Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ch-3 Small Scale Industries Notes
Uploaded by
Devashish SawantOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Ch-3 Small Scale Industries Notes
Uploaded by
Devashish SawantCopyright:
Available Formats
of productlon and
improve quality
services. Ess to conrol cost actor and
BRIEF oVERVIEW
3.1 Introduction:
power
arc
recognised
as
Small Scal
Smalls
and
Small scale Industries.
in industry plays
important role
an two categories of Small Sca
Scale
developing countries having
scarcity of capita
Inittally.
vi2. () Manufact
and abundant
labour. In uhe post independence
industries were recognised
Sector. An
An Incs..aring
industrta
period. more Sector a n d ()
Services
cmphasis Is
given to the
the capital ent
investment lIm
development of Small Scale Industries. However. unit which
fullils
the problem of Government of India according
unemployment is not overcome fixed by the
Enterp
as it was
country.
expected.
it is
In India. as adeveloping Micro
Small
and
Medium
1s calegorised as
Enterprise
s
essential to make
labour and other
avallable capital. Development
Act 2006
classification
of Business
Smal
on
resources for the development B u s i n e s s . The
of Small Scale according to Micro
industries. basis of investments Sma
3.1.1 Meaning Enterprises Develon.
Medtum
Scale and
Traditionally. Industries which produce goods (MSMED) are:
and services with
the help of machines. labour
Medium
Business Micro Small
25 lakhs
More t h a n55 crore
(1) Manufacturing Does not exceed 2 5 More than
exceed but does not exceed
Sector lakhs but does not
710crores.
5 crores.
(2) Service Sector Does not exceed 10 More than 10 lakhs
More than 7 2 crore
but does not
lakhs but does not exceed exceed
5 crores.
T 2 crores
. L . 2 : Definition : Any industrial unit is considered as Small Scale industy il its investmen
ent
Dxed assets like plant and equipment either held on ownership terms or on lease or hire purch
should not be more than one crore. However. the unit in no way can be owned or controlled .
auxiliary for any other industrial unit.
Classification of Small Scale Industries
Traditional Small Scale Industries Modern Small Scale Industries
(1) Handloom (1) Bicycle Parts
(2) Handicraft (2) Sewing Machines
(3) Coir (3) Blades, Razors
(4) Sericulture (4) Electric Appliances
(5) Khadi and Village Industries (5) Spare Parts
66 ORGANISATION OF COMMERCE AND MANAGEMENT DIGEST: STANDARD XI
3.2 Importance: The
Importance of small 3.3 Advantages of Small
Scale
Advantages :
endustries is shiown in the lollowlng chart:
scale Industrles are shown In the following chart:
Importance of Small Scale Industries
Advantages of Small Scale Industrles
Job opportunities
Large scale cmployment
Regional balance
Less capilal requlrement
Increase competitive strength
Uullsatlon of domestlc rcsources
Maximum use of natural resources
Increascs Industrlal output
Reduce migration Contributlon to export
Support large scale lndustries Equltable distribution
Developing new entreprencurs
Earning forcign exchange
(1) Job opportunities: Small business units Opportunitics for entreprencurshipP
(industries) have immensc Cost eflctency
employment
enerattng potentials and therefore provide Reduces migralton
areater employment opportunities to surplus Flextbility in operation
amount of labour i rural India. scale employment: Small scale
(1) Large
(2) Reglonal balance: As small scalc industries are labour Intensive. So they have
industries establishcd. spread and scattered all Immense employment generating potenials
and
over the rural areas. they help to remove provlde employment opportunities to large
reglonal
disparities. increase industriallsation and number of people.
contribute slgniflcantly to the balanced Small scale
(2) Less capital requirement:
development of the country.
industries necd less capital to run and manage
(3) Increase competitive strength: Small in comparison to large scale industrles.
scale industries use local resources at low cost
and thus enjoy thec advantages of low cost of (3) Utilisation of domesticresources: Small
scale industrics make use of local resources
productton. low overheads, low prices which in
which are avallable in large quantity. These
turn increase turnover and competitive strength.
Industrics mobilise and channelise savings into
(4) Maximum use of natural resources:
productive investnents which in turn increases
Small scale industrles ulisce the available
capital formation.
natural resources. labour and raw materials
from local arcas which resulls in low cost of (4) Increases industrial output: Small
production. They can alford to sell the goods at scale Industries produce both consumer goods
reasonable prices. and industrlal goods. A significant portion of
(5) Reduce migration: Small scale industries industries output of the nation is produced by
generate employment opporlunities and create the small scale industrles.
self employment. This ulttmalely reduces (5) Contribution to export: Nearly 40% of
migration of people from rural to urban arcas. total exports of Indla comes from small scale
(6) Support large scale industries: Many Industrial sector. The fînished and semi finished
small scale industrles provlde raw materlal, products of small scalc Industries are used by
semi finished goods to large scale industries. the large scale industries to produce goods for
c.g spare parts. export purpose. Thus small scale industries
(7) Developing new entrepreneurs: Small contribute directly and indirectly to Indla's
scale industries attract. create and develop exports.
entrepreneurs.
3. SMALL CALE INDUSTRY AND BUSINESS
67
(0) Equltable dlatributlon : Tr growth and n:The
(1) Old methoda of productlon: The na
dcvelopuent of nall buses n rural seetor sECale mdustries use outdated technology
iVOd
rorntratton of ncomes and weallh Inn a
old inetods of productlon whlch alfors ang
th
Iw hndn.
Thin reilla in hotli
cconomic i productivity adversely
oclal welfare. (2) Inadequate lnance: L.ack of fin:.
(7)
Earning forclgn Inders the growth and development of
Inanee
portlon of exchange: The major smal
the scale Industrles In Indla.
produrts mnufacturcd by ne
Iallscale Industrles are (3) Problem of raw materlal: Free
different countrles of cxporlcd to tne shortage and infertor quality of raw mater
quenm
the world which
valuable forclgn exchange. brings laly
affect capacity utlisatlon and profilablity
(8)
Opportunitles for small scale Industrles
The growth and entreprencurship:
devclopment of small (4) Labour problem: The problems l
Industries create scale
cntreprencurs. They contribute low labour productivity. absentectsm. labour
greatly to the
nation's dissatlsfaction, Improper shifts, lack of
(9) Cost development. Job
efficlency: Small scale
Industrles
securlty, lack of skilled labour, etc. hinder
the
mlcro
usc
productlon methods which progress of small scale industrles.
better quallty produce
products and more
varicty at
(5) Marketing problem: Marketng problem.
ms
lesser cost. Thclr overall
such as lack of advertising and
Thus they are most cost
expenscs arc
very low. publcth
effecüve. production of non-branded products, po
0or
(10) Reduces migration: The standard of quality, exploltatlon by
growth and middlemen
development of small scale
Industrles generate low prices, delayed payments, etc.
redue
cmployment opportunities. The people reslding turnover and ulumately production.
In rural areas (6) Problem of
get galnful employment and hence transport: On account af
do not lack of proper
migrate to
areas. urban
Thus, the transport system. it Is
diflcult to
Industries help In mlnimising transfer raw materlals from the
migration. places of origin
to the place of
(11) Flexibility factory and finished goods from
in
operation: The small
the place of
scale industrics are more flexible than factory to the consumers.
large (7) Sickness: Prevalence
scale industries. These Industries can sickness in
easily industrial units in rural areas is due to
adopt themsclves to changng market internal
causes such lack of skilled and
as
requlrements. labour. lack of
trained
managerlal and marketing skill
3.4 Challenges beforeScale Small ctc. and external causes such as
industries : Challenges before Small Scale delayed
payment, shortage of working capital,. raw
are shown In the following naterlals, etc.
chart
Challenges before Small Scale Industries (8) Power shortage and
irregular
Old methods of Problems of infrastructure such assupply:
producton acute
Inadequate finance shortage of powe. power cuts.
high power
Problem of raw materlal charges. low voltage level, etc.
hamper the
Labour problem growth and progress of small scale
industries.
Marketing problem (9) Global competition: Small
Scale
Problem of transport industries face problems on the
context of
SIckness Liberallsation. Privatisation and Globalilsation
Power shortage and irregular supply (LPG) policles being followed by many countries
Global competitlon in the world.
ORGANISATION OF cOMMERCE AND MANAGEMENT DIGEST: STANDARD XI
superlor uality
o
of helter and
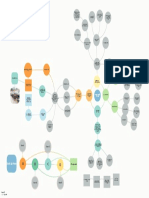
.5 Steps in setting up of a Small Scale production
Hoods and servlces
Business: The stleps n scttng up of a proposal: The
assessment
(6) Business
Small Scale Biuslness are shown n the scheme and projects
buslncss
(appralsal) of flnanclal,
following chart cconomlc,
tcchnlcal.
from
carefully of vlew Is
Steps in setting up of a management
polnt
sOclal and
buslness.
small
Small Scale Business necessary
beforc sctting up
of adequate
Declslon of business arca Finance: The
provlslon
(7) and manage
run
Study of business cnvironment to start,
finance Is requlred to
is requlred
Sclectlon of product small busIncss.
The cntrcpreneur
sources.
from diferent
Selection of place flnance
ralse needed
bencfits
obtain various
Selectuon of technology (8) Registration:To has to
the entreprencur
Business proposal from the government, Distrlet
business with
Finance hls proposcd
register documents.
with relevant
Reglstratlon Industries Ccntre (DIC)
of resources
Actual arrangement of resources (9) Actual arrangement
The entrepreneur
Production and marketng of product (1) Physical
resources:
industrlal
sufmctent space for
Review fecdback for future changes
or has to allocate
sultable production method.
(1) Decision of business area: The entre- actlvitles, sclect
install machlnerles, appoint
preneur has to decide whether he wishes to set purchase and
up sole proprletary concern. partnershlp workers, etc.
and water
organisation or corporauon. He has to analyse (i) Arrangement of power
to estimate the total
his strength and wealkness while deciding on an supply: He has
and deternmine the
entrepreneurship career. requlrements of power
make power avallable.
He has to
(2) Study of business environment: The nearest pole to
entrepreneur has to study and understand the the adequate water supply.
make arrangement to
and
business environment in whích the : He has to recruit qualified
(i) Staftlng
prevailing
business wll operate such as industrial policy. for different departments.
capable personnel
economic polcy, licensing policy. legal and This follows tralning and placement of recrulted
technological environment, etc. candidates.
(3) Selection of product: The entrepreneur (10) Production and marketing of product:
has to start the
must decide the product to manufacture or the The entrepreneur then
He has to
service to offer. For this, he has to conduct productton of goods and services.
declde about the marketing of those goods and
market research and understand the prevailing
competition in the market. servlces. He has to make proper arrangement of
(4) Selection of place : The entrepreneur is online business directions and varlous
traditional forms of selling. Advertising can be
required to select that place where transport.
used to gain exposure for the business.
labour, raw materials, banking facilities, market
(11) Review or feedback for future
are easily available. The success of small
changes: The entrepreneur has to carryout
business mostly depends on selection of right
place l.e. location.
perlodical evaluation of market, production
quality and profitablity. Accordingly. he has to
(5) Selection oftechnology: The installation
make necessary changes in quality and methods
and use of modern and sophisticated technology
of production for future growth.
and equipment are more important for
3. SMALL SCALE INDUSTRY AND BUSINESS 69
You might also like
- Ch-1-Business-Environmemt Mind MapDocument1 pageCh-1-Business-Environmemt Mind MapRolandi ViljoenNo ratings yet
- Sectors of Indian Economy With PYQDocument32 pagesSectors of Indian Economy With PYQAnkita DashNo ratings yet
- AKSET Webinar of 30 Nov - Session 2 - Paparan Dirjen. ILMATEDocument17 pagesAKSET Webinar of 30 Nov - Session 2 - Paparan Dirjen. ILMATEMuhammad Naufal FakhriyantoNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Industries NotesDocument5 pagesManufacturing Industries Notessahritesh630No ratings yet
- T-IEET001 - Business-Model-Canvas - Ta-Ay, Jay L. - MEE31Document1 pageT-IEET001 - Business-Model-Canvas - Ta-Ay, Jay L. - MEE31JayNo ratings yet
- Small Business and EnterprisesDocument21 pagesSmall Business and Enterprisesaachal0122No ratings yet
- IFC SMEDatabase 2-06Document13 pagesIFC SMEDatabase 2-06EdgarNo ratings yet
- Valve Services DivisionDocument2 pagesValve Services DivisionMohammad Safdar SadatNo ratings yet
- Private Employers - GurgaonDocument51 pagesPrivate Employers - GurgaonRishavv VermaNo ratings yet
- Mining & Construction: Out To OptimizeDocument27 pagesMining & Construction: Out To OptimizemertyurekemrahNo ratings yet
- Sectors of Indian Economy Shobhit NirwanDocument36 pagesSectors of Indian Economy Shobhit NirwanHONEYGAIN100% (2)
- Sectors of Indian Economy Shobhit NirwanDocument13 pagesSectors of Indian Economy Shobhit NirwandfgfdfggdfNo ratings yet
- Sectors of Indian EconomyDocument6 pagesSectors of Indian EconomySamarth banodiaNo ratings yet
- ZDA Spotlight - May 2009Document4 pagesZDA Spotlight - May 2009Chola Mukanga100% (3)
- Annual Report 2019Document27 pagesAnnual Report 2019Dan p.No ratings yet
- Uttarakhand Investor HandbookDocument106 pagesUttarakhand Investor Handbookprashant bhardwajNo ratings yet
- Ashok Leyland MergerDocument1 pageAshok Leyland Mergerramya patraNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Industries - Shobhit NirwanDocument15 pagesManufacturing Industries - Shobhit NirwanBhaskar 8287100% (1)
- Mesaieed Brochure 2019Document11 pagesMesaieed Brochure 2019Anwar HossainNo ratings yet
- Wijaya Karya (Persero) TBK WIKA: Last Close Fair Value Market CapDocument4 pagesWijaya Karya (Persero) TBK WIKA: Last Close Fair Value Market Capbala gamerNo ratings yet
- Expanding Economic Opportunities in Industry and Services Through Trabaho at NegosyoDocument4 pagesExpanding Economic Opportunities in Industry and Services Through Trabaho at NegosyohaykoNo ratings yet
- Excellon Software ET Coffee Table BookDocument1 pageExcellon Software ET Coffee Table BookManish SharmaNo ratings yet
- PIP 2023 2028 Chapter 6 As of March 22 2023Document6 pagesPIP 2023 2028 Chapter 6 As of March 22 2023Alex LucasNo ratings yet
- Se 11Document11 pagesSe 11dhvanisharma2527No ratings yet
- Group 1Document2 pagesGroup 1Ahmed MastanNo ratings yet
- MSME Infographic November 2021Document1 pageMSME Infographic November 2021RITIK RAJNo ratings yet
- Small Business and EntDocument22 pagesSmall Business and EntManmeet Kaur AroraNo ratings yet
- Sectors of Indian Economy Shobhit NirwanDocument12 pagesSectors of Indian Economy Shobhit NirwanNutan sinhaNo ratings yet
- MSMED ClassificationDocument1 pageMSMED ClassificationdkindoNo ratings yet
- Role and Development of Small Scale InduDocument13 pagesRole and Development of Small Scale Indushyam1200No ratings yet
- Rituraj Test - Impact of Industry 4.0 On Indian Manufacturing SectorDocument1 pageRituraj Test - Impact of Industry 4.0 On Indian Manufacturing SectorRituraj SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Private Employers - GurgaonDocument51 pagesPrivate Employers - Gurgaonsaurabh_shuklaNo ratings yet
- PPF, Unit - 1Document3 pagesPPF, Unit - 1tanishkaNo ratings yet
- IndustriesDocument6 pagesIndustriesAjay KrishnanNo ratings yet
- DMIC Influence Area: Madhya PradeshDocument2 pagesDMIC Influence Area: Madhya Pradeshvijayant contentNo ratings yet
- Sr. No Name Age Qualification Work Ex Summer Project Industry ProjectDocument18 pagesSr. No Name Age Qualification Work Ex Summer Project Industry ProjectJEVIN GANDHINo ratings yet
- Indo German 04 2022 - EDocument54 pagesIndo German 04 2022 - ESiddharthNo ratings yet
- EMIS Insights - Malaysia Consumer Electronics Sector Report 2018 - 2019Document77 pagesEMIS Insights - Malaysia Consumer Electronics Sector Report 2018 - 2019Patricia OoiNo ratings yet
- Business Requirement Modupur - UpdatedDocument5 pagesBusiness Requirement Modupur - UpdatedK.M. Fahad HussainNo ratings yet
- Indian Eco Unit 3 and Unit 4Document12 pagesIndian Eco Unit 3 and Unit 4Dhruv VasudevaNo ratings yet
- MorningStar ES0143416115Document4 pagesMorningStar ES0143416115José J. Ruiz SorianoNo ratings yet
- Sector Screenveurope1009Document1 pageSector Screenveurope1009buyanalystlondonNo ratings yet
- Advt 15 2023Document7 pagesAdvt 15 2023ujjal kr nathNo ratings yet
- Investor Presentation PDFDocument28 pagesInvestor Presentation PDFshub56jainNo ratings yet
- PSC ProfileDocument14 pagesPSC ProfilePSC RFQNo ratings yet
- Water Supply SystemDocument1 pageWater Supply SystemAkash SinghNo ratings yet
- Context: Location QuotientsDocument3 pagesContext: Location QuotientsIndriNo ratings yet
- Suchfeld - Land Firmenname - Produkt: Z.B. Flexible 3D Touch Sensor Technology Development Private/Public/etcDocument1 pageSuchfeld - Land Firmenname - Produkt: Z.B. Flexible 3D Touch Sensor Technology Development Private/Public/etcdantopanNo ratings yet
- Mint - Delhi - 14 03 2023 8Document1 pageMint - Delhi - 14 03 2023 8mangeshtakale13No ratings yet
- Feed Industry of Bangladesh:: Sustaining Covid-19 and Potentials in Upcoming DaysDocument41 pagesFeed Industry of Bangladesh:: Sustaining Covid-19 and Potentials in Upcoming Daysnandt bangladeshNo ratings yet
- Subros: An UpdateDocument29 pagesSubros: An UpdateSanjay KumarNo ratings yet
- Actividad 2 de Aprendiza MarketDocument3 pagesActividad 2 de Aprendiza MarketFelipe TorresNo ratings yet
- Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises: A Collection of Published DataDocument10 pagesMicro, Small, and Medium Enterprises: A Collection of Published Datamorrisonkaniu8283No ratings yet
- WhatsApp Image 2024-03-20 at IndiaDocument2 pagesWhatsApp Image 2024-03-20 at Indiarankweb.ioNo ratings yet
- Axiata IAR2022Document119 pagesAxiata IAR2022Priscilla KitNo ratings yet
- AnandRathi On Power MechDocument18 pagesAnandRathi On Power MechDhittbanda GamingNo ratings yet
- Case Study Chapter 1Document2 pagesCase Study Chapter 1demongamin2006No ratings yet
- Peru: Sample Size Definition For Phone Screen and Face-To-Face InterviewsDocument2 pagesPeru: Sample Size Definition For Phone Screen and Face-To-Face InterviewsMauricio PizarroNo ratings yet
- Setup Task Lists and TasksDocument795 pagesSetup Task Lists and TasksSrinivas GirnalaNo ratings yet
- Valuable OSS - Delivering a Return on Your Investment in Operational Support Systems (OSS)From EverandValuable OSS - Delivering a Return on Your Investment in Operational Support Systems (OSS)No ratings yet
- Project Audit MethodologyDocument2 pagesProject Audit MethodologyFariha AktarNo ratings yet
- Microsoft Power Point - Value Chain Analysis & Bench MarkingDocument23 pagesMicrosoft Power Point - Value Chain Analysis & Bench MarkingDillip Khuntia100% (3)
- REDcert EU SchemeDocument4 pagesREDcert EU Schemeahfaz ahmedNo ratings yet
- GO ShortDocument9 pagesGO Shortnoam josefNo ratings yet
- ISO 45001 Occupational Health & Safety Management Systems RequirementsDocument18 pagesISO 45001 Occupational Health & Safety Management Systems RequirementsSead Zejnilovic100% (1)
- GPPB NPMs Second HandDocument11 pagesGPPB NPMs Second HandLiane V.No ratings yet
- Notice Inviting TenderDocument27 pagesNotice Inviting Tenderelangbam nilakantaNo ratings yet
- SIP Guidelines For Students 2022-24Document9 pagesSIP Guidelines For Students 2022-24Navdeep TiwariNo ratings yet
- Madhur Confectioners PVT LTDDocument2 pagesMadhur Confectioners PVT LTDuniquebearingmpNo ratings yet
- FMEA BlankDocument4 pagesFMEA BlankJonjon SarmientoNo ratings yet
- Clemco Hollo Blast Internal Pipe Blast Tool Part Numbers and Schematics Guide 106m354Document12 pagesClemco Hollo Blast Internal Pipe Blast Tool Part Numbers and Schematics Guide 106m354JANETNo ratings yet
- Bilal Hussain - CVDocument2 pagesBilal Hussain - CVnasir elahiNo ratings yet
- DefineDocument40 pagesDefinerajeskumarNo ratings yet
- Umar Farooq Butt: Curriculum VitaeDocument3 pagesUmar Farooq Butt: Curriculum VitaeMunir HussainNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Engineering ManagementDocument6 pagesChapter 3 - Engineering ManagementJohn Philip Molina NuñezNo ratings yet
- 2023 Manufacturing EbookDocument54 pages2023 Manufacturing EbookRicky ChangNo ratings yet
- Internship Report - Cemds - Guidelines For Writing 2.7.22Document3 pagesInternship Report - Cemds - Guidelines For Writing 2.7.22JESSEL MAE SERACNo ratings yet
- Rethinking Project Management: A Structured Literature Review With A Critical Look at The Brave New WorldDocument3 pagesRethinking Project Management: A Structured Literature Review With A Critical Look at The Brave New WorldwywpoonNo ratings yet
- References of APA FormatDocument8 pagesReferences of APA FormatAK's CreationNo ratings yet
- Contract Law Assignment Name:p.v.n.s Ramya Topic: Invitation To Offer and Its Effects On Contract Law Batch-2021-2026 Submit:Manish Sir Amity Law School, Amity University, MaharastraDocument3 pagesContract Law Assignment Name:p.v.n.s Ramya Topic: Invitation To Offer and Its Effects On Contract Law Batch-2021-2026 Submit:Manish Sir Amity Law School, Amity University, Maharastraishika pNo ratings yet
- Consulting BD: Multi-Directional Support For EnterpriseDocument6 pagesConsulting BD: Multi-Directional Support For EnterpriseRajib Ul HaqueNo ratings yet
- Coa - Gov.ph-Step 2 Accept LOIs Issue Eligibility Documents and Conduct Eligibility CheckDocument2 pagesCoa - Gov.ph-Step 2 Accept LOIs Issue Eligibility Documents and Conduct Eligibility CheckPalanas A. VinceNo ratings yet
- Sunflower IncorporatedDocument2 pagesSunflower Incorporatedzokaze33% (3)
- Gallagherbrandguidelines 01-2022Document72 pagesGallagherbrandguidelines 01-2022Amol TiwariNo ratings yet
- Satair Case StudyDocument2 pagesSatair Case StudyWadzanai MuteroNo ratings yet
- Investment and Portfolio AnalysisDocument24 pagesInvestment and Portfolio Analysis‘Alya Qistina Mohd ZaimNo ratings yet
- Pertemuan 7 Akuntansi BiayaDocument33 pagesPertemuan 7 Akuntansi BiayaHanif MusyaffaNo ratings yet
- Nit No.: Juidco/ Nit/ RFP/ Jhb/394Document37 pagesNit No.: Juidco/ Nit/ RFP/ Jhb/394Akhil VermaNo ratings yet
- PWC Final Project CapstoneDocument17 pagesPWC Final Project CapstoneJerry John Ayayi AyiteyNo ratings yet
- Production in Operation ProcessDocument4 pagesProduction in Operation ProcessJolan MatucadingNo ratings yet