Professional Documents
Culture Documents
PHY 1015 2021 Exam
PHY 1015 2021 Exam
Uploaded by
KAPEMBWA MAPALO0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views7 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views7 pagesPHY 1015 2021 Exam
PHY 1015 2021 Exam
Uploaded by
KAPEMBWA MAPALOCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 7
The University of Zambia
Department of Physics
University Examinations 2020-21
PHY1040: Introductory Medical Physics
Time: Three hours. Maximum marks = 100.
All questions carry equal marks, The marks are shown in brackets. Question 3s ‘compulsory. Attempt
the cover page of the answer script which questions you
only four more questions. Cl
have attempted.
wn the answer book as well as on the answer sheet for
Write clearly only your computer number of
Question 1. Tie them together. Organise the answer script properly.
show your working clearly. Omission of essential work will ead to loss of marks.
For Question 1, you must use the blank answer sheet provided.
SECTION A
A. A footballer throws a soccer ball at 45° above horizontal with a velocity of 3.5 m/s. The
horizontal component. of the velocity will be:
(a) 3.0 m/s (b) 2.0 m/s (c) 3.5 m/s (d) 2.5 m/s
B. Which of the following physical quantities is not a vector:
(a) acceleration (b) current(c) momentum(d) speed ~~
C. A hunter on a hill aims at the head of a monkey hanging fromi a branch of a tree. The hunter
‘and the monkey are at the same height from the ground. Just the instant he fires, the monkey
drops. The bullet:
(a) will hit the head of the monkey. (b) will pass over the head of the monkey. (c) will pass
below the head of the monkey. (d) may or may not hit the head of the monkey
D. A person stands on a scale in an clevator. His apparent weight will be the greatest when the
elovator
(a) is standing still. (b) is accelerating downward. (c) is accelerating upward. (d) is moving
upward at constant velocity.
E, In an automobile collision, how docs an airbag lessen the blow to the passenger? Assume as a
result of the collision, the passenger stops.
(a) The stopping impulse is the same for either the hard objects or the airbag. Unlike
the windshield or dashboard, the air bag increases the stopping time and thus reduces the
average force on the passenger. (b) The airbag is there to insure the seatbelt holds. (c) The
air bag decreases the momentuin change of the passenger in the collision. (d) During the
collision, the force from the air bag is groater than would be the force from the windshicld
or dashboard so the passenger cannot hit the hard objects.
F. A body of radjus & and mass m is rolling horizontally without slipping with speed m. Tt then
rolls up @ hill to a maximum height h = 42. The body's rotational inertia is:
(a) dm. (b) $m? (c) $mR?. (d) mR?
G. Steam at 100°C is more dangerous than the same mass of water at 100°C because the steam
(a) contains more internal energy. (b)moves faster,
heat capacity.
(¢) is less dense, (d) has a higher specific
H. When the temporature of the ambient is equal to the body temperature, how does the body
Jose heat to maintain constant internal temperature?
(0) a. rough convection, (b) Uhrough sweating. (@) through conduction. (d) through
radiation,
The amount of work 0.0.6 KW electric drill can do in 1 minute is:
(a) A. 36-4. (b) 364d, (c) 0.6. (A) 0.6 kd.
K. ‘Tho first law of thermodynamics states that
(a) a, the heat energy pumped into a system goes to raise its internal energy and enable
it to perform work. (b) the hent energy pumped into a thermodynamic system goes into
performing work only. (c) the work done by a system raises its internal energy (d) the heat
jc system goes into lowering its internal energy and
energy pumped into a thermodyn
performing work by the system,
SECTION B : Answer any four.
Question two
(a) A 23 g bullet travelling at 230 m/s penetrates a 2.0 kg block of wood and emerges cleanly at
170 m/s. If the block is stationary on a frictionless surface when hit, how fasédoes it move
after the bullet emerges? '9)
(b) The speed of a nerve impulse in a human body is about 100 m/s. If you accidentally stub
your toe in the dark, estimate the time it takes the nerve impulse to travel to your brain.
‘What would happen if tho speod of the nerve impulse was much lower say 1 m/s? Assume
you are 1.7 m tall [4]
(c) While exploring a cave, a person starts at the entrance and moves the following successive
distances. She goes 75.0 m north, 250 m cast, 125 m at an. angle 30.0 ® north of west, and
150 m south, Find the resultant displacement from the cave entranée. 6]
(d) A horizontal force of 140N is needed to pull a 60.0kg box across the horizontal floor at a
constant speed. what is the coefficients of friction between the floor and box?
[4]
“Question three
(a) Explain how a body moving at constant speed can be accelerating. [2)
(b) An aeroplane carrying out a parcel drop releases a parcel while travelling a steady speed of
90 m/s at an altitude of 200 m, Calculate the :
(i) the time between the parcel leaving the aeroplane and it striking the ground, 5]
(ii) the horizontel distance travelled, 15]
(c) A car towing a caravan travels along a steady speed of 20 m/s If the force exrted by the engine
is 2 KN, what is the power output of the engine? [3]
(d) A 15-cm-long tendon was found to stretch 3.7 mm by a force of 13.4 N, The tendon was
approximately round with an average diameter of 8.5 mm, Calculate Young's inodulus of
this tendon. 15]
Question four
(a) How long will a 500 W heater take to melt 500 g of ice at -8 °C? Dat 2100 J/kg.K,
134000 J/kg [6]
‘72-mm long
Heat of fusion
(b) Police investigators examining the scene of an accident involving two cars, measure
skid marks of one of the cars, which nearly camo to a stop before colliding. The coefficient
of kinetic friction between the rubber and the pavement is about 0.80. Bstimate the initial
speed of the car assuming a level road. [6]
(c) Describe two situations when friction is welcome to: human body functions and two when itis
[4]
undesirable.
(d) A horizontal force of 140 N is needed to pull a 60.0 kg box across the horizontal floor at &
constant speed. what is the coefficients of friction between the floor and box?
(4)
Question five
chance of surviving a car crash if the deceleration is no more than
(a) A person has a reasonable
lergoing this acceleration.
30 ‘g's (g=9.8m/s2). Calculate’ the force on #70 kg person und
What distance is travelled if the person is brought to rest at this rate from 100 kin/h? [4] “
(b) A weight lifter lifts a 350-N sct of weights from ground level to a position over his head,
vertical distance of 2.00 m. How much work docs the weight lifter do, assuming he moves
the weights at constant speed? ae
very track travels 18 km north, 10 km east, and 16 km south. What is its final
(c) A Zambeef deli
Ie] ~
displacement from the origin?
(a) Zambian footballer Patson Daka kicks a football vertically upward in celebration after scoring
‘an Austrian Cup winning penalty with a speed of 35 m/s. What time does it take for the
football to reach maximum height [6] ~
‘Some Useful Equations
Uniformly accelerated motion:
4
eee erat
Projectile motion:
cos 6, = constant
rr (ano )-| gy)
Force and motion:
Fem wamg Fa=-Fe
Werk and Energy:
PE=wh=mgh — KE=4nw? W=Feeos pax Frese
t
FAt=Anw=m ¥,—%
Lin’
momentum: p =v
Circular motion and gravitation:
Fyn: = GAZE. trey = 360° = 2a rad
r
Rotational motion and angular momentum:
+0)
(25% ie $ gnop-+tot a, =0,+a1y= ar
Tmt? o} 20} +208 ante ake T= Sy? KE, =410
7
eFl=la WetOP=t0 L= I KE gy = tr +1Ia*
Properties of matter:
nm aL 1
otra Set
anv ZY
F,= pg , (submerged object)
E sl
de cada)
Thermal Properties of matter:
PV =nRT: aQ=meAT =nCaT : AL=aLAs
1, (1+at)
W = PAV (AQ/At)=(kAAT)/ AL
Q=ncw
=Vxp Leeder Cp=C, +R
t
37.RAT for Isobaric and Iso-volumetric processes
Thermodynamics:
AQ=AU+AW : W= pay PV =nRT n= BY = RVI TV" = TV"
¥, 1 ;
Se, PARTI Wes = 5 (PH BIA):
22% (ap) = 10.109
iz velocity of sound = 331.45 + 0.611 (°C)
8
2) 28 ph IE yx, costar) f, =10 W/m?
vw) @ 72m
Electric Field:
42
Fa DD or F:
KALB ; k = 8.9874 x 10° Num?.C?, k= (1/{4ne) where a is the
r
permittivity constant = 8.85 x 10" C2,(N.m?)+,
= 160% 10%; Balin, yg; Fe ge
Gest
R Axa eE Ax 5
Electric Potential:
Waa = QE. de; Vo ~ Vo = Mit Z
a &
a@ 7
14 Vy-y= Ed.;
ae
cada As for a parallel plate capacitor.
a. 5
You might also like
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
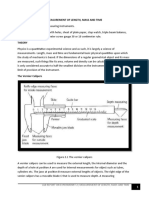
- Experiment 1 - Measurement of Length, Mass and TimeDocument11 pagesExperiment 1 - Measurement of Length, Mass and TimeKAPEMBWA MAPALO100% (1)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5810)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (348)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (844)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1092)
- Tutorial Assignment 1-1Document2 pagesTutorial Assignment 1-1KAPEMBWA MAPALONo ratings yet
- Assignment 2Document1 pageAssignment 2KAPEMBWA MAPALONo ratings yet
- Confirmation SlipDocument1 pageConfirmation SlipKAPEMBWA MAPALONo ratings yet
- Home AssignmenDocument2 pagesHome AssignmenKAPEMBWA MAPALONo ratings yet
- 2011-2012 CE219FinExamDocument4 pages2011-2012 CE219FinExamKAPEMBWA MAPALONo ratings yet
- Chemistry Phase Equilibrium QuizDocument23 pagesChemistry Phase Equilibrium QuizKAPEMBWA MAPALONo ratings yet
- 2007 P-191 First Semester ExamsDocument6 pages2007 P-191 First Semester ExamsKAPEMBWA MAPALONo ratings yet
- Frictional Forces and Motion On The InclineDocument15 pagesFrictional Forces and Motion On The InclineKAPEMBWA MAPALONo ratings yet
- Free Fall Motion Topic 3Document6 pagesFree Fall Motion Topic 3KAPEMBWA MAPALONo ratings yet
- Forces 2Document7 pagesForces 2KAPEMBWA MAPALONo ratings yet
- Experiment 2 - Graphical and Error Analysis FinalDocument18 pagesExperiment 2 - Graphical and Error Analysis FinalKAPEMBWA MAPALONo ratings yet
- Phy1010 Exam Final 2014Document11 pagesPhy1010 Exam Final 2014KAPEMBWA MAPALONo ratings yet
- Che 1010 Tutorial Sheet 5 Sampling and Data TreatmentDocument2 pagesChe 1010 Tutorial Sheet 5 Sampling and Data TreatmentKAPEMBWA MAPALONo ratings yet