Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Nucleic Acid and Protein Synthesis
Uploaded by
Laurence PriscillaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Nucleic Acid and Protein Synthesis
Uploaded by
Laurence PriscillaCopyright:
Available Formats
Nucleic Acid & Protein Synthesis
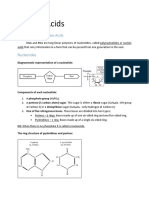
DNA or deoxyribonucleic acids are molecules that carries genetic information
macromolecule are also polymers, made up of many similar, smaller molecules joined
into a long chain.
DNA found in nucleus
DNA and chromosome have different structure
Dna is called molecule of life because dna is made up of protein
How DNA is organized in human cell:
DNA molecules consists of two parallel strands twisted around each other to form
double helix.
DNA wrapped around proteins to form a single chromatin thread
During cell division, chromatin threads coil tightly into structure called chromosome.
Smallest protein that made DNA is nucleic acid.
Basic unit of DNA is nucleotides, therefore nucleotides made up of:
Pentose sugar (deoxyribose utk dna, ribose utk rna)
Phosphate group
nitrogen containing base
Types of nitrogen base:
Adenine (A)
Cytosine (C)
Nucleic Acid & Protein Synthesis 1
Guanine (G)
Thymine (T)
Uracil (pengganti T di RNA)
Rule Pairing
1. Adenine always bond with thymine (A with T)
2. Guanine always bond with cytosine (G with C)
Differences between DNA and RNA:
DNA
1. made up of deoxyribose sugar
2. dna fixed ratio (nitrogen base semuanya 1)
3. contain thymine instead of uracil
4. insoluble
5. double strand
6. permanent
RNA
1. Made up of ribose sugar
2. contain uracil Instead of thymine
3. no fixed ratio
4. refers solubility, soluble
5. refers to strand, single strand
6. time period, temporary
DNA replication:
conservative
Nucleic Acid & Protein Synthesis 2
semi conservative
dispersive
related with inheritance during meiosis, semi conservative because there is the old one
from the parent and new one is because meiosis produce new characteristics
During meiosis it is a semi conservative because one of the helix comes form the
parents and the other helix is the one that is conserved from the parents
Nucleic Acid & Protein Synthesis 3
You might also like
- How Genes Work GENE - Biological Unit of HeredityDocument5 pagesHow Genes Work GENE - Biological Unit of HeredityAdonis Besa100% (1)
- What You'll Learn: You Will Distinguish Among Different Types of MutationsDocument35 pagesWhat You'll Learn: You Will Distinguish Among Different Types of MutationsSeemaNo ratings yet
- The Genetic Material-1Document48 pagesThe Genetic Material-1Windra TrivenNo ratings yet
- In-Depth Steps Towards Nucleic Acid and Protein SynthesisDocument21 pagesIn-Depth Steps Towards Nucleic Acid and Protein SynthesisGbenga AjaniNo ratings yet
- DR Linda Molecular BiosDocument73 pagesDR Linda Molecular BiosValency BathoNo ratings yet
- Expt. 7 Nucleic Acid WorksheetDocument9 pagesExpt. 7 Nucleic Acid WorksheetMary Ella Mae PilaNo ratings yet
- 1 Nucleic AcidsDocument11 pages1 Nucleic AcidsSafiya JamesNo ratings yet
- FHCG 4 - Nucleic Acids Gene ExpressionDocument58 pagesFHCG 4 - Nucleic Acids Gene ExpressionLeena AkhtarNo ratings yet
- Jeeheheb GRRDocument22 pagesJeeheheb GRRahhhyiNo ratings yet
- Biology Nucleic A-Level OCR NotesDocument11 pagesBiology Nucleic A-Level OCR Notestbrook2017No ratings yet
- X-Sheet 1 The Nucleus and DNA: Life Sciences X-SheetsDocument5 pagesX-Sheet 1 The Nucleus and DNA: Life Sciences X-SheetsYadhirNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Dna Structure and Dna ExtractionDocument8 pagesLesson 2 Dna Structure and Dna ExtractionGreatel Elijah TorregosaNo ratings yet
- Structure and Function of DNADocument27 pagesStructure and Function of DNAHaniya RijaNo ratings yet
- 2024 Term 1 NotesDocument30 pages2024 Term 1 Notesmakhensa345No ratings yet
- Dna StructureDocument32 pagesDna Structurealexagano4321No ratings yet
- Genetic MaterialDocument31 pagesGenetic MaterialANBC- 24- Safa AfreenNo ratings yet
- Molecular GeneticsDocument2 pagesMolecular GeneticsFaith YeNo ratings yet
- D - BW DNA & RNADocument2 pagesD - BW DNA & RNAWahaj MazherNo ratings yet
- Dna StructureDocument32 pagesDna StructureHONLETH ROMBLONNo ratings yet
- Dna Rna 11Document70 pagesDna Rna 11L CuevasNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acids Store and Transmit Hereditary InformationDocument28 pagesNucleic Acids Store and Transmit Hereditary InformationSerap BayramNo ratings yet
- Class 12-UNITS 3-4 NotesDocument4 pagesClass 12-UNITS 3-4 NotesDimas HernadyNo ratings yet
- Genetic Material Group 8Document13 pagesGenetic Material Group 8Jake Sta-anaNo ratings yet
- Genetic Control: By. Yasmine HadiastrianiDocument14 pagesGenetic Control: By. Yasmine HadiastrianiYasmine HadiastrianiNo ratings yet
- 6nucleic Acids - Boundless BiologyDocument15 pages6nucleic Acids - Boundless BiologyAmy SuarezNo ratings yet
- Basic Structures of Dna and Rna 2Document38 pagesBasic Structures of Dna and Rna 2Herajen DeadoNo ratings yet
- DNA Structure and ReplicationDocument12 pagesDNA Structure and ReplicationJhune Dominique GalangNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acid MetabolismDocument41 pagesNucleic Acid MetabolismPavani AkkalaNo ratings yet
- Nucleic-AcidDocument28 pagesNucleic-AcidIvan Jhon AnamNo ratings yet
- Cyto PL2Document17 pagesCyto PL2Danielle Anne Zamora-Matillosa LambanNo ratings yet
- Heredity and VariationsDocument18 pagesHeredity and VariationsLovely Syre LaysonNo ratings yet
- Case 1 SummeryDocument11 pagesCase 1 SummeryTtNo ratings yet
- Molecular Basis of InheritanceDocument21 pagesMolecular Basis of InheritancevidushivbpsNo ratings yet
- Guided Notes Lesson 4Document4 pagesGuided Notes Lesson 4Raine RagadioNo ratings yet
- First Aid Revised (Easiest Edition On Earth) @mueen - AhmadDocument2,144 pagesFirst Aid Revised (Easiest Edition On Earth) @mueen - AhmadAyub SadiqNo ratings yet
- Materi GenetikDocument3 pagesMateri GenetikAKMELIA NAJWANo ratings yet
- 3 - Structure of DNA, RNA, GenesDocument206 pages3 - Structure of DNA, RNA, GenesJustina VillageNo ratings yet
- Notes Chap 06Document21 pagesNotes Chap 06umamahfarooq75No ratings yet
- Week 10: November 15 - 19: MC 2: BiochemistryDocument6 pagesWeek 10: November 15 - 19: MC 2: BiochemistryMary Rose CuentasNo ratings yet
- 1.nucleic Acid Chemistry and Gene Manipulation IntroDocument85 pages1.nucleic Acid Chemistry and Gene Manipulation Introshruti shahNo ratings yet
- DNA Vs RNADocument28 pagesDNA Vs RNALeilani Joy Rivera GabitoNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acids: Structure and FunctionDocument45 pagesNucleic Acids: Structure and FunctionJahanzeb SafdarNo ratings yet
- Differences Between DNA and RNADocument6 pagesDifferences Between DNA and RNAGevo GegantoNo ratings yet
- 2.2. DNA RNA Transcr TranslatDocument35 pages2.2. DNA RNA Transcr TranslatClàudia VicenteNo ratings yet
- Dna and Rna StructureDocument26 pagesDna and Rna StructureVince Lenzer BeliganioNo ratings yet
- DNA and Genes PDFDocument29 pagesDNA and Genes PDFJerick Carbonel Subad100% (1)
- Nucleic Acids Fact SheetDocument1 pageNucleic Acids Fact Sheetasieee chimmyNo ratings yet
- Nucleic AcidDocument9 pagesNucleic AcidAjagu ChukwuebukaNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio 3rd QuarterDocument6 pagesGen Bio 3rd QuarterzafmustaphaNo ratings yet
- Dna Rna-101Document30 pagesDna Rna-101Hazel SioseNo ratings yet
- Cell CycleDocument23 pagesCell Cyclefrank menshaNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acids: DefinitionsDocument9 pagesNucleic Acids: DefinitionsMohammed RagabNo ratings yet
- HDTD-B-9 - Molecular Genetics IDocument25 pagesHDTD-B-9 - Molecular Genetics IMariam QaisNo ratings yet
- 2.3. Nucleotides and Nucleic AcidsDocument4 pages2.3. Nucleotides and Nucleic Acidsstu.suman-iftikharNo ratings yet
- Nucleiuc AcidDocument18 pagesNucleiuc AcidJunelle Ramos AquinoNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acids.Document18 pagesNucleic Acids.kasingabalyaandrewNo ratings yet
- Genetic Research PaperDocument10 pagesGenetic Research PaperDev raj regmiNo ratings yet
- DNA and RNADocument23 pagesDNA and RNAHazel SioseNo ratings yet
- DNA Vs RNADocument2 pagesDNA Vs RNAMegat AmirulNo ratings yet