100% found this document useful (1 vote)
3K views4 pagesPharmacy Management System Class Diagram
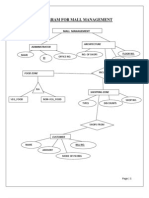
This document discusses the theory behind class diagrams in UML and how to represent different relationships between classes in a class diagram. It explains that a class diagram shows classes, interfaces, associations, and constraints. It also describes how to represent inheritance, simple association, aggregation, composition, and dependency relationships between classes using different symbols. The document provides details on how to denote visibility and multiplicity of attributes and operations in a class diagram.
Uploaded by
Satyam SinghCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
100% found this document useful (1 vote)
3K views4 pagesPharmacy Management System Class Diagram
This document discusses the theory behind class diagrams in UML and how to represent different relationships between classes in a class diagram. It explains that a class diagram shows classes, interfaces, associations, and constraints. It also describes how to represent inheritance, simple association, aggregation, composition, and dependency relationships between classes using different symbols. The document provides details on how to denote visibility and multiplicity of attributes and operations in a class diagram.
Uploaded by
Satyam SinghCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
- Experiment Details
- UML Concepts
- UML Diagram
- Assessment Sheet