Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Management by Objectives A Framework For Organizational Success
Uploaded by
SuhailShaikh0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views6 pagesManagement by Objectives A Framework for Organizational Success
Original Title
Management by Objectives A Framework for Organizational Success
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentManagement by Objectives A Framework for Organizational Success
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views6 pagesManagement by Objectives A Framework For Organizational Success
Uploaded by
SuhailShaikhManagement by Objectives A Framework for Organizational Success
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 6
Title: Management by Objectives: A Framework for
Organizational Success
Introduction
Management by Objectives (MBO) is a results-
oriented management philosophy and framework
that was introduced by management guru Peter
Drucker in his 1954 book "The Practice of
Management." It is a systematic and collaborative
approach to management that focuses on setting
clear objectives, establishing performance metrics,
and aligning individual and organizational goals to
drive success. MBO has played a pivotal role in
modern management practices, offering a structured
method for achieving organizational excellence
through goal alignment, employee engagement, and
continuous improvement.
The Principles of Management by Objectives
1. Goal Setting: The fundamental principle of MBO is
setting clear and specific objectives for individuals,
teams, and the organization as a whole. These
objectives should be SMART—Specific, Measurable,
Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound. When goals
are well-defined, employees have a clear sense of
direction and purpose.
2. Participation and Collaboration: MBO encourages
collaboration between managers and employees. It
involves setting objectives in a participatory manner,
with input from both sides. This not only promotes a
sense of ownership and commitment but also
harnesses the collective intelligence of the
organization.
3. Performance Metrics: To evaluate progress towards
objectives, MBO relies on quantifiable performance
metrics and key performance indicators (KPIs). These
metrics enable regular tracking and assessment of
progress, allowing for timely adjustments and
interventions when necessary.
4. Continuous Feedback: Effective MBO involves
continuous feedback and communication. Managers
and employees engage in regular discussions to
review progress, identify challenges, and explore
potential solutions. This ongoing dialogue helps
keep everyone aligned with organizational goals.
5. Performance Appraisal and Rewards: MBO integrates
performance appraisal and reward systems with the
achievement of objectives. Employees are assessed
based on their ability to meet their assigned goals,
and rewards are linked to the degree of success in
achieving those objectives.
Benefits of Management by Objectives
1. Goal Clarity: MBO ensures that everyone within the
organization understands their role and
responsibilities, as well as the broader objectives of
the organization. This clarity reduces ambiguity and
enhances focus.
2. Employee Motivation: By involving employees in the
goal-setting process and linking rewards to objective
attainment, MBO fosters a sense of ownership and
motivation. Employees are more likely to be
engaged and committed to achieving their goals.
3. Improved Performance: The systematic approach of
MBO encourages regular performance monitoring
and adjustment, which leads to improved
performance and increased efficiency. It also
facilitates the identification of underperforming
areas and the implementation of corrective
measures.
4. Alignment with Organizational Strategy: MBO
ensures that individual and team objectives are
aligned with the overarching goals of the
organization. This alignment helps the organization
make progress toward its strategic priorities.
5. Enhanced Communication: The continuous feedback
loop in MBO promotes open communication
between managers and employees. This leads to
better understanding, trust, and collaboration within
the organization.
Challenges and Criticisms
While Management by Objectives has many
advantages, it is not without its challenges and
criticisms. Some of the common challenges include:
1. Overemphasis on Quantitative Goals: Critics argue
that MBO may lead to an overemphasis on
quantitative objectives at the expense of qualitative
factors, potentially sacrificing long-term quality for
short-term gains.
2. Rigidity: In some cases, the rigid adherence to
predetermined objectives may hinder adaptability
and creativity, especially in rapidly changing
environments.
3. Potential for Micromanagement: If not implemented
properly, MBO can devolve into micromanagement,
with managers excessively monitoring employees'
activities to ensure goal achievement.
4. Unrealistic Goals: Setting overly ambitious objectives
can demotivate employees and lead to burnout if
expectations are not realistic or attainable.
Conclusion
Management by Objectives remains a valuable
management framework that promotes goal
alignment, employee engagement, and performance
improvement within organizations. When
implemented effectively, it can significantly
contribute to an organization's success by providing
a structured approach to goal setting, performance
measurement, and continuous improvement.
However, it is essential to strike a balance between
quantitative objectives and qualitative factors while
fostering a collaborative and adaptive organizational
culture. MBO, when applied thoughtfully and flexibly,
continues to be a relevant and powerful tool in the
hands of modern managers striving for
organizational excellence.
You might also like
- Favoritism in The Workplace and Its Effect On The OrganizationDocument11 pagesFavoritism in The Workplace and Its Effect On The OrganizationSuhailShaikhNo ratings yet
- How To Develop A Super Memory and Learn Like A Genius With Jim Kwik Nov 2018 LaunchDocument12 pagesHow To Develop A Super Memory and Learn Like A Genius With Jim Kwik Nov 2018 LaunchCarolina Ávila67% (3)
- 7 Steps To Start Goat Farming Business For ProfitDocument8 pages7 Steps To Start Goat Farming Business For ProfitSuhailShaikhNo ratings yet
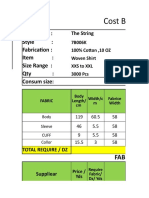
- Costing Sheet For Woven ShirtDocument9 pagesCosting Sheet For Woven ShirtSuhailShaikhNo ratings yet
- The Concept of Management by Objectives (MBO)Document6 pagesThe Concept of Management by Objectives (MBO)arunkollelilNo ratings yet
- Psychotherapy, Counseling and Career Counseling DiscussedDocument37 pagesPsychotherapy, Counseling and Career Counseling DiscussedVanda LeitaoNo ratings yet
- MBO2Document25 pagesMBO2Toqeer AhmadNo ratings yet
- Management by Objectives (Peter Drucker)Document7 pagesManagement by Objectives (Peter Drucker)Lawrence JoshuaNo ratings yet
- R. L. Stine Writing ProgramDocument17 pagesR. L. Stine Writing ProgramBrent ArnoldNo ratings yet
- MBO Guide for Healthcare ManagementDocument39 pagesMBO Guide for Healthcare ManagementAsha jiluNo ratings yet
- GoalDocument7 pagesGoalAmna SheikhNo ratings yet
- Performance Polos Classic PolosDocument37 pagesPerformance Polos Classic PolosSuhailShaikhNo ratings yet
- Assignment MBODocument4 pagesAssignment MBOSrinivas Polikepati0% (2)
- Programmed InstructionDocument17 pagesProgrammed Instructionakhimoloos88% (17)
- Industrial Training Company Contact ListDocument37 pagesIndustrial Training Company Contact ListJerome Wong75% (4)
- Introduction to Management Concepts and TechniquesDocument28 pagesIntroduction to Management Concepts and Techniquesnaseer_satti100% (1)
- Academic and Professional DevelopmentDocument16 pagesAcademic and Professional DevelopmenttrangNo ratings yet
- Structural Approach To OrganizationDocument3 pagesStructural Approach To OrganizationGhufran HussainNo ratings yet
- Question Bank Research MethodologyDocument5 pagesQuestion Bank Research Methodologyradhakrishnan0% (1)
- Performance Apraisal SystemDocument14 pagesPerformance Apraisal SystemUrvi ParekhNo ratings yet
- Management by Objectives: Carhla FungDocument23 pagesManagement by Objectives: Carhla FungNicoNgrace LimNo ratings yet
- Management by Objectives ExplainedDocument5 pagesManagement by Objectives ExplainedHimanshu DarganNo ratings yet
- Management by Objectives NotesDocument12 pagesManagement by Objectives NotesHazel KapurNo ratings yet
- Management by ObjectiveDocument5 pagesManagement by ObjectiveTanishka GuptaNo ratings yet
- Management by ObjectiveDocument7 pagesManagement by Objectivehopelyn youNo ratings yet
- Management by ObjectivesDocument9 pagesManagement by ObjectivesSakshi Poojari MSCP HRDMNo ratings yet
- MboDocument8 pagesMboSingh AngadNo ratings yet
- Objectives Management Employees: Management by Objectives (MBO) Is A Process of DefiningDocument10 pagesObjectives Management Employees: Management by Objectives (MBO) Is A Process of DefiningmeragaunNo ratings yet
- What Are The Benefits and Drawbacks of MBO Programs? ExplainDocument6 pagesWhat Are The Benefits and Drawbacks of MBO Programs? ExplainRehncy SinghNo ratings yet
- Management AssignmentDocument18 pagesManagement AssignmentSrishti OhriNo ratings yet
- Group Activity: in Groups Discuss The Different Topics We Have Discussed So Far and Give A SummaryDocument30 pagesGroup Activity: in Groups Discuss The Different Topics We Have Discussed So Far and Give A SummaryMohamed LisaamNo ratings yet
- Management Styles 2014Document16 pagesManagement Styles 2014muyakihumbaNo ratings yet
- Miafe Task 03Document3 pagesMiafe Task 03Mia BernardioNo ratings yet
- MBO Program Goal Setting in ActionDocument7 pagesMBO Program Goal Setting in ActionPhương UyênNo ratings yet
- Management by ObjectivesDocument22 pagesManagement by ObjectivesJayalakshmi RajanNo ratings yet
- MBO Lecture NotesDocument8 pagesMBO Lecture NotesDr reena SethiNo ratings yet
- Management by ObjectivesDocument11 pagesManagement by ObjectivesW-LunChinNo ratings yet
- MBO Steps GuideDocument5 pagesMBO Steps GuideViral RiteenNo ratings yet
- Unit - 5 Modern Management ConceptsDocument19 pagesUnit - 5 Modern Management ConceptsAlokShrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Management by Objectives (MBO)Document6 pagesManagement by Objectives (MBO)Sathyaraj MathivananNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5 Laboratory ManagementDocument8 pagesLesson 5 Laboratory Managementcarla raveloNo ratings yet
- Management by Objectives (Mbo)Document15 pagesManagement by Objectives (Mbo)Ayush GoelNo ratings yet
- MBO AND MANAGERIAL DECISION-MAKINGDocument3 pagesMBO AND MANAGERIAL DECISION-MAKINGp.sankaranarayananNo ratings yet
- ### Management by Objectives (MBO) in 5 StepsDocument3 pages### Management by Objectives (MBO) in 5 StepsDebamalya BhattacharyaNo ratings yet
- MPOBDocument16 pagesMPOBASHISHNo ratings yet
- MBODocument8 pagesMBOsimply_cooolNo ratings yet
- Organization Management and Leadership Course WorkDocument7 pagesOrganization Management and Leadership Course Workjennethalim734No ratings yet
- MBO Fundamentals and AdvantagesDocument10 pagesMBO Fundamentals and AdvantagesSajith KumarNo ratings yet
- Management by ObjectivesDocument8 pagesManagement by ObjectivesAjay Kiran PNo ratings yet
- MBO NotesDocument6 pagesMBO NotesSwapnil JadhavNo ratings yet
- Seminar On: Management by ObjectivesDocument15 pagesSeminar On: Management by ObjectivesGargi MPNo ratings yet
- Management by ObjectivesDocument8 pagesManagement by ObjectivesAtul ChandraNo ratings yet
- Management by Objectives: Dr. Gnanasekar Thirugnanam Assistant Professor Department of Hospital AdministrationDocument20 pagesManagement by Objectives: Dr. Gnanasekar Thirugnanam Assistant Professor Department of Hospital AdministrationGnanasekar ThirugnanamNo ratings yet
- Management by ObjectiveDocument10 pagesManagement by ObjectiveBekele Guta GemeneNo ratings yet
- MBO: Management by Objectives ExplainedDocument13 pagesMBO: Management by Objectives Explainedshaun244No ratings yet
- Management by Objectives (Mbo)Document13 pagesManagement by Objectives (Mbo)Vivek KumarNo ratings yet
- Management by ObjectivesDocument10 pagesManagement by Objectivespraveen joseNo ratings yet
- Manage Performance with MBODocument2 pagesManage Performance with MBODaniel Kiragu N.No ratings yet
- MBO Is One of The Rational School of Management's Successful ProductsDocument7 pagesMBO Is One of The Rational School of Management's Successful Productsdinesh07_1984No ratings yet
- Management by ObjectivesDocument1 pageManagement by ObjectivestsrivilasNo ratings yet
- MBO (Management by Objectives) Management by Objectives (MBO) Is ADocument6 pagesMBO (Management by Objectives) Management by Objectives (MBO) Is AsujithaNo ratings yet
- POM Ast#1 Muhammad UmairDocument7 pagesPOM Ast#1 Muhammad UmairMuhammad UmairNo ratings yet
- MBODocument29 pagesMBOSunaina DahiyaNo ratings yet
- MBO Presentation: Management by ObjectivesDocument12 pagesMBO Presentation: Management by Objectivesshivamgupt18No ratings yet
- 12th Commerce Lesson 3Document10 pages12th Commerce Lesson 3sonaiya software solutionsNo ratings yet
- MBO Management By Objectives ExplainedDocument13 pagesMBO Management By Objectives ExplainedVarun VanchinathanNo ratings yet
- MBO Guide to Goal Setting & Organizational EffectivenessDocument4 pagesMBO Guide to Goal Setting & Organizational EffectivenessIGnatiusMarieN.LayosoNo ratings yet
- MBO STEPS AND MDP IMPORTANCEDocument6 pagesMBO STEPS AND MDP IMPORTANCEAldrich FernandesNo ratings yet
- MboDocument19 pagesMboPriyaranjan JoseNo ratings yet
- Management by Objectives Mbo DiscussedDocument4 pagesManagement by Objectives Mbo DiscussedIGnatiusMarieN.LayosoNo ratings yet
- Management Science Its Historical DevelopmentDocument3 pagesManagement Science Its Historical DevelopmentSuhailShaikhNo ratings yet
- History and Development of Industrial EngineeringDocument2 pagesHistory and Development of Industrial EngineeringSuhailShaikhNo ratings yet
- History and Development of Industrial EngineeringDocument2 pagesHistory and Development of Industrial EngineeringSuhailShaikhNo ratings yet
- Applications of Industrial EngineeringDocument1 pageApplications of Industrial EngineeringSuhailShaikhNo ratings yet
- The Tools of Management ScienceDocument3 pagesThe Tools of Management ScienceSuhailShaikhNo ratings yet
- The Role of An Industrial EngineerDocument2 pagesThe Role of An Industrial EngineerSuhailShaikhNo ratings yet
- The Role of An Industrial EngineerDocument2 pagesThe Role of An Industrial EngineerSuhailShaikhNo ratings yet
- Production Management The Key To Efficient ManufacturingDocument2 pagesProduction Management The Key To Efficient ManufacturingSuhailShaikhNo ratings yet
- The Concept of Industrial Engineering Enhancing Efficiency and ProductivityDocument2 pagesThe Concept of Industrial Engineering Enhancing Efficiency and ProductivitySuhailShaikhNo ratings yet
- The Role of An Industrial EngineerDocument2 pagesThe Role of An Industrial EngineerSuhailShaikhNo ratings yet
- The Role of An Industrial EngineerDocument2 pagesThe Role of An Industrial EngineerSuhailShaikhNo ratings yet
- Production Management The Key To Efficient ManufacturingDocument2 pagesProduction Management The Key To Efficient ManufacturingSuhailShaikhNo ratings yet
- The Concept of Industrial Engineering Enhancing Efficiency and ProductivityDocument2 pagesThe Concept of Industrial Engineering Enhancing Efficiency and ProductivitySuhailShaikhNo ratings yet
- Applications of Industrial EngineeringDocument1 pageApplications of Industrial EngineeringSuhailShaikhNo ratings yet
- The Art and Science of Decision-MakingDocument2 pagesThe Art and Science of Decision-MakingSuhailShaikhNo ratings yet
- History and Development of Industrial EngineeringDocument2 pagesHistory and Development of Industrial EngineeringSuhailShaikhNo ratings yet
- The Concept of Industrial Engineering Enhancing Efficiency and ProductivityDocument2 pagesThe Concept of Industrial Engineering Enhancing Efficiency and ProductivitySuhailShaikhNo ratings yet
- Personnel Management Nurturing Human Capital For Organizational SuccessDocument2 pagesPersonnel Management Nurturing Human Capital For Organizational SuccessSuhailShaikhNo ratings yet
- Online Restaurant Delivery Guide To Getting Started: Will You Deliver Yourself?Document1 pageOnline Restaurant Delivery Guide To Getting Started: Will You Deliver Yourself?SuhailShaikhNo ratings yet
- Applications of Industrial EngineeringDocument1 pageApplications of Industrial EngineeringSuhailShaikhNo ratings yet
- Production and Productivity Driving Forces of Economic GrowthDocument2 pagesProduction and Productivity Driving Forces of Economic GrowthSuhailShaikhNo ratings yet
- Welcome: A Guide To Accessibility ofDocument18 pagesWelcome: A Guide To Accessibility ofSuhailShaikhNo ratings yet
- National HealthDocument60 pagesNational HealthSuhailShaikhNo ratings yet
- Aina - e - Qismat October 2019Document60 pagesAina - e - Qismat October 2019SuhailShaikhNo ratings yet
- Welcome: A Guide To Accessibility ofDocument18 pagesWelcome: A Guide To Accessibility ofSuhailShaikhNo ratings yet
- Production Planning in The Clothing Industry:: Failing To Plan Is Planning To FailDocument5 pagesProduction Planning in The Clothing Industry:: Failing To Plan Is Planning To Failjatinder.kaler100% (2)
- NSTP ReactionDocument1 pageNSTP ReactionSEAN ANDREX MARTINEZNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan - Chemistry - Grade 9 - Week 20Document10 pagesLesson Plan - Chemistry - Grade 9 - Week 20Sara HdaifeNo ratings yet
- Pre-Colonial Philippines: A History of Science and TechnologyDocument26 pagesPre-Colonial Philippines: A History of Science and TechnologyRoss TornNo ratings yet
- 7822 Morris Road, Hilliard, OH 43026 - (614) 623-9039 - : Objective EducationDocument2 pages7822 Morris Road, Hilliard, OH 43026 - (614) 623-9039 - : Objective Educationapi-435027159No ratings yet
- Practical Applications of PsychologyDocument4 pagesPractical Applications of PsychologySaffa TariqNo ratings yet
- Talent Management PHD Thesis PDFDocument7 pagesTalent Management PHD Thesis PDFvsiqooxff100% (2)
- Top 10 Teachers in Philippines 2016 Elementary Licensure ExamDocument4 pagesTop 10 Teachers in Philippines 2016 Elementary Licensure ExamLeonardo LimNo ratings yet
- ISB PGPMAX Program OverviewDocument38 pagesISB PGPMAX Program OverviewRajakarthik RajarathinamNo ratings yet
- Research PaperDocument7 pagesResearch PaperTULAIB KHANNo ratings yet
- Image Captioning: - A Deep Learning ApproachDocument14 pagesImage Captioning: - A Deep Learning ApproachPallavi BhartiNo ratings yet
- LLB 3 PDFDocument73 pagesLLB 3 PDFMayur DingankarNo ratings yet
- Business Communication 2014 Course OutlineDocument4 pagesBusiness Communication 2014 Course OutlineAhmad WarraichNo ratings yet
- MATH 2014 - Assignment 1Document2 pagesMATH 2014 - Assignment 1Ovøxö RãjïvNo ratings yet
- Geography Coursework Lake DistrictDocument5 pagesGeography Coursework Lake Districtgbfcseajd100% (2)
- Notre Dame Performance EvaluationDocument2 pagesNotre Dame Performance EvaluationChris WongNo ratings yet
- ESU Newsletter - Aug 2018Document11 pagesESU Newsletter - Aug 2018curiousEngineNo ratings yet
- Case Study 1 p.35Document2 pagesCase Study 1 p.35Sherisse' Danielle WoodleyNo ratings yet
- 04 Quiz 1Document1 page04 Quiz 1cdnarido7535valNo ratings yet
- Parenting QuestionnaireDocument4 pagesParenting QuestionnaireshobhaNo ratings yet
- Search Results: CELTA Assignment 1 - Perfect (Grammar) - Hairstyle - ScribdDocument1 pageSearch Results: CELTA Assignment 1 - Perfect (Grammar) - Hairstyle - ScribdRania ChokorNo ratings yet
- Social Influence: Social Influenced Is The Effect That People Have Upon The Beliefs or Behaviors of OthersDocument1 pageSocial Influence: Social Influenced Is The Effect That People Have Upon The Beliefs or Behaviors of Otherslorelyn panisNo ratings yet
- History of AnhsDocument1 pageHistory of AnhsMelvin Gayta Failagao100% (1)
- Tcnchs Reading Implementation Matrix 2022 2023Document5 pagesTcnchs Reading Implementation Matrix 2022 2023Jhona Mae JabajabNo ratings yet