0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes) 8K views40 pagesPhysics Record Class 12
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content,
claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online on Scribd
Date
INDEX
Pariulars/ Experiment
[Page No|
Remarks
versus current:
atu. Ke
Scanned with CamScanner
A balbery elnino a key a rheostat,an_ammete
a_volkmecker, ¢
screw guage
ory:
Ohm's law states tha th weurrenk @ flowing
ur nical _sbeai constant -�ee
Model Graph:
7
v (volts) —+
Observations:
LC of Ammeter = 0-05 4
LC of voltmeter + Ol v
<
Length of the given wire :
From v-I graph
Slope of AG* tane = av
ar
Slope AB = ®
Ae '3h-5 cm
2854107
m
8 + Battery
K> key
Rh - Rheostat
R-Resistance wil
I> Current:
Dae: jt
I= Current through i conalbdbor (in)
iq] of the wire is
Scanned with CamScanner
R — Resistance of the given wire
#— radius of the wire (in m)
L— Length of ke wire (in m)
Pro se 3
}e
up thé circvit as per the ctrevit diqgram-
‘IClose_the key
Adjust Rheostat knob
‘[Nobe volbmeber and ammeter readings from the
respective meters.
Find R= v_ value
1 7
Repeat steps 3 Z b to et a few sets of readings
‘Note the length o f resistance wi'r
Plok v=z graph and find its slope to get valu.
2�F icall
Also measure the diameter of the wire with
Ww &_ different :
Precautions:
Connections
Volkmeter should be connected in a bo the
Scanned with CamScanner
resistance coil and ammeter should be connecta
in_serles bo the resistance coil:
The volbmeber and ammeter should be of proper
range and their readings should be carefully noted
4
The connecting wires, should be thick copper
wiees
neadings bo avoid a ing
The length of the wire should be measured
guvrakely +
sulk:
the v-1 relationship is established by ohm’.
jw experiment and js verified to be brue-
The v-I graph is plotted and is verified to be
rve-and sloping upwards
The value of + nee coil�Specific resistance of material
Pe Rie
it
a
of the wire i's
Scale
Y axis 2ctn=0-25unit
a Kaxiseiem=
3
a
os
o2 Om of Okt
Current [Amperes@)] —>
See ty i
|
|
|
|
Scanned with CamScanner
|
ePTEPATTTTTTT�TT]
i |
|
bh i Fath
| HET |
| | feb fda be} |
| I fe. {|} [| | |
R42 : - : |
eR
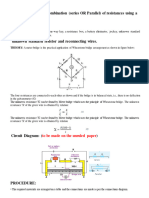
Mai�Circuib diag rqm-
AC + im wire
BE Batlery
k— Key’
X— Unknown resistance
R-B—> Resistance box
G— Galvanometer
I Jockey
owe: py
EXPERIMENT No: 2
Air :-
using a metre bridge-
requir
Metre bridge, standard sesistance box, jockey key
galvanometer, istance coil,
Scanned with CamScanner
Theory: + D .
Tt works on wheatsbenes network principle:-
i te ii
Gas 1 ; a5
where» P.9,R and § ar
various arms of the bridge-
Formula:
Zakoown resistance of the coil
x= ps
100-2
where.
X—+ Unknown resistance of coil @)�Observation:
The length of #
Tabular Column -
Dee J
3
he wire UD + 345 em 7} = tnoun resistance @
tf Bealancing length md.
: s
P; lyre = 9
unknown tl arrange all =
wha diagram : Z 3
3 2l| Connect the yokuiolun resistance (X) in the lefl ©
0890 gap and the resistance box in the right gap 8
a5 | 334 34h | 656 | home Connect the battery through a key across AC
at 2 aes | F385 | 081 and a galvanometer between 8 and J:
20-4 | 208 | aoe | #44 | 10st 4:1 Check connections, by keeping the jockey at two
155 | IFS | abs | 83S 0-988 extremes A and C-« -
12 | th) | 13h, | Bbw | 07928 ll Adjust value of R so that when jockey ts moved
ws 122, B48 | 0-972 overs the wire the. deflection. in_ the_galvqnometer
i +2_| 88-8 | 1-009 Deceimes. 2end =
Mean x+ | 0-994 2 “ellRecord the values of R and length £ of the wire-
+| Repeat the previous observations by rncreasing
and decreasing the value of R by tor 2 ohm
8: Thy Sibi f the resistance box Rand the
nown resistance x gre interchanged and the
steps ave repeated again:
cautions:
‘|The connection:
neat and tight-�mest
Calculations * i - 2
“ e -Plugs in the resistance box should be bight &
= 3lek — §
Pru on) piarob com 3| Jockey should be moved gently over the wire - g
Aeyhlon oan 100-4-45:6em ae yyconnecking wires should be as shart as possible &
100-4+52-4cm 0.89.0 el Pa ; : a
r 2
ak ames Rey he a8 ay sulb : 3
: fi 220° g zi —€
estore Bo Teas, r Thi own resist 5
100-62 73. ti
(BT apenas Lost 40-994 2 3
R50 Xt SKS Roa K7 IBY A
Jeskgiey Bes Lels-qem 6
Oa ciate gle hae e = 0.9282 4
R70 ariaa@ lesan
LelaQem 7-8 Letter
100-t+87-8em 00-4 » 88-Bem + /-009.2�X. =>, Unknown. resistance -
R-B—> Resistance Box (.Known)
G = Galvanometer
Bin=>: Battery Eliminator
Panda— Left and veght gaps.
Series Combination
—emnatien x, xy
Scanned with CamScanner
‘stance bow
MMA—�48.5
45
X= 5.1
X2= 44h
64-6
60
5g
‘Scanned with CamScanner
ae |
No a plate the éevies combination of X,and >
eft idge�OKT +
i 1.1993
2-27
V5147
—
= Rb i
too-L Pie
= 0.6990+
soya, a
‘24027
ett
Xz RL 0:-1086;
Lgcsh | 5.02
~= 5X 50-55 5.04
49-5 51
= Salyer 10.24
Reo
1=6210m
100-4 = 31-50m,
1 =50.55¢m
100-d = 49-45.
% and X,iin series :
esp bid ai sok Rl Miah hp O.1024 +
= i5s0ly HEM nlal oo
: A154
= 10.39 a
26.05
{ qa 2-34)
cpert are
aleulakearmanad Experimental values
nearly equal.�Deflection in | Shunk
resistance
60-6)
60S)
60-45
60-36
Kee
(Rr6)0 40"
by_half-d.
lefleckion method and find its figure.
of merit
Apparatus Required:
|
Scanned with CamScanner
A western type galvanometer resistance box of
vange © -5000 ohm, resistance box of range 0-506 ohm
A batbery, Two one-way keys and connecting wires.
Theor *
The resistance of the galvahometer by half deflection
method i's given by,
Gs 8S
R-S
where g is the resrstance connected in series
with the galvanometer and § is the shuni resistance
Figure of merit K, is given as
o
west Pb
[ [eta] @
where 61's the deflectlon produced with
resistance & qnd & ts emf of the cell-
u“�CikculT DiAGRAMS.
Circuit. diagram for half-defl ection
method
Circuit diag ram for Figure of
merit:
/).
£ of galvanometer by half defl clon methad
Make 4 neqgb and ttght connections as shown In
circuit diagram and clean insulations of wires with
the help of sandpaper also check all the plugs and *
confirm that they are tight:
Now ‘ntroduce_q high resrstance (qbout S000 2) ii
the resigk 18, insert the
Scanned with CamScanner
Adjusi the value of R so that the deflection in
bhe galvanometer fs mgximum, even number ghd
within the scale-Record this valve of R and
deflection 6+ .
Now insert the key Ka glso and without changing
the value of &, adjust the valve of shunt resistance
S, so that the deflection in the galvanometer reduces
bo exactly half the valve @ ; ie-%/ note the valve
of § and ©
Repegt deps 3-5 thus more bimes by teking
different valves of R and adjusting § everytime.
emf of the batter:
help of the voltmeter _by conni cHng_the terminal
of the voltmeter with the sve of the battery�bee:
and _-ve oF voltmeter and
terminal of bathery-
t connections
[ieee degen neg
Totroduce 4 resi'stance R from resistance box an
insert the plugs in Key k, to get the deflectior
ein the gqlvanometer: Note the valves of R and
6
Now change the value of R From the resistance
Scanned with CamScanner
box_and_wribe the galvanometer deflection again
Repeat the steps 9-10 for 3 more observations
Precaybions:- .
All the connections should be neab,clean and
bight
All the plugs in both resistance boxes should be
Eight
First the high resistance from resistance bo,
shovld be introduced, then the bathery key K,
to
plug should b Inserted to qvoi
the galvannmeter:
the em-f of battery bust be constant
I
1 Tue of R shoviol_be targe as compared
to Ge�awe: j_y
8 000 eZ
—
The plugs of the resistance bozes may not be
clean and _ tight:
«the emf of the battery may not be constant
«|| the galvanometer divistons may not be equal:
Resulé =
Resistance of galvanometer = 60-5! A/div
Figure of _mecit = I-24 Aldiv
Scanned with CamScanner
14�Date:
o
2
€
&
§
nO
§
For vazious values of v ©
Focal length by plobting , =
a)u-v_ graph b) 3
Observations ;
servaclons: i
Required: B
ea [Asparatvs Required: —_____________g
The ough foca Gd ea Optical bench, convex lens lens holder screen,
object mabch box, metce scale etc:
! :
Tabular column e Fowmulg:
; : Focal length of.
s? object Image Lem | Len |fs uv om
distance (wen) distance vend] | Y ed
f= uv
1] 26 36 0038 |6027 15-09 sn
s sh 32 0-035 |o-03) 1494 where.
tale 30 10-033 | 0-033 u— object distance from the lens (incm)
* er ee i fe lens Ci
ay 15:09
Proce,
convex
Fitid_the rough focal length of the giv
the image of 4 bright and_
wall easurin. e dish
Ss�M4 Seale
+ 16m? 2-5 units
ems 25 unite
[Link] em >)
aes)
Scanned with CamScanner
slightly so that a cb
Woke the object distance (u) and_image distance&
Repeat the observations by changing the
image distance -
jong :-
oF
n
a of r
screen must lie on the same sbralght line
The scales baken on the x-qxis and y-ax/s
equal:
e 45° exactly
While drawing u-V_graph tak
[take four readings above 2e and four readings
below 2F value-
sult
|| The U-v_gzaph is _pl�graph:
___-3\| The focal length. of the given lens.
q) by v-v
b) by u-v ee = 15 om
Q by 1-1 graph | = 15-15 em
v
Calculations :-
Fe ov
dev
+ 30430 + 900 - 1 ae
deugn eee ,
Scanned with CamScanner�_—
:
Scanned with CamScanner
ay degree
|
y. Ns Using CONVEX LEN
OS lApparatus “Peguired: nn
oncave |. - xd wt Foc th], optice
bench, candle screen lens stand
Formula
+) combination _of lenses “Fe ov The focal fen
A fa» Fi em
vo fink
where, é
4
AN of lenses (in cm)
Sa SH ffied the rough focal length of the convex lens by
Obtaining the real image of 4 bright and distant
lobject on a white paper or a wall and meqsure
the distance bet nvex | ind the wi�oe rset.
| a
servation 3
Se tel length of the ae ith tI oF q metre rod: E
given convex lens by distant 2|Mount the convex lens on a lens stand B
object method (F) [For different object distances, find the corespond! &
image distance g
Jabular_column: y|Recosd the ‘observations in a tabular column 3
5:| Now, introduce the given concave lens and the &
focal length of co ) image. center of th 5
. lenses are sin. the sqme_Iim 8
object Image || For different ob ct distances Find the
Distance (uew)| distance (vem) rresponding image distances -
Ie ag
f a||Record the observations in the tqbular column-
18
20
aa
an,
20
19
Precqutio,
ah 18
Mean 1 = 2iWhile looking, For the im: Fo. 2
‘ combinatron the Field of view bezomes narrow
and image gets mi ust be taken
k
hi sll Obcesvations should be obkained with greab
F GI To locate position of image the eye mu. a
bovk 25�) fo Find focanl
length of combingtion
1018-21-02,
5719+ Fy om
o
fi
The focal length of given concave lens
2-19-74 om
AA
Scanned with CamScanner
Qo�Ape — equilateral glass pris
pq — incident ray
qr — refracted ray
RS — emergenb ray
i angle of incidence
e+ angle of emergence
d— angle of devig tion
A= angle of prism (60°)
Model_Graph :
Expegmens Nop
é
&
S
a
£
&
°
é
and Lo determine the refractive index of H's
materiql of glass prism: Also plot i-d grap ©
£
E
Apparatus Required: 8
lass prism
protractor, board pins, office pins, a sharp pointe
pencil, a ruler a graph sheet-
Foxmulg :
Refractive index, 4 « sin (A*2™)
sin Ala i
where
A= angle of prism (o*)
Dm angle of minimum deviation (in*)
rv Ure
-14Place the drawing ed oe on the laboratory table
and fix the sheet of white paper on the
d $+
2 Select the susface of prism to be used as base
au�Observation
Qosenvarier
‘Angle of the given prism =
Tabular column:
Angle of
ua)
60
@
incidence | Angle of deviation,
35°
40"
45°
50°
55°
Calculations
oo
43°
42
40°
al
4
43
°
Bo 0 ED os age (6240)
f
sina)
= sins
1532
0
flat
atest
and mark ib-
Place the base on the white sheet and drqw _
its outline-
th
After removi
of ibs sf
on
Now, draw 4 ray of light making 99 angle of 3
with the normal:
Fix_two alpins vertically on the drawn Ine q
Scanned with CamScanner’
least 5 om apart:
Place the ugh the
other face of the prism:
Fix two more alping vertically, such that they
coincide with the images of the earlter placed
ray a emer: aieat & fay:
The angle they make with each other, gives the
12|Record the abeesvalien in the tabylax
column.
13:|Repegt the above steps of varinvs angles of
incidence and record the observations:
22�wens. d= 43" iH) seh? | de yar
vi) i =60" , d= 4a°
Scanned with CamScanner�Seqle
em
Yaxis# 2cm
units
unit
The di tween
pins must b
least 5 em.
The angle of incidence must not be more than
O° or less than 30°.
:|A_shasp pencil cast be used to draw lines:
les
Scanned with CamScanner
‘The arrow heads as be drawn
In (i-d) graph a smooth curve should be drawn.
Result:
of deviation js studied using a gtass prism
and _i-d graph is_plobed:
23�Scanned with CamScanner
observation
Rough focal length of concave a
morro; f= lOcm. ( :
i C ‘ . he focal length of the given concave mivrar —
feu
= Fe
" usher
cm
¥. .
petee | ees {=> object distance from mirror (cro)
Sa pearey — image distance “fora mivror (cm)
eae f > focal length of mirror (crn)
0-045 |y656] 4. : t
0-041 1a.05@ | 10-�37
the rough facal lengta by holding
the given concave mirror tn the mirror
and_obtatn the sharp image of an
Scanned with CamScanner
eee
t the pstion afte cveen tn such
ar image is obtained on
The pole of the mivroy, abject and: screen
chould [ive én the same [ines
|�f
Iw els
afs 8)8 Ele
O tx =
RIS
nee
¢ y — * :
TERED SY pur parqoid sy ure Key sq [7
— 4-8 a_sesistor_and a capacitor -
paper
‘ Theory:
: A_vesistor, capacitor neta are two terminal
‘ 0 devices: A bransistor_ has three terminals gnd an IC
©) Diodes €) Integrated, cirwit has_minimum of erght legs-Most of 1 package have
=o
lust looking at the varfovs components +
m'| &
For identiffidg the bus termina) devites. the following
be utilised -
chardcteristics of component ma:
Resistor: when connected in q d-¢ drcvit, it shows a
constant current:
Capacitor: Wher connected in a dic clewib,a multimeter
32�Device
re,
Transistor .
gcitor, diode or resistor|
Both
Gin)
Toitfally + bub +
bo _zero-
exo_very quickly.
Diode: Only a
rrenk, ¢
lend marked Portis at a Hisher reat diode.
ts Forward biased it conducts -when reversed it
would not conduck-Note that the multimeter, +ve
terminal of battery ts connected to its commen
Scanned with CamScanner
terminal: Therefore the diode rs forward biased
when its p is connected te wmmon terming!-
rocedure: :
Look at th:
ene with maximum _no-of legs _j-e, more than 3 legs-
This compon: oul: ve I d_ its
legs are of flat metal strip such that the bip of
legs is thinner than the top:Thts component i's IC-
‘The component with 3 legs is a transistor -
be be
dlUse _q multimeter with selector switch tumed on
to position R for checking the continvity-The
on the multimeter as common and Pif such that
prove [metal ends are inserted in termingls marked.
the black one is in common and red probe is in P-
lon touching the #wo ends of the device to the two
33�There is @ continuity tm both the directions
[directly connected and reversed] the meter needle,
shows a definite detlectron the component is
vesistor-
il}
There is only unidirectional flow of current i-e when
probes are connected such that the metal tip of
black probe ig connected to the terminal of deflection
device marked +ve and _that of red probe bo common
“Scanned with CamScanner
erm inal, current flows but no current Flows on
reversing the polarity, then the component is a diode.
Observe whether the diode while conducting emits
light, iF it does not it 1 simply q diode, if ibemite
light ifs pight Emitting piode (eo |
When the device on connecting +0 the probes of the
vitimeter shows a full scqle deflection _Initiglly but
[the deflection decays 40, zero. valve with passag
of
Result: t
A diode LED, transistor, IC, resistor and 4
ME)�sroergent ray
PQRS — Glass slab
Li — Angle of incidence
Ze — Angle of refraction
Le—> Angle of emergence
Ld— tater: fourm ents
4 beam of light incident chlguely ania glass
slqb-
Apparatus Reguir.
R sheet of white paper glass slah, penci! drawing
‘Scanned with CamScanner
board wo thin long needles metre scale ete+
Theory: i
Refraction
Let PQRS be a glass slab «Consider a ray of light
AE entering the glass slab, so it bends towards
the normal cepresenbed by EF
The ray EF while travelling through the glass meets
the other Face se oF the slab and refracts into
alr_which is q rarer medium: Lt emerges out glong |
Fp, devighton quay from the normal.
Fp emergent ray
[th-té observed that
cident ra
emergent ray is parallel to
emergent ray is latecally displaced by a distance
d_from incident ray-�‘Scanned with CamScanner�5S en ——————
= |iateral Gon a ered ee
: , ;
oe fi cee displacement a] Fix the sheet of white paper on the drqwing
degree board with the help of drawin
g_ pins: Put the glass
la,
pencil -
al|Remove the slab from the sheet and draw a
Eraight ling with help of a ruler which intersect
the slab boundary at g and _£- Put the glass
slab back on its drawn boundary:
_3[Place one of the needle long the line AB and
look for its tmage on the other side Place the
° second needle in such a way that it coincides
with ‘enage of the first:
4iDraw a Fine line along the needle and remove
the slab and needle
S‘|Repeat the experime.
wise: Only the Iqteral displacement d’ will be
affected.
Scanned with CamScanner
esulé
tl Thé Tray of light emerging from q glass slab ts lit
to the incident light and is laterally displaced
The laterql dis
ith ing ein thickness of slqb-