Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Sclera
Uploaded by
Mohamed GhanemCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Sclera
Uploaded by
Mohamed GhanemCopyright:
Available Formats
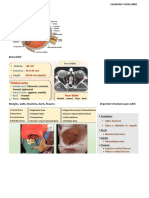
Staphyloma Episcleritis Scleritis
Ectasia of outer coat lined by atrophic middle +/- inner Etiology 1. Non-infective : 50% with rheumatoid arthritis
coat . 2. infective : herpes zoster
3. idiopathic
Anterior staphyloma Types 1) Diffuse 1) Diffuse
2) Nodular 2) Nodular
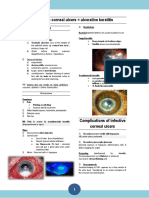
Healing of a large perforated corneal ulcer forming an 3) Necrotizing : may result in
ectatic scar in which the iris is incarcerated. perforation
4) scleromalacia perforans :
scleral melting {rare
perforation}
5) posterior scleritis : +/-
Scleral staphyloma exudative retinal detachment.
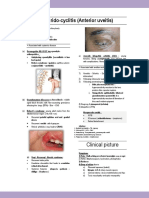
Clinical picture Discomfort and lacrimation + Severe pain
The sclera bulges either because of a
Redness - Tenderness +/- blurred vision
high IOP as in absolute glaucoma or
weakness of the sclera as in scleritis Complications 1) Uveitis
2) keratitis
The sclera yields at the site of weakness: 3) Staphyloma
1) intercalary : at the limbus – lined by root of iris Treatment Of cause +/- atropine
NSAID +/- oral steroids
2) ciliary: at anterior ciliary vessels – lined by ciliary
topical steroids +/- immunosuppressive
body
3) equatorial : at the vortex veins - lined by choroid DD Phlycten
and retina
DD of a blue sclera
1. Neonates
2. Buphthalmos
3. High axial myopia
4. Over staphyloma
5. Osteogenesis imperfecta { deafness - fragile bones
Treatment :
if blind, ugly and painful = evisceration or enucleation
NB :posterior staphyloma :
in cases with high axial myopia
seen by fundus or US .
You might also like
- OPHTHALMOLOGY KMU PAST PAPERS SOLVED SEQSDocument70 pagesOPHTHALMOLOGY KMU PAST PAPERS SOLVED SEQSem khan100% (2)
- Piroxicam Drug Study: NSAIDs Reduce InflammationTITLE Ciprofloxacin Antibiotic Treats Bacterial Infections TITLE Salbutamol Nebulizer Relieves Asthma SymptomsDocument3 pagesPiroxicam Drug Study: NSAIDs Reduce InflammationTITLE Ciprofloxacin Antibiotic Treats Bacterial Infections TITLE Salbutamol Nebulizer Relieves Asthma SymptomsBheiatriz de VeraNo ratings yet
- Parasitology Guide Questions 1Document2 pagesParasitology Guide Questions 1Cess LacatangoNo ratings yet
- (Bioethics 2) 2.02.01 - Case - Kimberly Bergalis (Pat G)Document3 pages(Bioethics 2) 2.02.01 - Case - Kimberly Bergalis (Pat G)Asylum AllegoryNo ratings yet
- IeltsDocument65 pagesIeltskitten_alina92% (13)
- Hallows Around LightDocument6 pagesHallows Around Lightviewsonic5No ratings yet
- Cornea and ScleraDocument144 pagesCornea and SclerakhabibtopgNo ratings yet
- Orbit: Orbital OpeningDocument18 pagesOrbit: Orbital Openingعبدالسلام ميلاد درباشNo ratings yet
- Cornea 2022 FinalDocument63 pagesCornea 2022 Finalsalah almozahemNo ratings yet
- Ectropion-Entropion: A Tale of a Lax LidDocument5 pagesEctropion-Entropion: A Tale of a Lax LidStevy SuothNo ratings yet
- Diseases of CorneaDocument28 pagesDiseases of CorneaGAURAVNo ratings yet
- CNMC Eye OSPE Problems With SolutionsDocument26 pagesCNMC Eye OSPE Problems With SolutionsShahbaz AAnsariNo ratings yet
- Ocular TraumaDocument2 pagesOcular TraumaMohannad AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Corneal Dystrophies: What Are The Four Categories of Corneal Dystrophies?Document95 pagesCorneal Dystrophies: What Are The Four Categories of Corneal Dystrophies?Bashayer KhalidNo ratings yet
- Anatomy'S Modul 10 Blok: Laboratory Anatomy Medical Faculty Muhammadiyah University of Purwokerto 2016Document21 pagesAnatomy'S Modul 10 Blok: Laboratory Anatomy Medical Faculty Muhammadiyah University of Purwokerto 2016Sari MentariNo ratings yet
- 7,8 CorneaDocument20 pages7,8 Corneadykesu1806No ratings yet
- Past Years Ophthalmology Q&asDocument24 pagesPast Years Ophthalmology Q&asmhasbullah_725% (4)
- CorneaDocument5 pagesCorneaMohamed GhanemNo ratings yet
- Palpebral Fissure: Process of GrievingDocument9 pagesPalpebral Fissure: Process of Grievingأبوأحمد الحكيمNo ratings yet
- Integumentary SystemDocument6 pagesIntegumentary SystemClark LlameraNo ratings yet
- Uveal TractDocument4 pagesUveal TractMohamed GhanemNo ratings yet
- Acute Iridocyclitis: Sunil Pai B Roll No:78Document21 pagesAcute Iridocyclitis: Sunil Pai B Roll No:78Sunil PaiNo ratings yet
- Ophthalmology Anatomy and Physiology GuideDocument13 pagesOphthalmology Anatomy and Physiology GuidesafrinaNo ratings yet
- Presentation Ocular LeprosyDocument25 pagesPresentation Ocular LeprosyCut Aja ChairunaNo ratings yet
- Cornea Anatomy and Physiology GuideDocument38 pagesCornea Anatomy and Physiology GuideSamirNo ratings yet
- Diseases of The Cornea Prof. Zoltán Zsolt NagyDocument123 pagesDiseases of The Cornea Prof. Zoltán Zsolt NagydebbyNo ratings yet
- Pa MataDocument115 pagesPa MataIchsan WidjanarkoNo ratings yet
- L10.3-OPHTHA-Uvea (Sept3022)Document5 pagesL10.3-OPHTHA-Uvea (Sept3022)Erald PaderangaNo ratings yet
- Ophthalmology Card AnswersDocument29 pagesOphthalmology Card AnswersRaihan MahmudNo ratings yet
- Cornea: DR Mafruha Afrin MCPS, FCPS, FRCS (Glasgow) Assist-Prof Dept of Ophthalmology Green Life Medical CollegeDocument72 pagesCornea: DR Mafruha Afrin MCPS, FCPS, FRCS (Glasgow) Assist-Prof Dept of Ophthalmology Green Life Medical CollegeLamia Rawnak HridiNo ratings yet
- T1505C13Document9 pagesT1505C13Gheorgian HageNo ratings yet
- Treating Stye, Chalazion and TrichiasisDocument4 pagesTreating Stye, Chalazion and TrichiasishiNo ratings yet
- Anterior UveitisDocument65 pagesAnterior UveitisHardy vlogsNo ratings yet
- Ophthalmic Manifestations of Systemic Diseases: A Guide to Eye Exam FindingsDocument6 pagesOphthalmic Manifestations of Systemic Diseases: A Guide to Eye Exam Findingshalf_frozen_cho6435No ratings yet
- Frequently Asked Questions in A Uveitis CaseDocument9 pagesFrequently Asked Questions in A Uveitis CasePooja SharmaNo ratings yet
- Fuchs Dystrophies and Pseudophakic Bullous Keratopathy: Resident of Ophthalmology 3 Year: UN LengDocument18 pagesFuchs Dystrophies and Pseudophakic Bullous Keratopathy: Resident of Ophthalmology 3 Year: UN LengAditha Fitrina AndianiNo ratings yet
- Corne A: Dr. Yulia Fitriani, SPMDocument47 pagesCorne A: Dr. Yulia Fitriani, SPMYuga ParsadaanNo ratings yet
- Corne A: Dr. Yulia Fitriani, SPMDocument47 pagesCorne A: Dr. Yulia Fitriani, SPMEdsel QasswaraNo ratings yet
- Head and Facial TraumaDocument36 pagesHead and Facial TraumaensiNo ratings yet
- Pathology of The: John R. Minarcik, M.DDocument78 pagesPathology of The: John R. Minarcik, M.Drush73No ratings yet
- Comprehensive Key For ENT Cases All TeamDocument21 pagesComprehensive Key For ENT Cases All TeamReham AshourNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Diseases of The UveaDocument102 pagesAnatomy and Diseases of The UveaVishakh IsloorNo ratings yet
- Cataract: Galactosaemia Lowe SyndromeDocument2 pagesCataract: Galactosaemia Lowe SyndromeAnas AbuseifNo ratings yet
- Management of Corneal Abrasions: STEPHEN A. WILSON, M.D., and ALLEN LAST, M.D., University of Pittsburgh Medical CenterDocument6 pagesManagement of Corneal Abrasions: STEPHEN A. WILSON, M.D., and ALLEN LAST, M.D., University of Pittsburgh Medical CenterGokull ShautriNo ratings yet
- Diseasesofthelens Aaa 120229140048 Phpapp02Document61 pagesDiseasesofthelens Aaa 120229140048 Phpapp02GermanyNo ratings yet
- LBM 3 LI FathiaDocument29 pagesLBM 3 LI FathiakadinfathiaNo ratings yet
- LBM 3 LI FathiaDocument29 pagesLBM 3 LI FathiakadinfathiaNo ratings yet
- Eyelid Anatomy and DisordersDocument36 pagesEyelid Anatomy and Disordersعبدالسلام ميلاد درباشNo ratings yet
- Degenerative and Miscellaneous Corneal ConditionsDocument2 pagesDegenerative and Miscellaneous Corneal ConditionsNikki Sharmaine VillahermosaNo ratings yet
- 7 Lens and Cataract 1Document57 pages7 Lens and Cataract 1Devi Melissa RiupassaNo ratings yet
- Ophthalmo Short CasesDocument15 pagesOphthalmo Short CasesDeepika LamichhaneNo ratings yet
- Alterations in Refraction and Ocular MovementsDocument4 pagesAlterations in Refraction and Ocular Movementsraquel maniego100% (1)
- Chapter 5 Crystalline Lens - Abdelmonem Hamed EditionDocument16 pagesChapter 5 Crystalline Lens - Abdelmonem Hamed EditionAbdelmonem HamedNo ratings yet
- Ophtho - Neuro Exam 1Document21 pagesOphtho - Neuro Exam 1AbbyNo ratings yet
- Eyelids Slides PDFDocument72 pagesEyelids Slides PDFMariam QaisNo ratings yet
- Ectropión Entropión Ptosis: Etiologia: Etiologia: EtiologiaDocument1 pageEctropión Entropión Ptosis: Etiologia: Etiologia: EtiologiaOvejita GaleanaNo ratings yet
- Diseases of Eyelid: Prepared by DR - Sourab Kumar DasDocument66 pagesDiseases of Eyelid: Prepared by DR - Sourab Kumar Dasসপ্নে ছোয়া মনNo ratings yet
- Comprehensive Key For ENT Cases: CSOM Never Painful Except inDocument21 pagesComprehensive Key For ENT Cases: CSOM Never Painful Except inSaya Menang100% (1)
- Trauma MataDocument57 pagesTrauma MataFatmala Umi MaisarahNo ratings yet
- Eye Lid DiseasDocument59 pagesEye Lid DiseasJohanna Tania PriatoNo ratings yet
- Corneal Dystrophy and DegenerationsDocument12 pagesCorneal Dystrophy and Degenerationsamritnam satyadasNo ratings yet
- v10 Literature Review Auricular Disorders Part 2 - Benign NeoplasmsDocument5 pagesv10 Literature Review Auricular Disorders Part 2 - Benign NeoplasmsAlisNo ratings yet
- Disease of Orbit, LacrimalDocument73 pagesDisease of Orbit, LacrimalMarshet GeteNo ratings yet
- Artificial Pancreas Technology Offers Hope For Childhood DiabetesDocument11 pagesArtificial Pancreas Technology Offers Hope For Childhood DiabetesDiana PeñalozaNo ratings yet
- ICD10 Coding InstructionsDocument55 pagesICD10 Coding Instructionsanton_susanto10No ratings yet
- AcceptedDocument28 pagesAcceptedChistian LassoNo ratings yet
- 01 - 6573-M. K. Yadav-RDocument4 pages01 - 6573-M. K. Yadav-RMuthu ArasuNo ratings yet
- Generador Marcapaso Osypka Pace101h IfuDocument35 pagesGenerador Marcapaso Osypka Pace101h IfuJordan BonnettNo ratings yet
- Periodontics (Review Center)Document9 pagesPeriodontics (Review Center)yellow ranger100% (1)
- Theoretical Framework - GiannaDocument2 pagesTheoretical Framework - GiannaAnne MarielNo ratings yet
- Molar PregnancyDocument7 pagesMolar PregnancyFelix Valerian HalimNo ratings yet
- Funda 2Document9 pagesFunda 2Alex OlivarNo ratings yet
- Vomiting in ChildrenDocument41 pagesVomiting in ChildrenWiresa RenaltaNo ratings yet
- Clinical Pharmacy Case on CAD ManagementDocument41 pagesClinical Pharmacy Case on CAD ManagementLouie Fernand LegaspiNo ratings yet
- Antihistamine: I. HistoryDocument6 pagesAntihistamine: I. HistoryAnaliza Kitongan LantayanNo ratings yet
- JR Science Quiz 19-20 Class VI - VIIIDocument43 pagesJR Science Quiz 19-20 Class VI - VIIIDAVV IQACNo ratings yet
- Mhps-Ts Newsletter: MHPS Technical Services CorporationDocument21 pagesMhps-Ts Newsletter: MHPS Technical Services Corporationjonel.javierNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan for Urinary Tract Infection (UTIDocument19 pagesNursing Care Plan for Urinary Tract Infection (UTIYudistiro Adi Nugroho100% (1)
- Anatomy and Physiology of Adrenal GlandDocument26 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of Adrenal GlandYAMINIPRIYANNo ratings yet
- Durian Technology Package: Growing Guide & Pest ManagementDocument7 pagesDurian Technology Package: Growing Guide & Pest ManagementPutchong Sara100% (1)
- ENT AyaSalahEldeenDocument147 pagesENT AyaSalahEldeenFatma ShnewraNo ratings yet
- The Importance of NutritionDocument16 pagesThe Importance of NutritionRonna DipasupilNo ratings yet
- Elaj Al SalikinDocument80 pagesElaj Al SalikinMohammed Abdul Hafeez, B.Com., Hyderabad, India100% (1)
- Electronic Pill PaperDocument16 pagesElectronic Pill Paper2JH18EC005 Aishwarya GundmiNo ratings yet
- Recommendations For The Use of Immunoglobulin Therapy For Immunomodulation and Antibody ReplacementDocument7 pagesRecommendations For The Use of Immunoglobulin Therapy For Immunomodulation and Antibody ReplacementChih-I LeeNo ratings yet
- 1692 Salmonella Flipbook BAM V2 FFDocument15 pages1692 Salmonella Flipbook BAM V2 FFMiguel GómezNo ratings yet
- Quiz BiochemistryDocument100 pagesQuiz BiochemistryMedShare88% (25)
- Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental DisordersDocument16 pagesDiagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental DisordersKen MurrayNo ratings yet
- Fast F A S T: Recognizing Stroke: Ace Rms Peech ImeDocument25 pagesFast F A S T: Recognizing Stroke: Ace Rms Peech ImeIliescu DenisaNo ratings yet