0% found this document useful (0 votes)
189 views2 pagesMatrices Summary
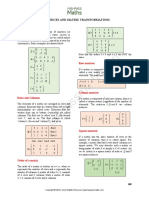
The document defines key concepts related to matrices including:
- The order of a matrix is defined by the number of rows and columns.
- Matrix addition and subtraction are defined if the matrices have the same order. Matrix multiplication is defined if the number of columns in the first matrix equals the number of rows in the second.
- There are different types of matrices including row, column, square, diagonal, symmetric, triangular, zero and identity matrices.
- The transpose of a matrix switches the rows and columns.
- Matrix multiplication by a scalar multiplies each element by the scalar.
- The inverse of a 2x2 matrix is defined if the determinant is not equal to 0.
Uploaded by
Edris ZamaryalCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
189 views2 pagesMatrices Summary
The document defines key concepts related to matrices including:
- The order of a matrix is defined by the number of rows and columns.
- Matrix addition and subtraction are defined if the matrices have the same order. Matrix multiplication is defined if the number of columns in the first matrix equals the number of rows in the second.
- There are different types of matrices including row, column, square, diagonal, symmetric, triangular, zero and identity matrices.
- The transpose of a matrix switches the rows and columns.
- Matrix multiplication by a scalar multiplies each element by the scalar.
- The inverse of a 2x2 matrix is defined if the determinant is not equal to 0.
Uploaded by
Edris ZamaryalCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd