answers To Common English QuestionsDocument9 pages100 Answers To Common English Questionsflemus_1No ratings yet
- Development Plan-Part IV, 2022-2023Document3 pagesDevelopment Plan-Part IV, 2022-2023Divina bentayao100% (5)
- IELTS2 Video ScriptsDocument5 pagesIELTS2 Video ScriptskanNo ratings yet
- Return Snowball Device SafelyDocument1 pageReturn Snowball Device SafelyNoneNo ratings yet
- Petroleum Research: Khalil Shahbazi, Amir Hossein Zarei, Alireza Shahbazi, Abbas Ayatizadeh TanhaDocument15 pagesPetroleum Research: Khalil Shahbazi, Amir Hossein Zarei, Alireza Shahbazi, Abbas Ayatizadeh TanhaLibya TripoliNo ratings yet
- Update in Living Legal Ethics - Justice Dela CruzDocument13 pagesUpdate in Living Legal Ethics - Justice Dela CruzRobert F Catolico IINo ratings yet
- Abnormal Psychology Unit IDocument14 pagesAbnormal Psychology Unit IMahadevan K V100% (1)
- Fabric Trademark and Brand Name IndexDocument15 pagesFabric Trademark and Brand Name Indexsukrat20No ratings yet
- EasyGreen ManualDocument33 pagesEasyGreen ManualpitoupitouNo ratings yet