Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Budget Analysis Activity PDF
Uploaded by
api-685545642Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Budget Analysis Activity PDF
Uploaded by
api-685545642Copyright:
Available Formats
Name
Budget Analysis Activity
Read through the 3 budget scenarios below. With a partner, discuss each scenario and answer
the questions on the last page of the document. Turn in ONE document per partnership on
Canvas. Be sure to type both names at top of page.
Josh is a senior in high school and works 30 hours per week at a neighborhood coffee shop. His
net income after taxes is $1,500 and he is saving up for college. He owns a car and makes
payments toward it each month, but he lives with his parents so he saves on rent, utilities and
food costs. He occasionally goes out with friends and buys things for himself, but he tries to
hold back on these things so he can save more for college next year.
Below is Josh’s estimated budget and what he actually spent in one month’s time. Analyze his
spending to see why he is not on track to meet his goal and determine what he can do to get
back on track.
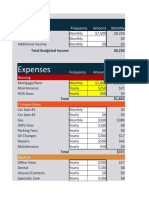
Budget Actual
Fixed Expenses
College Savings $870 $820
Car Payment $125 $125
Car Insurance $95 $95
Cell Phone $85 $85
Variable Expenses
Gas $100 $105
Entertainment $50 $75
Personal Shopping $50 $95
Occasional Spending (gifts, repairs, etc.) $100 $100
Total $1,475 $1,500
Name
Molly just graduated from college and accepted her first job as a social media manager for a
real estate company. Her monthly net income will be $3,000. She just moved into a one-
bedroom apartment, so she is responsible for rent, utilities, food and other household
expenses. She is paying off a student loan and she wants to save as much money as she can to
buy a house someday. She owns a car and enjoys going out with friends on the weekend.
Below is Molly’s estimated budget and what she actually spent in one month’s time. Analyze
her spending to see why she is not on track to meet her goal and to determine what she can
do to get back on track.
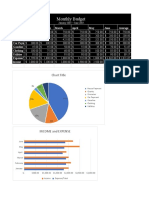
Net Income: $3,000/month
Budget Actual
Fixed Expenses
Savings for House $450 $150
Rent $600 $600
Car Payment $350 $350
Car Insurance $150 $150
Internet/Cable TV $110 $110
Cell Phone $75 $105
Student Loan $300 $300
Variable Expenses
Gas $100 $175
Food $250 $300
Entertainment $100 $250
Personal Shopping (clothes, makeup, home items etc.) $75 $300
Utilities $200 $275
Occasional Spending (gifts, repairs, etc.) $150 $250
Total $2,910 $3,315
Name
Nathan is a junior in high school. He works 15 hours a week at the mall, and his net income
after taxes is $600 a month. He lives with his parents, so he doesn’t have rent, utility or food
expenses. His older brother owns a car and lets him borrow it to drive to work for $50 each
month; otherwise Nate takes the bus. He really wants to buy a car, so he puts any leftover
money toward savings. Nate also pays for his cell phone and personal expenses, such as going
to the movies, buying video games and purchasing gifts.
Below is Nathan’s estimated budget and what he actually spent in one month’s time. Analyze
Nate’s spending to determine why he is not on track to save for that new car, and what
changes he can make to get on track.
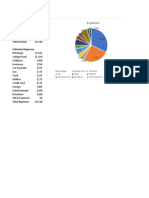
Net Income: $600/month
Budget Actual
Fixed Expenses
Savings for a Car $100 $0
Cell Phone $75 $100
Car Payment to his Brother $50 $100
Variable Expenses
Public Transportation $50 $60
Entertainment $50 $65
Personal Shopping $50 $175
Occasional Spending (gifts, repairs, etc.) $25 $100
Total $400 $600
1. What is Josh’s budget variance?
Name
-$25
2. What is Molly’s budget variance?
-$405
3. What is Nathan’s budget variance?
-$200
4. Develop a SMART goal for each of the budgeters. Record below:
• Josh’s SMART goal:
Spend less on variable expenses
No budget variance
Less on entertainment
Only must cut down for a couple months
Short term
• Molly’s SMART goal:
Spend less on variable expenses
Less of a budget variance
Less on personal shopping
Only must cut down for a couple months
Short term
• Nathan’s SMART goal:
Spend less on variable expenses
Less to no budget variance
Less on personal shopping
Only must cut down for a couple months
Short term
5. Which budget is the most successful in meeting the budgeters’ goals? Why?
Josh’s, because he has the lowest variance.
6. What adjustments could be made to each budget so the budgeters’ goals could be met sooner?
He could take $25 out of his actual entertainment.
You might also like
- Financial statements activityDocument2 pagesFinancial statements activityAditya Nigam100% (1)
- IWT Conscious Spending Plan 2023Document12 pagesIWT Conscious Spending Plan 2023GEO654No ratings yet
- Moneyunder30 Free Budget v2.1Document51 pagesMoneyunder30 Free Budget v2.1Sarah NyenkeNo ratings yet
- Uvo O. Motion To Vacate DefaultDocument5 pagesUvo O. Motion To Vacate DefaultMarcy AbitzNo ratings yet
- Budget Analysis ActivityDocument4 pagesBudget Analysis Activityapi-685760092No ratings yet
- Budget Analysis ActivityDocument4 pagesBudget Analysis Activityapi-627144387No ratings yet
- Budget Analysis PDFDocument5 pagesBudget Analysis PDFapi-626791287No ratings yet
- Budget Analysis Activity-1 Kaitlyn NealDocument5 pagesBudget Analysis Activity-1 Kaitlyn Nealapi-627152429No ratings yet
- Monthly Cash Flow EX Ercise: Use The Following Scenario Cards To Fill Out The Monthly Cash Flow Statement WorksheetDocument2 pagesMonthly Cash Flow EX Ercise: Use The Following Scenario Cards To Fill Out The Monthly Cash Flow Statement WorksheetNafa FadilaNo ratings yet
- Budget Template: Monthly Income Monthly ExpensesDocument1 pageBudget Template: Monthly Income Monthly ExpensesipasetiNo ratings yet
- 1 Math 9 Startup AssignmentDocument8 pages1 Math 9 Startup Assignmentstephanie.rcNo ratings yet
- Projected Budget Spreadsheet 1Document10 pagesProjected Budget Spreadsheet 1Ismail UsmanNo ratings yet
- Budget Worksheet: Career Graphic DesignerDocument5 pagesBudget Worksheet: Career Graphic DesignerArkoNo ratings yet
- Monthly College Expense BudgetDocument4 pagesMonthly College Expense BudgetYaseen Al-QadasiNo ratings yet
- Budgetingtemplate 1Document2 pagesBudgetingtemplate 1api-593642356No ratings yet
- Gabrielle's BudgetDocument3 pagesGabrielle's BudgetRH - 10PS 790469 Streetsville SSNo ratings yet
- Monthly Budget WorksheetDocument2 pagesMonthly Budget Worksheetapi-534083600No ratings yet
- Goals and financial plans for retirement, education, and home purchaseDocument5 pagesGoals and financial plans for retirement, education, and home purchaseChintu WatwaniNo ratings yet
- Family BudgetDocument2 pagesFamily Budgetapi-532124283No ratings yet
- Roxas MP6Document1 pageRoxas MP6josh lagdaminNo ratings yet
- State Income: Post College Budget WorksheetDocument4 pagesState Income: Post College Budget Worksheetapi-397100309No ratings yet
- Budget SheetDocument6 pagesBudget Sheetapi-660331252No ratings yet
- Home BudgetDocument6 pagesHome Budgetapi-316937239No ratings yet
- Budgeting Basics: A Companion Guide To Keeping It Real: How To Get The Support You Need For The Life You WantDocument20 pagesBudgeting Basics: A Companion Guide To Keeping It Real: How To Get The Support You Need For The Life You WantAngelo HuligangaNo ratings yet
- My College Budget 1Document1 pageMy College Budget 1BrahmanaNo ratings yet
- Don and Daisy BudgetDocument2 pagesDon and Daisy BudgetRH - 10PS 790469 Streetsville SSNo ratings yet
- Budget Worksheet: Number of Members in Your Household 6Document6 pagesBudget Worksheet: Number of Members in Your Household 6api-377100979No ratings yet
- Career BudgetDocument1 pageCareer Budgetapi-435326846No ratings yet
- Income Amounts Expenses Amounts Monthly Savings Yearly SavingsDocument12 pagesIncome Amounts Expenses Amounts Monthly Savings Yearly SavingsTyandTeresa NixonNo ratings yet
- DrewDocument14 pagesDrewapi-457175113No ratings yet
- Cicero 6Document5 pagesCicero 6Bryan CiceroNo ratings yet
- Traditional-College-Student 3 - 2 1 6Document6 pagesTraditional-College-Student 3 - 2 1 6api-735540493No ratings yet
- Budget Worksheet: Number of Members in Your Household 2Document6 pagesBudget Worksheet: Number of Members in Your Household 2api-377088908No ratings yet
- Couples BudgetDocument6 pagesCouples BudgetIzamar RiveraNo ratings yet
- Where's My Money Going? Spending Log: $$ Out $$ in Date Description StoreDocument38 pagesWhere's My Money Going? Spending Log: $$ Out $$ in Date Description StorePro ResourcesNo ratings yet
- Personal Budget Spreadsheet 10 2020-2 2Document4 pagesPersonal Budget Spreadsheet 10 2020-2 2api-685542779No ratings yet
- Lagdamin MP6Document2 pagesLagdamin MP6josh lagdaminNo ratings yet
- Budget ProjectDocument6 pagesBudget Projectapi-698801018No ratings yet
- Family ExpensesDocument2 pagesFamily Expensesapi-531444255No ratings yet
- Trevor Kernan - LifeHappensDocument3 pagesTrevor Kernan - LifeHappensTrevor KernanNo ratings yet
- The Art of Personal Finance Budget Project Worksheet - IncomeDocument7 pagesThe Art of Personal Finance Budget Project Worksheet - Incomeecauthor5No ratings yet
- Untitled Spreadsheet-3Document3 pagesUntitled Spreadsheet-3api-434964251No ratings yet
- Expenses Per Month Type of Expense (Fixed or Variable) : Budget Performance TaskDocument3 pagesExpenses Per Month Type of Expense (Fixed or Variable) : Budget Performance TaskKrystal ZhangNo ratings yet
- Maguirre BDocument6 pagesMaguirre Bapi-735267339No ratings yet
- Bookkeeping Basics: Name - Block - DateDocument12 pagesBookkeeping Basics: Name - Block - DateMaria AparicioNo ratings yet
- BudgetDocument66 pagesBudgetBrian MenzieNo ratings yet
- PaulosDocument8 pagesPaulosapi-638325728No ratings yet
- Transition PlanDocument2 pagesTransition Planapi-641176810No ratings yet
- Budget Template: Monthly Income Monthly ExpensesDocument1 pageBudget Template: Monthly Income Monthly ExpensesJuridic nortekNo ratings yet
- Student Budget Plan 1Document2 pagesStudent Budget Plan 1api-515880411No ratings yet
- Budget Worksheet For ProjectDocument6 pagesBudget Worksheet For Projectapi-659586586No ratings yet
- Budget DoneDocument6 pagesBudget Doneapi-695864872No ratings yet
- Traditional AdultDocument6 pagesTraditional Adultapi-699037645No ratings yet
- Family Budget 3Document2 pagesFamily Budget 3api-531481708No ratings yet
- Financial Literacy-Student Guide (7) 8Document8 pagesFinancial Literacy-Student Guide (7) 8Sandra- MarroquinNo ratings yet
- Traditional College Student Budget WorksheetDocument20 pagesTraditional College Student Budget WorksheetManishTewaniNo ratings yet
- 1.09 - Jackson Combass 09.22.2023Document5 pages1.09 - Jackson Combass 09.22.2023jackson combassNo ratings yet
- Budget Sheet For Economics Project 2Document6 pagesBudget Sheet For Economics Project 2api-735280131No ratings yet
- Budget ProjectDocument10 pagesBudget Projectapi-356220742No ratings yet
- Get Smart About MoneyDocument11 pagesGet Smart About MoneyJ.A.MorganNo ratings yet
- The Young Adult's Guide to The Galaxy - The Young Adult's TextbookFrom EverandThe Young Adult's Guide to The Galaxy - The Young Adult's TextbookNo ratings yet
- Nepal ProjectDocument56 pagesNepal ProjectSubash SilwalNo ratings yet
- 5 Marks - House PropertyDocument188 pages5 Marks - House Propertyjashwant yadavNo ratings yet
- Florida Housing's Homebuyer Loan ProgramsDocument1 pageFlorida Housing's Homebuyer Loan ProgramsAnwar BrooksNo ratings yet
- IOB's New NPA Recovery Policy 2011-12Document56 pagesIOB's New NPA Recovery Policy 2011-12Nithya Ganesh75% (4)
- Effect of Monthly Income on Car Loan ChoiceDocument11 pagesEffect of Monthly Income on Car Loan ChoiceNubasyer QallinsmanNo ratings yet
- Balance Sheet of WiproDocument3 pagesBalance Sheet of Wiproishit9No ratings yet
- Banking QPDocument5 pagesBanking QPDeepthi NivasiniNo ratings yet
- South Bay Digs 7.5.13Document107 pagesSouth Bay Digs 7.5.13South Bay Digs100% (1)
- Contemporary Issue in StrategyDocument13 pagesContemporary Issue in Strategypatrick wafulaNo ratings yet
- Exercise PF Chapter 2Document3 pagesExercise PF Chapter 2Duy Trần TấnNo ratings yet
- Charge Type Home Loan (INR) Non Home Loan (INR)Document1 pageCharge Type Home Loan (INR) Non Home Loan (INR)NISHA BANSALNo ratings yet
- NHB Vishal GoyalDocument24 pagesNHB Vishal GoyalSky walkingNo ratings yet
- 04 Receivables - Additional DrillsDocument2 pages04 Receivables - Additional DrillsRazel MhinNo ratings yet
- Rbi DiscussionDocument3 pagesRbi DiscussionSanjeev KhanNo ratings yet
- SBI Education Loan For Abroad StudyDocument14 pagesSBI Education Loan For Abroad StudyGurbani Kaur SuriNo ratings yet
- What is a Kisan credit card? Everything you need to knowDocument5 pagesWhat is a Kisan credit card? Everything you need to knowbhaskar sarmaNo ratings yet
- Ingles Taxation Two CompleteDocument151 pagesIngles Taxation Two Completevelasquez0731No ratings yet
- Why Companies Choose Corporate Bonds Over Bank LoansDocument31 pagesWhy Companies Choose Corporate Bonds Over Bank Loansতোফায়েল আহমেদNo ratings yet
- 34 Ruiz v. Court of AppealsDocument1 page34 Ruiz v. Court of AppealsJanWacnangNo ratings yet
- Agriculture Lending ProcessDocument3 pagesAgriculture Lending ProcessShubham ParmarNo ratings yet
- Retirement PlanningDocument27 pagesRetirement Planningvinodkp1947100% (1)
- National Power Corporation vs. The Court of AppealsDocument17 pagesNational Power Corporation vs. The Court of AppealsSam AndresNo ratings yet
- 5 Bank Lending PrinciplesDocument4 pages5 Bank Lending PrinciplesManu DhuparNo ratings yet
- The Role of The Commercial and Development Banks in Nigeria As Recognised Under The LawDocument9 pagesThe Role of The Commercial and Development Banks in Nigeria As Recognised Under The LawSeedu ElijahNo ratings yet
- Asia Academic School, IncDocument3 pagesAsia Academic School, IncZahra Margrette SchuckNo ratings yet
- Request For Proposal (RFP) : Implementation of Cloud Based Loan Management SystemDocument25 pagesRequest For Proposal (RFP) : Implementation of Cloud Based Loan Management Systemanubalan100% (1)
- JSB Cargo and Freight Forwarder (P) LTD v. State and Anr.Document28 pagesJSB Cargo and Freight Forwarder (P) LTD v. State and Anr.Rakshit GuptaNo ratings yet
- BPI FAMILY SAVINGS BANK v. St. MichaelDocument2 pagesBPI FAMILY SAVINGS BANK v. St. MichaelNicki Vine CapuchinoNo ratings yet
- Income From Other SourcesDocument31 pagesIncome From Other SourcesNeeraj AgarwalNo ratings yet