Professional Documents
Culture Documents
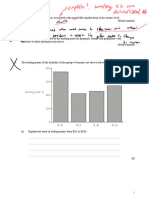
IGCSE 1 37to1 50DA Bondingexercise
Uploaded by
seth sheldrakeOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
IGCSE 1 37to1 50DA Bondingexercise
Uploaded by
seth sheldrakeCopyright:
Available Formats
iGCSE.DA.1.37-1.
50: Ideas on Structure and Bonding
Complete the sentences with appropriate words
Ionic Compounds
1. Ionic compounds are made from ..…………………………………… and …………………………………………….. elements reacting together
2. Ions are electrically charged particles with different numbers of electrons…………………………………. and ………………………………….
3. When atoms react to form ions, there is a Movement……………………………….. of electrons between the atoms
4. The positive……………………………………atoms lose electrons and the negative…………………………………….atoms gain electrons in the
process.
5. The metal ions formed are positively………………………………………..charged and the non-metal ions are
negatively…………………………………………charged
6. If an atom (M) with 12 protons reacts with an atom (X) with 6 protons, the symbols of the ions formed are magnesium……………
and carbon…………..
7. Ionic bonds are formed by strong electrostatic……………………………………….attractions between the positive…………………………and
negative………………………. ions
8. The structure of an ionic compound is a stable/solid……………………………..….arrangement of positive and negative ions
9. The properties of a typical ionic compound are:
a. High……………melting and boiling points, because of the strong electrostatic
attractions………………………………………………………………….between ions
b. Strong …………..strength because of the strong electrostatic attractions…………………..
…………………………………………………………………. between ions
c. Bad……………electrical conductors when solid because the atoms………………..are not free to move..………… ……
…………………and carry charge
d. Good……………electrical conductors when molten or solution because the atoms…………….can now freely
move…………….…….and carry charge
Covalent Compounds
1. Covalently bonded compounds are formed between non metal……………………………………………… and
metal…………………………………………..elements
2. A covalent bond is a shared………………..……..pair of electrons that hold together the two positive ions ……………………….
together
3. In forming covalent bonds, the atoms try to achieve full or empty Number…………………… Of shells…………………….. of
electrons
4. A covalent bond is a brittle…………………………… bond (takes a lot of energy to break)
5. Covalent compounds can exist as two structure types: molecular covalent and giant lattice………………. covalent structures
(giantmolecules)
6. In molecular covalent structures, the ions……………………….are held together by strong covalent bonds and the molecules are
attracted to each other by weak electrostatic forces………………………………………………….forces
7. In giantmolecules, all of the ions…………………….. are held together by strong electrostatic…………………………………………… bonds.
The atoms are arranged in a ……………………………….., three ………………………………..structure
8. Molecular compounds have:
a. Low…………………….melting & boiling points because of the weak electrostatic……………………………………forces between
ions……………………..
b. This means they very often exist as liquid ………………..……………. or gas………….………………… (states of matter)
c. They are weak…………………….and easy to break…………………………….when solids because of the weak…………………………
intermolecular forces
d. They are bad………………..conductors of electricity in any state. There are no atoms ……………………………….. which are
free to move
9. Giantmolecular structures have
a. Very high …………… melting and boiling points because all the atoms ae joined by
electrostatic……………………………………………………bonds
b. Are very strong………………….. and brittle…………………….. if hit with a hammer because of the structure
c. Are soluble…………………………………. In any solvents
d. Are very bad ………………………………conductors of electricity in any state (exception graphite …………………………………)
General
What is the name of the compounds and type of structure (ionic or covalent) formed from the following elements
1. Copper and chlorine makes copper chloride……………………………………………………which is a covalent ……………………………………
structure
2. Magnesium and oxygen makes magnesium oxide …………………………………………………………….which is a covalent
…………………………………………….structure
3. Phosphorus and bromine makes phosphorus bromide …………………………………………………………… which is a
covalent……………………………………structure
4. Silicon and oxygen makes silicon oxide ………………………………………………………………….. which is a covalent ……………………………………
structure
You might also like
- CHAPTER 5-Modul Bimbingan SPMDocument11 pagesCHAPTER 5-Modul Bimbingan SPMNovah GurulooNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure and Chemical BondingDocument5 pagesAtomic Structure and Chemical BondingKOVLEEN SAHNINo ratings yet
- 5 Chemical BondsDocument10 pages5 Chemical BondsNor Fairul Bin SudarmanNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 5 Chem BondDocument6 pagesTutorial 5 Chem BondaribniminnakNo ratings yet
- Waja Chemistry Chapter 2: Structure of The AtomDocument10 pagesWaja Chemistry Chapter 2: Structure of The AtomChewfun KhooNo ratings yet
- 3.4 Electrolytic and Voltaic CellsDocument3 pages3.4 Electrolytic and Voltaic CellsSY ChowNo ratings yet
- Wrap Up 1 Lesson 1 Chemical Combination: Question OneDocument2 pagesWrap Up 1 Lesson 1 Chemical Combination: Question OneMohamed AitaNo ratings yet
- Prep 1 Classes PracticeDocument2 pagesPrep 1 Classes PracticeMohamed AitaNo ratings yet
- Unit One Lesson One: Matter and Its Characteristics: 1-Write The Scientific TermDocument19 pagesUnit One Lesson One: Matter and Its Characteristics: 1-Write The Scientific TermAshraf SakerNo ratings yet
- Module 606Document20 pagesModule 606Hema LataNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5: Chemical Bonds: A Formation of Compounds Learning OutcomesDocument9 pagesChapter 5: Chemical Bonds: A Formation of Compounds Learning OutcomesWong Wai Lun100% (1)
- Science Booklet M1U1Document20 pagesScience Booklet M1U1Muhammad MotaweaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Chemical Bond 1Document9 pagesTutorial Chemical Bond 1Izhan 7658No ratings yet
- WS2.1 The AtomDocument1 pageWS2.1 The AtomAjmain AmainNo ratings yet
- F4 Che C5 ExeDocument11 pagesF4 Che C5 ExeVulcan Chong100% (1)
- GCSE C2 Revision + Exam Questions (1) - Chemi-BondingDocument35 pagesGCSE C2 Revision + Exam Questions (1) - Chemi-BondingPrincess KimNo ratings yet
- 1st Prep - Final RevDocument25 pages1st Prep - Final RevGaber HassanNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reactions WorksheetDocument4 pagesChemical Reactions WorksheetVictoria LowmanNo ratings yet
- 2 Bonding SADocument9 pages2 Bonding SA장채윤No ratings yet
- c2 Higher Revision Questions - Sets 12 3 Higher Tier OnlyDocument110 pagesc2 Higher Revision Questions - Sets 12 3 Higher Tier Onlyapi-320022467No ratings yet
- Name Class: 10-IGCSE Date: Topic: MetalsDocument6 pagesName Class: 10-IGCSE Date: Topic: MetalsNamrata MaheshwariNo ratings yet
- HighSchool-Chemistry G10 To G12Document444 pagesHighSchool-Chemistry G10 To G12patkhsheng@hotmail.com100% (1)
- Copia de Practica Segundo Parcial MecaDocument2 pagesCopia de Practica Segundo Parcial MecaNelson Benjamín Albornoz RissoNo ratings yet
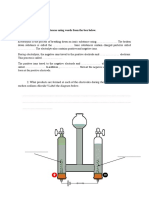
- Electrolysis Worksheet 1: 1. A) Complete The Sentences Using Words From The Box BelowDocument1 pageElectrolysis Worksheet 1: 1. A) Complete The Sentences Using Words From The Box BelowMenaga A/P IlangkovanNo ratings yet
- 2 The Structure of The Atomic StructureDocument9 pages2 The Structure of The Atomic StructureSiti NursahidahNo ratings yet
- مذكرة اسئلة شاملة فى Science للصف الاول الاعدادى اللغات الترم الاول -الامتحان التعليمىDocument23 pagesمذكرة اسئلة شاملة فى Science للصف الاول الاعدادى اللغات الترم الاول -الامتحان التعليمىAli RafaatNo ratings yet
- Jasmine Caulder 3/5/21: Periodic Trends WorksheetDocument2 pagesJasmine Caulder 3/5/21: Periodic Trends Worksheetjasmine caulder50% (2)
- Solid State Physics-2Document183 pagesSolid State Physics-2Tauseef AhmadNo ratings yet
- Remedial Test PAS 2017 Kelas 11Document2 pagesRemedial Test PAS 2017 Kelas 11dodolipet enakNo ratings yet
- I 11 6prim S Term2Document11 pagesI 11 6prim S Term2JFJannahNo ratings yet
- 635Document550 pages635RAJANo ratings yet
- SSP TextDocument168 pagesSSP Textjagadeeshkumar116No ratings yet
- 5epsctim Am Enu01Document1 page5epsctim Am Enu01Antnio MaríaNo ratings yet
- Name: .. Grade 8Document2 pagesName: .. Grade 8MuhammadNo ratings yet
- Prep.1 Final Revision 2023 - 2024Document21 pagesPrep.1 Final Revision 2023 - 2024Mohamed AmerNo ratings yet
- General Final RevisionDocument14 pagesGeneral Final RevisionbehejazyNo ratings yet
- اسئلة مراجعة على الوحدة الاولى فى Science للصف الثانى الاعدادى اللغات الترم الاول-الامتحان التعلDocument4 pagesاسئلة مراجعة على الوحدة الاولى فى Science للصف الثانى الاعدادى اللغات الترم الاول-الامتحان التعلhend ahmed chemistry teacherNo ratings yet
- Magnetism Booklet - DifferentiatedDocument18 pagesMagnetism Booklet - DifferentiatedDominic Wynes-DevlinNo ratings yet
- Test On Electrolysis Grade IXDocument13 pagesTest On Electrolysis Grade IXkrisnuNo ratings yet
- Atomic StructureDocument5 pagesAtomic StructureKrystalNo ratings yet
- ملزمة اسئلة على كل درس فى Science للصف الثانى الاعدادى اللغات الترم الاول-الامتحان التعليمىDocument22 pagesملزمة اسئلة على كل درس فى Science للصف الثانى الاعدادى اللغات الترم الاول-الامتحان التعليمىhend ahmed chemistry teacherNo ratings yet
- 2 The Structure of The AtomDocument10 pages2 The Structure of The Atom陈力玮No ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document14 pagesChapter 5Ishraqi IlyasNo ratings yet
- Ilovepdf MergedDocument24 pagesIlovepdf MergedabskNo ratings yet
- Electrostatic Charge - QuestionDocument1 pageElectrostatic Charge - QuestionSarah KKCNo ratings yet
- Tema 5 ElectricityDocument4 pagesTema 5 ElectricityJonathan LeachNo ratings yet
- 6 ElectrochemistryDocument20 pages6 ElectrochemistryhanifzainolNo ratings yet
- Reactivity of Metals and Nonmetals MATTHEW CORREIADocument6 pagesReactivity of Metals and Nonmetals MATTHEW CORREIAFrank MassiahNo ratings yet
- 2 The Structure of The AtomDocument11 pages2 The Structure of The Atomlh_mooNo ratings yet
- Chemical ReactionsDocument2 pagesChemical ReactionsHiên KimNo ratings yet
- Science: QuestionsDocument14 pagesScience: QuestionsZeinab ElkholyNo ratings yet
- Science Grade 6 (Electricity, Magnet, Soil)Document2 pagesScience Grade 6 (Electricity, Magnet, Soil)Nurwulan Yuni HapsariNo ratings yet
- Final Revision ScienceDocument7 pagesFinal Revision ScienceAl Shimaa MamdouhNo ratings yet
- Vocabulary: Science Grade 6: ElectricityDocument11 pagesVocabulary: Science Grade 6: ElectricityKyo ToeyNo ratings yet
- Final Exam of Physical Chemistry 2017-2018Document4 pagesFinal Exam of Physical Chemistry 2017-2018Ramiz FareedNo ratings yet
- امتحانات ساينس - 1 ع - أكتوبر - ذاكروليDocument17 pagesامتحانات ساينس - 1 ع - أكتوبر - ذاكروليayoussefNo ratings yet
- MYP 4 & 5 1st Trimester ExamsDocument12 pagesMYP 4 & 5 1st Trimester Examsishaq.yakubuNo ratings yet
- Design Calculation Sheet: General AssumptionsDocument8 pagesDesign Calculation Sheet: General AssumptionsHSEI Jatim - NSU 2020No ratings yet
- Electrochemical Investigations of Some Newly Synthesized Arylazapyrazole DerivativesDocument11 pagesElectrochemical Investigations of Some Newly Synthesized Arylazapyrazole DerivativesMUHAMMAD NADEEMNo ratings yet
- CHM031L - Exercise 1 ThermodynamicsDocument10 pagesCHM031L - Exercise 1 ThermodynamicsKath CarmonaNo ratings yet
- Din en 10327 9 - 2004 EnglishDocument25 pagesDin en 10327 9 - 2004 EnglishAdolfo100% (1)
- Uem Cse 2020 SyllabusDocument220 pagesUem Cse 2020 SyllabusAvradip DasNo ratings yet
- Eng4140 8905Document4 pagesEng4140 8905Jennifer AdvientoNo ratings yet
- Insert Bonded Metal CombinationsDocument1 pageInsert Bonded Metal CombinationsnorthstarleoNo ratings yet
- Study On A New Synthesis Approach of GlyphosateDocument7 pagesStudy On A New Synthesis Approach of GlyphosateJoana AlvesNo ratings yet
- Introductory Chemistry 4th Edition Russo Test BankDocument23 pagesIntroductory Chemistry 4th Edition Russo Test Bankkarakulichth.yic5f100% (33)
- A Review On The Calculation and Application of Lignin Hansen Solubility ParametersDocument11 pagesA Review On The Calculation and Application of Lignin Hansen Solubility ParametersFanfan DuNo ratings yet
- Unit 8 Chemical ReactionsDocument5 pagesUnit 8 Chemical ReactionsNixon GrahamNo ratings yet
- Product Analysis Certificate: Propanol-2 (Iso-Propanol) A.RDocument1 pageProduct Analysis Certificate: Propanol-2 (Iso-Propanol) A.RAMMARNo ratings yet
- 5b. Structural Engineering HO CH 04bDocument17 pages5b. Structural Engineering HO CH 04bThompson kayodeNo ratings yet
- CH 10Document13 pagesCH 10patilamardip0078122No ratings yet
- E-CAPS-28 - For CoE (XI) - Chemistry - (Que. - Answer Key)Document3 pagesE-CAPS-28 - For CoE (XI) - Chemistry - (Que. - Answer Key)darling deanNo ratings yet
- 6 - ch5 Aa 0Document49 pages6 - ch5 Aa 0Edlyn RamirezNo ratings yet
- (Edexcel International GCSE) Cliff Curtis-Edexcel Igcse Chemistry. Revision Guide. Solution Manual-Pearson Education (2011) PDFDocument16 pages(Edexcel International GCSE) Cliff Curtis-Edexcel Igcse Chemistry. Revision Guide. Solution Manual-Pearson Education (2011) PDFMohamed AlserNo ratings yet
- Expt 4 Pka of Methyl Red Lab ManualDocument5 pagesExpt 4 Pka of Methyl Red Lab ManualAditya BasuNo ratings yet
- COI-T.20-Doc.-No-33-Rev.-1-2017 (Fatty Acid MOA)Document16 pagesCOI-T.20-Doc.-No-33-Rev.-1-2017 (Fatty Acid MOA)KhalidNo ratings yet
- Thermo Scientific iCAP 7200 ICP-OES: Cost Effective Analysis For Low Sample Thru-Put RequirementsDocument4 pagesThermo Scientific iCAP 7200 ICP-OES: Cost Effective Analysis For Low Sample Thru-Put RequirementscurtisvaleroNo ratings yet
- Advanced-PP 1102LQ - 0Document1 pageAdvanced-PP 1102LQ - 0Narender RawatNo ratings yet
- Conducting Test Item Analysis...Document7 pagesConducting Test Item Analysis...Micah Barroa BernalesNo ratings yet
- Histopath Lect-P2 Exam A4 4Document7 pagesHistopath Lect-P2 Exam A4 4RuchieNo ratings yet
- Steriochemistry SteriochemistryDocument98 pagesSteriochemistry SteriochemistryPankaj SenNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 9 - Science - CH3 - Atoms and Molecules (MCQS)Document3 pagesCBSE Class 9 - Science - CH3 - Atoms and Molecules (MCQS)Rajiv KabadNo ratings yet
- Yl 9100 PlusDocument16 pagesYl 9100 PlusAmica LeeNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Matter and Its PropertiesDocument12 pagesModule 1 Matter and Its PropertiesShane Sayno100% (2)
- Common, Possible Patterns of ResonanceDocument13 pagesCommon, Possible Patterns of ResonanceFarhana Mohd RazaliNo ratings yet
- Extrusion Processing of Wheat Gluten Bioplastic: Effect of The Addition of Kraft LigninDocument11 pagesExtrusion Processing of Wheat Gluten Bioplastic: Effect of The Addition of Kraft LigninXuan Phuong HuynhNo ratings yet
- Chemistry LOsDocument44 pagesChemistry LOsYoussef samehNo ratings yet