Professional Documents
Culture Documents
A Short Guide To Arrows in Chemistry
Uploaded by
Jefferson RibeiroOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
A Short Guide To Arrows in Chemistry
Uploaded by
Jefferson RibeiroCopyright:
Available Formats
COMPOUND
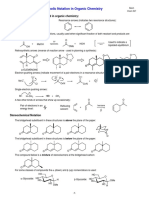
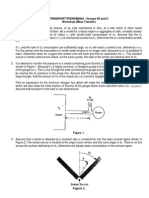
A Short Guide to Arrows in Chemistry Ci INTEREST
Chemical reaction arrows Electron movement arrows
Reaction arrow Multiple steps arrow Broken arrow Resonance arrow
or
These arrows point from the reactants to the Chemists use stacked multiple arrows to Chemists use these arrows to indicate Chemists use these arrows to show different
products of a chemical reaction. Reaction indicate that there are several reaction steps chemical reactions that do not take place. resonance forms of the same molecule. The
conditions, reagents or catalysts may be between the reagents and the products The reactants shown cannot be transformed forms differ in electron arrangements; the
written above or below the reaction arrow. shown on either side of the arrows. into the products shown. true structure of the molecule is an average.
Examples Example Examples Example
O2N NO2
HCl + NaOH NaCl + H2O CH3 Cu + MgSO4 CuSO4 + Mg
Cr 2 O 72–/H 2 SO 4
C 2H 5OH + 2[O] CH 3COOH + H 2O NO2 Br2 + 2 KCl Cl 2 + 2 KBr
reflux
Reversible reaction arrow Equilibrium arrow Retrosynthesis arrow Curly arrow
Chemists use these arrows to indicate that a These arrows show that a reversible reaction Organic chemists use these arrows to show Curly arrows show electron movement in
reaction is reversible — the reactants react to is at equilibrium: the forward and reverse that the molecule on the left can be made reaction mechanisms in organic chemistry.
produce the products, but the products can reactions occur at the same rate. The length from the starting materials on the right, A double-headed arrow shows movement of
also react to make the reactants. of the arrows can be varied to show if often through several reaction steps. an electron pair, while a single-headed arrow
reactants or products are favoured. shows movement of a single electron.
Examples Example OH
Examples Example
H
CuSO4 .5H2O CuSO4 + 5 H2O OH H2N O H H O H3O+
N2 + 3 H 2 2 NH3 O
+ H3C H3C H H3C H3C
H3C C Br H3C C H3C C O H H3C C OH
O O
CaCO 3 CaO + CO 2 CH 3 COOH + C 2 H 5 OH CH 3 COOC 2 H 5 + H 2 O
N
H
H3C H3C H3C H H3C
O
www.compoundchem.com © Andy Brunning/Compound Interest 2022 | Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives licence.
BY NC ND
You might also like
- Schaum's Easy Outline of Organic Chemistry, Second EditionFrom EverandSchaum's Easy Outline of Organic Chemistry, Second EditionRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Named Reaction ProjectDocument2 pagesNamed Reaction Projectrajnibhati437No ratings yet
- Suggested Solutions For Chapter 38: Purpose of The ProblemDocument14 pagesSuggested Solutions For Chapter 38: Purpose of The ProblemJennifer Carolina Rosales NoriegaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry: Name TeacherDocument57 pagesChemistry: Name TeacherKei'mani McIntoshNo ratings yet
- Organic Chem 1 Practice ProblemsDocument6 pagesOrganic Chem 1 Practice ProblemshfweouNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Chemical Reactions 2011-2012Document45 pagesIntroduction To Chemical Reactions 2011-2012Carl OrtegaNo ratings yet
- Retrosintesis AspirinDocument18 pagesRetrosintesis AspirinYasaKaryadaNo ratings yet
- Organic Unit Quiz Assignment 2020Document6 pagesOrganic Unit Quiz Assignment 2020ludihemicarNo ratings yet
- Synthesis of Heterocyclic CompoudsDocument13 pagesSynthesis of Heterocyclic CompoudsYaqeen Alhaqq F. GhaziNo ratings yet
- Synthesis of Heterocyclic CompoudsDocument13 pagesSynthesis of Heterocyclic CompoudsYaqeen Alhaqq F. GhaziNo ratings yet
- Synthesis of Heterocyclic CompoudsDocument13 pagesSynthesis of Heterocyclic CompoudsYaqeen Alhaqq F. GhaziNo ratings yet
- Synthesis of Heterocyclic CompoudsDocument13 pagesSynthesis of Heterocyclic CompoudsYaqeen Alhaqq F. GhaziNo ratings yet
- RetrogDocument9 pagesRetrogapi-3761322No ratings yet
- G.O.C. Iws-1Document50 pagesG.O.C. Iws-1Lakshya ChandakNo ratings yet
- KIM 101E - Week 3 - BDocument70 pagesKIM 101E - Week 3 - Baliyasin200000No ratings yet
- 1 IR NMR Practice ProblemsetDocument12 pages1 IR NMR Practice ProblemsetJustin BuiNo ratings yet
- Molecules, Moles, and Chemical Equation: Chemistry For EngineersDocument46 pagesMolecules, Moles, and Chemical Equation: Chemistry For Engineersjoshuajoshua3913No ratings yet
- Is It Balanced and Ch-12 Lesson 1 Content PracticeDocument3 pagesIs It Balanced and Ch-12 Lesson 1 Content Practicejeehoonkim78No ratings yet
- Cataliza Enzime Si ProteineDocument10 pagesCataliza Enzime Si Proteineseranim22No ratings yet
- Stoichiometry: Igcse ChemistryDocument41 pagesStoichiometry: Igcse ChemistryYoshitaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 16 KineticsDocument22 pagesChapter 16 KineticsUdop CharlesNo ratings yet
- UNIT 3-Organic Reactions My VersionDocument47 pagesUNIT 3-Organic Reactions My VersionMohammad JunaidNo ratings yet
- Reactions, Counting Atoms, and Balancing Chemical EquationsDocument23 pagesReactions, Counting Atoms, and Balancing Chemical Equationspanida SukkasemNo ratings yet
- GENERAL CHEMISTRY 2 Module 1Document8 pagesGENERAL CHEMISTRY 2 Module 1Hassel AbayonNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reactions and Reaction Stoichiometry: Lecture PresentationDocument71 pagesChemical Reactions and Reaction Stoichiometry: Lecture PresentationJinNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 11Document9 pagesGeneral Chemistry 11Rowelyn BakekeNo ratings yet
- Development and Validation of HPTLC For Simultaneous Estimation of Montelukast Sodium, Levocetirizine Dihydrochloride and Ambroxol in Bulk and in Three-Component Capsule FormulationDocument7 pagesDevelopment and Validation of HPTLC For Simultaneous Estimation of Montelukast Sodium, Levocetirizine Dihydrochloride and Ambroxol in Bulk and in Three-Component Capsule FormulationmeghavathnaikNo ratings yet
- 200610chapter 16 Kinetics PDFDocument22 pages200610chapter 16 Kinetics PDFfearlessinchrist100No ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry II The Report of PracticumDocument8 pagesOrganic Chemistry II The Report of PracticumpranggajatiNo ratings yet
- SamRobinson Lecture Notes 3Document24 pagesSamRobinson Lecture Notes 3Pigeon BNo ratings yet
- 3 PDocument3 pages3 PHồ Đức ViệtNo ratings yet
- Exam2 Practice A KG SirDocument8 pagesExam2 Practice A KG Sirkg4freeNo ratings yet
- Wolaita Sodo University: General Chemistry (Chem.1012) Chapter FourDocument56 pagesWolaita Sodo University: General Chemistry (Chem.1012) Chapter FourAbdulmajid AbdellaNo ratings yet
- (L8) - (JLD 2.0) - Reaction Mechanisms - 17 SeptDocument55 pages(L8) - (JLD 2.0) - Reaction Mechanisms - 17 Septchirag birlaNo ratings yet
- 1 Chemical ReactionDocument2 pages1 Chemical Reactionmafiamain160No ratings yet
- LAS 15 Genchem1Document20 pagesLAS 15 Genchem1Maria concepcion MangonlayNo ratings yet
- Aromatic Chemistry Assignment #3 2018-2019 ANSWERSDocument5 pagesAromatic Chemistry Assignment #3 2018-2019 ANSWERSZoe NorvilleNo ratings yet
- Stoichiometry Part 2:: Chemical EquationsDocument70 pagesStoichiometry Part 2:: Chemical EquationsJessica Louise GaluteraNo ratings yet
- Part 1Document70 pagesPart 1Mehnaz SafdarNo ratings yet
- Chem E2b ReviewDocument203 pagesChem E2b ReviewPreserve OladipoNo ratings yet
- L8 - Balancing EquationsDocument53 pagesL8 - Balancing Equationsdanglebaolinh4No ratings yet
- Monte-Carlo Methods For Simulating The Catalytic Oxidative Dehydrogenation of Propane Over Vmgo CatalystDocument10 pagesMonte-Carlo Methods For Simulating The Catalytic Oxidative Dehydrogenation of Propane Over Vmgo CatalystMayteNo ratings yet
- PP 19 Balancing Chemical EquationsDocument15 pagesPP 19 Balancing Chemical EquationsRufi RizwanNo ratings yet
- Chapter1 Bonding and Isomerism Practice2Document4 pagesChapter1 Bonding and Isomerism Practice2sugNo ratings yet
- For 1-4 ClassDocument45 pagesFor 1-4 ClassNanditha ANo ratings yet
- Gen Chem. Module-7Document29 pagesGen Chem. Module-7dzai leigh75% (4)
- Fundamentals of Mechanism and Stereochemistry: CHEM0005 Chemical Foundations: Section CDocument174 pagesFundamentals of Mechanism and Stereochemistry: CHEM0005 Chemical Foundations: Section Cssayed1No ratings yet
- Chapter FourDocument52 pagesChapter Fourgebrewahidbiniam75No ratings yet
- BioorganicchemistryDocument246 pagesBioorganicchemistryveneta gizdakovaNo ratings yet
- Química OrgânicaDocument16 pagesQuímica OrgânicaDanilo AbiboNo ratings yet
- Organoboranes in Organic Syntheses Including Suzuki Coupling ReactionDocument29 pagesOrganoboranes in Organic Syntheses Including Suzuki Coupling Reactionratul mahataNo ratings yet
- Electron Pushing PDFDocument3 pagesElectron Pushing PDFGiacomo Dal PraNo ratings yet
- TheoryDocument18 pagesTheoryKelsierNo ratings yet
- Abousekkina 2014Document6 pagesAbousekkina 2014Ajeng IftitaNo ratings yet
- 4.a Intro Organic ChemDocument16 pages4.a Intro Organic Chemytshortsfromopus65No ratings yet
- Stoichiometry Mole-II (XI)Document29 pagesStoichiometry Mole-II (XI)Raju SinghNo ratings yet
- CHEMICALDocument25 pagesCHEMICALken BaceaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Equations & ReactionsDocument78 pagesChemical Equations & ReactionsIshvarya100% (1)
- Experiment No. 6 Formula WritingDocument6 pagesExperiment No. 6 Formula WritingKent Kylle Andreas SaraososNo ratings yet
- Periodic Table of Element Hazard Symbols: #IYPT2019Document1 pagePeriodic Table of Element Hazard Symbols: #IYPT2019Nasim ZulfiqarNo ratings yet
- Periodic Table: Element Name Origins: UnicateDocument1 pagePeriodic Table: Element Name Origins: UnicateBobNo ratings yet
- 23 - Periodic Table of Element PricesDocument1 page23 - Periodic Table of Element PricesBogdan NechitaNo ratings yet
- Periodic Table: Element Name Origins: UnicateDocument1 pagePeriodic Table: Element Name Origins: UnicateBobNo ratings yet
- Flowmeter Model MP KytolaDocument2 pagesFlowmeter Model MP KytolaJimmy MirandaNo ratings yet
- Question BankDocument7 pagesQuestion BankmunirajNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Vibration: Course InstructorsDocument26 pagesMechanical Vibration: Course Instructorspavan_1988No ratings yet
- Flow Regimes On Sieve Trays For Gas Liquid ContactingDocument196 pagesFlow Regimes On Sieve Trays For Gas Liquid ContactingGrant FirthNo ratings yet
- Polarography: Pharmaceutical Chemistry IIIB 516-T Course Incharge: Dr. Somia GulDocument17 pagesPolarography: Pharmaceutical Chemistry IIIB 516-T Course Incharge: Dr. Somia GulTayyab Siddiqui100% (1)
- Periodic TableDocument29 pagesPeriodic Tablepraveen bukkaNo ratings yet
- Local Winds: Land and Sea BreezesDocument8 pagesLocal Winds: Land and Sea Breezesravi rathodNo ratings yet
- Gate 1533Document7 pagesGate 1533Darshit D RajNo ratings yet
- Nap-Gard 7-2500 PDFDocument2 pagesNap-Gard 7-2500 PDFPietro ViganNo ratings yet
- ACI 301 Section 2 and 3 - MilwaukeeDocument16 pagesACI 301 Section 2 and 3 - MilwaukeeerosNo ratings yet
- Science 10 Second QuarterDocument3 pagesScience 10 Second Quarterprince adilan planas100% (5)
- FEM - 8 Stiffness MatrixDocument26 pagesFEM - 8 Stiffness Matrixwiyorejesend22u.infoNo ratings yet
- Workshop Mass TransferDocument2 pagesWorkshop Mass TransferYessica Viviana Solano PradoNo ratings yet
- Ansys LabDocument47 pagesAnsys LabPraveen KumarNo ratings yet
- ASCE 7 10 Vs ASCE 7 16 1657453966Document53 pagesASCE 7 10 Vs ASCE 7 16 1657453966MANOJNo ratings yet
- 2.3 Section Properties of Built-Up Steel Sections PDFDocument5 pages2.3 Section Properties of Built-Up Steel Sections PDFthongchai_007No ratings yet
- Pneumatic HacksawDocument6 pagesPneumatic HacksawAvinash Lad100% (1)
- App110 20210510Document7 pagesApp110 20210510Luen HopNo ratings yet
- MTechDocument42 pagesMTechRahul YuvarajNo ratings yet
- IntroductionDocument24 pagesIntroductionHabibi1451No ratings yet
- BS en 10228 4 2016 Non Destructive Testi PDFDocument30 pagesBS en 10228 4 2016 Non Destructive Testi PDFDaryna KupriianovaNo ratings yet
- Amte 116LDocument3 pagesAmte 116LRebecca Lepon LegaspiNo ratings yet
- Emission Reduction TechniquesDocument10 pagesEmission Reduction TechniquesiocsachinNo ratings yet
- SCI 10 Module 2 NotesDocument9 pagesSCI 10 Module 2 NotesSeviNo ratings yet
- Enzyme Lab ReportDocument9 pagesEnzyme Lab ReportSafaa TatouNo ratings yet
- 200 MW - Unit, Generator Seal Oil SystemDocument3 pages200 MW - Unit, Generator Seal Oil SystemNikhilNo ratings yet
- Non-returns-DampersDocument1 pageNon-returns-DampersProject enghvacNo ratings yet
- Internal Combustion EngineDocument40 pagesInternal Combustion EngineMingNo ratings yet
- Thermowell CalculationDocument1 pageThermowell Calculationdilo0987No ratings yet
- HDPEDocument14 pagesHDPESandy YansikuNo ratings yet