Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Energy in Earth's Atmosphere - G6 Lesson Notes
Uploaded by
Jung Ahn Hong0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views2 pagesThe document discusses energy transfer from the sun to Earth. It states that nearly all of Earth's atmospheric energy comes from the sun as electromagnetic radiation, primarily visible light and infrared. When it reaches Earth, some sunlight is reflected or absorbed by the atmosphere while the rest reaches the surface, where around 50% is absorbed and heats the land and water. The absorbed solar energy is then radiated back into the atmosphere as infrared radiation, trapping heat via the greenhouse effect and maintaining a livable temperature on Earth.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses energy transfer from the sun to Earth. It states that nearly all of Earth's atmospheric energy comes from the sun as electromagnetic radiation, primarily visible light and infrared. When it reaches Earth, some sunlight is reflected or absorbed by the atmosphere while the rest reaches the surface, where around 50% is absorbed and heats the land and water. The absorbed solar energy is then radiated back into the atmosphere as infrared radiation, trapping heat via the greenhouse effect and maintaining a livable temperature on Earth.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views2 pagesEnergy in Earth's Atmosphere - G6 Lesson Notes
Uploaded by
Jung Ahn HongThe document discusses energy transfer from the sun to Earth. It states that nearly all of Earth's atmospheric energy comes from the sun as electromagnetic radiation, primarily visible light and infrared. When it reaches Earth, some sunlight is reflected or absorbed by the atmosphere while the rest reaches the surface, where around 50% is absorbed and heats the land and water. The absorbed solar energy is then radiated back into the atmosphere as infrared radiation, trapping heat via the greenhouse effect and maintaining a livable temperature on Earth.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
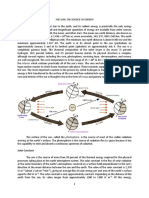
Energy in Earth’s Atmosphere
Learning Objectives
1. State in what form energy travels from the sun to Earth.
2. Explain what happens to the sun’s energy in the atmosphere and at Earth’s
surface
How Does Energy From the Sun Travel to Earth?
Nearly all the energy in Earth’s atmosphere comes from the sun.
This energy travels to Earth as electromagnetic waves, a form of energy that
can move through the vacuum of space.
Electromagnetic waves can be classified according to wavelength, or distance
between waves.
Most of the energy from the sun travels to Earth in the form of visible light
and infrared radiation. A small amount arrives as ultraviolet radiation.
Visible light includes all the colors of the rainbow.
The different colors you see are the result of different wavelengths.
The direct transfer of energy by electromagnetic waves is called radiation.
One form, infrared radiation, has wavelengths longer than red light. It is
invisible to humans but can be felt as heat.
The sun also gives off ultraviolet radiation, which is an invisible form of energy
with wavelengths shorter than violet light.
What Happens to the Sun’s Energy When It Reaches Earth?
Some sunlight is absorbed or reflected by the atmosphere before it can
reach the surface. The rest passes through the atmosphere to the surface.
Different wavelengths of radiation are absorbed by different layers in the
atmosphere.
Some ultraviolet radiation is absorbed by the ozone layer.
Infrared radiation passes farther before some is absorbed by water vapor and
carbon dioxide.
In the troposphere, clouds reflect some sunlight back into space.
Dust-sized particles and gases in the atmosphere disperse light in all directions
in a process called scattering.
About 50% of the sun’s energy that reaches Earth’s surface is absorbed. It heats
land and water
Earth’s surface radiates some energy back into the atmosphere as infrared
radiation.
Some travels all the way back into space, but much is absorbed by water vapor,
carbon dioxide, and other gases in the atmosphere, heating them.
These gases hold heat in the atmosphere in a process called the greenhouse
effect.
The greenhouse effect keeps Earth’s atmosphere at a comfortable temperature.
But scientists have evidence that human activities may be altering this process.
You might also like
- Sun (Sol) : NamesakeDocument7 pagesSun (Sol) : NamesakeJermaine QuinteroNo ratings yet
- Enegy in The Earth's Atmosphere Lesson 4Document4 pagesEnegy in The Earth's Atmosphere Lesson 4Anonymous jIZSqP6YMjNo ratings yet
- Environmental Science: What Is Environmental Physics?Document5 pagesEnvironmental Science: What Is Environmental Physics?AtifMuhammadNo ratings yet
- SunDocument1 pageSunShavinni UrsuaNo ratings yet
- Subtopic: Analysing The Sun The Sun: 24.85% Carbon 0.29% Iron 0.12%Document22 pagesSubtopic: Analysing The Sun The Sun: 24.85% Carbon 0.29% Iron 0.12%Logaprakash RajendranNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Physical Processes On EarthDocument65 pagesChapter 2 - Physical Processes On EarthClydeNo ratings yet
- s.4 Notes GalaxiesDocument8 pagess.4 Notes GalaxiesakyatwinejoshuaNo ratings yet
- PE3 NotesDocument4 pagesPE3 NotesKuo SarongNo ratings yet
- Life Giving Sun Written Report 1Document10 pagesLife Giving Sun Written Report 1Jeraldine ManipolNo ratings yet
- Module For Climate Change Chapter 2 - Physical Processes On EarthDocument23 pagesModule For Climate Change Chapter 2 - Physical Processes On EarthAngelo CabrerosNo ratings yet
- Blue Sky Tech WritingDocument1 pageBlue Sky Tech WritingAndy LeNo ratings yet
- Module 8 - Atmosphere Structure and TemperatureDocument3 pagesModule 8 - Atmosphere Structure and TemperaturejuliaroxasNo ratings yet
- Science Guide Earth, Moon and SunDocument13 pagesScience Guide Earth, Moon and SunМеrlyn CursiNo ratings yet
- Civ300 NotesDocument5 pagesCiv300 Notessupermusician12345No ratings yet
- Chapter 7: Weather Hazards: Learning Outcomes Essential QuestionsDocument25 pagesChapter 7: Weather Hazards: Learning Outcomes Essential Questionsapi-270268482No ratings yet
- Lesson 2-Solar RadiationDocument78 pagesLesson 2-Solar RadiationZyra Yvonne MangligotNo ratings yet
- Science Q3Document7 pagesScience Q3Jaycel StudiesNo ratings yet
- Types of LightDocument1 pageTypes of LightAngelo John R. Javinez100% (1)
- Agro-Meteorology For BSC Agriculture StudentsDocument54 pagesAgro-Meteorology For BSC Agriculture StudentsMadan ThapaNo ratings yet
- The Passage of Solar Radiation Through The AtmosphereDocument2 pagesThe Passage of Solar Radiation Through The AtmosphereSam SelinNo ratings yet
- Geography Worksheet Grade 13 NOVEMBER 18, 2020: Instruction: Answer All Questions On The PaperDocument4 pagesGeography Worksheet Grade 13 NOVEMBER 18, 2020: Instruction: Answer All Questions On The PaperAmelia TaylorNo ratings yet
- The AtmosphereDocument4 pagesThe AtmosphereNina CervantesNo ratings yet
- SunDocument18 pagesSunDheeraj KumarNo ratings yet
- Unit 2: Micro EnvironmentDocument8 pagesUnit 2: Micro EnvironmentHasini KadaruNo ratings yet
- How Does The Sun Produce EnergyDocument3 pagesHow Does The Sun Produce Energycyber linkNo ratings yet
- Ce319 AssignmentDocument9 pagesCe319 Assignmenttoba ziaeeNo ratings yet
- 2 - Pieces of EvidenceDocument27 pages2 - Pieces of EvidenceChosen ExeNo ratings yet
- Stars N GalaxiesDocument56 pagesStars N Galaxiesnozel77No ratings yet
- Science 7 - Lesson 11 - ConsolidationDocument31 pagesScience 7 - Lesson 11 - ConsolidationDrexel DalaygonNo ratings yet
- Solar radiation (Sunlight) : By Suray Abdil Hameed ديشر ديمحلا دبع يرسDocument5 pagesSolar radiation (Sunlight) : By Suray Abdil Hameed ديشر ديمحلا دبع يرسDhiyaa HmdanNo ratings yet
- All Document Reader 1702874093129Document6 pagesAll Document Reader 170287409312961 SURAJ KUMAR TIRKINo ratings yet
- Assignment: Topic Name: Ionosphere Name: Muhammad RizwanDocument22 pagesAssignment: Topic Name: Ionosphere Name: Muhammad RizwanMuhammad RizwanNo ratings yet
- Unit-III Solar EnergyDocument27 pagesUnit-III Solar Energyabhishekbachchan626No ratings yet
- Insolation and Heat Balance of The EarthDocument10 pagesInsolation and Heat Balance of The EarthDevraj H SNo ratings yet
- Radiasi Matahari Dan BumiDocument14 pagesRadiasi Matahari Dan BumiIlham ClinkersNo ratings yet
- Class Note 1 B - 2B - Radiation and Temperature-1Document23 pagesClass Note 1 B - 2B - Radiation and Temperature-1Mangal MurmuNo ratings yet
- Class Note 1 B - 2B - Radiation and Temperature-1Document23 pagesClass Note 1 B - 2B - Radiation and Temperature-1Mangal MurmuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7: Weather Hazards: Learning Outcomes Essential QuestionsDocument60 pagesChapter 7: Weather Hazards: Learning Outcomes Essential Questionsapi-285089552No ratings yet
- Chapter 04 Lecture NotesDocument5 pagesChapter 04 Lecture Notesfirst lastNo ratings yet
- The Sun Is The Star at The Center of The Solar SystemDocument3 pagesThe Sun Is The Star at The Center of The Solar SystemTonatiuh Albarran CordobaNo ratings yet
- Review of LiteratureDocument5 pagesReview of LiteratureAllen HabibovicNo ratings yet
- Class 11 Chap 8Document9 pagesClass 11 Chap 8Vishal Deep SarangalNo ratings yet
- Properties of LightDocument43 pagesProperties of LightKaezeth Jasmine AñanaNo ratings yet
- The Electromagnetic SpectrumDocument5 pagesThe Electromagnetic SpectrumSamantha AmoreNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7, Factors Affecting Insolation On EarthDocument19 pagesChapter 7, Factors Affecting Insolation On EarthPrachi AshmiNo ratings yet
- The Electromagnetic Spectrum by Cindy GriggDocument2 pagesThe Electromagnetic Spectrum by Cindy GriggMae Dil G. Tirariray - PaladNo ratings yet
- Applied Physics:-Cosmic Rays: Name GR - NO. Roll NoDocument10 pagesApplied Physics:-Cosmic Rays: Name GR - NO. Roll NoRAJ KOKARENo ratings yet
- Module 1 Lesson 2Document6 pagesModule 1 Lesson 2MARK BRIAN FLORESNo ratings yet
- Solar Radiation: Department of Physics and Astronomy, The Ohio State University, Columbus 10Document14 pagesSolar Radiation: Department of Physics and Astronomy, The Ohio State University, Columbus 10Fawziah NasserNo ratings yet
- CH 9Document9 pagesCH 9anil.gelra5140No ratings yet
- Sia83 3notesDocument5 pagesSia83 3notesAmaechi ZalNo ratings yet
- Solar RadiationDocument6 pagesSolar RadiationMaizan IsmailNo ratings yet
- Solar Cooker and Water HeaterDocument59 pagesSolar Cooker and Water HeaterDIPAK VINAYAK SHIRBHATE100% (5)
- Solar Radiation: Sunlight and More: Non Conventional Sources OF EnergyDocument15 pagesSolar Radiation: Sunlight and More: Non Conventional Sources OF EnergyAnutosh BhaskarNo ratings yet
- Course Outline For ESI-101: Environmental Problems of Urban Areas Air Pollution Due To Vehicles and Fire CrackersDocument19 pagesCourse Outline For ESI-101: Environmental Problems of Urban Areas Air Pollution Due To Vehicles and Fire CrackersManakan AdityaNo ratings yet
- Page 288-301Document17 pagesPage 288-30105 陳宗榮 RYAN GERALD CHUANo ratings yet
- CHAPTER-3 Solar EnergyDocument53 pagesCHAPTER-3 Solar Energyaman jainNo ratings yet
- Discovering The Essential Universe 6th Edition Comins Solutions ManualDocument6 pagesDiscovering The Essential Universe 6th Edition Comins Solutions Manualkathleenkim22101990bfs100% (37)
- Ebook Discovering The Essential Universe 6Th Edition Comins Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument27 pagesEbook Discovering The Essential Universe 6Th Edition Comins Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFMorganLoganposxg100% (10)
- The Sun: Its Spots and Flares - Astronomy Book for Beginners | Children's Astronomy BooksFrom EverandThe Sun: Its Spots and Flares - Astronomy Book for Beginners | Children's Astronomy BooksNo ratings yet