Professional Documents
Culture Documents
The Dangers of Excessive Sun Tanning
Uploaded by
dsjkfhkjsdhfCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
The Dangers of Excessive Sun Tanning
Uploaded by
dsjkfhkjsdhfCopyright:
Available Formats
Sun tanning, the act of exposing the skin to sunlight to achieve a darker skin tone, has been
a popular practice for decades. While moderate sun exposure can have some benefits, such
as vitamin D production, excessive tanning poses significant health and cosmetic risks. Here
are the primary dangers associated with too much sun tanning:
1. Skin Cancer:
○ Melanoma: This is the most dangerous form of skin cancer and is strongly
linked to intense sun exposure, especially sunburns during childhood.
○ Basal Cell Carcinoma & Squamous Cell Carcinoma: These are the most
common forms of skin cancer and are directly related to cumulative sun
exposure over time.
2. Premature Aging:
○ Wrinkles: Excessive sun exposure breaks down the skin's collagen, leading
to the formation of wrinkles earlier than they might otherwise appear.
○ Age Spots: These are flat, brown spots on the skin that are caused by
prolonged sun exposure.
○ Loss of Skin Elasticity: The sun damages elastin fibers in the skin, causing
it to sag and lose its ability to stretch and return to its original shape.
3. Eye Damage:
○ Cataracts: Prolonged sun exposure without protective eyewear can increase
the risk of developing cataracts, a clouding of the eye's lens.
○ Macular Degeneration: This is a leading cause of blindness, and excessive
sun exposure can accelerate its onset.
○ Pterygium: Also known as "surfer's eye," this is a growth on the white of the
eye that can eventually interfere with vision.
4. Sunburn: Overexposure to the sun can cause the skin to become red, swollen, and
painful. Severe sunburns can lead to blisters and increase the risk of skin cancer.
5. Heat-Related Illnesses:
○ Heat Exhaustion: Symptoms include heavy sweating, weakness, dizziness,
nausea, and headache.
○ Heat Stroke: This is a life-threatening condition where the body's temperature
rises above 104°F (40°C). It requires immediate medical attention.
6. Immune System Suppression: Excessive sun exposure can suppress the skin's
immune function, making it more susceptible to infections.
7. Photosensitivity: Certain medications and cosmetics can make the skin more
sensitive to sunlight, leading to burns or rashes after even short periods of sun
exposure.
8. Allergic Reactions: Some people may develop sun allergies, leading to itchy red
rashes or blisters after sun exposure.
Protective Measures:
1. Sunscreen: Always apply a broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of at least 30,
even on cloudy days.
2. Protective Clothing: Wear long-sleeved shirts, wide-brimmed hats, and sunglasses
with UV protection.
3. Limit Exposure: Avoid the sun between 10 a.m. and 4 p.m., when its rays are the
strongest.
4. Seek Shade: Use umbrellas or other shade structures when outdoors for extended
periods.
In conclusion, while the sun can provide warmth and a bronzed glow, it's essential to respect
its power and take precautions to protect your skin and overall health. Moderation and
protection are key to enjoying the sun safely.
You might also like
- Sun, Skin and HealthFrom EverandSun, Skin and HealthTerry SlevinNo ratings yet
- Health Risks SunDocument2 pagesHealth Risks Sunpruncu.alianmNo ratings yet
- Untitled DocumentDocument4 pagesUntitled Documentdanishfiverr182No ratings yet
- Sunburn (Suntan) & Insect Bites and StingsDocument5 pagesSunburn (Suntan) & Insect Bites and StingsJaz MnNo ratings yet
- The Risks of InfraredDocument1 pageThe Risks of InfraredEricha AbadNo ratings yet
- 09 Sun SafetyDocument2 pages09 Sun SafetyNuragus HariyadiNo ratings yet
- Effects of Sun 1Document1 pageEffects of Sun 1Anna Marie BoloNo ratings yet
- 世界顶级英文杂志特刊珍藏版vol16Your Health Now - 皮肤Document21 pages世界顶级英文杂志特刊珍藏版vol16Your Health Now - 皮肤newstarchj3No ratings yet
- Persuasive Speech (Outline) - ENGKU AISYAH NUHA PDFDocument5 pagesPersuasive Speech (Outline) - ENGKU AISYAH NUHA PDFengkuNo ratings yet
- Why Are Sunscreens ImportantDocument2 pagesWhy Are Sunscreens ImportantSharppy UZUMAKINo ratings yet
- SkinpamphDocument2 pagesSkinpamphjana_cortezNo ratings yet
- Skin Cancer Prevention at Work An Employee Sun Safety ProgramDocument33 pagesSkin Cancer Prevention at Work An Employee Sun Safety ProgramLicca ArgallonNo ratings yet
- Biophys14tav 14Document32 pagesBiophys14tav 14gizex2013No ratings yet
- Sun Safety Reading Comprehension ActivityDocument4 pagesSun Safety Reading Comprehension Activityandrei67% (3)
- Fadia Sherli Asyifa - 20210310068 - Ku 2Document1 pageFadia Sherli Asyifa - 20210310068 - Ku 2Lisa RLNo ratings yet
- Why You Must Wear SunscreenDocument5 pagesWhy You Must Wear SunscreenAin AmirahNo ratings yet
- Why People Should Stay Safe in The SunDocument1 pageWhy People Should Stay Safe in The SunKiranaaNo ratings yet
- Project NotesDocument3 pagesProject Notesapi-743482525No ratings yet
- SS FactPack Final 100504Document26 pagesSS FactPack Final 100504Kelly Egenes WeetsNo ratings yet
- Skin ProtectionDocument4 pagesSkin ProtectionAmaury MaiguaNo ratings yet
- Information Drive Task 2 JAVIER, C.T 10DDocument46 pagesInformation Drive Task 2 JAVIER, C.T 10DXianNo ratings yet
- Persuasive Speech Outline - 1Document4 pagesPersuasive Speech Outline - 1api-242372492No ratings yet
- Library-media-documents-Solar Urticaria Jan 2013 - Lay Reviewed Jan 2013Document5 pagesLibrary-media-documents-Solar Urticaria Jan 2013 - Lay Reviewed Jan 2013Aihara ReikoNo ratings yet
- Sunblock BenefitsDocument4 pagesSunblock BenefitsMccoy DiyNo ratings yet
- Osha 3166 Sun ProtectionDocument2 pagesOsha 3166 Sun ProtectionHasan ShakeelNo ratings yet
- Sunscreen FAQ - 5 19Document10 pagesSunscreen FAQ - 5 19Theresia Loelita100% (1)
- Melasma Updated March 2018 - Lay Reviewed March 2018Document6 pagesMelasma Updated March 2018 - Lay Reviewed March 2018SUBHADIPNo ratings yet
- Melasma Updated March 2018 - Lay Reviewed March 2018Document6 pagesMelasma Updated March 2018 - Lay Reviewed March 2018Nateen MyanmarNo ratings yet
- To A Class of Drugs Known As Keratoplastics To Treat The Itching, Scaling, and Flaking Due To Psoriasis and Also Anthralin Was Also Used To Help Slows Down The Growth of Skin Cells. 13. Answer: 2Document1 pageTo A Class of Drugs Known As Keratoplastics To Treat The Itching, Scaling, and Flaking Due To Psoriasis and Also Anthralin Was Also Used To Help Slows Down The Growth of Skin Cells. 13. Answer: 2May Ann Ann ButaranNo ratings yet
- PCE Final Written ReportDocument9 pagesPCE Final Written ReportwwwaaaiiiNo ratings yet
- What Causes Sunburn?: Consequences of SunburnsDocument2 pagesWhat Causes Sunburn?: Consequences of SunburnsadmassuNo ratings yet
- You Are The New GP in A Small Country Town and The Local Radio Station Has Asked You To Give An Interview About Sun ProtectionDocument3 pagesYou Are The New GP in A Small Country Town and The Local Radio Station Has Asked You To Give An Interview About Sun Protectionfire_n_iceNo ratings yet
- Science 1Document2 pagesScience 1api-267887741No ratings yet
- Suncream EnglíshDocument5 pagesSuncream EnglíshMAI NGUYỄN PHƯƠNGNo ratings yet
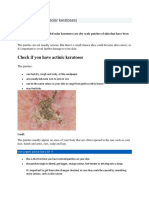
- Actinic KeratosesDocument2 pagesActinic KeratosesًNo ratings yet
- Personal Health Lesson 19 Webinar Slides PDFDocument39 pagesPersonal Health Lesson 19 Webinar Slides PDFsri maNo ratings yet
- Eczema and The Sun: FactsheetDocument4 pagesEczema and The Sun: FactsheetNader M. FayadhNo ratings yet
- Presentation 2Document10 pagesPresentation 2Ieva PetrylaiteNo ratings yet
- Sun-Safety 0512Document2 pagesSun-Safety 0512api-309082881100% (1)
- Shelby Groves GO! WCH03 H1 - Skin Protection Research Paper 2.1Document4 pagesShelby Groves GO! WCH03 H1 - Skin Protection Research Paper 2.1Shelby GrovesNo ratings yet
- Sun's Effects On Skin-1Document2 pagesSun's Effects On Skin-1eclouyNo ratings yet
- Actinic PrurigoDocument5 pagesActinic PrurigodgumelarNo ratings yet
- Science Quarter 4 Week 7-8Document45 pagesScience Quarter 4 Week 7-8princess_aguilera29No ratings yet
- Dialogo Mejorado InglesDocument1 pageDialogo Mejorado InglesAxel PonceNo ratings yet
- Sunscreen: A Cream For The Skin ProtectionDocument1 pageSunscreen: A Cream For The Skin ProtectionJhon Franko GarciaNo ratings yet
- UvraylabDocument3 pagesUvraylabapi-208387749No ratings yet
- Skin Cancer Is Produced by Too Much Exposure To The SunDocument1 pageSkin Cancer Is Produced by Too Much Exposure To The SunOktaviani OktavianiNo ratings yet
- What Happens When You Get A Sunburn?Document10 pagesWhat Happens When You Get A Sunburn?Doc JT BylnNo ratings yet
- Actinic Keratosis PIL Revision 2007Document3 pagesActinic Keratosis PIL Revision 2007flashjetNo ratings yet
- Changes in The Integumentary System of Older Adults 1Document48 pagesChanges in The Integumentary System of Older Adults 1Winter SpringNo ratings yet
- Case Study IGDocument2 pagesCase Study IGCheha PaikNo ratings yet
- Best Way To Reduce Post Vacation Tan: Skin Whitening SurgeonDocument2 pagesBest Way To Reduce Post Vacation Tan: Skin Whitening Surgeontagore11111993 seoNo ratings yet
- Internship ProjectDocument3 pagesInternship Projectapi-743482525No ratings yet
- Harmful Effects of The Sun On Living ThingsDocument2 pagesHarmful Effects of The Sun On Living Thingsrizzalyn sumangNo ratings yet
- Harmful and Good Effects of SunlightDocument2 pagesHarmful and Good Effects of SunlightMike MimNo ratings yet
- Sunbathing Another Bad HabitDocument25 pagesSunbathing Another Bad HabitEftychia PapanikolaouNo ratings yet
- Importance of Wearing SunscreenDocument1 pageImportance of Wearing SunscreenmicelforuniNo ratings yet
- 3E Skin ProtectionDocument4 pages3E Skin ProtectioncarolinangelicaNo ratings yet
- Actinic Keratosis: SymptomsDocument2 pagesActinic Keratosis: SymptomsJoed Vergara Dela PeñaNo ratings yet
- 3E Skin ProtectionDocument4 pages3E Skin ProtectionelmerdanielNo ratings yet
- Wet Wipes and Plastic The Hidden Connection and Its ImplicationsDocument2 pagesWet Wipes and Plastic The Hidden Connection and Its ImplicationsdsjkfhkjsdhfNo ratings yet
- Types of BananasDocument1 pageTypes of BananasdsjkfhkjsdhfNo ratings yet
- History of ElectricityDocument2 pagesHistory of ElectricitydsjkfhkjsdhfNo ratings yet
- Breeds of CatsDocument2 pagesBreeds of CatsdsjkfhkjsdhfNo ratings yet
- Breeds of DogsDocument2 pagesBreeds of DogsdsjkfhkjsdhfNo ratings yet
- Our Solar SystemDocument2 pagesOur Solar SystemdsjkfhkjsdhfNo ratings yet
- Genetic EngineeringDocument1 pageGenetic EngineeringdsjkfhkjsdhfNo ratings yet
- Genetically Modified AnimalsDocument1 pageGenetically Modified AnimalsdsjkfhkjsdhfNo ratings yet
- Uses of Transgenic AnimalsDocument1 pageUses of Transgenic AnimalsdsjkfhkjsdhfNo ratings yet
- History of YogaDocument2 pagesHistory of YogadsjkfhkjsdhfNo ratings yet
- Formative Gen EdDocument119 pagesFormative Gen EdDan GertezNo ratings yet
- VeneerDocument48 pagesVeneerAli IhsanNo ratings yet
- Transforming Growth Factor Beta TGFBDocument8 pagesTransforming Growth Factor Beta TGFBxxxxxxxNo ratings yet
- Do No Harm by Henry Marsh ExtractDocument15 pagesDo No Harm by Henry Marsh ExtractAyu Hutami SyarifNo ratings yet
- Detect Pharmaceutical Health Hazards and ActDocument81 pagesDetect Pharmaceutical Health Hazards and Acttemesgen dinsaNo ratings yet
- Surgery MCQDocument24 pagesSurgery MCQMoiz Khan88% (8)
- Syphilis: Jessica Lyons Period D STD Project 4/22/13Document3 pagesSyphilis: Jessica Lyons Period D STD Project 4/22/13jesssielynnn33No ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Risk Factors in Airline PilotsDocument4 pagesCardiovascular Risk Factors in Airline Pilotsluis11256No ratings yet
- Gingival Inflammation in Mouth Breathing PatientsDocument5 pagesGingival Inflammation in Mouth Breathing PatientsCamiLunaNo ratings yet
- Seminar On: Organisation and Management of Neonatal Services and NicuDocument27 pagesSeminar On: Organisation and Management of Neonatal Services and NicuDimple SweetbabyNo ratings yet
- Presentation List Language Disorders in ChildrenDocument3 pagesPresentation List Language Disorders in Childrenramandeep kaurNo ratings yet
- Assisting IV BTDocument89 pagesAssisting IV BTmhelshy villanuevaNo ratings yet
- Knowledge Regarding Immunization Among Mothers of Under Five ChildrenDocument3 pagesKnowledge Regarding Immunization Among Mothers of Under Five ChildrenEditor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- Rufenal EmulgelDocument2 pagesRufenal EmulgelDr.2020No ratings yet
- Assessment, Northwick ParkDocument2 pagesAssessment, Northwick ParkMelian Anita100% (1)
- Is Fast Food The New Tobacco PDFDocument6 pagesIs Fast Food The New Tobacco PDFCustom Writing ServicesNo ratings yet
- Budget Justification Fy2021Document418 pagesBudget Justification Fy2021Lisa FabianNo ratings yet
- TOP 10 WI LD Foods: A Free Download FromDocument12 pagesTOP 10 WI LD Foods: A Free Download Fromlifelonglearner1100% (3)
- Patients' Perceptions of Barriers To Self-Managing Bipolar DisorderDocument10 pagesPatients' Perceptions of Barriers To Self-Managing Bipolar DisorderMilton MurilloNo ratings yet
- Molecular Biology of BacteriaDocument57 pagesMolecular Biology of BacteriaSean ArifinNo ratings yet
- CENE Course Outline On Psychiatric NursingDocument3 pagesCENE Course Outline On Psychiatric NursingJohn Ryan BuenaventuraNo ratings yet
- Efficacy of Doctorvox On Mutational FalsettoDocument8 pagesEfficacy of Doctorvox On Mutational FalsettoANA CRISTINA MENDEZ DIAZNo ratings yet
- FNCP (Open Drainage) For Soft BoundDocument3 pagesFNCP (Open Drainage) For Soft BoundSean Maghinay BanicoNo ratings yet
- Clandestine Sorbolene !!: Sorbolene Cream, What Is It & What Is It Made From ?Document6 pagesClandestine Sorbolene !!: Sorbolene Cream, What Is It & What Is It Made From ?Indika Lakshmana PathirathneNo ratings yet
- Source and Transmission of InfectionDocument10 pagesSource and Transmission of InfectionInam AliNo ratings yet
- Assessment Dianosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesAssessment Dianosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluationkyaw100% (1)
- MedicalerrorDocument38 pagesMedicalerrorchanda jabeenNo ratings yet
- Bird Nets PDFDocument4 pagesBird Nets PDFPaul LawlessNo ratings yet
- Preoperative Assessment, Premedication & Perioperative DocumentationDocument18 pagesPreoperative Assessment, Premedication & Perioperative DocumentationOxy GenNo ratings yet
- Armohib 28 MSDSDocument8 pagesArmohib 28 MSDSdalton2004No ratings yet