Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Grade 8 Chemistry Pressure
Uploaded by
dodo0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views2 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views2 pagesGrade 8 Chemistry Pressure
Uploaded by
dodoCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
Grade 8 Chemistry
Pressure Notes
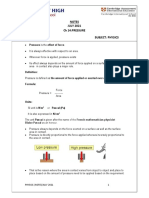
Pressure
Pressure is the force per unit area.
This means that the pressure a solid object exerts on another
solid surface is its weight in newtons divided by its area in
square metres
To increase pressure - increase the force or reduce the area
the force acts on. To cut up your dinner you can either press
harder on your knife or use a sharper one (sharper knives
have less surface area on the cutting edge of the blade).
To reduce pressure - decrease the force or increase the area
the force acts on. If you were standing on a frozen lake and
the ice started to crack you could lie down to increase the
area in contact with the ice. The same force (your weight)
would apply, spread over a larger area, so the pressure would
reduce. Snow shoes work in the same way.
Pressure in fluids
Liquids and gases are both called fluids because they are both
capable of flowing. The pressure in fluids that are at rest acts
equally in all directions
Barometers
Barometers can be used to predict the weather. They measure
changes in atmospheric pressure over time.
Differences in pressure are seen on weather forecast maps as
a pattern of isobars. These changes in pressure are used to
make predictions and, if used with wind readings, are
reasonably accurate.
Many traditional barometers contain mercury. The mercury is
in a long glass tube with an open reservoir at the bottom:
higher atmospheric pressure exerts a downward force on
the mercury in the reservoir - and pushes the mercury up
the tube
lower atmospheric pressure cannot hold up the weight
of the mercury column as effectively - so the mercury
moves lower down the tube
You might also like
- BuoyancyDocument32 pagesBuoyancyamithabhmNo ratings yet
- SV Notes Density PressureDocument9 pagesSV Notes Density PressuresmithaNo ratings yet
- PRESSURE - PowerpointDocument42 pagesPRESSURE - PowerpointJohn OsborneNo ratings yet
- Bab3,4,5 (Fizikt4)Document53 pagesBab3,4,5 (Fizikt4)Mohd Sufian TokimanNo ratings yet
- FluidsDocument55 pagesFluidsdanena88No ratings yet
- Pressure FundamentalsDocument30 pagesPressure Fundamentalsartup3l0nNo ratings yet
- What Is PressureDocument2 pagesWhat Is Pressurewalidderbel1981No ratings yet
- Atmospheric PressureDocument12 pagesAtmospheric Pressureanwar9602020No ratings yet
- Pressure FundamentalsDocument29 pagesPressure FundamentalsJesus Osornio RamirezNo ratings yet
- Fluid Motion.Document3 pagesFluid Motion.Oscar OchoaNo ratings yet
- Physics PressureDocument3 pagesPhysics Pressurelajuli.niliNo ratings yet
- FluidsDocument55 pagesFluidsOsama Abd ElkawiNo ratings yet
- Pressure - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument11 pagesPressure - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaLeo Kyaw MinNo ratings yet
- Pressure PDFDocument19 pagesPressure PDFAbdul rafay ImranNo ratings yet
- Pressure Is The Concentration of A ForceDocument11 pagesPressure Is The Concentration of A ForceNorKamilahMakhtarNo ratings yet
- Class 11 Physics Best Notes For English Medium Session (2023-2024) Chapter-Mechanical Properties of FluidsDocument73 pagesClass 11 Physics Best Notes For English Medium Session (2023-2024) Chapter-Mechanical Properties of FluidsAyushi ShahNo ratings yet
- Fluids: Bernoulli's PrincipleDocument55 pagesFluids: Bernoulli's Principleprince15873No ratings yet
- What Is PressureDocument3 pagesWhat Is PressureJordan MosesNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2022-03-23 at 4.14.26 PMDocument14 pagesScreenshot 2022-03-23 at 4.14.26 PMVariaEsportsNo ratings yet
- G9 Physics - Monday Lesson NoteDocument2 pagesG9 Physics - Monday Lesson NotemicahxNo ratings yet
- Fluid Pressure and Pressure GaugesDocument47 pagesFluid Pressure and Pressure GaugesSin Za DolaNo ratings yet
- Pressure RevisedDocument5 pagesPressure ReviseddanielNo ratings yet
- PressureDocument24 pagesPressureKhrl KentNo ratings yet
- Pressure Is The Concentration of A ForceDocument11 pagesPressure Is The Concentration of A ForceNorKamilahMakhtarNo ratings yet
- Ismail Yusuf: Arts, Science and Commerce College, MumbaiDocument43 pagesIsmail Yusuf: Arts, Science and Commerce College, MumbaiBapu ThoratNo ratings yet
- Pressure in FluidsDocument23 pagesPressure in FluidsANDREW BMGONo ratings yet
- PressureDocument36 pagesPressureAbdullahi K. AbdulwahabNo ratings yet
- Nota Padat Fizik F4 Forces and Pressure NotesDocument24 pagesNota Padat Fizik F4 Forces and Pressure Notesslokkro98% (61)
- Aneroid BarometerDocument4 pagesAneroid BarometerBritney valladaresNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 Mechanical Properties of FluidsDocument49 pagesChapter 9 Mechanical Properties of FluidsimailsoniadeviNo ratings yet
- 202301171673942857PRESSURE8Document40 pages202301171673942857PRESSURE8renjun gfNo ratings yet
- 3 Forces and Pressure 3 1 UnderstandingDocument24 pages3 Forces and Pressure 3 1 UnderstandingLance ShahNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 8.2 Pressure and Gas PressureDocument34 pagesChapter 8 8.2 Pressure and Gas PressureChuahSiewHoon100% (1)
- Reading 08 ADocument11 pagesReading 08 AGREGORIO GOBWAYNo ratings yet
- AP Physics - : Fluid StuffDocument9 pagesAP Physics - : Fluid Stuffnanio_7No ratings yet
- 8.3 Pressure in FluidsDocument5 pages8.3 Pressure in FluidsMatthew ScherbatyNo ratings yet
- GRADE 8 CHEMISTRY Explaining PressureDocument15 pagesGRADE 8 CHEMISTRY Explaining PressuredodoNo ratings yet
- Pressure PPT With AnswersDocument47 pagesPressure PPT With AnswersAngeelina AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Physics NoteDocument8 pagesPhysics NotePoul GonaNo ratings yet
- Force Pressure N 3 PrinciplesDocument57 pagesForce Pressure N 3 PrinciplesSyiera RahmanNo ratings yet
- Haven't Already: Please Pick Up Your Midterm If YouDocument27 pagesHaven't Already: Please Pick Up Your Midterm If YousptbalaNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics Lecture Cat2 2012Document10 pagesFluid Mechanics Lecture Cat2 2012Jithin Sri100% (1)
- Notes JULY 2021 CH 14:pressure Grade: 8 Subject: PhysicsDocument6 pagesNotes JULY 2021 CH 14:pressure Grade: 8 Subject: PhysicsAkshara ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- PleteDocument47 pagesPletediamantechennieNo ratings yet
- PressureDocument7 pagesPressureHakim AbbasNo ratings yet
- Sorsogon National High School: Self-Directed Learning Activity Sheet in General Chemistry 1 (Las 7)Document4 pagesSorsogon National High School: Self-Directed Learning Activity Sheet in General Chemistry 1 (Las 7)Jorgia lianne UrbanoNo ratings yet
- 3 Pressure, Flow, TemperatureDocument66 pages3 Pressure, Flow, TemperatureShamnoor Arefin RatulNo ratings yet
- Pressure, Heat and Temperature - Physics for Kids - 5th Grade | Children's Physics BooksFrom EverandPressure, Heat and Temperature - Physics for Kids - 5th Grade | Children's Physics BooksNo ratings yet
- 71+10 New Science Activities: An interactive approach to learning scienceFrom Everand71+10 New Science Activities: An interactive approach to learning scienceNo ratings yet
- Weather Projects for Young Scientists: Experiments and Science Fair IdeasFrom EverandWeather Projects for Young Scientists: Experiments and Science Fair IdeasRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- 71+10 New Science Project Junior (with CD): learning science - the fun wayFrom Everand71+10 New Science Project Junior (with CD): learning science - the fun wayNo ratings yet
- The Physiology of Decompression: Understanding the Human Body Under PressureFrom EverandThe Physiology of Decompression: Understanding the Human Body Under PressureNo ratings yet
- 52 Transition - Metal - Basics - Ial Edexcel Chemistry - QPDocument17 pages52 Transition - Metal - Basics - Ial Edexcel Chemistry - QPdodoNo ratings yet
- Damaging Food Webs Whats The ConnectionDocument14 pagesDamaging Food Webs Whats The ConnectiondodoNo ratings yet
- 51 Electrochemistry - Ial Edexcel Chemistry - QPDocument15 pages51 Electrochemistry - Ial Edexcel Chemistry - QPdodoNo ratings yet
- 53.2-Reactions Applications of Transition Metals - Ial-Edexcel-Chemistry - QPDocument12 pages53.2-Reactions Applications of Transition Metals - Ial-Edexcel-Chemistry - QPdodoNo ratings yet
- 53.3-Reactions Applications of Transition Metals - Ial-Edexcel-Chemistry - QPDocument14 pages53.3-Reactions Applications of Transition Metals - Ial-Edexcel-Chemistry - QPdodoNo ratings yet
- Answers Fifth Grade Endothermic Reading Comprehension ActivityDocument1 pageAnswers Fifth Grade Endothermic Reading Comprehension ActivitydodoNo ratings yet
- Bioaccumulation: Lesson 6Document16 pagesBioaccumulation: Lesson 6dodoNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry Unit TestDocument17 pagesElectrochemistry Unit TestdodoNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Year 6 ScienceDocument30 pagesCambridge Year 6 ScienceEric ChewNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 Yearly PlanDocument6 pagesGrade 7 Yearly PlandodoNo ratings yet
- Chemsheets A2 1024 Naming Aromatic CompoundsDocument2 pagesChemsheets A2 1024 Naming Aromatic Compoundsxl:D cNo ratings yet
- Class Test 2 MSDocument15 pagesClass Test 2 MSdodoNo ratings yet
- ARENES AND PHENOLS (Autosaved)Document85 pagesARENES AND PHENOLS (Autosaved)dodoNo ratings yet
- Answer-1 IMG 1197 MergedDocument2 pagesAnswer-1 IMG 1197 MergeddodoNo ratings yet
- Answer-1 IMG 1197 MergedDocument2 pagesAnswer-1 IMG 1197 MergeddodoNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 Exam Portion For The 2ND SemesterDocument1 pageGrade 8 Exam Portion For The 2ND SemesterdodoNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 Chemistry Acids Bases WorksheetDocument2 pagesGrade 9 Chemistry Acids Bases WorksheetdodoNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 Chemistry 2ND Semester Final Exam MS Paper 1Document4 pagesGrade 9 Chemistry 2ND Semester Final Exam MS Paper 1dodoNo ratings yet
- Acid Base Equilibria WS (AutoRecovered)Document6 pagesAcid Base Equilibria WS (AutoRecovered)dodoNo ratings yet
- Make Your Own PH ScaleDocument2 pagesMake Your Own PH Scaletdung512No ratings yet
- Grade 9 Chemistry Acids Bases WorksheetDocument2 pagesGrade 9 Chemistry Acids Bases WorksheetdodoNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 2ND Semester Final Exam Paper 1Document14 pagesGrade 9 2ND Semester Final Exam Paper 1dodoNo ratings yet
- Ch2PresStudent PDFDocument13 pagesCh2PresStudent PDFErwin TablizoNo ratings yet
- States of Matter QuizDocument43 pagesStates of Matter QuizMonalisaNo ratings yet
- Physics Transition GuideDocument70 pagesPhysics Transition GuideMagan AliNo ratings yet
- Symbols, Elements, Compounds and Chemical ReactionsDocument30 pagesSymbols, Elements, Compounds and Chemical ReactionsCamaya RumbleNo ratings yet
- 13 - States of MatterDocument5 pages13 - States of MatterdodoNo ratings yet
- 8th Grade Science Eog PacketDocument177 pages8th Grade Science Eog PacketdodoNo ratings yet
- 8th Grade Science Eog PacketDocument177 pages8th Grade Science Eog PacketdodoNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 Short Test 2nd Sem 2Document3 pagesGrade 9 Short Test 2nd Sem 2dodoNo ratings yet