Professional Documents
Culture Documents
SIP Chapter II Body
Uploaded by
ThatOneAhmed VirtudazoOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
SIP Chapter II Body
Uploaded by
ThatOneAhmed VirtudazoCopyright:
Available Formats
MATERIALS AND METHODS
This chapter is composed of three: Phase I- Gathering of the
materials, Phase II- Creation of Mixtures, Phase III- Making an
Hypothesis and Phase IV- Testing of the Hypothesis. The
experimental procedures were conducted at Lanzona Subdivision,
Matina Aplaya.
PHASE I: Gathering of the Materials
Collection of Biodegradable Waste
Non-biodegradable waste was gathered from Matina
Central Elementary School (MCES) for the purpose of analysis.
The 1-liter and 237ml polyethylene terephthalate (PET) bottles
were retrieved from the GSIS Heights Subdivision, Matina
Crossing.
PHASE II: Creation of Mixtures
Planning of the Concrete Blend
The non-biodegradable waste was put through a washing
procedure and then ground into a fine powder. The glass bottles
were fragmented into powder. Gravel was added to the mixture,
followed by the addition of water. The mixture was put into the
mold, then let it sit to dry.
PHASE III: Hypothesis
Hypothesis on Plastic Bricks
Non-biodegradable bricks offer benefits over traditional clay
bricks. Quick assembly in construction projects can be achieved
efficiently using them. These Bricks offer you the opportunity to
invest by deciding your preferred selling price for these bricks.
These bricks provide quick, cost-effective, and environmentally
sustainable options for construction.
Plastic bricks are strong, waterproof, and resistant to weathering,
making them ideal for construction in areas that experience
extreme temperatures.
Overall, the use of plastic bricks has the potential to offer a wide
range of benefits, from reducing waste and increasing a
structure’s durability, to providing sustainable building solutions
for communities in need.
Figure 1: The brick before the
Observation
PHASE IV- Observation
Figure 1: Experimental Setup
The setup is placed on a durable surface. The brick is tested
based on durability using the “Drop Test” method. The brick will
be dropped on different heights as seen on the table below. On
the 1st Drop (5’’), the brick was standing firm. On the 2 nd Drop
(1ft), still, the brick was standing strong. On the 3 rd Drop (1’5), the
brick was still strong, except, cracks began forming on the other
sides of the brick. On the 4th Drop (2ft) the brick, fortunately, the
brick still was unbreakable.
DROPS HEIGHT
1ST DROP 5’’
2ND DROP 12’’ (1ft)
3RD DROP 18’’ (1’5)
4TH DROP 24’’ (2ft)
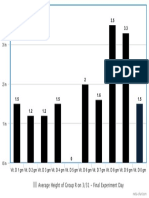
On Figures I, II, III and IV- The following charts and descriptions
explains the data gathered.
Drop 1 Drop 2
4
4
3.5
3.5
3
3
2.5
2.5
2
2
1.5
1.5
1
1
0.5
0.5
0
0 Drop 3 Drop
Durability 4
1 Fragility
Durability1 Fragility
Figure 1: The brick is still at it’s normal pace
3.5 Figure 2: Fragility3.5 Rates
are rising 3
3
2.5 2.5
2 2
1.5 1.5
1 1
0.5 0.5
0 Durability Fragility 0 Durability Fragility
1 1
This was the Result of the Brick at Drop 4. Many
Cracks had formed, but fortunately, it didn’t break.
Figure 3 and Figure 4: Fragility rates are rising, due
to the forming of cracks but, slowly.
Main Writer: Ahmed Virtudazo
Secondary Writer: John Cyrel Gallenero
You might also like
- Floor PlanDocument1 pageFloor PlanGinoDayo16No ratings yet
- Technology Term 2 2016 June MemoDocument4 pagesTechnology Term 2 2016 June MemocaviourNo ratings yet
- Paper Exam Subject Name Roll Number: State Service Mains Exam - 2022:: 03: Genral Studies - I 2228144910Document38 pagesPaper Exam Subject Name Roll Number: State Service Mains Exam - 2022:: 03: Genral Studies - I 2228144910Atul SinghNo ratings yet
- QUESTIONNAIRE For MusicDocument4 pagesQUESTIONNAIRE For Musicjhanvi tandonNo ratings yet
- Collins Quick HittersDocument12 pagesCollins Quick HittersabilodeauNo ratings yet
- ReedcomparisonchartDocument1 pageReedcomparisonchartPhilippe ARNOULDNo ratings yet
- Quiz #1 Quiz #1Document1 pageQuiz #1 Quiz #1Jorhally B EdzraphilNo ratings yet
- CMRHM Re - RevisDocument32 pagesCMRHM Re - RevisAyush SharmaNo ratings yet
- PROBLEM SET AnovaDocument1 pagePROBLEM SET AnovaRhia Mae TeporaNo ratings yet
- A) A Screen Shot of Your Bayesian Network and A Concise Description Explaining The Overall Purpose of This Expert System and The Meaning of NodesDocument18 pagesA) A Screen Shot of Your Bayesian Network and A Concise Description Explaining The Overall Purpose of This Expert System and The Meaning of NodesSierra StewartNo ratings yet
- ID 384542548-EDMG101 HVA VulnerabilityDocument7 pagesID 384542548-EDMG101 HVA VulnerabilityndutaNo ratings yet
- Evaluation Test Grade: 8 (L1) Textbook: Cambridge English For Schools 4, Cambridge University Press Authors: AndrewDocument4 pagesEvaluation Test Grade: 8 (L1) Textbook: Cambridge English For Schools 4, Cambridge University Press Authors: AndrewAnonymous Wfl201YbYoNo ratings yet
- GreenSleeve Tab (Version 1) .XLSBDocument2 pagesGreenSleeve Tab (Version 1) .XLSBcervantexNo ratings yet
- Microsoft Word - Horezontal Well ControlDocument20 pagesMicrosoft Word - Horezontal Well Controlmohanned salahNo ratings yet
- Analytical Attributes ApproachesDocument24 pagesAnalytical Attributes ApproachesBro HoeNo ratings yet
- Answer Sheet Science 4Document2 pagesAnswer Sheet Science 4Emil SabuyaNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Curved Graphs Tangents and GradientsDocument15 pagesGrade 10 Curved Graphs Tangents and GradientsSri Devi NagarjunaNo ratings yet
- Off Call SheetDocument6 pagesOff Call Sheetquay85No ratings yet
- Book 1Document14 pagesBook 1Wan AzriNo ratings yet
- Answer Sheet TemplateDocument1 pageAnswer Sheet TemplateBEA ACASIONo ratings yet
- Click To Add SubtitleDocument16 pagesClick To Add SubtitleImelda RubiyahNo ratings yet
- Meta Chart PDFDocument1 pageMeta Chart PDFAbdallah AbuhamdaNo ratings yet
- Selmer Saxophone Pad Sizes ChartDocument2 pagesSelmer Saxophone Pad Sizes ChartClaudius100% (4)
- #TeamFastModel - Player DevelopmentDocument50 pages#TeamFastModel - Player DevelopmentJohn KerisNo ratings yet
- PDP Small PDP Big Enermax Megamix Crackcorn GF 2K 7 Kinds BSCDocument4 pagesPDP Small PDP Big Enermax Megamix Crackcorn GF 2K 7 Kinds BSCjanica rose maloloy-onNo ratings yet
- Obesity and Health: What Increases Your Risk of Obesity and How Does It Affect Your Health?Document11 pagesObesity and Health: What Increases Your Risk of Obesity and How Does It Affect Your Health?Susan LawrenceNo ratings yet
- Procedure: Student Copy - Foldable Fault Blocks 1 of 4Document4 pagesProcedure: Student Copy - Foldable Fault Blocks 1 of 4Jaimros RobiatoNo ratings yet
- PASTOR ProjectDocument4 pagesPASTOR ProjectJames StanfordNo ratings yet
- Gabions: Standard Sizes in Mesh 80mm, Wire Diameter 2.7mm Length M Width M Height MDocument1 pageGabions: Standard Sizes in Mesh 80mm, Wire Diameter 2.7mm Length M Width M Height MsohrabprNo ratings yet
- Iteam of WorksDocument19 pagesIteam of WorksJatin CoolNo ratings yet
- Ballou Inventory Throughput Curve ExampleDocument4 pagesBallou Inventory Throughput Curve ExampleAMIT AMBRENo ratings yet
- Speed Controller of Servo Trainer Part 2Document8 pagesSpeed Controller of Servo Trainer Part 2jameswattNo ratings yet
- Vacanta de VaraDocument5 pagesVacanta de Varadelia stoicaNo ratings yet
- HMS S Curve - Progress Update 29 Dec'18Document22 pagesHMS S Curve - Progress Update 29 Dec'18Ashadi AmirNo ratings yet
- Heriot-Watt University - Reservoir Engineering PDFDocument931 pagesHeriot-Watt University - Reservoir Engineering PDFLuis Alberto Colan Garcia100% (1)
- Paper Exam Subject Name Roll Number: State Service Mains Exam - 2022:: 07: Genral Studies - V 2228144910Document38 pagesPaper Exam Subject Name Roll Number: State Service Mains Exam - 2022:: 07: Genral Studies - V 2228144910Atul SinghNo ratings yet
- Fractions Decimals and Percentages WorkpackDocument9 pagesFractions Decimals and Percentages WorkpackDavid ReesNo ratings yet
- FV - Pitch Deck - Company NameDocument12 pagesFV - Pitch Deck - Company NameAman SaxenaNo ratings yet
- TIMO BRICKS PANEL LUAR BetulDocument19 pagesTIMO BRICKS PANEL LUAR Betuljamal kingsmanNo ratings yet
- Direct Manpower: Project Owner Location Scope of Works SubjectDocument2 pagesDirect Manpower: Project Owner Location Scope of Works SubjectMarivic D. SantosNo ratings yet
- Newage Roundness Correction Factors: Diameters of Convex Cylindrical SurfacesDocument2 pagesNewage Roundness Correction Factors: Diameters of Convex Cylindrical SurfacesIdan Zvi FriedbergNo ratings yet
- Material Estimation Description of Item No. Length of FT Width FT Height FT Dry FactorDocument4 pagesMaterial Estimation Description of Item No. Length of FT Width FT Height FT Dry FactorJahid HassanNo ratings yet
- Dan Majerle Half Court OffenseDocument7 pagesDan Majerle Half Court OffenseEdward MoralesNo ratings yet
- Template TwoDocument11 pagesTemplate TwoDaivick BhaskarNo ratings yet
- Dribble Drive Motion Offense - Fran Fraschilla PlaybookDocument10 pagesDribble Drive Motion Offense - Fran Fraschilla PlaybookIgnacioNo ratings yet
- PT Slab PDFDocument72 pagesPT Slab PDFLuis AhmedNo ratings yet
- Department of Civil Engineering Design of Pavements TCE675 Assignment No. 1Document1 pageDepartment of Civil Engineering Design of Pavements TCE675 Assignment No. 1Chetan ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Final EstimatesDocument445 pagesFinal EstimatesChristina Aguilar Dela VegaNo ratings yet
- English PTDocument3 pagesEnglish PTNiccolo Gerard NoverosNo ratings yet
- Metodo DovelasDocument3 pagesMetodo DovelasDiego Acosta QuirozNo ratings yet
- 7 2YieldCurveDocument4 pages7 2YieldCurveAbdul BasithNo ratings yet
- Technology Grade 8 2017 March Memo 1Document2 pagesTechnology Grade 8 2017 March Memo 1Nokuthula NdhlovuNo ratings yet
- Certificate III Acknowledgement IV V List of Figures VI List of Tables VIIIDocument3 pagesCertificate III Acknowledgement IV V List of Figures VI List of Tables VIIIrahulNo ratings yet
- Diagramas Painel 18-08Document2 pagesDiagramas Painel 18-08RibeiroRicardo191No ratings yet
- Philippines' Civil Service Professional Reviewer Answer KeyDocument7 pagesPhilippines' Civil Service Professional Reviewer Answer KeyDennis Aldwin Aguilar67% (3)
- Aluminum Structures: A Guide to Their Specifications and DesignFrom EverandAluminum Structures: A Guide to Their Specifications and DesignRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Thermowell MaterialsDocument2 pagesThermowell Materialswhite9013No ratings yet
- Rheological Properties and Microstructure of Fresh Cement Pastes With Varied Dispersion Media and SuperplasticizersDocument9 pagesRheological Properties and Microstructure of Fresh Cement Pastes With Varied Dispersion Media and SuperplasticizersBattsengel NomindelgerNo ratings yet
- Vedra Trade Services (VTS) ProfileDocument94 pagesVedra Trade Services (VTS) ProfileMathias OnosemuodeNo ratings yet
- Niir Soaps Detergents Disinfectants Technology HandbookDocument12 pagesNiir Soaps Detergents Disinfectants Technology Handbookjinnah143640% (1)
- Investigating The Action of Zeolite in Laundry DetergentDocument2 pagesInvestigating The Action of Zeolite in Laundry DetergenttamabietNo ratings yet
- PriceList 2022Document83 pagesPriceList 2022Hany GhanemNo ratings yet
- Caulking Compound and Sealants PDFDocument7 pagesCaulking Compound and Sealants PDFibrahim100% (1)
- Industrial Attachment Report On Micro Fibre GroupDocument125 pagesIndustrial Attachment Report On Micro Fibre GroupDigonto Das50% (2)
- TL 52622 en 07-2012Document12 pagesTL 52622 en 07-2012Juan Carlos Jaramillo LariosNo ratings yet
- Hi-Flo 6 Hi-Flo 9 Twin Hi-Flo 6 Twin Hi-Flo 9 Filters 1999 LineDocument34 pagesHi-Flo 6 Hi-Flo 9 Twin Hi-Flo 6 Twin Hi-Flo 9 Filters 1999 LineДмитрий ЧерныхNo ratings yet
- Conbextra GP 0419Document4 pagesConbextra GP 0419Rabjan JaniNo ratings yet
- BasicDocument3 pagesBasicvivek singhNo ratings yet
- Deoflow - F - DogDocument2 pagesDeoflow - F - Dogex caliburNo ratings yet
- X Chem Book2018.LatestDocument69 pagesX Chem Book2018.LatestChayan SinhaNo ratings yet
- B. Arch. Sem-Ix Rar-902 Constructi0N & Materials-ViiiDocument4 pagesB. Arch. Sem-Ix Rar-902 Constructi0N & Materials-ViiiMAHAK GUPTANo ratings yet
- Concrete Specification (BS8500)Document3 pagesConcrete Specification (BS8500)teh100% (1)
- Shorts JUNE 2021Document26 pagesShorts JUNE 2021washington nyamandeNo ratings yet
- Aluminium PhosphateDocument3 pagesAluminium PhosphateanoopstudieNo ratings yet
- Compro KonveksiDocument15 pagesCompro KonveksiorsainstituteNo ratings yet
- Blood ExaminationDocument5 pagesBlood ExaminationDr Lalit Chandravanshi (SUSAH Associate Professor)No ratings yet
- L7 ViscoelasticityDocument17 pagesL7 ViscoelasticityjustmenobleskNo ratings yet
- Woven Fabric Formation Technique - Part 1Document29 pagesWoven Fabric Formation Technique - Part 1ramstexNo ratings yet
- TDS - Micro-Air 120Document3 pagesTDS - Micro-Air 120aahtagoNo ratings yet
- Roof DrainsDocument1 pageRoof DrainsAhmed RamzyNo ratings yet
- Wood Finishing-2017Document13 pagesWood Finishing-2017PauloSilvaNo ratings yet
- Naming Compounds 1 PDFDocument42 pagesNaming Compounds 1 PDFtherese angelieNo ratings yet
- Lauke 1994Document5 pagesLauke 1994lami75No ratings yet
- Заварување на P91 челик (труд)Document10 pagesЗаварување на P91 челик (труд)Kristijan AngelovskiNo ratings yet
- Turbine Parts MOC Blog 2Document15 pagesTurbine Parts MOC Blog 2kattukoluNo ratings yet
- Estimation of Protien by Lowry'S Method Aim PrincipleDocument20 pagesEstimation of Protien by Lowry'S Method Aim PrincipleSanaNo ratings yet