Professional Documents
Culture Documents
NEET Important Questions For Class 12 Chemistry Polymers
Uploaded by
MAG MarvelOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
NEET Important Questions For Class 12 Chemistry Polymers
Uploaded by
MAG MarvelCopyright:
Available Formats
NEET Important Questions
Chemistry
Polymers
Single Correct Type
1. Which of the following statements is not true about low-density polythene?
(A) Hard
(B) Tough
(C) Highly branched structure
(D) Poor conductor of electricity
2. Natural rubber has
[NEET-2016]
(A) All cis-configuration
(B) All trans-configuration.
(C) Alternate cis-and trans-configuration.
(D) Random cis-and trans-configuration
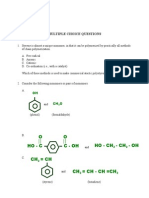
3. Which of the monomers of neoprene in the following
[NEET 2003, 2013]
(a) CH2 CH C CH2
(b)
(c) CH2 CH CH CH2
(d)
4. Arrange the following in ascending order of intramolecular force.
(a) Nylon-6, 6 (b) Buna-S (c) Polythene.
(A) a<b<c
Class XII Chemistry www.vedantu.com 1
(B) b<a<c
(C) b<c<a
(D) a=b=c
5. Natural rubber or gutta-percha
(A) Sis-polyisoprene and trans-polyisoprene
(B) Both are cis-polyisoprene
(C) Both are trans polyisoprene.
(D) Trans-polychloride and cis-polychloroprene
6. Soft drinks and baby bottles usually include
(A) Polyester
(B) Polyurethane
(C) Polystyrene
(D) Polyamide.
7. Non-stick cookware is generally coated with a polymer whose monomer is an
organic compound.
(A) CH 2 CH 2
(B) CH 2 CHCN
(C) CH 2 CHCl
(D) CF2 CF2
8. What percentage of sulphur is used in vulcanized rubber?
(A) 5%
(B) 3%
(C) 55%
(D) 30%
9. Which of the following cannot be used as a monomer in the polymerization
reaction?
(A) C2 H 4
(B) C2 H 2
Class XII Chemistry www.vedantu.com 2
(C) C3H6
(D) C4 H 6
10. Calculate the amount of polythene formed from 10 kg of calcium carbide from
the reactions given below
CaC2 2 H 2O Ca OH 2 C2 H 2 ;
pd BaSO4
CH CH H 2
CH 2 CH 2
nCH 2 CH 2 CH 2 CH 2 n
(A) 28g
(B) 9g
(C) 4 kg
(D) 64 kg
11) Which of the following is the radical initiator.
(A) R N N R
(B) Dibenzoyl peroxide.
(C)
(D) All
12.
The polymer obtained by the above compound is:
(A) Bakelite
(B) Urea formaldehyde resin
(C) Melamine formaldehyde resin
Class XII Chemistry www.vedantu.com 3
(D) Teflon
13. Emphasize the most diverse polymerization forms of CH 2 CH CH CH 2
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
Multiple correct type
14. Which of the following monomers form biodegradable polymers?
[NEET 2015]
(A) 3-hydroxybutanoic acid + 3-hydroxypentanoic acid
(B) Glycine + amino caproic acid
(C) Ethylene glycol + phthalic acid
(D) Caprolactam
Class XII Chemistry www.vedantu.com 4
15. Which of the following is a natural polymer?
[NEET --2020]
A) poly (Butadiene-styrene)
B) polybutadiene
C) poly (Butadiene-acrylonitrile)
D) cis-1, 4-polyisoprene
16. Which of the following glucose polymers is preserved by the animal?
(A) Cellulose
(B) Amylose
(C) Amylopectin
(D) Glycogen.
17. When vulcanized, it becomes rubber
(A) More elastic
(B) Soluble in inorganic solvent
(C) Crystalline
(D) More stiff
18. Nylon-66 is made by using
(AIIMS-1997)
(A) Succinic acid
(B) Benzyl chloride
(C) Benzaldehyde
(D) Adipic acid
19. Which of the following substances cannot be used as a plasticizer?
(A) Di-n-octylpythalate
(B) Di-n-butyl phthalate
(C) Tri cresol phosphate
(D) Sodium hexametaphosphate
20. Polymer used in bullet proof glass
(A) PMMA
Class XII Chemistry www.vedantu.com 5
(B) Lexan
(C) Nomex
(D) Kevlar
21. Chain-growth polymerization can proceed by the following mechanism.
(A) Condensation polymerization.
(B) Cationic polymerization.
(C) Anionic polymerization
(D) Free radical polymerization.
22. Which of the following is/are correct about polymers
(A) They are made by condensation of monomers in step growth polymerisation
(B) Nylon-66 is step-growth polymer
(C) Polystyrene is chain-growth polymer.
(D) The end of the chain is reactive because it is a radical, a cation or anion in chain
polymerisation.
23. Examples of a biodegradable polymer pair is
(A) Nylon-6,6 and terylene.
(B) PHBV and dextron
(C) Bakelite and PVC
(D) PET and polyethylene
Assertion (A) and Reason (R) type Questions
1) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A)
2) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is not the correct explanation of (A)
3) (A) is true but (R) is false
4) Both (A) and (R) are false.
24. (A): Glyptal is a condensation homopolymer
(R): Glyptal is used to prepare computer discs
25. (A): P.V.C is an addition copolymer
(R): P.V.C is used to prepare handles of utensils.
Class XII Chemistry www.vedantu.com 6
26. (A) Natural rubber is a polymer is isoprene.
(R): Isoprene is a pentene.
(AIIMS-2014)
27. (A): Teflon is a chemically inert substance
(R): Chloroform when treated with antimony trifluoride gives Teflon.
(AIIMS-2015)
28. (A): Polypropylene is an addition polymer
(R): Additional polymer is also named as step-growth polymer.
29. (A): PHBV is a homopolymer
(R): PHBV is a biodegradable polymer.
SOLUTIONS:
Single correct type
1. D
It's not difficult. It's hard, but it's mechanically weak. Due to its poor conductivity,
it is used as an insulator for cables. It is a branched polymer. High density
polyethylene is a linear polymer.
2. A
All-natural rubber is cis-arranged. A linear polymer of cis-isoprene or cis-2-methyl-
1,3-butadiene is the chemical formula of rubber.
3. A
Chloroprene is the monomer of neoprene.
4. C
Different types of polymers have different intermolecular attractive forces.
Elastomers or rubbers are the weakest and fibers have the strongest intermolecular
attraction. Plastic has an intramolecular attractive force. Therefore, the ascending
order of the intramolecular force of a given polymer is as follows: b<c<a
Class XII Chemistry www.vedantu.com 7
5. A
Natural rubber or gutta-percha is cis-polyisoprene and trans-polyisoprene. Isoprene
is 2-methyl-1,3-butadiene. The natural rubber has long flexible chains, weak
intramolecular force, and is elastic. Gutta-percha has a zigzag chain that fits together.
It is inelastic and crystalline.
6. C
Polystyrene is a synthetic thermoplastic polymer composed of styrene. It can be
easily molded and is commonly used in protective packaging (such as peanut
packaging), disposable cutlery, containers, bottles, trays, cups, baby bottles, and
tissues.
7. D
Non-stick cookware usually has a polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) coating, a Teflon
monomer
8. A
5% sulphur is used to increase the rigidity of the vulcanized rubber.
9. C
C3H6 Is propylene, a monomer unit for the polymerization of polypropylene.
10. C
Molecular weight of CaC2 40 24 64
64 kg of CaC2 gives 28 kg of ethene
28 7 10
10 kg of CaC2 gives 10 4.37kg
64 16
11. D
All are free-radical initiators and catalyze the free radical polymerisation
12. B
The given polymer is called urea-formaldehyde resin because it is made up of urea
and formaldehyde.
Class XII Chemistry www.vedantu.com 8
13. D
Both the double bonds are preserved i.e., they are not involved in polymerization,
hence it is most unlike form of polymerization.
14. A, B
Polymers that are easily decomposed are known as biodegradable polymers. PHBV
is biodegradable in nature. It is formed by the copolymerization of 3-hydroxybutyric
acid and 3-hydroxypentanoic acid. Glycine + aminocaproic acid copolymerize to
form nylon-2-nylon 6. This is also biodegradable
15. B, C
Buna-S and neoprene require at least one diene monomer at the time of manufacture.
The copolymerization of 1,3-butadiene and styrene produces Buna-S in the presence
of a peroxide catalyst. The free radical polymerisation of chloroprene forms
neoprene.
16. D
Animals store glycogen
Carbohydrates are stored in animals as glycogen. It has a structure similar to that of
amylopectin and is slightly branched, so it is also called animal starch. It is present
in the liver, muscles and brain.
17. A, D
Vulcanization is a chemical process in which rubber is heated with sulphur to form
crosslinks between rubber molecules. This process is performed to improve the
physical properties such as elasticity of natural rubber. It makes the rubber stiffer.
18. C
Nylon 66 is a type of polyamide or nylon. Nylon 66 and Nylon 6 are the two most
commonly used elements in the textile and plastics industry. Nylon 66 is made up of
Class XII Chemistry www.vedantu.com 9
two monomers, each containing six carbon atoms, hexamethylenediamine and adipic
acid, and is named after Nylon 66.
19. B, C
20. B
Lexan is a type of polycarbonate. H. Thermosetting polymer containing carbonic
acid groups. They are strong, durable materials and are optically transparent. For this
reason, laminated polycarbonate (Lexan) is used to manufacture bullet proof glass.
21. B
Condensation polymers are formed by a condensation reaction in which molecules
bind and loose small molecules as a by-product. For example, nylon 6, 6 is formed
by condensation polymerization of adipic acid and hexamethylenediamine.
Polystyrene, Teflon, and rubber, on the other hand, are all formed by chain-growth
polymerization of the monomer’s styrene, tetrafluoroethylene, and isoprene,
respectively.
Here, unsaturated monomer molecules are added individually to the active site of
the growing polymer chain.
22. C
TEP growth polymerization refers to a type of polymerization mechanism in which
bifunctional or multifunctional monomers react to form a dimer first, then a trimer,
a longer oligomer, and finally a long-chain polymer. .
For example, nylon is polymerized by a step-by-step growth polymerization process
in which bifunctional monomers containing equal amounts of amines and carboxylic
acids react to form amides at both ends of each monomer.
Polyacrylonitrile, polyisoprene, and polyethylene are polymerized by chain-growth
polymerization of acrylonitrile, isoprene (2-methyl-1,3-butadiene), and ethane,
respectively.
Chain-growth polymerization (or addition polymerization) involves the bonding of
molecules, including double or triple carbon-carbon bonds.
23. B
Class XII Chemistry www.vedantu.com 10
Biodegradability is defined as the ability to be degraded by other organisms. Nylon-
2-Nylon-6, Dextran, and PHBV are biodegradable, but Nylon-6,6 is not.
However, both dextran and PHBV are polyester, and nylon-2-nylon-6 is polyamide.
The polymerization of many sugar molecules forms dextran.
24. D
Glyptal is a copolymer of ethylene glycol and phthalic acid. Bakelite is a condensed
polymer (copolymer) of phenol and formaldehyde.
25. D
Polyvinyl chloride (PVCA) is a thermoplastic copolymer of vinyl chloride and
acetate.
26. C
Isoprene is 2-methyl-1, 3-butadiene.
27. C
Treatment of chloroform with antimony trifluoride and hydrofluoric acid produces
tetrafluoroethylene. Upon polymerization, tetrafluoroethylene forms Teflon.
28. A
Polypropylene is an example of an additive polymer. b. Additional polymers result
from repeated additions of monomer units. The monomers involved are unsaturated
compounds, usual derivatives of ethene. Example: Propylene undergoes additional
polymerization to form polypropylene. In addition to polymerization, monomeric
units are continuously added to the growing chain. By chain reaction, it is called
chain-growth polymerization
29. A
The copolymer is PHBV. Poly (hydroxybutyrate-covariate) (PHBV) is a fully
biodegradable thermoplastic polyester produced by microbial fermentation.
Class XII Chemistry www.vedantu.com 11
You might also like
- Matriculation Chemistry (Polymers)Document19 pagesMatriculation Chemistry (Polymers)ridwanNo ratings yet
- As Biochemistry QuizDocument7 pagesAs Biochemistry QuizFati QuaynorNo ratings yet
- Biomolecules MCQs - 01Document24 pagesBiomolecules MCQs - 01Types100% (1)
- Biochemistry Tutorial BCH 301: True or False SectionDocument7 pagesBiochemistry Tutorial BCH 301: True or False SectionTheo SantoNo ratings yet
- PolimerDocument31 pagesPolimerAlief MoulanaNo ratings yet
- (CM2213&2223) Organic Chemistry Principles in Context - Green PDFDocument722 pages(CM2213&2223) Organic Chemistry Principles in Context - Green PDFSreedevi Krishnakumar100% (1)
- PolymersDocument6 pagesPolymersRaman Deep100% (1)
- Excercise QuestionsDocument13 pagesExcercise QuestionsSavarinathan Maria RayappanNo ratings yet
- Cross-Linking Styrene Acrylic PolymerDocument7 pagesCross-Linking Styrene Acrylic PolymerpiyushparikNo ratings yet
- Synthetic Fibre - TESTDocument4 pagesSynthetic Fibre - TESTpankaj16xiss100% (2)
- Polyvinylchloride — 2: Main Lectures Presented at the Second International Symposium on Polyvinylchloride, Lyon-Villeurbanne, France, 5 - 9 July 1976From EverandPolyvinylchloride — 2: Main Lectures Presented at the Second International Symposium on Polyvinylchloride, Lyon-Villeurbanne, France, 5 - 9 July 1976A. GuyotNo ratings yet
- Objective Questions WithoutDocument94 pagesObjective Questions Withoutadhitya100% (3)
- Flame-Retardants Risk AssessmentDocument129 pagesFlame-Retardants Risk Assessmentvijaymwagh100% (1)
- PolymerDocument6 pagesPolymerABHAY VISHWAKARMA100% (1)
- MCQ Test of PolymerDocument4 pagesMCQ Test of PolymerDrAman Khan Pathan100% (2)
- Correct AnswerDocument120 pagesCorrect Answerdebaprasad ghosh100% (1)
- JEE - Chemistry - PolymersDocument19 pagesJEE - Chemistry - Polymersofficial.archit234No ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Chemistry - Polymers AssignmentDocument5 pagesCBSE Class 12 Chemistry - Polymers AssignmentsrideviNo ratings yet
- Chinmaya Vidyalaya, Tripunithura-2020 Chemistry-Class Xii PolymersDocument3 pagesChinmaya Vidyalaya, Tripunithura-2020 Chemistry-Class Xii PolymersRanjith MNo ratings yet
- Biomolecules and Polymers - DTS 1Document2 pagesBiomolecules and Polymers - DTS 1Shreyas MuthaNo ratings yet
- Unit - 15 Polymers: - CO - NH - ) Amide Bond in Nylon Gets HydrolysedDocument4 pagesUnit - 15 Polymers: - CO - NH - ) Amide Bond in Nylon Gets HydrolysedSakshi BachhetyNo ratings yet
- POLYMERSDocument5 pagesPOLYMERSkavitha2511977No ratings yet
- ChemistryQB Topic8c SQ eDocument27 pagesChemistryQB Topic8c SQ eNg Swee Loong StevenNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual 2Document51 pagesLab Manual 2NUR AINA SYAHMINA MOHD AMRANNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Polymer Questions AnswersDocument6 pagesCBSE Class 12 Chemistry Polymer Questions AnswersgulshanNo ratings yet
- 12 Chemistry Notes Ch15 Polymers - UnlockedDocument7 pages12 Chemistry Notes Ch15 Polymers - UnlockedriyashejiNo ratings yet
- Test Polymer Unit With Answer KeyDocument10 pagesTest Polymer Unit With Answer KeyWaliur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Macromolecules (Polymers, Carbohydrates, Proteins, and Fats)Document27 pagesMacromolecules (Polymers, Carbohydrates, Proteins, and Fats)Melva SibaraniNo ratings yet
- Unit 14,15ccDocument5 pagesUnit 14,15cceaselife0003No ratings yet
- Polymers and BiomoleculesDocument93 pagesPolymers and BiomoleculesSajaNo ratings yet
- Exercise # 01 (Polymer) : Single Correct ChoiceDocument5 pagesExercise # 01 (Polymer) : Single Correct Choicerishav kumarNo ratings yet
- Polymers K-CET Crash: Homework QuestionsDocument3 pagesPolymers K-CET Crash: Homework QuestionsCHIRAG GOWDANo ratings yet
- Grade 12 Work Sheet 4Document3 pagesGrade 12 Work Sheet 4abdimoh7522No ratings yet
- IIT JEE13-Chemistry-Hand Out-Chem Polymer PDFDocument7 pagesIIT JEE13-Chemistry-Hand Out-Chem Polymer PDFSusmitNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Work Sheet For Grade 12th On PolymersDocument4 pagesChemistry Work Sheet For Grade 12th On Polymersousmanwizdan6No ratings yet
- CH09 EOC QuestionsDocument22 pagesCH09 EOC QuestionsSuresh ShahNo ratings yet
- Polymers PDFDocument6 pagesPolymers PDFvidushi1121No ratings yet
- Marking Scheme: Single Correct (+3,-1) M M: 176 Time: 1 HR 30 MinDocument9 pagesMarking Scheme: Single Correct (+3,-1) M M: 176 Time: 1 HR 30 MinAbdulaziz-- SHNo ratings yet
- Assignment Unit 4Document5 pagesAssignment Unit 4ARI ESNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Class: O-Level Time: 50 Min Marks: 45Document7 pagesChemistry Class: O-Level Time: 50 Min Marks: 45Zainab ShigriNo ratings yet
- RChE PCP DIAG 4Document5 pagesRChE PCP DIAG 4Paulo Emmanuele BetitaNo ratings yet
- Practice Text 1Document5 pagesPractice Text 1Juan Rodriguez OrdoñezNo ratings yet
- Biomolecules (Premium)Document31 pagesBiomolecules (Premium)Niranjan UvarajaNo ratings yet
- Notes of ClassDocument9 pagesNotes of ClassRishi PrakashNo ratings yet
- PolymersDocument11 pagesPolymersEzhil MukilNo ratings yet
- Biomolecules NotesDocument11 pagesBiomolecules NotesAyush jaatNo ratings yet
- Polymers IntroductionDocument28 pagesPolymers Introductionleela777No ratings yet
- Ncert Exemplar Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 15 PolymersDocument13 pagesNcert Exemplar Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 15 PolymersYash SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- 12 Chemistry Notes ch15 Polymers PDFDocument7 pages12 Chemistry Notes ch15 Polymers PDFpakhi tanejaNo ratings yet
- Polymer Chemistry PDFDocument4 pagesPolymer Chemistry PDFSuyog TekamNo ratings yet
- Unit 20, Polymer Chemistry (Multiple Choice)Document15 pagesUnit 20, Polymer Chemistry (Multiple Choice)Thomas AlfieNo ratings yet
- Polymers: Short Answer QuestionsDocument6 pagesPolymers: Short Answer QuestionspavanNo ratings yet
- PolymerDocument6 pagesPolymertyagiabhishek145No ratings yet
- Polymers: Short Answer QuestionsDocument6 pagesPolymers: Short Answer QuestionsHema KamatNo ratings yet
- Mehboob Ali (M.Phil Chemistry)Document57 pagesMehboob Ali (M.Phil Chemistry)Abdul RazzaqNo ratings yet
- QB - DPT I - Fund. of Polymer ScienceDocument9 pagesQB - DPT I - Fund. of Polymer ScienceAryank mishraNo ratings yet
- ReviewerDocument19 pagesReviewerCarlos Miguel Dacaimat100% (1)
- 12 Chemistry Chap-3 DPP-3 PDFDocument4 pages12 Chemistry Chap-3 DPP-3 PDFPurab PatelNo ratings yet
- Set 17Document1 pageSet 17Nurul FarhanaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Synthesis of OligosDocument12 pagesChemical Synthesis of OligosJulia JimenezNo ratings yet
- 2017 OD Chemistry 12th CBSE PYPDocument8 pages2017 OD Chemistry 12th CBSE PYPLakshya AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Transition Metal-Catalyzed Pyridine Synthesis: Transition Metal-Catalyzed Heterocycle Synthesis SeriesFrom EverandTransition Metal-Catalyzed Pyridine Synthesis: Transition Metal-Catalyzed Heterocycle Synthesis SeriesNo ratings yet
- Sustainable synthesis of ciclopentene derivatives through multicomponent reactions in continuous flow regimeFrom EverandSustainable synthesis of ciclopentene derivatives through multicomponent reactions in continuous flow regimeNo ratings yet
- Product Bulletin: Hydroxyl Terminated Polybutadiene Resins and Derivatives - Poly BD and KrasolDocument42 pagesProduct Bulletin: Hydroxyl Terminated Polybutadiene Resins and Derivatives - Poly BD and Krasol13673067No ratings yet
- End Group AnalysisDocument8 pagesEnd Group AnalysisShivani Upadhyay100% (1)
- Science MatterDocument38 pagesScience MatterAlezander GalindoNo ratings yet
- Prof Krishna Jonnalagadda PDFDocument5 pagesProf Krishna Jonnalagadda PDFpankajNo ratings yet
- 3 DPDDocument21 pages3 DPDbalaji817150No ratings yet
- Material Descriere Dimensiuni Comercializare Culori UM: Pret Lista Din 03.01.2022 Euro (Fara TVA)Document16 pagesMaterial Descriere Dimensiuni Comercializare Culori UM: Pret Lista Din 03.01.2022 Euro (Fara TVA)cipos posNo ratings yet
- TDDS #Document52 pagesTDDS #britoraj100% (2)
- Strain-Induced Crystallization of Natural RubberDocument10 pagesStrain-Induced Crystallization of Natural RubberChanin NgudsuntearNo ratings yet
- Polytronics - An Emerging Technology and Its ApplicationsDocument7 pagesPolytronics - An Emerging Technology and Its ApplicationsVinay SaiNo ratings yet
- Concrete Micro-Structure, Properties and MaterialsDocument26 pagesConcrete Micro-Structure, Properties and MaterialsEddie MupaziNo ratings yet
- Effect Matrix Toughness Composite Fracture BehaviorDocument13 pagesEffect Matrix Toughness Composite Fracture BehaviormshameliNo ratings yet
- Topical Test Chapter 9 Form 4Document4 pagesTopical Test Chapter 9 Form 4rosabalinaNo ratings yet
- Advanced Materials, Robotics and NanotechnologyDocument43 pagesAdvanced Materials, Robotics and NanotechnologyIsabella MagallanesNo ratings yet
- Hyperdispersants - Technology & BenefitsDocument16 pagesHyperdispersants - Technology & BenefitsSean RichardsonNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 5Document14 pagesProblem Set 5mcjohn551No ratings yet
- Dr. Saleem CVDocument8 pagesDr. Saleem CVazeb514No ratings yet
- CROSSLINKEDHADocument10 pagesCROSSLINKEDHABrian BeeNo ratings yet
- Tensile Strength and Elongation at Yield - ASTM D638Document7 pagesTensile Strength and Elongation at Yield - ASTM D638Silverio AcuñaNo ratings yet
- Chapters Wise Previous QuestionsDocument15 pagesChapters Wise Previous QuestionsYatishwar MSNo ratings yet
- SBR and Natural Rubber LatexDocument33 pagesSBR and Natural Rubber Latexain kamarudinNo ratings yet
- Erapol ECP95A: Technical DatasheetDocument3 pagesErapol ECP95A: Technical Datasheet82865200No ratings yet
- Inorganic Polymers CBZ 2Document54 pagesInorganic Polymers CBZ 2Shrawani DeshmukhNo ratings yet
- Polymer SolubilityDocument13 pagesPolymer SolubilityDr. Stan Wardel BA, MA, MChem, MBA, DPhil, DSc.No ratings yet
- 674 PDFDocument94 pages674 PDFsivaenotesNo ratings yet
- The Complete Technology Book On Textile Processing With Effluent TreatmentDocument8 pagesThe Complete Technology Book On Textile Processing With Effluent TreatmentAsif AhmedNo ratings yet
- A comparative study on Poly (ε-caprolactone) film degradation atDocument8 pagesA comparative study on Poly (ε-caprolactone) film degradation atHugo David Enriquez EspinosaNo ratings yet
- Agentes AntiescalaDocument7 pagesAgentes AntiescalaFabian ArboledaNo ratings yet