0% found this document useful (0 votes)
741 views1 pageConcept Map Group 2
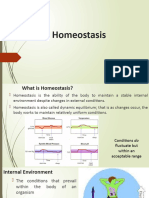
Homeostasis refers to the body's ability to maintain stable internal conditions despite external changes. Receptors detect changes in physiological variables like temperature and blood pressure. Control centers like the brain receive this information from receptors and determine an appropriate response. Effectors such as muscles and glands then enact changes to restore the variable to its optimal range and maintain homeostasis.
Uploaded by
mike jesterCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
741 views1 pageConcept Map Group 2
Homeostasis refers to the body's ability to maintain stable internal conditions despite external changes. Receptors detect changes in physiological variables like temperature and blood pressure. Control centers like the brain receive this information from receptors and determine an appropriate response. Effectors such as muscles and glands then enact changes to restore the variable to its optimal range and maintain homeostasis.
Uploaded by
mike jesterCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd