Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Tax 1 Reviewer - Compress Vol 1
Uploaded by
bingo0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views4 pagesOriginal Title
Tax 1 Reviewer_compress Vol 1
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views4 pagesTax 1 Reviewer - Compress Vol 1
Uploaded by
bingoCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
TAXATION LAW REVIEWER
Based on the lectures of Atty. Gerald Yu
SRT Faelnar Notes
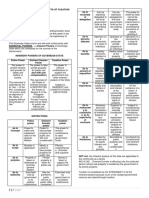
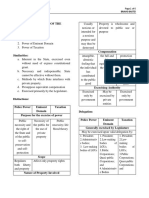
May be exercised only by the There is no transfer of rights.
government or its political At most, there is restraint on
I. June 27, 2018 subdivisions. the injurious use of property.
a. Regarding the 3 inherent powers of the 2) As to purpose: 5) As to Amount of Disposition
State enumerate: Taxation Taxation
The property (generally in the Generally there is no limit on
i. Similarities form of money) is taken for the amount of tax may be
the support of the imposed.
Ans: government.
Eminent Domain
1) They are inherent in the state and Eminent Domain No amount imposed but
maybe exercise by it without need of The property taken for public rather the owner is paid the
express constitutional grant; use; must be compensated. market value of the property
taken.
2) They are not only necessary but
Police Power
indispensable, the state cannot continue or
The use of the property is Police Power
be effective unless it is able to exercise
regulated for the purpose of Amount imposed should not
them;
promoting the general be more than sufficient to
3) They are methods by which the state welfare; it is not cover the cost of the license
interferes with private rights; compensable. and necessary expenses.
4) They are presupposes an equivalent 3) As to persons affected: 6) As to Relationship to Constitution
compensation for the private rights Taxation Taxation
interfered with; and Operates upon a (1) Is subject to certain
Community; or (2) Class of constitutional limitations.
5) They are exercise merely by the Individuals. Including the prohibition
legislators. against impairment of the
Eminent Domain obligations of contracts.
ii. Distinctions Operates on an individual as
(Source: Mamalateo) the owner of a particular Eminent Domain
property. Inferior to the impairment
Ans:
prohibition; government
Police Power cannot expropriate private
1) As to the Authority who exercise the
Operates upon a (1) property which under a
power:
Community; or (2) Class of contract it had previously
Taxation
individuals. bound itself to purchase from
May be exercised only by the
other contracting party.
government or its political
4) As to Effect:
subdivisions
Taxation Police Power
The money contributed Relatively free from
Eminent Domain
becomes part of the public constitutional limitations. Is
May be: (1) Exercised by the
funds superior to the impairment of
government or its political
contract provisions.
subdivisions;
Eminent Domain
(2) Granted to public service
There is a transfer of the b. What are the requisites for Municipal
companies or public utilities.
right to property Ordinances to be Valid?
Police Power
Police Power Ans: To test its validity, following requirements
must be applied for a municipal ordinance to be
TAXATION LAW REVIEWER
Based on the lectures of Atty. Gerald Yu
SRT Faelnar Notes
government is a necessity and this power is an essential BAR Q 2005
valid as laid down by the accepted principles and inherent attribute of sovereignty, belonging as a
governing Municipal Corporations: matter of right to every independent state or Q: May legislative bodies enact laws to raise
government. No sovereign state can continue to exist revenues in the absence of constitutional
1) Must not contravene the Constitution or without the means to pay its expenses; and that for provisions granting said body the power of tax?
any statute; those means, it has the right to compel all citizens and Explain. (2005 Bar)
2) Must not be unfair or oppressive; property within its limits to contribute, hence, the
3) Must not be partial or discriminatory; emergence of the power to tax (51 Am. Jur., Taxation A: YES. The constitutional provisions relating to the
4) Must not prohibit but may regulate trade; 40). power of taxation do not operate as grants of the power
5) Must be reasonable; of taxation to the government, but instead merely
2) Legislative in Character – the power to tax constitute a limitation upon a power which would
is exclusively lodged in the Congress. otherwise be practically without limit.
6) Must be general and consistent with public
policy.
Moreover, it is inherent in nature, being an attribute of
e. What does the power of tax include? sovereignty. There is, thus, no need for a constitutional
c. Define Taxation as a:
grant for the State to exercise this power.
i. Power
Refers to the inherent power of Ans: The power to tax includes the authority to
----
the State, coextensive with (1) determine the (a) nature; (b) object; (c)
sovereignty to demand extent; (d) coverage; (e) apportionment of the
Q: Can police power and taxation co-exist in one
contributions for public purposes tax; (f) situs of the imposition; and (g) method
act of the government?
to support the government. of collection;
(2) grant tax exemptions or condonations; and A: YES. Taxation is no longer envisioned as a measure
ii. Process (3) specify or provide for the administrative as merely to raise revenue to support the existence of the
As a process or act of imposing a well as judicial remedies that either the government. Taxes may be levied with a regulatory
charge by governmental authority government or the taxpayers may avail purpose to provide a means for the rehabilitation and
on property, individuals or themselves in the proper implementation of stabilization of a threatened industry which is affected
transactions to raise money for the tax measure. with public interest as to be within the police power of
public purposes. the state (Caltex Philippines, Inc. v. Commission on
f. When is delegation of the Power to Tax Audit, 208 SCRA 726). Thus, the power of taxation may
iii. Means allowed? be exercised to implement police power (Tiu v.
By which the sovereign state and Videogram Regulatory Board, 151 SCRA 208).
Ans:
apportioning the costs of
GN: The power to tax is purely legislative -----
government among those who
However, delegation of the power to tax is
are privileged to enjoy its
allowed in the following cases:
benefits.
Q: Galaxia Telecommunications Company
To local governments in constructed a telecommunications tower for the
d. Briefly explain the two fold nature of
respect of matters of local purpose of receiving and transmitting cellular
Taxation Power.
concern to be exercised by communications. Meanwhile, the municipal
Ans: the local legislative bodies authorities passed an ordinance entitled “An
1) Inherent in Character – that it co-exist with thereof; Ordinance Regulating the Establishment of Special
the State. It doesn’t need a law; When allowed by the Projects” which imposed fees to regulate activities
constitution; particularly related to the construction and
BAR Q 2003 When the delegation relates maintenance of various structures, certain
merely to administrative construction activities of the identified special
Q: Why is the power to tax considered inherent in implementation that may call projects, which includes “cell sites” or
a sovereign State? (2003 Bar) for some degree of telecommunications towers. Is the imposition of
discretionary powers under a the fee an exercise of the power of taxation?
A: It is considered inherent in a sovereign State because set of sufficient standards
it is a necessary attribute of sovereignty. Without this expressed by law.
power no sovereign State can exist or endure. The
power to tax proceeds upon the theory that the
existence of a
TAXATION LAW REVIEWER
Based on the lectures of Atty. Gerald Yu
SRT Faelnar Notes
Taxes, being the lifeblood of the
government, that should be collected
A: NO. The designation given by the municipal without unnecessary hindrance, every It is a destructive power which interferes with the
authorities does not decide whether the imposition is precaution must be taken not to unduly personal and property rights of the people and takes
properly a license tax or a license fee. The determining suppress it (Republic v. Caguioa, 536 from them a portion of their property for the support of
factors are the purpose and effect of the imposition as SCRA 193 (2007)). the government (Paseo Realty & Development
may be apparent from the provisions of the ordinance. If Corporation v. CA, G.R. No. 119286, October 13, 2004).
the generating of revenue is the primary purpose an 4. Supreme – It is supreme insofar as the
regulation is merely incidental, the imposition is a tax; selection of the subject of taxation is Therefore, it should be exercised with caution to
but if regulation is the primary purpose, the fact that concerned, but it does not mean that it is minimize injury to the proprietary rights of the taxpayer.
incidentally revenue is also obtained does not make the superior to the other inherent powers of It must be exercised fairly, equally and uniformly, lest
imposition a tax (Gerochi v. Department of Energy, 527 the State. the tax collector kill the ‘hen that lays the golden egg’
SCRA 696, 2007). (McCulloch v. Maryland, 4 Wheat, 316 4 L ed. 579,
607) (Roxas v.
The fees in the ordinance are not impositions on the CTA, 23 SCRA 276).
building or structure itself; rather, they are impositions Question: Explain the concept of “wide spectrum
on the activity subject of government regulation, such of taxation”. NOTE: It is more reasonable to say that the
as the installation and construction of the structures. It maxim “the power to tax is the power to destroy” is to
is primarily regulatory in nature, and not primarily A: It means that taxation is one that extends to every describe degree of vigor with which the taxingpower
revenue- raising. While the fees may contribute to the business, trade or occupation; to every object of may be employed in order to raise revenue, and not the
revenues of the municipality, this effect is merely industry; use or enjoyment; and to every species of purposes for which the taxing power may be used
incidental. Thus, the fees imposed in the said ordinance possession. It imposes a burden which, in case of failure (Cooley, 1876).
are not taxes (Smart Communications, Inc., v. to discharge the same, may be followed by the seizure
Municipality of Malvar, Batangas, G.R. No. 204429, and confiscation of property after the observance of due 2. Justice Holmes dictum – “The power to tax is not
February 18, 2014). process. the power to destroy while this Court sits.”
While taxation is said to be the power to destroy, it is by
no means unlimited. When a legislative body having the
h. CHARACTERISTICS of Taxation (10) power to tax a certain subject matter actually imposes
g. What are the SCOPE of Taxation? Briefly (based on the book of Domondon) such a burdensome tax as effectually to destroy the
explain each. (CUPS) right to perform the act or to use the property subject to
1) Inherent in the State; the tax, the validity of the enactment depends upon the
Ans: The following are the charateristics: 2) Subject to Constitutional and Inherent nature and character of the right destroyed. If so great
Limitations; an abuse is manifested as to destroy natural and
1. Comprehensive – It covers persons, 3) Essentially legislative function; fundamental rights which no free government
businesses, activities, professions, rights 4) For public purpose; consistently violate, it is the duty of the judiciary to hold
and privileges, it covers all (Ex. 5) Territorial in operation; such an act unconstitutional.
persons,activities,business) 6) Tax exemption by the government subject to
qualification;
2. Unlimited – It is so unlimited in force and 7) Generally imprescriptible;
searching in extent that courts scarcely In not more than 4 sentences, harmonize/
8) Applies proscriptively;
venture to declare that it is subject to any reconcile Marshal Dictum with Holmes Doctrine.
9) Maybe exercised jointly by police power;
restrictions, except those that such rests 10) Strongest among inherent powers.
in the discretion of the authority which
exercises it (Tio v. Videogram Regulatory
Ans: Marshall’s view refers to a valid tax while Holmes’
Board, G.R. No. 75697, June 18, 1987). i. Expound Marshall Dictum and Holmes view refers to an invalid tax.
Doctrine.
The power to tax involves the power to destroy since the
3. Phenary – it is complete. Under NIRC, the Ans: There are two views on this: power to tax includes the power to regulate even to the
BIR may avail of certain remedies to extent of prohibition or destruction, when it is used
ensure the collection of taxes. 1. US Chief Justice Marshall dictum - The power to
validly as an implement of police power in discouraging
tax involves the power to destroy.
and
TAXATION LAW REVIEWER
Based on the lectures of Atty. Gerald Yu
SRT Faelnar Notes
You might also like
- Nfpa Codes PDFDocument12 pagesNfpa Codes PDFphe zenNo ratings yet
- General Principles of TaxationDocument171 pagesGeneral Principles of TaxationAlexis Von TeNo ratings yet
- Sas Clinical Data Integration Fact SheetDocument4 pagesSas Clinical Data Integration Fact SheetChandrasekhar KothamasuNo ratings yet
- University of The Cordilleras Process CostingDocument5 pagesUniversity of The Cordilleras Process CostingJane PadillaNo ratings yet
- Taxation NotesDocument27 pagesTaxation NotesRound RoundNo ratings yet
- San Beda College of Law Memory Aid in TaxDocument127 pagesSan Beda College of Law Memory Aid in TaxSephronJdm100% (1)
- Privatising Justice: The Security Industry, War and Crime ControlFrom EverandPrivatising Justice: The Security Industry, War and Crime ControlNo ratings yet
- Constitutional Law II Midterms ReviewerDocument26 pagesConstitutional Law II Midterms ReviewerLm RicasioNo ratings yet
- Threaded Weld-In Socket Weld and Limited Space ThermowellsDocument2 pagesThreaded Weld-In Socket Weld and Limited Space ThermowellsRajadurai SinghNo ratings yet
- Token Economics BookDocument81 pagesToken Economics BookNara E Aí100% (3)
- OSN 9800 U64, U32, U16, UPS Installation GuideDocument157 pagesOSN 9800 U64, U32, U16, UPS Installation GuidedonekeoNo ratings yet
- Constitutional Law II Notes on Police Power, Eminent Domain, and TaxationDocument59 pagesConstitutional Law II Notes on Police Power, Eminent Domain, and TaxationKê MilanNo ratings yet
- Taxation Reviewer SAN BEDADocument128 pagesTaxation Reviewer SAN BEDAjustineNo ratings yet
- CPALE REVIEWER in Principles of Income TaxationDocument9 pagesCPALE REVIEWER in Principles of Income TaxationAce LimpinNo ratings yet
- Health 10 Performance TaskDocument4 pagesHealth 10 Performance TaskMary Kryss DG SangleNo ratings yet
- Taxation ReviewerDocument145 pagesTaxation ReviewerNeka Mariel Zarceno StaAnaNo ratings yet
- Tax ReviewerDocument43 pagesTax Reviewerchowchow123No ratings yet
- Consti 2 MidtermsDocument3 pagesConsti 2 MidtermsJayson LanuzaNo ratings yet
- Dimaampao: Doctrine of Symbiotic Relationship: Taxes AreDocument3 pagesDimaampao: Doctrine of Symbiotic Relationship: Taxes AreCelestino LawNo ratings yet
- Notes and Cases On Constitutional Law Ii: Regulatory Board) Landowners Vs Sec. of Agrarian Reform)Document54 pagesNotes and Cases On Constitutional Law Ii: Regulatory Board) Landowners Vs Sec. of Agrarian Reform)Elaiza CarmelNo ratings yet
- Decentralization in the Philippines: A Review of Fiscal, Political and Service Delivery AspectsDocument13 pagesDecentralization in the Philippines: A Review of Fiscal, Political and Service Delivery AspectsDaniel Paulo MangampatNo ratings yet
- Tax 1 ReviewerDocument15 pagesTax 1 ReviewerSheena Rhea FaelnarNo ratings yet
- San Beda College of Law Memory Aid in Taxation LawDocument127 pagesSan Beda College of Law Memory Aid in Taxation LawKim OrquizaNo ratings yet
- General Principles of TaxationDocument10 pagesGeneral Principles of TaxationJustineMaeMillanoNo ratings yet
- Taxation Law 1 - San BedaDocument127 pagesTaxation Law 1 - San Bedalicarl benitoNo ratings yet
- BAR 2023 Coverage in TaxationDocument14 pagesBAR 2023 Coverage in TaxationkbayudanNo ratings yet
- University of Perpetual Help System Dalta: Chapter 1.0 - Principle of Taxation (10 Items)Document15 pagesUniversity of Perpetual Help System Dalta: Chapter 1.0 - Principle of Taxation (10 Items)Derick Ocampo FulgencioNo ratings yet
- Module 1: General Principles of Taxation: "Inherent" Because It Co-Exists With The StateDocument16 pagesModule 1: General Principles of Taxation: "Inherent" Because It Co-Exists With The StateRey Clarence BanggayanNo ratings yet
- Taxation Reviewer General Principles of Taxation: 2. Legislative in CharacterDocument8 pagesTaxation Reviewer General Principles of Taxation: 2. Legislative in CharacterTomas FloresNo ratings yet
- TAXATION MODULE 1: GENERAL PRINCIPLES AND CONCEPTSDocument13 pagesTAXATION MODULE 1: GENERAL PRINCIPLES AND CONCEPTSJurian Jaan PeligroNo ratings yet
- Income TaxationDocument20 pagesIncome TaxationPiolo fuentesNo ratings yet
- TAX TaxationDocument29 pagesTAX TaxationcontactmaydanNo ratings yet
- Scbar Stag Notes (2018) Bravo Baste!: Page 1 of 6Document6 pagesScbar Stag Notes (2018) Bravo Baste!: Page 1 of 6Princess Janine SyNo ratings yet
- Fundamental Powers of StateDocument1 pageFundamental Powers of Statebernardinovitto18No ratings yet
- Constitutional Law II Notes From Atty. Pio Martin Borja's ClassDocument14 pagesConstitutional Law II Notes From Atty. Pio Martin Borja's Classlydie bonacuaNo ratings yet
- People. It Is Considered To Be The Most All-Encompassing of The Three PowersDocument1 pagePeople. It Is Considered To Be The Most All-Encompassing of The Three PowersMary Ann AmbitaNo ratings yet
- Tax SanityDocument8 pagesTax Sanitycruisincruz.jdNo ratings yet
- Income Taxation 1Document7 pagesIncome Taxation 1Lilia Rose ClementeNo ratings yet
- General Principles of TaxationDocument12 pagesGeneral Principles of TaxationRover RossNo ratings yet
- Bill of RightsDocument8 pagesBill of RightsRafeliza CabigtingNo ratings yet
- Regulatory Board) Landowners Vs Sec. of Agrarian Reform)Document14 pagesRegulatory Board) Landowners Vs Sec. of Agrarian Reform)Jeric RealNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1-3 (Reviewer)Document17 pagesChapter 1-3 (Reviewer)LeeshNo ratings yet
- Income TaxationDocument15 pagesIncome TaxationViky Rose EballeNo ratings yet
- Ch. 1 Introduction To Taxation PresentationDocument56 pagesCh. 1 Introduction To Taxation PresentationCarmen SorianoNo ratings yet
- Fundamental Powers of the StateDocument15 pagesFundamental Powers of the StateDanica ConcepcionNo ratings yet
- m1 Taxation Concepts PrinciplesDocument29 pagesm1 Taxation Concepts PrinciplesBryan A.No ratings yet
- Economics and Taxation ReviewerDocument23 pagesEconomics and Taxation ReviewerTettersNo ratings yet
- Income Taxation NotesDocument45 pagesIncome Taxation NotesIlonah HizonNo ratings yet
- Differences:: Doctrine of Proper SubmissionDocument12 pagesDifferences:: Doctrine of Proper SubmissionTheGood GuyNo ratings yet
- Taxation Law I Part I: Taxation in General Chapter I: General Principles of TaxationDocument6 pagesTaxation Law I Part I: Taxation in General Chapter I: General Principles of TaxationAessie Anne Morilla CaguranganNo ratings yet
- ACFrOgAOxBav-Xcpg5xkO3PoGNLgFiDCzt406qsmO3x rVhDMEIi40dvOuvfBxfWFfNm4oc50nimsGPaQx70OjijtkDQ-T02EMF XJGJ E dYVVBdYzQHaO70DRiT2opx96W6zq51LaGXWcvKoYtDocument4 pagesACFrOgAOxBav-Xcpg5xkO3PoGNLgFiDCzt406qsmO3x rVhDMEIi40dvOuvfBxfWFfNm4oc50nimsGPaQx70OjijtkDQ-T02EMF XJGJ E dYVVBdYzQHaO70DRiT2opx96W6zq51LaGXWcvKoYtSha LeenNo ratings yet
- Module 1 - Part 1Document3 pagesModule 1 - Part 1trixie maeNo ratings yet
- Ba223: Taxation (Income Taxation) Module 1: General Principles and Concepts of Taxation - Part 1Document14 pagesBa223: Taxation (Income Taxation) Module 1: General Principles and Concepts of Taxation - Part 1Sh1njo SantosNo ratings yet
- Midterm - Constitution II-uscDocument5 pagesMidterm - Constitution II-uscladyjanelexNo ratings yet
- Taxation Police Power Eminent Domain NatureDocument4 pagesTaxation Police Power Eminent Domain NaturePeytNo ratings yet
- Reviewer - TaxationDocument2 pagesReviewer - TaxationjatalNo ratings yet
- 1 Basic Principles of TaxationDocument13 pages1 Basic Principles of TaxationElsie GenovaNo ratings yet
- 3 Inherent Powers of The StateDocument1 page3 Inherent Powers of The StateJessa Mae CamposNo ratings yet
- Income Taxation Week 2Document16 pagesIncome Taxation Week 2Hannah Rae ChingNo ratings yet
- BA223-Module 1-Lesson ProperDocument12 pagesBA223-Module 1-Lesson ProperMark Bryan ComAyaNo ratings yet
- TaxaaationnnDocument5 pagesTaxaaationnnTrisha Gwynneth BootanNo ratings yet
- TAXATION Chapter 1-2Document3 pagesTAXATION Chapter 1-2shielamaemae0No ratings yet
- Philippine Tax System and Principles of TaxationDocument16 pagesPhilippine Tax System and Principles of TaxationRylleMatthanCorderoNo ratings yet
- Taxation LawDocument127 pagesTaxation LawMark SorianoNo ratings yet
- Taxation Notes SummaryDocument129 pagesTaxation Notes SummaryLove-Love Jeraldine Mondia DalupinesNo ratings yet
- Taxation LawDocument71 pagesTaxation LawEd NerosaNo ratings yet
- Tax 1801 Basic Principles of TaxationDocument26 pagesTax 1801 Basic Principles of TaxationMohammadNo ratings yet
- CONSTI REVIEWERDocument4 pagesCONSTI REVIEWERRiri AnredapNo ratings yet
- Harvard Algorithms cs124 NotesDocument6 pagesHarvard Algorithms cs124 NotesYamini DasguptaNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Engineering and Design: Koki Hibi, Kunihiro Itoh, Kazuo Ikeda, Kenji KonashiDocument11 pagesNuclear Engineering and Design: Koki Hibi, Kunihiro Itoh, Kazuo Ikeda, Kenji KonashiWalid BadrNo ratings yet
- Colloquium: A Learner-Centric View of Mobile Seamless Learning Lung-Hsiang WongDocument5 pagesColloquium: A Learner-Centric View of Mobile Seamless Learning Lung-Hsiang WongWayne LeungNo ratings yet
- Objective: Ofdm ModulationDocument10 pagesObjective: Ofdm ModulationxxNo ratings yet
- Haslinda Mohd Anuar Senior Lecturer School of Law ColgisDocument24 pagesHaslinda Mohd Anuar Senior Lecturer School of Law ColgisSHAHEERANo ratings yet
- Power Solutions GuideDocument60 pagesPower Solutions Guidetheodoiq100% (1)
- Board Resolution for Execution of Sale DeedDocument3 pagesBoard Resolution for Execution of Sale DeedRizwan GhafoorNo ratings yet
- BABOK V3 10. Glossary PDFDocument16 pagesBABOK V3 10. Glossary PDFAakash ChhibberNo ratings yet
- توصية - مستشار زيوت التشحيمDocument4 pagesتوصية - مستشار زيوت التشحيمhasm caadNo ratings yet
- Mobile Scaffold Inspection ChecklistDocument3 pagesMobile Scaffold Inspection Checklistanthony murphyNo ratings yet
- Content Analysis Research Paper ExampleDocument5 pagesContent Analysis Research Paper Examplefvfzfa5d100% (1)
- Quy Trình AgencyDocument4 pagesQuy Trình Agencyson nguyenNo ratings yet
- Ethernet Networking EssentialsDocument5 pagesEthernet Networking Essentialsjmiguel000No ratings yet
- Colonial Comparison Powerpoint TemplateDocument10 pagesColonial Comparison Powerpoint TemplateGraham NicholsNo ratings yet
- Notaries Act 1999 rules for Dutch notariesDocument45 pagesNotaries Act 1999 rules for Dutch notariesAnt1603No ratings yet
- 9 Principles of Income Tax LawsDocument82 pages9 Principles of Income Tax LawsVyankatesh GotalkarNo ratings yet
- Fullpapers Kmp31ce4c51eafullDocument11 pagesFullpapers Kmp31ce4c51eafullyohana biamnasiNo ratings yet
- Example of An Essay CAEDocument3 pagesExample of An Essay CAEJon ArriaranNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Metal Matrix CompositesDocument19 pagesFundamentals of Metal Matrix CompositesAstriaNo ratings yet
- Optex Vibro DatasheetDocument2 pagesOptex Vibro DatasheetGabriel ChiriacNo ratings yet
- IH May-June 2022Document60 pagesIH May-June 2022Omkar R PujariNo ratings yet
- PDF Vertical Axis Wind Turbines DDDocument38 pagesPDF Vertical Axis Wind Turbines DDKunal AhiwaleNo ratings yet