Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chemsheets A2 1024 Naming Aromatic Compounds
Uploaded by
xl:D cOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chemsheets A2 1024 Naming Aromatic Compounds
Uploaded by
xl:D cCopyright:
Available Formats
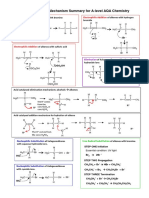
NAMING AROMATIC COMPOUNDS
Aromatic compounds are often named as derivatives of benzene, so benzene forms the root of the name. Some aromatic
compounds have old non-systematic names – some of these are shown underneath in brackets. Chemists are sometimes
less systematic in naming aromatic compounds than other organic compounds.
CH3 Cl NO2 COOH
methylbenzene chlorobenzene nitrobenzene benzenecarboxylic acid
(toluene) (benzoic acid)
If two or more substituents are present on the benzene ring, their positions must be indicated by the use of numbers. This
should be done to give the lowest possible numbers to the substituents. When two or more different substituents are
present, they are listed in alphabetical order.
CH3 CH3 COOH COOH
OH
CH3 O2N NO2
Cl
1,3-dimethylbenzene 4-chloromethylbenzene 2-hydroxybenzenecarboxylic 3,5-dinitrobenzenecarboxylic
(m-xylene) acid acid
The benzene ring can be regarded as a substituent on another molecule, like alkyl groups are. The C 6H5- group is known as
the phenyl group.
NH2 CH CH2 CH3 CH2 CH2 CH3 O CH3
C
phenylamine phenylethene 2-phenylbutane phenylethanone
(aniline)
O O O O
C CH3
C NH C CH3
O CH3
phenyl ethanoate methyl benzenecarboxylate N-phenylethanamide
(methyl benzoate)
There are some other compounds to be aware of, such as phenol.
OH OH OH OH
Cl Cl OH NO2
Cl
phenol 2,4,6-trichlorophenol benzene-1,2-diol 2-nitrophenol
(TCP)
© www.CHEMSHEETS.co.uk 25-May-2016 Chemsheets A2 1024
a b c
d e f
g h i
j k l
m n o
© www.CHEMSHEETS.co.uk 25-May-2016 Chemsheets A2 1024
You might also like
- Aqa A Level Chemistry Cheatsheet 3Document24 pagesAqa A Level Chemistry Cheatsheet 3David AdigboNo ratings yet
- Nucleophilic Substitution and Electrophilic Addition ReactionsDocument4 pagesNucleophilic Substitution and Electrophilic Addition Reactionsjohn mNo ratings yet
- Aqa Mechanisms A Level SummaryDocument5 pagesAqa Mechanisms A Level SummaryRS JNo ratings yet
- Classified Paper 4Document401 pagesClassified Paper 4Reda Zuhair AlQasimNo ratings yet
- Ocr Chem SpecificationDocument104 pagesOcr Chem SpecificationHanaNo ratings yet
- Final Revision Short Qs PDFDocument8 pagesFinal Revision Short Qs PDFketamine100% (1)
- Extracting MetalsDocument13 pagesExtracting MetalsFaridah ShazlinaNo ratings yet
- Maths Ebook OLevelDocument61 pagesMaths Ebook OLevelnomoszengNo ratings yet
- Common Questions IGCSE Physics - Version 1Document3 pagesCommon Questions IGCSE Physics - Version 1RidwanAbrarNo ratings yet
- IGCSE EdExcel 9 1 Chemistry Topic 1 Principles of ChemistryDocument115 pagesIGCSE EdExcel 9 1 Chemistry Topic 1 Principles of ChemistryRobnawaz KhanNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Coordinated Sciences Biological MoleculesDocument9 pagesIGCSE Coordinated Sciences Biological MoleculesSeonaid McDonaldNo ratings yet
- Chapter 22 - Physics - Coordinated Science - IGCSE CambridgeDocument154 pagesChapter 22 - Physics - Coordinated Science - IGCSE CambridgeAlvin DuaneNo ratings yet
- Final Revision P2 (2023) Protected-2Document110 pagesFinal Revision P2 (2023) Protected-2MariamNo ratings yet
- English Olevels Exam Revision NotesDocument17 pagesEnglish Olevels Exam Revision NotesFarhad AlamNo ratings yet
- Topic 2 Lab Skills and Separating MethodsDocument9 pagesTopic 2 Lab Skills and Separating MethodsCHIO SHEUNG YONGNo ratings yet
- Chapter 19 - Carboxylic Acids and Derivatives IDocument8 pagesChapter 19 - Carboxylic Acids and Derivatives INabindra RuwaliNo ratings yet
- 2.1. The Nuclear Atom - Atomic StructureDocument65 pages2.1. The Nuclear Atom - Atomic StructureSaniya DautovaNo ratings yet
- Static Electricity and Current FlowDocument26 pagesStatic Electricity and Current FlowAirul YantiNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSEDocument20 pagesCambridge IGCSEMr. RobotNo ratings yet
- Edexcel IGCSE Biology 9-1 Checklist - Double AwardDocument13 pagesEdexcel IGCSE Biology 9-1 Checklist - Double AwardHenry Exham (Mr Exham)No ratings yet
- Name Class Date: Twenty Electronic ConfigurationsDocument5 pagesName Class Date: Twenty Electronic ConfigurationsLeslie Vanessa CarrilloNo ratings yet
- Chemical Energetics Textbook AnswersDocument7 pagesChemical Energetics Textbook AnswerstrishaNo ratings yet
- KS3 Chemistry Baseline TestDocument14 pagesKS3 Chemistry Baseline Testfadua barakatNo ratings yet
- Caie As Biology 9700 Theory v4Document31 pagesCaie As Biology 9700 Theory v4USMAN JUNAID LAKHA NINo ratings yet
- IGCSE Biology: Practice Essay Questions BDocument12 pagesIGCSE Biology: Practice Essay Questions BDaniel ConwayNo ratings yet
- Chemistry: Pearson Edexcel International GCSE (9-1)Document32 pagesChemistry: Pearson Edexcel International GCSE (9-1)YinMyat MonNo ratings yet
- C10 Organic ChemistryDocument36 pagesC10 Organic ChemistryAlice NgaNo ratings yet
- Gcse Revision 8: Atomic Structure, Structure & Bonding, Formulae & EquationsDocument2 pagesGcse Revision 8: Atomic Structure, Structure & Bonding, Formulae & EquationsWill ShuteNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE Chemistry (0620) (PDFDrive)Document131 pagesCambridge IGCSE Chemistry (0620) (PDFDrive)Kazi Mazzad AhmedNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE™: Co-Ordinated Sciences 0654/41Document15 pagesCambridge IGCSE™: Co-Ordinated Sciences 0654/41TimNo ratings yet
- 0625 Y14 SQ 191114Document114 pages0625 Y14 SQ 191114mydadawalfnNo ratings yet
- Balancing EqueationsDocument6 pagesBalancing EqueationsSurendra ZirpeNo ratings yet
- Substitution and EliminationDocument79 pagesSubstitution and Eliminationjana srutiNo ratings yet
- Cracking Bgcse PhysicsDocument96 pagesCracking Bgcse Physicstmoatshe96No ratings yet
- Flashcards Topic 10 Metals CIE Chemistry IGCSEDocument99 pagesFlashcards Topic 10 Metals CIE Chemistry IGCSEoscarbecNo ratings yet
- Biology Paper-2Document12 pagesBiology Paper-2sollu786_889163149No ratings yet
- CamScanner Scans PDFs from PhotosDocument3 pagesCamScanner Scans PDFs from PhotosAref DahabrahNo ratings yet
- Specimen QP - Paper 1H Edexcel Maths (A) IGCSEDocument20 pagesSpecimen QP - Paper 1H Edexcel Maths (A) IGCSEpanya prachachit100% (1)
- June 1999 Paper 2Document16 pagesJune 1999 Paper 2Yasir100% (1)
- Chemical Reactions O Level NotesDocument22 pagesChemical Reactions O Level Notesveryveryhappyfeet100% (1)
- Student Edexce Moles Workbook Unit 1 PDFDocument112 pagesStudent Edexce Moles Workbook Unit 1 PDFdhawana20% (1)
- Lower Secondary SpecDocument46 pagesLower Secondary SpectharangaNo ratings yet
- Olympiad Model Paper 2018Document9 pagesOlympiad Model Paper 2018deeyamullaNo ratings yet
- Tag Name Code Example Browser ViewDocument9 pagesTag Name Code Example Browser ViewmuzabhaiNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Revision WebsitesDocument1 pageIGCSE Revision WebsitesHakim Teaching CentreNo ratings yet
- Amount of Substance 4: © WWW - CHEMSHEETS.co - Uk 08-April-2020 Chemsheets AS 1247 1Document4 pagesAmount of Substance 4: © WWW - CHEMSHEETS.co - Uk 08-April-2020 Chemsheets AS 1247 1Ahmad RazaNo ratings yet
- IGSCE Business Studies Question PaperDocument12 pagesIGSCE Business Studies Question PaperLamarNo ratings yet
- Answers To Questions: Section 6Document1 pageAnswers To Questions: Section 6rachelNo ratings yet
- Scheme of Work Science Stage 8 - 2018 - tcm143-353967Document90 pagesScheme of Work Science Stage 8 - 2018 - tcm143-353967Seema ChaturvediNo ratings yet
- Physics Most Commonly Asked Questions Paper 2-8Document61 pagesPhysics Most Commonly Asked Questions Paper 2-8Sayuri De AlwisNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE ANSWERS Chemistry Study and Revision Guide Third EditionDocument11 pagesCambridge IGCSE ANSWERS Chemistry Study and Revision Guide Third EditionNermine Abdel GelilNo ratings yet
- S3 Level 2 Assessment 1 Term 2 2009: Section A: MCQ (1 Mark Each)Document5 pagesS3 Level 2 Assessment 1 Term 2 2009: Section A: MCQ (1 Mark Each)Zna101No ratings yet
- Statistics Booklet For NEW A Level AQADocument68 pagesStatistics Booklet For NEW A Level AQAFarhan AktarNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE™: Chemistry 0620/41 May/June 2021Document10 pagesCambridge IGCSE™: Chemistry 0620/41 May/June 2021Mina AbdouNo ratings yet
- Syllabus: Cambridge IGCSE (9-1) First Language English 0990Document35 pagesSyllabus: Cambridge IGCSE (9-1) First Language English 0990Epicmaster27No ratings yet
- Cambridge O Level: Chemistry 5070/21Document11 pagesCambridge O Level: Chemistry 5070/21Pahal KalraNo ratings yet
- Benzene and Its DerivativesDocument21 pagesBenzene and Its DerivativesChristland De jesusNo ratings yet
- Aromatic HydrocarbonsDocument7 pagesAromatic HydrocarbonskailashNo ratings yet
- CHE 232 AromaticDocument38 pagesCHE 232 AromaticMompati LetsweletseNo ratings yet
- Yr13WPQ W3Document1 pageYr13WPQ W3xl:D cNo ratings yet
- This Study Resource Was: OCR Chemistry ADocument3 pagesThis Study Resource Was: OCR Chemistry ASamir HaqNo ratings yet
- Chemsheets A2 1025 Reactions of AromaticsDocument5 pagesChemsheets A2 1025 Reactions of Aromaticsxl:D cNo ratings yet
- WPQYear 13 W2Document1 pageWPQYear 13 W2xl:D cNo ratings yet
- WPQYear 13 W1Document1 pageWPQYear 13 W1xl:D cNo ratings yet
- Hammer Mill NewDocument15 pagesHammer Mill NewViveAunNo ratings yet
- Magnesium Sulphate.Document3 pagesMagnesium Sulphate.Abinov Kumar KTNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Lecture NotesDocument30 pagesChapter 4 Lecture Notessama abubakerNo ratings yet
- M.SC Chemistry SyallabusDocument78 pagesM.SC Chemistry SyallabusSaimeen SayeedNo ratings yet
- Crystalline vs Noncrystalline MaterialsDocument5 pagesCrystalline vs Noncrystalline MaterialsReiniel Cirujano AntonioNo ratings yet
- Empirical and Molecular Formulae WorksheetDocument3 pagesEmpirical and Molecular Formulae WorksheetJohnclyde Ferry100% (1)
- 0 - Acid Base Equilibrium Notes PDFDocument48 pages0 - Acid Base Equilibrium Notes PDFGary VeeNo ratings yet
- WC 500142231Document18 pagesWC 500142231abiazizNo ratings yet
- Mineral solubilities of three quaternary salt systemsDocument13 pagesMineral solubilities of three quaternary salt systemsgabogarreroNo ratings yet
- Leavening Agents To Avoid A PassoverDocument3 pagesLeavening Agents To Avoid A PassoverJames MullenNo ratings yet
- Sulphuric Acid Anodising of en AC-46500 CastDocument9 pagesSulphuric Acid Anodising of en AC-46500 CastgnanasekarNo ratings yet
- Analisis Protein: Disampaikan Oleh Sri Naruki FTP UGM Sudah Di Edit Untuk SmtiDocument42 pagesAnalisis Protein: Disampaikan Oleh Sri Naruki FTP UGM Sudah Di Edit Untuk SmtiBoku Hero-heroNo ratings yet
- Chem Written ReportDocument3 pagesChem Written ReportLexean John Pasayloon Lagaras100% (1)
- 9701 s11 QP 23Document12 pages9701 s11 QP 23Fred H HalderNo ratings yet
- Formative Quiz 4 PS 3rd QuarterbqbqbqDocument2 pagesFormative Quiz 4 PS 3rd QuarterbqbqbqjajajajNo ratings yet
- calibration of congo red colorDocument12 pagescalibration of congo red colorJelena MitrovicNo ratings yet
- Atq Exp 3 Chem 28.1Document6 pagesAtq Exp 3 Chem 28.1Lester Jason T. ChengNo ratings yet
- Plastic Marking DocumentDocument21 pagesPlastic Marking DocumentbobNo ratings yet
- Mwakican Joint Examination Form 4 Chemistry Pp. 3 (Marking Scheme)Document5 pagesMwakican Joint Examination Form 4 Chemistry Pp. 3 (Marking Scheme)andy gideonNo ratings yet
- Natural Product Chemistry Journal Highlights Dietary Phenolics and Health EffectsDocument44 pagesNatural Product Chemistry Journal Highlights Dietary Phenolics and Health EffectsPredrag DjurdjevicNo ratings yet
- Reagents for Water Boiler AnalysisDocument2 pagesReagents for Water Boiler AnalysisArief GatotNo ratings yet
- Lubri Oil Additives PDFDocument47 pagesLubri Oil Additives PDFTejas PatelNo ratings yet
- 17 Carbon and Its CompoundsDocument14 pages17 Carbon and Its Compoundsaustinfru7No ratings yet
- M.sc. ChemistryDocument20 pagesM.sc. Chemistrykunalprabhu148No ratings yet
- ContentsDocument115 pagesContentsNadeem khanNo ratings yet
- Faradays 1 Law of Electrolysis States That The Mass of A Substance Produce, Liberated At/ or DissolvedDocument3 pagesFaradays 1 Law of Electrolysis States That The Mass of A Substance Produce, Liberated At/ or DissolvedAlex noslenNo ratings yet
- DefectsDocument26 pagesDefectsbobblytastic100% (1)
- Problem 1: 50 International Mendeleev Olympiad, 2016 Moscow 1 Theoretical Tour ProblemsDocument8 pagesProblem 1: 50 International Mendeleev Olympiad, 2016 Moscow 1 Theoretical Tour Problemshakuna mata taNo ratings yet
- B464Document3 pagesB464AVINASH CHAVANNo ratings yet
- Hempadur Mastic 45880: Page 1 of 2 Issued: January 2010Document2 pagesHempadur Mastic 45880: Page 1 of 2 Issued: January 2010daimaheshNo ratings yet