0% found this document useful (0 votes)
195 views3 pagesFEM (Finite Element Method)
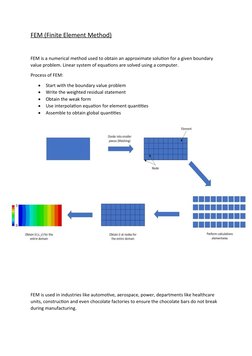
FEM (Finite Element Method) is a numerical method used to obtain approximate solutions to boundary value problems by dividing a body into smaller pieces called finite elements. The method involves writing a weighted residual statement, obtaining the weak form, using interpolation equations for element quantities, and assembling the equations to obtain global quantities. FEM is used across many industries to analyze how physical systems, such as structures and materials, will react to real-world forces.
Uploaded by
rohanCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
195 views3 pagesFEM (Finite Element Method)
FEM (Finite Element Method) is a numerical method used to obtain approximate solutions to boundary value problems by dividing a body into smaller pieces called finite elements. The method involves writing a weighted residual statement, obtaining the weak form, using interpolation equations for element quantities, and assembling the equations to obtain global quantities. FEM is used across many industries to analyze how physical systems, such as structures and materials, will react to real-world forces.
Uploaded by
rohanCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd