Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Vitamin C
Uploaded by
J-eliCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Vitamin C
Uploaded by
J-eliCopyright:
Available Formats
The solubility of organic molecules is often summarized by the phrase, "like dissolves like.
" This means
that molecules with many polar groups are more soluble in polar solvents, and molecules with few or no
polar groups (i.e., nonpolar molecules) are more soluble in nonpolar solvents. (You encountered these
concepts in the "Membranes and Proteins" experiment and the related tutorial, "Maintaining the Body's
Chemistry: Dialysis in the Kidneys".) Hence,
Vitamins are either water-soluble or fat-soluble (soluble in lipids and nonpolar compounds), depending
on their molecular structures. Water-soluble vitamins have many polar groups and are hence soluble in
polar solvents such as water. Fat-soluble vitamins are predominantly nonpolar and hence are soluble in
nonpolar solvents such as the fatty (nonpolar) tissue of the body.
What makes polar vitamins soluble in polar solvents and nonpolar vitamins soluble in nonpolar solvents?
The answer to this question lies in the types of interactions that occur between the molecules in a
solution. Solubility is a complex phenomenon that depends on the change in free energy (DG) of the
process. For a process (in this case, a vitamin dissolving in a solvent) to be spontaneous, the change in
free energy must be negative (i.e., DG<0). The green box below describes the thermodynamic processes
that govern solubility.
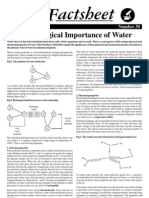
well, consider what you can gather from it just by looking at the molecule…you can make some
educated guesses before you even get a sample and drop it in some water and notice it dissolving..hint
hint..the molecule is not symmetrical..and it has an abundance of hydroxyl groups in various
orientations so considering that those hydroxyl groups are absolutely great at forming hydrogen bonds
with water molecules you could say with some confidence that it is likely to be polar…and you’d be
right.
Electrical charge of a molecule is determines the polarity. A polar molecule has a positive charge at one
end and a negative charge at the other.But non-polar molecule does not have any charge on both
side.Non-polar vitamins are fat soluble. They have few or no polar groups.Polar molecules are very
soluble in water and their charge is neutral.Examples of some polar molecules are,
Vitamin C
Based on its nature, Vitamin C is essentially an Ascorbic acid that has the tendency to produce hydrogen
ions when in an aqueous solution. When drop it in some water and notice it dissolving, it shows an
abundance of hydroxyl groups in various orientations, so considering that those hydroxyl groups are
absolutely great at forming hydrogen bonds with water molecules. And, Polar molecules are very soluble
in water and their charge is neutral. Therefore it’s an acid, and a polar.
You might also like
- AQA Biology Unit 1: Revision Notes: myrevisionnotes, #1From EverandAQA Biology Unit 1: Revision Notes: myrevisionnotes, #1Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Year 12 Additional Questions (Cell Structure)Document25 pagesYear 12 Additional Questions (Cell Structure)dramitrajp9602No ratings yet
- Books Suggested For M.sc. Semester 2Document1 pageBooks Suggested For M.sc. Semester 2gsv988No ratings yet
- Edexcel Alevel Bio2b June 2006 QPDocument12 pagesEdexcel Alevel Bio2b June 2006 QPredrose_17100% (1)
- Cell Structure QuestionsDocument16 pagesCell Structure QuestionsDila OzdolNo ratings yet
- The Effect of Temperature On The Rate of Reaction of YeastDocument8 pagesThe Effect of Temperature On The Rate of Reaction of YeastMatt BeaumontNo ratings yet
- Feversham College A-level Biology Cell StructureDocument7 pagesFeversham College A-level Biology Cell StructureHanoobftwNo ratings yet
- Synthesis of AspirinDocument3 pagesSynthesis of AspirinDella Karissa100% (1)
- Edexcel A2 Chemistry Paper 5Document386 pagesEdexcel A2 Chemistry Paper 5AbdulRahman Mustafa100% (1)
- Chemistry PracticalDocument16 pagesChemistry PracticalAakashNo ratings yet
- SCH4C Esters LabDocument8 pagesSCH4C Esters LabSteve M HallNo ratings yet
- Energy and Respiration Part 2Document28 pagesEnergy and Respiration Part 2Eva SugarNo ratings yet
- Cells 2 FDocument10 pagesCells 2 FEANo ratings yet
- CP 5 - Investigating The Rates of Hydrolysis of HalogenoalkanesDocument2 pagesCP 5 - Investigating The Rates of Hydrolysis of HalogenoalkanesPOPNo ratings yet
- Cell SignalingDocument38 pagesCell SignalingShyrene Mamanao GumbanNo ratings yet
- Esterification LabDocument4 pagesEsterification LabJasmine KolanoNo ratings yet
- Lab 8 Enzyme KineticsDocument5 pagesLab 8 Enzyme KineticsSiti Mastura Abdul RahmanNo ratings yet
- IB Biology Photosynthesis IADocument12 pagesIB Biology Photosynthesis IAAshwinNo ratings yet
- LAPRAK KafeinDocument7 pagesLAPRAK KafeindikabellNo ratings yet
- What Is Hydrogen BondingDocument6 pagesWhat Is Hydrogen BondingKate MagpayoNo ratings yet
- CHEM 22161 Lab 1 :synthesis of Medicinal Agent: Synthesis of AspirinDocument8 pagesCHEM 22161 Lab 1 :synthesis of Medicinal Agent: Synthesis of AspirinKasun WekasingheNo ratings yet
- IB HL Chemistry Assessment Statements Topics 8 and 18Document4 pagesIB HL Chemistry Assessment Statements Topics 8 and 18AndrewNo ratings yet
- Lab ReportDocument12 pagesLab ReportNAEEM MALIKNo ratings yet
- Ap Biology Exam Review Questions OnlyDocument20 pagesAp Biology Exam Review Questions Onlyapi-57781915100% (1)
- Micro Paper On Unknown BacteriaDocument10 pagesMicro Paper On Unknown BacteriaPedro Alonso Titi Benavente100% (1)
- AS Biology Unit 3 Practical ExamDocument30 pagesAS Biology Unit 3 Practical ExamShamaNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration FlowchartDocument1 pageCellular Respiration FlowchartAndrew100% (5)
- How Temperature and pH Affect Enzyme ReactionsDocument5 pagesHow Temperature and pH Affect Enzyme Reactionsanna rothNo ratings yet
- Titration Chemistry Lab Report Vitamin CDocument4 pagesTitration Chemistry Lab Report Vitamin CAlias AliquidNo ratings yet
- How thermochemistry explains daily life reactionsDocument13 pagesHow thermochemistry explains daily life reactionsNicholas LeongNo ratings yet
- Updated Applied Chemistry Programme on CatalysisDocument54 pagesUpdated Applied Chemistry Programme on CatalysisRajatSonkarNo ratings yet
- A2 Further Practical SkillsDocument8 pagesA2 Further Practical SkillsFiaz medico0% (1)
- 17.nitrogen Compounds Lecture NotesDocument34 pages17.nitrogen Compounds Lecture Notesgeoboom12No ratings yet
- Biologically Important Molecules Chemical Tests LabDocument8 pagesBiologically Important Molecules Chemical Tests LabJames DaurayNo ratings yet
- 03 Cell StucturesDocument125 pages03 Cell StucturesAnwar815100% (1)
- Reducing and Non-Reducing Sugars Test: Lab Activity in Preparation For Practical Exam AS Level BiologyDocument36 pagesReducing and Non-Reducing Sugars Test: Lab Activity in Preparation For Practical Exam AS Level BiologyAmisha JuraiNo ratings yet
- Investigating An Enzyme Controlled Reaction - Catalase and Hydrogen PeroxideDocument4 pagesInvestigating An Enzyme Controlled Reaction - Catalase and Hydrogen Peroxidevictoria.crausazNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 112 Dye Kinetics Laboratory 2011Document4 pagesChemistry 112 Dye Kinetics Laboratory 2011Lavenia Alou MagnoNo ratings yet
- Rate ReactionDocument10 pagesRate ReactionTsabit AlbananiNo ratings yet
- Redox TitrationDocument13 pagesRedox TitrationAsif Hasan NiloyNo ratings yet
- Preview of "Acid Dissociation Constant - Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia"Document22 pagesPreview of "Acid Dissociation Constant - Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia"Ange Joey LauNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology Practice 2 Questions and AnswersDocument15 pagesCell Biology Practice 2 Questions and AnswersNgMinhHaiNo ratings yet
- Biology Catalase Experiment DesignDocument6 pagesBiology Catalase Experiment DesignNimisha SharmaNo ratings yet
- Ap Chem 21pdfDocument9 pagesAp Chem 21pdfapi-224463157No ratings yet
- TOPIC: Biological Molecules AIM: Identification of Biochemicals in Pure FormDocument46 pagesTOPIC: Biological Molecules AIM: Identification of Biochemicals in Pure FormManmohan SinghNo ratings yet
- Joshua Haholongan - Science Rate of Reaction ReportDocument13 pagesJoshua Haholongan - Science Rate of Reaction ReportJoshua HaholonganNo ratings yet
- Reaction RateDocument19 pagesReaction RateMuhd Hafiz NizamNo ratings yet
- Buffer SolutionDocument14 pagesBuffer SolutionSony0% (1)
- Gravimetric Analysis of Iron PDFDocument3 pagesGravimetric Analysis of Iron PDFEmrico Luiz PerezNo ratings yet
- Caffeine Extraction 1 PDFDocument25 pagesCaffeine Extraction 1 PDFShanay ShahNo ratings yet
- 30 Water Page 1Document2 pages30 Water Page 1ryuzaki589100% (1)
- Chemical Reactions and Enzymes 2Document26 pagesChemical Reactions and Enzymes 2api-240096234100% (1)
- Amylase Enzyme and Temperature LabDocument4 pagesAmylase Enzyme and Temperature LabJames DaurayNo ratings yet
- Titus John - Enthalpy Prac ReportDocument12 pagesTitus John - Enthalpy Prac Reportapi-295071132No ratings yet
- WM Chemistry Ia Final Risma RemsudeenDocument12 pagesWM Chemistry Ia Final Risma RemsudeenPriyanshi PeelwanNo ratings yet
- 14.hydroxyl Compounds Lecture NotesDocument22 pages14.hydroxyl Compounds Lecture Notesgeoboom12100% (4)
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Kinetics and Equilibrium with AnswersFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Kinetics and Equilibrium with AnswersNo ratings yet
- Group PoliceDocument1 pageGroup PoliceJ-eliNo ratings yet
- Dear Friend PaulDocument1 pageDear Friend PaulJ-eliNo ratings yet
- Exam Sched-Format1Document2 pagesExam Sched-Format1J-eliNo ratings yet
- Beauty Sched-Format1Document2 pagesBeauty Sched-Format1J-eliNo ratings yet
- Performance Checklist ID and IM MedicationsDocument7 pagesPerformance Checklist ID and IM MedicationsJ-eliNo ratings yet
- Neutrophil Function - From Mechanisms To DiseaseDocument33 pagesNeutrophil Function - From Mechanisms To DiseaseCristianNo ratings yet
- 3b MeiosisDocument9 pages3b MeiosisJhaii Sumi-og BerongesNo ratings yet
- Biology Form 4Document9 pagesBiology Form 4Ashlyn OoiNo ratings yet
- Sbi 4U1 Exam Evaluation Outline: Section Marks Time (Min) Student Score Knowledge Thinking/InvestigationDocument2 pagesSbi 4U1 Exam Evaluation Outline: Section Marks Time (Min) Student Score Knowledge Thinking/InvestigationEmanNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 - Diffussion and OsmosisDocument9 pagesUnit 2 - Diffussion and OsmosisWaseem AhmedNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 The Structure and Functions of Biological Molecules, Biols300Document99 pagesChapter 2 The Structure and Functions of Biological Molecules, Biols300mariamNo ratings yet
- Cells Science Year 9 GZDocument4 pagesCells Science Year 9 GZLabeenaNo ratings yet
- Targeted Genome Editing With A DNA-dependent DNA Polymerase and Exogenous DNA-containing TemplatesDocument21 pagesTargeted Genome Editing With A DNA-dependent DNA Polymerase and Exogenous DNA-containing TemplatesSabranth GuptaNo ratings yet
- 1 RhizopodaDocument24 pages1 RhizopodaMohammad Fadel SatriansyahNo ratings yet
- 4 Molecular MachinesDocument15 pages4 Molecular Machinesharshit khareNo ratings yet
- Hint & Sheet Your Hard Work Leads To Strong Foundation: Pre-Nurture: Class - IxDocument5 pagesHint & Sheet Your Hard Work Leads To Strong Foundation: Pre-Nurture: Class - IxAmit RoutNo ratings yet
- Docking AnticancerDocument9 pagesDocking Anticanceradeliyaa khansaNo ratings yet
- pgl3 Luciferase Reporter Vectors Protocol PDFDocument31 pagespgl3 Luciferase Reporter Vectors Protocol PDFSr. RZNo ratings yet
- 2017 OL Cell Cycle Exam ReviewDocument3 pages2017 OL Cell Cycle Exam ReviewAnne Romo50% (8)
- Chapter 7 Neoplasia 1 2 Robbins and Cotran Pathologic Basis of Disease PDFDocument9 pagesChapter 7 Neoplasia 1 2 Robbins and Cotran Pathologic Basis of Disease PDFChethranNo ratings yet
- Action Potential StagesDocument8 pagesAction Potential StagesAhmad HaNo ratings yet
- EDEXCEL- BIOLOGY- IAL Stem Cells: Natural Reservoir and Unique AbilitiesDocument12 pagesEDEXCEL- BIOLOGY- IAL Stem Cells: Natural Reservoir and Unique AbilitiesSwarnapaliliyanageNo ratings yet
- GPCR Mediated Control of Calcium Dynamics A Systems PerspectiveDocument13 pagesGPCR Mediated Control of Calcium Dynamics A Systems PerspectiveLeonel LedezmaNo ratings yet
- 9 Mid Term Xam Paper 2020Document2 pages9 Mid Term Xam Paper 2020om guptaNo ratings yet
- January 2015 (IAL) QP - Unit 4 Edexcel BiologyDocument24 pagesJanuary 2015 (IAL) QP - Unit 4 Edexcel BiologyamjadakramNo ratings yet
- The Muscular System: Essentials of Anatomy & PhysiologyDocument74 pagesThe Muscular System: Essentials of Anatomy & PhysiologySwetaNo ratings yet
- Dna Extraction From Bananas: Group 4 Bio-Drrr-MDocument16 pagesDna Extraction From Bananas: Group 4 Bio-Drrr-MRevirae Camil AriolaNo ratings yet
- FACILITATED DIFFUSIONDocument2 pagesFACILITATED DIFFUSIONCarlo CondeNo ratings yet
- Komunikasi Antar Sel untuk Homeostasis dan Pertumbuhan Seluler/TITLEDocument43 pagesKomunikasi Antar Sel untuk Homeostasis dan Pertumbuhan Seluler/TITLEiikNo ratings yet
- Microbial GrowthDocument12 pagesMicrobial GrowthJosé MolinerosNo ratings yet
- DNA, RNA and Protein SynthesisDocument74 pagesDNA, RNA and Protein SynthesisNabilah Rizky Khairunnisa100% (1)
- Pathology Concept BookDocument481 pagesPathology Concept Bookram dheer100% (2)
- Capturing Light Energy in PhotosynthesisDocument3 pagesCapturing Light Energy in PhotosynthesisJulia ZouNo ratings yet
- Cell Membrane Transport NotesDocument3 pagesCell Membrane Transport NotesJAN PAULINE BABINANo ratings yet
- Worksheet in BloodDocument12 pagesWorksheet in BloodBryan Mae H. DegorioNo ratings yet