Professional Documents
Culture Documents
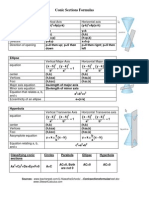
Parabola - Formulae
Parabola - Formulae
Uploaded by
Mustafa TalhaOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Parabola - Formulae
Parabola - Formulae
Uploaded by
Mustafa TalhaCopyright:
Available Formats
CH # 8: Parabola, Ellipse and Hyperbola
Parabola
*A parabola is the set of all points P in the plane which are equidistance from a fixed line (directrix) and a fixed
point (focus) in the plane.
Standard Parabola
Case 1: CUP - RIGHT PARABOLA
1. Vertex, V (0, 0)
2. Focus, S (a, 0)
3. End-Points of Latus Rectum,
L1, (a, 2a) and L2 (a, -2a)
4. Length of Latus Rectum, |L1L2| = |4a|
5. Equation of Directrix: x + a = 0
6. Equation of Parabola: y2 = 4ax
Case 2: CUP - LEFT PARABOLA
1. Vertex, V (0, 0)
2. Focus, S (-a, 0)
3. End-Points of Latus Rectum,
L1, (-a, 2a) and L2 (-a, -2a)
4. Length of Latus Rectum, |L1L2| = |4a|
5. Equation of Directrix: x - a = 0
6. Equation of Parabola: y2 = -4ax
Case 3: CUP - UP PARABOLA
1. Vertex, V (0, 0)
2. Focus, S (0, a)
3. End-Points of Latus Rectum,
L1, (2a, a) and L2 (-2a, a)
4. Length of Latus Rectum, |L1L2| = |4a|
5. Equation of Directrix: y + a = 0
6. Equation of Parabola: x2 = 4ay
Case 4: CUP - DOWN PARABOLA
1. Vertex, V (0, 0)
2. Focus, S (0, -a)
3. End-Points of Latus Rectum,
L1, (2a, -a) and L2 (-2a, -a)
4. Length of Latus Rectum, |L1L2| = |4a|
5. Equation of Directrix: y - a = 0
6. Equation of Parabola: x2 = -4ay
General Parabola
Case 1: Principal axis of parabola parallel to x-axis
1. Vertex, V (h, k)
2. Focus, S (h + a, k)
3. End-Points of Latus Rectum,
L1, (h + a, k + 2a) and L2 (h + a, k - 2a)
4. Equation of Directrix: (x – h) + a = 0
5. Equation of Parabola: (y – k)2 = 4a(x – h)
Case 2: Principal axis of parabola parallel to y-axis
1. Vertex, V (h, k)
2. Focus, S (h, k + a)
3. End-Points of Latus Rectum,
L1, (h + 2a, k + a) and L2 (h - 2a, k + a)
4. Equation of Directrix: (y – k) + a = 0
5. Equation of Parabola: (x – h)2 = 4a(y – k)
You might also like
- Conic Sections FormulasDocument1 pageConic Sections FormulasAmira Cato100% (2)
- Pre - Calculus (Stem)Document87 pagesPre - Calculus (Stem)Chris Tine Pacete86% (7)
- DemoDocument35 pagesDemoAnne Tricia AlmanzorNo ratings yet
- PC Parabola Part 2Document10 pagesPC Parabola Part 2gayle naldoNo ratings yet
- PTG 0116 Note 4.2 PDFDocument23 pagesPTG 0116 Note 4.2 PDFHuges ApolNo ratings yet
- 1 PRECAL Aug 9-13Document74 pages1 PRECAL Aug 9-13Timotei22 Abaya RoldanNo ratings yet
- ParabolaDocument17 pagesParabolaJamella P. MagoNo ratings yet
- Math B Reviewer ParabolaDocument4 pagesMath B Reviewer ParabolarosaNo ratings yet
- Conic Sections ParabolaDocument32 pagesConic Sections ParabolaPubgm JeroNo ratings yet
- 07 Parabola and Ellipse - Handouts PDFDocument28 pages07 Parabola and Ellipse - Handouts PDFMark ReyesNo ratings yet
- Detailed Revision Notes Conic Section: e C by Ax y XDocument53 pagesDetailed Revision Notes Conic Section: e C by Ax y XPiyKakdeNo ratings yet
- Maths PPT On Conic SectionDocument24 pagesMaths PPT On Conic SectionShubhrasmita Patel100% (1)
- TEKS A2 Unit 5 Lesson 3 - Writing Parabola EquationsDocument35 pagesTEKS A2 Unit 5 Lesson 3 - Writing Parabola EquationsJalizahNo ratings yet
- Parabola Theory EDocument16 pagesParabola Theory Ethinkiit100% (1)
- Chapter 1 Coordinate Geometry and Conic SectionsDocument17 pagesChapter 1 Coordinate Geometry and Conic SectionsAik0% (1)
- Week 5-ParabolaDocument10 pagesWeek 5-ParabolaNichole Balao-asNo ratings yet
- Parabola Basics and Shortcut FormulaDocument15 pagesParabola Basics and Shortcut FormulaNicole Isabelle BasmayorNo ratings yet
- Stem 1 - Pre Calculus: Lesson 3 - Conic Sections - ParabolaDocument12 pagesStem 1 - Pre Calculus: Lesson 3 - Conic Sections - ParabolaMary Jasmine AzulNo ratings yet
- Study Package: Subject: Mathematics Topic: Conic Section Parabola, Ellipse, HyperbolaDocument11 pagesStudy Package: Subject: Mathematics Topic: Conic Section Parabola, Ellipse, Hyperbolaharshit100% (1)
- Unit 4 PT 1 PT 4 Conic SectionsDocument7 pagesUnit 4 PT 1 PT 4 Conic Sectionssprinklesdb16No ratings yet
- Conic Section: Baliton, Mary Khristel Mateo, Nica Louisa Ronquillo, Deniece Semana, Llyra Zamora, JerichoDocument21 pagesConic Section: Baliton, Mary Khristel Mateo, Nica Louisa Ronquillo, Deniece Semana, Llyra Zamora, JerichoDeniece RonquilloNo ratings yet
- Precal - Lesson 3Document3 pagesPrecal - Lesson 3alayca cabatanaNo ratings yet
- Conic Section PDFDocument17 pagesConic Section PDFAjinkya Patil0% (1)
- Pre-Calculus Quarter 1 - Module 3: ParabolasDocument35 pagesPre-Calculus Quarter 1 - Module 3: ParabolasAbby Gayle Nacino88% (8)
- Circle and Parabola PDFDocument16 pagesCircle and Parabola PDFNoisekaiforyouNo ratings yet
- Parabola With Vertex at (H, K)Document16 pagesParabola With Vertex at (H, K)Coleen AldanaNo ratings yet
- Pre-Calculus Lesson 2: Jean B. Corpuz, LPT InstructorDocument24 pagesPre-Calculus Lesson 2: Jean B. Corpuz, LPT InstructorJean CorpuzNo ratings yet
- l5 Further Geometry2Document47 pagesl5 Further Geometry2Corrine ChanNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Conic Sections Part 1Document54 pages1.1 Conic Sections Part 1Robie Vasquez CamposanoNo ratings yet
- My LecturesDocument53 pagesMy Lecturesbanhus20No ratings yet
- Conic Sections: ParabolaDocument92 pagesConic Sections: ParabolaJR DevienteNo ratings yet
- Parabola Notes For IIT JEE - pdf-56 PDFDocument9 pagesParabola Notes For IIT JEE - pdf-56 PDFSubbu SarabuNo ratings yet
- Precalculus: Senior High School Grade 11Document28 pagesPrecalculus: Senior High School Grade 11Gerlie Jay-ann RamosNo ratings yet
- Conic SectionsDocument15 pagesConic SectionsParth KaushalNo ratings yet
- Parabola Chap PDF From RS AGARWALDocument10 pagesParabola Chap PDF From RS AGARWALMeenakshiNo ratings yet
- Unit1 Lesson3-ParabolaDocument45 pagesUnit1 Lesson3-Parabolachristine faith seducoNo ratings yet
- Conic Sections EquationsDocument11 pagesConic Sections EquationsMindy DyarNo ratings yet
- Deped Learning Activity Sheets (Las) Name of Learner: Grade Level: Section: Date: Pre-Calculus Parabola Week No. 2Document5 pagesDeped Learning Activity Sheets (Las) Name of Learner: Grade Level: Section: Date: Pre-Calculus Parabola Week No. 2Evangeline Martinez-FechalinNo ratings yet
- Conic Sections-A Figure Formed by Intersection of A Plane and A Right Circular ConeDocument20 pagesConic Sections-A Figure Formed by Intersection of A Plane and A Right Circular ConeJron Keith TuazonNo ratings yet
- 11.conic SectionsDocument14 pages11.conic Sections123saanvisinha6dNo ratings yet
- Obj. 28 Parabolas (Presentation)Document11 pagesObj. 28 Parabolas (Presentation)Sandra MillerNo ratings yet
- SPLM Analytic Geometry Part 2Document85 pagesSPLM Analytic Geometry Part 2Joey TelinNo ratings yet
- Analgeom. Parabola 2Document8 pagesAnalgeom. Parabola 2RiNo ratings yet
- Conic SectionsDocument39 pagesConic SectionsKalpana BhadouriaNo ratings yet
- Conic SectionsDocument40 pagesConic SectionsMariel Milan100% (1)
- Algebra 2 Chapter 7Document27 pagesAlgebra 2 Chapter 7April Anne FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Analyzing Conic Sections: Jennifer HussDocument27 pagesAnalyzing Conic Sections: Jennifer HussAlfred Navea100% (1)
- Parabola-01 - TheoryDocument21 pagesParabola-01 - TheoryRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- Parabola Week 2: Content StandardsDocument9 pagesParabola Week 2: Content StandardsJackylyn FalejoNo ratings yet
- Pre CalculusDocument11 pagesPre CalculusBea LouellaNo ratings yet
- Conic Sections - A Figure Formed by The Intersection of A Plane and A RightDocument8 pagesConic Sections - A Figure Formed by The Intersection of A Plane and A RightKenneth Anrie MoralNo ratings yet
- Conic Sections - ParabolaDocument19 pagesConic Sections - ParabolaFrederick ImperialNo ratings yet
- Parabola (TN)Document27 pagesParabola (TN)Raju Singh100% (1)
- Precal SHS 1 - W3Document4 pagesPrecal SHS 1 - W3Chaelin CLNo ratings yet
- Difference Equations in Normed Spaces: Stability and OscillationsFrom EverandDifference Equations in Normed Spaces: Stability and OscillationsNo ratings yet
- An Introduction to Linear Algebra and TensorsFrom EverandAn Introduction to Linear Algebra and TensorsRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Transformation of Axes (Geometry) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandTransformation of Axes (Geometry) Mathematics Question BankRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Ten-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesFrom EverandTen-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesNo ratings yet