Professional Documents
Culture Documents
(August 25, 2021) Basic Concepts in Nutrition and Diet Therapy
Uploaded by
Ma. Ferimi Gleam Bajado0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views3 pagesOriginal Title
[August 25, 2021] Basic Concepts in Nutrition and Diet Therapy
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views3 pages(August 25, 2021) Basic Concepts in Nutrition and Diet Therapy
Uploaded by
Ma. Ferimi Gleam BajadoCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
1
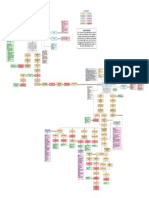
NCM 35 Lecture What is food made of?
Instructor: Mark Genove ● Nutrients → chemical components needed by the body
Transcribed by: Claire J. Tenaja ○ Three general General Functions
a. Provide energy
Link source: (139) NCM35 Session 1 2020 - YouTube b. Build and repair tissues
c. Regulate life processes
Basic Concepts in Nutrition and Diet Therapy
Nutrition Other substances in food
- [WHO] is the intake of food, considered in relation to the body’s dietary ● Anti-nutrients → substances in food that are natural poisons or toxins
needs ○ Ex. Poison found in bitter cassava
- Added that a cornerstone of good health good nutrition is an ● Food additives → chemicals added to some processed foods
adequate well-balanced diet combined with regular physical activity ○ Improve taste or appearance, nutritive value, antioxidants
adequate diet means that one eats the right amount of food in ○ Mark the real appearance of food to make it look fresh and deceive
relation to the person's height health age and physical activity the customers
- Balanced diet → would mean that a person should have consumed ● Contaminants → chemicals, poisons, microorganism, and dirt which gets into food
the right amounts of macronutrients (go, grow, and glow foods) by accident
- Physical activity → done even in as low as 30 mins per day is just ○ Biological contaminants: can be parasites, bacteria, molds, viruses,
the right etc.
→ walking, doing chores, at home, gardening, etc. ■ Can include fertilizers, insecticides, lead, and mercury
→ does not have to be a full-on exercise ○ Physical contaminant: can be fragments of insects, animal hair,
- Science of foods and the nutrients and other substances they contain human hair, wood, soil, etc.
- Study of food we eat and how our body uses them ■ Ex. hair in rice
→ different types of food we consume are used by the body in different ○ Radiological contaminant: radioactive contaminants like Iodine 131
ways and Barium
- Concerned with how food is produced, processed, handled, prepared, ● Harmless microorganisms → used to ferment food
shared, and eaten ○ Can be yeast in bread, yeast in making wine, bacteria in making
→ if not taken seriously, it could lead to disease cheese
- Concerned with what happens to food in the body
→ e.g. carbohydrates are used as energy source Types of food
- Ingestion, digestion, absorption, and utilisation of nutrients ● Basic foods
- Concerned with the study of the environment in the context of food ○ Milk and milk products, meats, poultry, vegetables, dried beans,
production and availability peas, fruits, and grains
- Concerned with human behavior because food choices are personal ○ Can be enriched or fortified
→ food can mean different things to a person (ex. A person may salivate ○ Easily identifiable when you see it
with mangoes instead of chocolates; chocolates can give you a set of ● Enriched food → Foods that are added with vitamins and minerals to restore
unexplainable emotions) what was lost during processing
○ Prior to processing, the food had vitamins and minerals
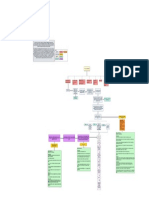
Food ○ During processing, vitamins and minerals are lost
- Nutrition comes from food ○ After processing, vitamins and minerals are added back
- Any substance that is inorganic/organic ● Fortified foods → Addition of one or more nutrients such as vitamins,
- When ingested, it nourishes the body by building and repairing tissues, minerals, amino acids, or protein concentrates in the food so that it contains
supplying heat and energy, and regulating body processes more than what was originally present
- All nutrient that the body needs ● Fast food → Restaurant foods that are available within minutes after
- Basic human need that is able to sustain life (aside from air) customers have ordered
TENAJA 2021 | NCM 35 Lecture
2
○ Eg. French fried, hamburgers, milk shakes; salads, vegetable ■ Eg. outside layer of skin are dead cells, new cells are growing
dishes (healthier options are popping up lately) underneath to replace them → dead skin cells get removed when
● Functional foods → A group of foods known to possess nutrient or non bathing and brushing
nutrients that might lend protection to diseases (although all nutritious can ● Repair tissues
support health in some ways) ○ Usually happens after injury, illness, or vigorous exercise
● Natural foods ○ Body makes new cells to repair the damaged ones
○ No legal definition
○ Could be basic food grown naturally 6 General Groups of Nutrients
● Organic food → Food grown without synthetic pesticides or fertilizers → First 3 are MACRONUTRIENTS: required in large amounts in the diet (measured in
● Nutraceutical food → term with no legal/scientific meaning but sometimes used to grams, not kilograms)
refer to food, nutrients, or dietary supplements believed to have medicinal effects → 4 and 5 are MICRONUTRIENTS: required in trace amounts (milligrams)
● Partitioned foods → foods that are composed of parts of whole food → 6 is the universal solvent
○ Butter comes from milk
○ Sugar come from sugar canes 1. Carbohydrate
○ Corn oil comes from corn - Made of CHO (Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen)
● Processed foods → foods that were subjected to any process such as milling, - Major source of fuel for the body
alteration of texture, addition of additives, cooking, etc. - Easy to convert to ATP (“adenosine triphosphate”)
● Staple goods → foods used frequently or daily - Can be found in grains, vegetables, legumes, and fruits
○ If well-chosen, these foods are NUTRITIOUS - Spares proteins from being used as energy sources
2. Protein
Nutrients - Has the unique function of building and repairing cells
- All the food mentioned above contain nutrients - Contains CHON (Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen, and Nitrogen)
- Nutrients are chemical components needed by the body - Made of smaller building blocks called amino acids
→ Recall the functions of nutrients Can be classified as
a. Provide energy ● Essential → cannot be synthesized in the body and has to be taken from
b. Build and repair tissues exogenous sources
c. Regulate life processes ● Semi-essential → can spare essential amino acids but cannot completely
take its place
Uses of Nutrients in the body ● Non-essential → can be synthesized in the body
● For growth 3. Fat / Lipids
○ Cells use nutrients as a building material for the new cells and other - Concentrated source of energy: For every 1g fat = 9Kcal
nutrients as fuel for energy - Provides structure for the body cells
○ Cells continue to absorb nutrients then grow and divide until there - Protects organs from temperature extremes and mechanical shock
are millions of cells which form the different tissues (such as skin, - Carriers several vitamins
muscle, and bone) - Starting material for making many hormones
● During pregnancy 4. Vitamins
○ Nutrients are used for the baby and the placenta - Regulate body processes such as energy production, blood
○ Increases the size of uterus and the breast clotting, and calcium balance
○ Make more blood and stores fat and other nutrients - Keeps organs and tissue function healthy
● Secretion of body fluids 2 groups of Vitamins
○ The body keeps on making fluids such as saliva, other digestive ● Fat-soluble vitamins (A,D,E,K) → absorbed and transported in the body
juices, tears, and breast milk using fat
● Replace cells ● Water-soluble vitamins (B, C)
○ Cells live only for a short time ○ Most of vitamin B is involved with the pathways for energy
○ Cell replacement happens throughout life production
TENAJA 2021 | NCM 35 Lecture
3
○ Present in watery compartments of food and are easily ● Highest average daily nutrient intake level likely to pose no
excreted adverse health effects to almost all individuals in the
5. Minerals general population
- Simple inorganic substances
- Non-caloric
- Found in structural roles like calcium, phosphorus, and fluoride in Quiz: 1 September 2021
the bones and teeth
- Regulatory roles when it helps control fluid balance and regulation
of muscle contraction
2 groups of Minerals
● Macrominerals → needed in relatively large amounts
● Microminerals → needed in trace amounts
6. Water
- Universal solvent
- Provides a medium where most of the body’s activities are
conducted
- Participates in metabolic reactions
- Medium for transporting vital materials to cells and waste products
away from them
- Controls temperature
- Lubricates joints
- Found in beverages and most food products
- Fruit and vegetables have high water content
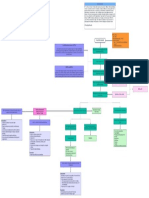
Dietary Reference Intakes
- The collective term comprising reference value for energy and nutrient levels
of intakes
Includes:
1. Estimated Average Requirements (EAR)
● Daily nutrient intake level that meets the median or
average requirement of healthy individuals, in particular:
life stage and sex group, corrected for incomplete
utilization or dietary nutrient bioavailability
2. Recommended Dietary Allowance (RDA)
● Level of intake of energy or nutrient which is considered
adequate for the maintenance of health and well-being of
healthy persons in the population
3. Adequate Intake (AI)
● Daily nutrient intake level that is based on observed or
experimentally-determined approximation of the average
nutrient intake by a group(s) of apparently healthy people
that are assumed to sustain a defined nutritional state
4. Tolerable Upper Intake Levels (UL)
TENAJA 2021 | NCM 35 Lecture
You might also like
- The Plant-Powered Revolution: The Benefits of a Plant-Based DietFrom EverandThe Plant-Powered Revolution: The Benefits of a Plant-Based DietNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in General Biology Ii - Long QuizDocument14 pagesReviewer in General Biology Ii - Long QuizBernardine Angela YanezaNo ratings yet
- NDT LectureDocument58 pagesNDT LectureAkira PinedaNo ratings yet
- NutrientsDocument17 pagesNutrientsdlogiudiceNo ratings yet
- Biopsych Trans Chap 12Document20 pagesBiopsych Trans Chap 12Chantelle SiyNo ratings yet
- Presentation-Biology in Healthcare-Stage2Document41 pagesPresentation-Biology in Healthcare-Stage2alanmauriciohdzNo ratings yet
- 1.2.1 Nutri Lab - Energy and Dimensions of Health - Rle 1Document6 pages1.2.1 Nutri Lab - Energy and Dimensions of Health - Rle 1angelsonarguellesNo ratings yet
- Natalie Kranick Student - Heritagehs - Furlough - U2l3 Special Diet Meal Planning WorksheetDocument9 pagesNatalie Kranick Student - Heritagehs - Furlough - U2l3 Special Diet Meal Planning Worksheetapi-551717392100% (1)
- Summary Unit 3Document1 pageSummary Unit 3Lexxon 29No ratings yet
- Nutrient & Diet Therapy: Chapter 1: Introduction To NutritionDocument4 pagesNutrient & Diet Therapy: Chapter 1: Introduction To NutritionMacy DysancoNo ratings yet
- Nutrition and Diet Therapy ReviewerDocument10 pagesNutrition and Diet Therapy ReviewerNicole CastillaNo ratings yet
- M1 NutritionAndDietTherapy-TRANSESDocument5 pagesM1 NutritionAndDietTherapy-TRANSESrishellemaepilonesNo ratings yet
- 01 - LEC Introduction To Nutrition and Its Principles As A ScienceDocument10 pages01 - LEC Introduction To Nutrition and Its Principles As A ScienceJAN CAMILLE LENONNo ratings yet
- Science Notes 1st SemsterDocument11 pagesScience Notes 1st SemsterEllaNo ratings yet
- Prelims NutridietDocument6 pagesPrelims Nutridietuma crespoNo ratings yet
- GPE1 Module3Document5 pagesGPE1 Module3Bb ParkNo ratings yet
- Quick Revision Notes: Chirkut StudyDocument16 pagesQuick Revision Notes: Chirkut StudyRiya KumariNo ratings yet
- 01 - Introduction - NDT LecDocument9 pages01 - Introduction - NDT LecAndrea Bella SumergidoNo ratings yet
- MODULE 1 - Why Is Nutrition ImportantDocument6 pagesMODULE 1 - Why Is Nutrition ImportantDonna MarieNo ratings yet
- Module: Healthy Eating, Healthy Living: Movement Enhancement 1Document7 pagesModule: Healthy Eating, Healthy Living: Movement Enhancement 1Cyra JimenezNo ratings yet
- Ncma 215 Lec 1 2Document4 pagesNcma 215 Lec 1 2KENSEY MOORE EBROLENo ratings yet
- Midterm MovementDocument7 pagesMidterm Movement트리샤귀엽다No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Nutrition and Diet TherapyDocument59 pagesChapter 1 - Nutrition and Diet TherapySami Ingles100% (1)
- Primary Science 5 Student Book PDFDocument160 pagesPrimary Science 5 Student Book PDFEfe EgeNo ratings yet
- NCM105 (Lec) - Prelim ReviewerDocument3 pagesNCM105 (Lec) - Prelim ReviewerAlthea ManarpiisNo ratings yet
- Healthy Eating Lesson 1 March 29Document4 pagesHealthy Eating Lesson 1 March 29api-487917897No ratings yet
- NCM105 Nutrition - Diet Therapy - Module 1Document13 pagesNCM105 Nutrition - Diet Therapy - Module 1Terrence AntonioNo ratings yet
- NCM 105 LectureDocument17 pagesNCM 105 LectureAaron De DiosNo ratings yet
- Food Science and Tech 1st Lec Batch 3Document41 pagesFood Science and Tech 1st Lec Batch 3Shafaat HussainNo ratings yet
- 1 PL Lect NCM105NDT IntroductionDocument2 pages1 PL Lect NCM105NDT IntroductionMa Ellen LumauagNo ratings yet
- Permaculture Ethics & Principles, Sarah WuDocument11 pagesPermaculture Ethics & Principles, Sarah WucitlalliNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science SHS 1.1 DigestionDocument21 pagesEarth and Life Science SHS 1.1 DigestionLora Lynne KakilalaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Nutrition and Diet Therapy PDFDocument16 pagesIntroduction To Nutrition and Diet Therapy PDFOfficially RandomNo ratings yet
- Unit3-4-5 NutriDocument17 pagesUnit3-4-5 NutriRomm JacobNo ratings yet
- NDT LecDocument19 pagesNDT LecGummy BearsNo ratings yet
- Selected Indigenous Science and TechnologiesDocument7 pagesSelected Indigenous Science and TechnologiesBernard LongboanNo ratings yet
- Fit MeDocument7 pagesFit MelouisesulagueNo ratings yet
- Nutrition and Diet TherapyDocument24 pagesNutrition and Diet TherapyKimberly Marie BayangNo ratings yet
- Biology Lesson 1: Properties of LifeDocument1 pageBiology Lesson 1: Properties of LifeSkye MNo ratings yet
- NCM 105 Prelim Notes Nutrition and Diet TherapyDocument21 pagesNCM 105 Prelim Notes Nutrition and Diet Therapys.labita.sherynejoelNo ratings yet
- FDS - Lesson 1-4Document6 pagesFDS - Lesson 1-4Fides Marie De LeonNo ratings yet
- W1-L2-Script - Concept of Nutrition and Functions of Food PDFDocument6 pagesW1-L2-Script - Concept of Nutrition and Functions of Food PDFIshita SinghNo ratings yet
- Sports and Nutrition Physical Educatin Class 12Document11 pagesSports and Nutrition Physical Educatin Class 12Srushti BhagitNo ratings yet
- Basic Nutrition 2009 RevisedDocument25 pagesBasic Nutrition 2009 Revisedken100% (3)
- Unit 1 - Lesson 2 - CarbohydratesDocument19 pagesUnit 1 - Lesson 2 - CarbohydratesNidhi VyasNo ratings yet
- TRANSFORMATION OF ENERGY (Nutri)Document5 pagesTRANSFORMATION OF ENERGY (Nutri)mroxandeeNo ratings yet
- Nutrition Introduction - NotesDocument5 pagesNutrition Introduction - NotesLudymae BulahanNo ratings yet
- M2 Lesson 1Document10 pagesM2 Lesson 1Catherine Sinen ObinqueNo ratings yet
- Food, Nutrition, and HealthDocument3 pagesFood, Nutrition, and HealthMelissa AlexandraNo ratings yet
- Dinámicas de GruposDocument96 pagesDinámicas de GruposVíctor Hugo Álvarez GonzálezNo ratings yet
- Nutrition Natalie C. Maramba, M.DDocument4 pagesNutrition Natalie C. Maramba, M.DJoan LuisNo ratings yet
- 1.3.6 - 7 BiomoleculesDocument36 pages1.3.6 - 7 BiomoleculesLovely ManaloNo ratings yet
- Nutrition Education ModulesDocument46 pagesNutrition Education ModulesChloe TangonanNo ratings yet
- 111 - Definition of TermsDocument4 pages111 - Definition of TermsCharisa Antonette HuelvaNo ratings yet
- Health Wellness Unit PlanDocument10 pagesHealth Wellness Unit Planapi-645806664No ratings yet
- Nutrients-Ppt. - BandoyDocument20 pagesNutrients-Ppt. - BandoyKenneth caizer BandoyNo ratings yet
- (00:00:43) Class Discussion Digestive SystemDocument11 pages(00:00:43) Class Discussion Digestive SystemMorgan ChristNo ratings yet
- Unit I Nutrition Diet TherapyDocument35 pagesUnit I Nutrition Diet TherapyAlec Anon100% (1)
- Kriyayoga Research Institute: Dietary PrinciplesDocument9 pagesKriyayoga Research Institute: Dietary PrinciplesSaubhagya KarNo ratings yet
- Pe1 Module 3Document7 pagesPe1 Module 3Albert Fabros GapasinNo ratings yet
- Passive Ent Pe2qDocument1 pagePassive Ent Pe2qMa. Ferimi Gleam BajadoNo ratings yet
- Annotated Reading - DHF (Pedia)Document5 pagesAnnotated Reading - DHF (Pedia)Ma. Ferimi Gleam BajadoNo ratings yet
- NCP Part 1 Overview of NCPDocument23 pagesNCP Part 1 Overview of NCPMa. Ferimi Gleam BajadoNo ratings yet
- 7 Nurses Notes Charting FDAR PDocument2 pages7 Nurses Notes Charting FDAR PMa. Ferimi Gleam BajadoNo ratings yet
- 10 1016j Teln 2018 12 005Document6 pages10 1016j Teln 2018 12 005Ma. Ferimi Gleam BajadoNo ratings yet
- FINAL MedsheetDocument1 pageFINAL MedsheetMa. Ferimi Gleam BajadoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Diagnosis and Nursing Interventions For Dengue Hemorrhagic FeverDocument2 pagesNursing Diagnosis and Nursing Interventions For Dengue Hemorrhagic FeverMa. Ferimi Gleam BajadoNo ratings yet
- FHP and NCP (Ravera)Document11 pagesFHP and NCP (Ravera)Ma. Ferimi Gleam BajadoNo ratings yet
- AKI vs. CKD FinalDocument1 pageAKI vs. CKD FinalMa. Ferimi Gleam BajadoNo ratings yet
- D.S.E.B Patient's Initials Submitted By: Josiah David P. Maraat Kyrah Mae Nerez Submitted To: Asst. Prof. Zorrina Luague Date: 10/24/2022Document15 pagesD.S.E.B Patient's Initials Submitted By: Josiah David P. Maraat Kyrah Mae Nerez Submitted To: Asst. Prof. Zorrina Luague Date: 10/24/2022Ma. Ferimi Gleam BajadoNo ratings yet
- FHP and NCPDocument12 pagesFHP and NCPMa. Ferimi Gleam BajadoNo ratings yet
- Simulated Care (Bajado)Document6 pagesSimulated Care (Bajado)Ma. Ferimi Gleam BajadoNo ratings yet
- (REVISED) CRANIOTOMY-CmapDocument1 page(REVISED) CRANIOTOMY-CmapMa. Ferimi Gleam BajadoNo ratings yet
- Simulated Care (Bajado)Document6 pagesSimulated Care (Bajado)Ma. Ferimi Gleam BajadoNo ratings yet
- PDF 1Document101 pagesPDF 1Ma. Ferimi Gleam BajadoNo ratings yet
- Bajado - Annotated Reading (CHN RLE)Document8 pagesBajado - Annotated Reading (CHN RLE)Ma. Ferimi Gleam BajadoNo ratings yet
- Prostate Cancer - Group 12Document1 pageProstate Cancer - Group 12Ma. Ferimi Gleam BajadoNo ratings yet
- Nursing-Care-Plan-J P VDocument8 pagesNursing-Care-Plan-J P VMa. Ferimi Gleam BajadoNo ratings yet
- Fractures - LeafletDocument2 pagesFractures - LeafletMa. Ferimi Gleam BajadoNo ratings yet
- Orthopaedic Surgery - Pre and Post Operative Management in AdultsDocument30 pagesOrthopaedic Surgery - Pre and Post Operative Management in AdultsMa. Ferimi Gleam BajadoNo ratings yet
- NCP Cholecystectomy RevisedDocument7 pagesNCP Cholecystectomy RevisedMa. Ferimi Gleam BajadoNo ratings yet
- Prostate CancerDocument39 pagesProstate CancerMa. Ferimi Gleam BajadoNo ratings yet
- Worksheet On Nursing Management of Fluid Electrolyte and Acid Base ImbalancesDocument3 pagesWorksheet On Nursing Management of Fluid Electrolyte and Acid Base ImbalancesMa. Ferimi Gleam BajadoNo ratings yet
- Care of Postcraniotomy Patients Leaflet 3Document2 pagesCare of Postcraniotomy Patients Leaflet 3Ma. Ferimi Gleam BajadoNo ratings yet
- Black and Brown Business BrochureDocument2 pagesBlack and Brown Business BrochureMa. Ferimi Gleam BajadoNo ratings yet
- Survey Questionnaire B. Socio-Economic DataDocument5 pagesSurvey Questionnaire B. Socio-Economic DataMa. Ferimi Gleam BajadoNo ratings yet
- World Psychiatry - 2016 - Maslach - Understanding The Burnout Experience Recent Research and Its Implications ForDocument9 pagesWorld Psychiatry - 2016 - Maslach - Understanding The Burnout Experience Recent Research and Its Implications ForMa. Ferimi Gleam BajadoNo ratings yet
- HIV - AIDSDocument1 pageHIV - AIDSMa. Ferimi Gleam BajadoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 21 - What Adds Action To A Sentence - PG 45-46Document2 pagesLesson 21 - What Adds Action To A Sentence - PG 45-46Joanne ZhuoNo ratings yet
- Reikland 2515Document6 pagesReikland 2515Ratcatcher GeneralNo ratings yet
- The Puerto Rican StoryDocument11 pagesThe Puerto Rican StoryellenquiltNo ratings yet
- This Book Can Save The Earth - Robert IonescuDocument114 pagesThis Book Can Save The Earth - Robert IonescuRobert IonescuNo ratings yet
- RefineryDocument14 pagesRefinerykrishna sharmaNo ratings yet
- The Hungry Empire - How Britain's Quest For Food Shaped The Modern WorldDocument3 pagesThe Hungry Empire - How Britain's Quest For Food Shaped The Modern WorldHellen CristanchoNo ratings yet
- Max's Wine Dive (Fairview) Brunch MenuDocument1 pageMax's Wine Dive (Fairview) Brunch MenuEater HoustonNo ratings yet
- Panorama Humanitario Mundial 2020 (ONU)Document88 pagesPanorama Humanitario Mundial 2020 (ONU)Carmen RengelNo ratings yet
- TPK 48 Dive Resort New RateDocument9 pagesTPK 48 Dive Resort New RateFatimaNo ratings yet
- How To Write An IELTS Writing Task 1Document3 pagesHow To Write An IELTS Writing Task 1Alex ChireaNo ratings yet
- 2013-3-May-Attitude and Buying Behaviour of Consumers - MasuDocument5 pages2013-3-May-Attitude and Buying Behaviour of Consumers - MasuSakthirama VadiveluNo ratings yet
- Science5 Q1 M2 W4Document26 pagesScience5 Q1 M2 W4CARICRIS MARATANo ratings yet
- Sugar BeatDocument13 pagesSugar Beatijazqamar7704No ratings yet
- Present SimpleDocument6 pagesPresent SimpleKarlNo ratings yet
- Khmer Culture & Religion: Customs and TraditionsDocument44 pagesKhmer Culture & Religion: Customs and TraditionsDom PouchNo ratings yet
- APPLICATIONS Food-Compendium en 161024Document130 pagesAPPLICATIONS Food-Compendium en 161024Omar turco curiNo ratings yet
- Final Draft Native AmericanDocument3 pagesFinal Draft Native AmericanEma NoveloNo ratings yet
- AmulDocument32 pagesAmulVishal DaveNo ratings yet
- Chocolate CrumbleDocument2 pagesChocolate CrumbleSridhar ManickamNo ratings yet
- Breadbee Company Business PlanDocument41 pagesBreadbee Company Business PlanGiNo ratings yet
- Meet OUR Ambas Sadors: Ramon PerezDocument5 pagesMeet OUR Ambas Sadors: Ramon PerezAntonisMavridisNo ratings yet
- Holden Manz BrochureDocument4 pagesHolden Manz Brochureapi-177458342No ratings yet
- Parenteral Nutrition CalculationsDocument62 pagesParenteral Nutrition Calculationsmikosoft2010No ratings yet
- Science 4 - q1 - Module 4of6 - Changes That Mareials Undergowhen Mixed With Other Materials - v2Document20 pagesScience 4 - q1 - Module 4of6 - Changes That Mareials Undergowhen Mixed With Other Materials - v2Mary Ann BernalesNo ratings yet
- Astoria Jada User ManualDocument32 pagesAstoria Jada User ManualphreichNo ratings yet
- De Cuong Tieng Anh 2012Document60 pagesDe Cuong Tieng Anh 2012Dao Xuan Phuong TrangNo ratings yet
- Varieties of Guatemalan TamalesDocument1 pageVarieties of Guatemalan TamalesMet TechniciansNo ratings yet
- Sequencing Events: By: Lucila O. Mellomida T-Iii Cawayan Elem. SchoolDocument21 pagesSequencing Events: By: Lucila O. Mellomida T-Iii Cawayan Elem. SchoolAndrea PielagoNo ratings yet
- Elementary Unit 6b PDFDocument2 pagesElementary Unit 6b PDFPatrick VásquezNo ratings yet
- New Hope For Malnourished Mothers and ChildrenDocument12 pagesNew Hope For Malnourished Mothers and ChildrenthousanddaysNo ratings yet