Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Tutorial (Optics - New)
Tutorial (Optics - New)
Uploaded by
rlollchundOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Tutorial (Optics - New)
Tutorial (Optics - New)
Uploaded by
rlollchundCopyright:
Available Formats
OPTICS TUTORIAL
Recall: Fresnel’s Equations for Reflection and Transmission at an interface
(1) (3)
(2) (4)
(5)
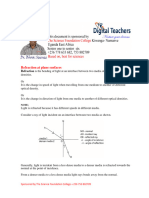
Note that s-polarized light is also called TE-polarization and p-polarized light is also
called TM-polarization, where TE=Transverse Electric and TM=Transverse Magnetic.
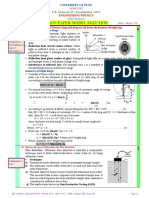
Q1. Calculate the transmission angle for a ray of light incident in air at 30 on a block of crown glass with
refractive index of 1.52.
Q2. A ray of yellow light from a Na discharge lamp falls on the surface of diamond in air at 45. If at that
frequency nd=2.42, compute the angular deviation suffered upon transmission.
Q3. Given an interface between water (nw=1.33) and glass (ng=1.50) compute the transmission angle for
a beam incident in the water at 45.
If the transmitted beam is reversed so that it impinges on the interface, show that 𝜃𝑡 = 45o .
Q4. A beam of 12 cm planar microwaves strikes the surface of a dielectric at 45.
4
If 𝑛𝑡𝑖 = 3, compute
(a) The wavelength in the transmitting medium.
(b) The angle 𝜃𝑡 .
𝑛𝑡 𝑐/𝜆 𝜆
Note: 𝑛𝑡𝑖 = = 𝑐/𝜆𝑡 = 𝜆𝑖 , where i: incident medium, t: transmitted medium.
𝑛𝑖 𝑖 𝑡
Q5. Show that at the Brewster angle, the reflected and transmitted rays are orthogonal.
Q6. For normal incidence, 𝜃𝑖 = 𝜃𝑟 = 𝜃𝑡 = 0.
(a) Write down the Fresnel’s Equations for normal incidence.
(b) Consider air-glass interface
Page 1 of 2
Q7. Show that an s-polarized wave cannot be totally transmitted to another medium.
Q8.
Page 2 of 2
You might also like
- Goos HanchenDocument3 pagesGoos HanchenJoel PaddockNo ratings yet
- 2023 Fall Optics (I) Homework #2, Due 10/26: 0 R I R 0 I 0 - 1Document1 page2023 Fall Optics (I) Homework #2, Due 10/26: 0 R I R 0 I 0 - 1藍博懷No ratings yet
- TutorialDocument12 pagesTutorialSougata HalderNo ratings yet
- HF SystemDocument44 pagesHF Systemmarwan khalilNo ratings yet
- PHYS 5583 (E & M Ii) Home Work #13Document3 pagesPHYS 5583 (E & M Ii) Home Work #13William HammerNo ratings yet
- PHYS 5583 (E & M Ii) FinalDocument4 pagesPHYS 5583 (E & M Ii) FinalwmhammerNo ratings yet
- General Instructions:: Sample Question Paper - 17 Physics (042) Class-XII, Session: 2021-22Document5 pagesGeneral Instructions:: Sample Question Paper - 17 Physics (042) Class-XII, Session: 2021-22bruno we dont talk aboutNo ratings yet
- 32 Waves RefractionDocument12 pages32 Waves RefractioneltytanNo ratings yet
- Determination of The Wave-Length of A Monochromatic Light by Using Newton's RingsDocument15 pagesDetermination of The Wave-Length of A Monochromatic Light by Using Newton's Ringsshehabmustafa23No ratings yet
- REFRACTION AT PLANE SURFACES Glass Block and Liquids A LevelDocument47 pagesREFRACTION AT PLANE SURFACES Glass Block and Liquids A Levelssenyonjotrevor01No ratings yet
- Elecdy Finals BrionesDocument5 pagesElecdy Finals BrionesJonathan Briones Mses MsphyNo ratings yet
- NUMERICAL PROBLEMS ON FIBRE OPTICS - Image.Marked - 1Document4 pagesNUMERICAL PROBLEMS ON FIBRE OPTICS - Image.Marked - 1ANKURANNo ratings yet
- Ejercicios Sobre OndasDocument6 pagesEjercicios Sobre OndasGrabiel RiveroNo ratings yet
- Physics Practice Paper (Laser Light)Document1 pagePhysics Practice Paper (Laser Light)Vansh KumarNo ratings yet
- Total Internal Re EctionDocument169 pagesTotal Internal Re EctionHarshNo ratings yet
- Engineering Physics (PHY 1051)Document11 pagesEngineering Physics (PHY 1051)Harshita GauravNo ratings yet
- The Nature of Light and The Principles of Ray Optics: Chapter OutlineDocument59 pagesThe Nature of Light and The Principles of Ray Optics: Chapter OutlineTran Huy HauNo ratings yet
- Physical Optics and Optical Fibers L04Document36 pagesPhysical Optics and Optical Fibers L04Moamen MohamedNo ratings yet
- E3877 Optics FormulasDocument6 pagesE3877 Optics FormulasKaran DoshiNo ratings yet
- SPPU PHYSICS QP Solution 2012-13 sem-IIDocument8 pagesSPPU PHYSICS QP Solution 2012-13 sem-IIHemantNo ratings yet
- Wave Optics NotesDocument16 pagesWave Optics NotesNarenNo ratings yet
- 10wave OpticsDocument20 pages10wave OpticsrgryjhgsdvrtNo ratings yet
- RefractionDocument19 pagesRefractionYugandhar Veeramachaneni50% (2)
- 1970 A Survey of Clear-Air Propagation Effects Relevant To Optical CommunicationsDocument23 pages1970 A Survey of Clear-Air Propagation Effects Relevant To Optical Communicationsrahulec79No ratings yet
- Chapter 22.1 4Document34 pagesChapter 22.1 4Richard Renz VillafuerteNo ratings yet
- Photonics 02 Light PropertiesDocument39 pagesPhotonics 02 Light PropertiesVandana SharmaNo ratings yet
- Optical Waveguide TheoryDocument17 pagesOptical Waveguide Theory23213mNo ratings yet
- Emw 2010Document2 pagesEmw 2010Ahmed EzioNo ratings yet
- Ray Theory Transmission: Refractive IndexDocument7 pagesRay Theory Transmission: Refractive IndexranjithNo ratings yet
- Theory Week 4Document6 pagesTheory Week 4Miguel EgaNo ratings yet
- FresnelFormulae HebertDocument11 pagesFresnelFormulae HebertJavier TutilloNo ratings yet
- Propagation of VLF Radio Waves in A Model Earth-Ionosphere Waveguide of Arbitrary Height and Finite Surface Impedance Boundary: Theory and ExperimentDocument14 pagesPropagation of VLF Radio Waves in A Model Earth-Ionosphere Waveguide of Arbitrary Height and Finite Surface Impedance Boundary: Theory and ExperimentWhuionoerNo ratings yet
- Polarization SheetDocument2 pagesPolarization SheetModyKing99No ratings yet
- SANKALP - PsdfHASE VII - GO - 4Document5 pagesSANKALP - PsdfHASE VII - GO - 4Unfortunate GamerNo ratings yet
- HW2 and SolutionDocument2 pagesHW2 and Solution藍博懷No ratings yet
- Newtons RingsDocument7 pagesNewtons RingsRavi KumarNo ratings yet
- Assignment Feb2024Document1 pageAssignment Feb2024lifecrazy657No ratings yet
- Rosenzweig 1998 0154Document19 pagesRosenzweig 1998 0154Particle Beam Physics LabNo ratings yet
- Refraction and ReflectionDocument11 pagesRefraction and ReflectionSuresh MedaboinaNo ratings yet
- Opto Electronics NotesDocument40 pagesOpto Electronics NotesDhamodharan Srinivasan100% (1)
- Secret BankingDocument8 pagesSecret BankingberryberryNo ratings yet
- Newton - S Law EntranceDocument4 pagesNewton - S Law EntranceSai pavanNo ratings yet
- The Essential Components of A Communication System Are The TransmitterDocument5 pagesThe Essential Components of A Communication System Are The TransmitterjnvchindwaraonlineexamNo ratings yet
- Physics Class 12 Sample PaperDocument7 pagesPhysics Class 12 Sample PaperAkhilesh ArdcNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Sheet-I Fermat's Principle and Electromagnetic WavesDocument1 pageTutorial Sheet-I Fermat's Principle and Electromagnetic Wavespriyanka choudharyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Wave Reflection and TransmissionDocument34 pagesChapter 3 Wave Reflection and TransmissionDuy TrầnNo ratings yet
- Lecture 14Document8 pagesLecture 14captainhassNo ratings yet
- Encounters With The Golden Ratio in Fluid DynamicsDocument11 pagesEncounters With The Golden Ratio in Fluid DynamicsDeepak Kumar Singh Res. Scholar., Dept. of Mechanical Engg., IIT (BHU)No ratings yet
- PolarizationDocument10 pagesPolarizationMarco San Martín HormazábalNo ratings yet
- Total Internal ReflectionDocument12 pagesTotal Internal ReflectionHarsh WardhanNo ratings yet
- 3 - Refraction at Plane Surface ExerciseDocument10 pages3 - Refraction at Plane Surface ExerciseblehboNo ratings yet
- Lecture 9Document22 pagesLecture 9ShwetaNo ratings yet
- ISAT-2011 Previous Year Question PaperDocument30 pagesISAT-2011 Previous Year Question Paperktktkt01No ratings yet
- Definitions Atm Radiance Transmittance 1983Document4 pagesDefinitions Atm Radiance Transmittance 1983Amarjargal DavaadorjNo ratings yet
- Wave Optics: Important PointsDocument25 pagesWave Optics: Important PointsHimanshu PraneethNo ratings yet
- Sem VI - PHSH - CC13 PDFDocument3 pagesSem VI - PHSH - CC13 PDFÂřîjìť PāłNo ratings yet
- 6 2 Formulae Wave OpticsDocument12 pages6 2 Formulae Wave OpticsNathanian50% (2)
- EE ProblemsDocument33 pagesEE ProblemsSaied Aly SalamahNo ratings yet
- Advances in Structure Research by Diffraction Methods: Fortschritte der Strukturforschung mit BeugungsmethodenFrom EverandAdvances in Structure Research by Diffraction Methods: Fortschritte der Strukturforschung mit BeugungsmethodenR. BrillNo ratings yet
- Macromolecular Microsymposium — 16: Main Lectures Presented at the Sixteenth Microsymposium on Macromolecules (Advances in Scattering Methods), Prague, 12 - 16 July 1976From EverandMacromolecular Microsymposium — 16: Main Lectures Presented at the Sixteenth Microsymposium on Macromolecules (Advances in Scattering Methods), Prague, 12 - 16 July 1976B. SedláčekNo ratings yet