Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Multiple Crossing Over
Uploaded by
Tisha Tabhita0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views11 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views11 pagesMultiple Crossing Over
Uploaded by
Tisha TabhitaCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 11
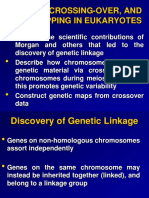
• Analysis of the genetic behaviour of three or
more linked loci may show evidence of multiple
cross-overs.
• When three loci are involved, there will be two
parental types, four recombinant classes with
single cross-overs and two recombinant types
showing cross-overs between all three loci ( =
double cross-over).
• The two parental types will be most abundant,
the four single cross-over (SCO) recombinants
will be next while the two double cross-over
(DCO) recombinants will be least abundant.
• The phenomenon of a cross - over
occurs when homologous chromatids
in the tetrad (one from each of the
two parents) exchange segments of
varying length during prophase
• The point of crossover is known as a
chiasma (pl. chiasmata)
• Multiple crossover is the event when
there is two or more crossover
between 2 sister chromatids
• Multiple crossover requires 3 linked
gene pairs to observe
Parental:
a+b+c+
abc
Multiple Crossover Single Crossover
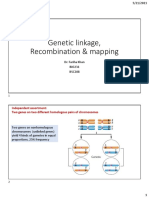
How often crossing over occured?
Depends on the distance of two
genes,
(the closer the genes the less likely
crossover happens)
Why are double crossover events
expected in lower frequency?
Because crossover occur If two mutations show 0% recombination
randomly along the lengths of in linkage experiments they may be ___?
chromosome, within any
1) in different genes but so close to
region, the occurence of 2
eachother that crossovers are never
events is less likely than the
detected
occurence of 1 event
or
2) mutations in the same gene
• Recombination frequency is a
measure of genetic linkage and is The purple gene, with a dominant
used in the creation of a genetic
linkage map. Recombination pr+ allele that specifies normal,
frequency (θ) is red eyes and a recessive pr allele
the frequency with which a single
chromosomal crossover will take that specifies purple eyes.
place between two genes during
meiosis.
• One way that recombination
frequencies have been used The vestigial gene, with a
historically is to build linkage dominant vg+ allele that specifies
maps, chromosomal maps based
on recombination frequencies. normal, long wings and a
recessive vg allele that specifies
• The example would be Drosophila short, "vestigial" wings
melangaster
Recombinant Freguency
𝑅𝑒𝑐𝑜𝑚𝑏𝑖𝑛𝑎𝑛𝑡
× 100%
𝑇𝑜𝑡𝑎𝑙 𝑂𝑓𝑓𝑠𝑝𝑖𝑛𝑔
𝑅𝑒𝑐𝑜𝑚𝑏𝑖𝑛𝑎𝑛𝑡
× 100%
𝑇𝑜𝑡𝑎𝑙 𝑂𝑓𝑓𝑠𝑝𝑟𝑖𝑛𝑔
151 + 154
× 100% = 10.7%
1334 + 1195 + 151 + 154
The recombination frequency between the purple and vestigial genes
is 10.7%
You might also like
- Finding Your Roots: The Official Companion to the PBS SeriesFrom EverandFinding Your Roots: The Official Companion to the PBS SeriesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Nama: Dewi Fatmawati NPM: 1814141016 Produksi Ternak: Genes Are Located On ChromosomesDocument8 pagesNama: Dewi Fatmawati NPM: 1814141016 Produksi Ternak: Genes Are Located On ChromosomesDewi FatmawatiNo ratings yet
- Genetic LinkageDocument82 pagesGenetic LinkagesahiddinpvictoryNo ratings yet
- Gene MappingDocument13 pagesGene MappingNishat FatimaNo ratings yet
- LinkageDocument47 pagesLinkageTony BernardNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 GeneticsDocument20 pagesChapter 7 Geneticsedomin00No ratings yet
- Student - Morgan ExptDocument38 pagesStudent - Morgan ExptqwwwNo ratings yet
- Genetics - Chapter 5 - Linked Gene InheritanceDocument46 pagesGenetics - Chapter 5 - Linked Gene InheritanceDuy AnhNo ratings yet
- (L-3) - Modern Genetics - Sept 29, 2019 - SundayDocument61 pages(L-3) - Modern Genetics - Sept 29, 2019 - SundayShaswata SutradharNo ratings yet
- Genetic Linkage: Presented By:ayush Jain (Alm 3008) University of Agricultural Science, BangloreDocument32 pagesGenetic Linkage: Presented By:ayush Jain (Alm 3008) University of Agricultural Science, BangloreTeflon SlimNo ratings yet
- Linkage & RecombinationDocument76 pagesLinkage & RecombinationshivamalikejiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Linkage, Recombination, and Eukaryotic Gene MappingDocument20 pagesChapter 7 Linkage, Recombination, and Eukaryotic Gene MappingSiamHashan100% (1)
- LinkageDocument35 pagesLinkageRaj MalhotraNo ratings yet
- Inheritance: 441 Linkage Exception To Independent Assortment)Document3 pagesInheritance: 441 Linkage Exception To Independent Assortment)ArchanaNo ratings yet
- Linkage: Harshraj Subhash Shinde KKW, Cabt, NashikDocument14 pagesLinkage: Harshraj Subhash Shinde KKW, Cabt, Nashiksivaram888No ratings yet
- Linkage and Crossing Over 3 MapsDocument37 pagesLinkage and Crossing Over 3 MapsKhushbuNo ratings yet
- Gene Linkage and Genetic MappingDocument32 pagesGene Linkage and Genetic MappingM Ian Benedict MaruyaNo ratings yet
- 7.1 Linkage and Crossing OverDocument34 pages7.1 Linkage and Crossing OverDhungana Surya RdNo ratings yet
- Discovery of Linkage: William Bateson and R.C. Punnett Were Working With Several Traits in Sweet Peas, Notably A Gene ForDocument12 pagesDiscovery of Linkage: William Bateson and R.C. Punnett Were Working With Several Traits in Sweet Peas, Notably A Gene ForYhan Brotamonte BoneoNo ratings yet
- The Chromosomal Basis of InheritanceDocument33 pagesThe Chromosomal Basis of InheritanceSangkaran KumarNo ratings yet
- Module 3 Mendelian GeneticsDocument14 pagesModule 3 Mendelian GeneticsRaiza AwatNo ratings yet
- 12-Linkage Crossing-Over and Gene Mapping in EukaryotesDocument43 pages12-Linkage Crossing-Over and Gene Mapping in EukaryotesgustiNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Word DocumentDocument4 pagesNew Microsoft Word DocumentGina Portuguese GawonNo ratings yet
- BASIC Genetics 1205 Lecture10 LinkageDocument21 pagesBASIC Genetics 1205 Lecture10 LinkageMarvin JeaNo ratings yet
- (REVISI) Peran Two Locus and Multi Locus Genetic InheritanceDocument35 pages(REVISI) Peran Two Locus and Multi Locus Genetic InheritanceDaryanti Wahyu Lestari100% (1)
- Gene Mapping Techniques: ObjectivesDocument10 pagesGene Mapping Techniques: ObjectivesPramanshu RajputNo ratings yet
- Principle of Inheritance Variations: Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument23 pagesPrinciple of Inheritance Variations: Multiple Choice QuestionsUrja Moon100% (1)
- Genetic Linkage & Mapping (Article) - Khan AcademyDocument22 pagesGenetic Linkage & Mapping (Article) - Khan Academy嘉雯吳No ratings yet
- QCB 540 Genetic Basis For VariationDocument55 pagesQCB 540 Genetic Basis For VariationjonathanyewNo ratings yet
- Linkage & Pedigree AnalysisDocument29 pagesLinkage & Pedigree AnalysisPAVITHRA VNo ratings yet
- Genetic Linkage, Recombination, Mapping - BIO231-FKDocument9 pagesGenetic Linkage, Recombination, Mapping - BIO231-FKmalik husnainNo ratings yet
- Genetics and EvolutionDocument6 pagesGenetics and EvolutionCherry Grace Articulo DabuconNo ratings yet
- Genetics Linkage and MappingDocument29 pagesGenetics Linkage and MappingbodnarencoNo ratings yet
- Types of Gene MappingDocument7 pagesTypes of Gene MappingJay MenonNo ratings yet
- Dihybrid CrossesDocument10 pagesDihybrid CrossesTejashree VinodNo ratings yet
- Bio Pearson HL Chapter 3 AnswersDocument4 pagesBio Pearson HL Chapter 3 AnswersKunakorn KunthamasNo ratings yet
- Linkage MappingDocument5 pagesLinkage MappingDhakshayani GNo ratings yet
- HWE and Simple DeviationsDocument22 pagesHWE and Simple Deviationskk singhNo ratings yet
- Chromosome MappingDocument9 pagesChromosome MappingPuddyNo ratings yet
- Linkage and RecombinationDocument31 pagesLinkage and RecombinationBob UrbandubNo ratings yet
- Genes, Chromosomes, and Human GeneticsDocument61 pagesGenes, Chromosomes, and Human GeneticsDimo PratannaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15 NotesDocument5 pagesChapter 15 NotesjonlimeNo ratings yet
- Sect 15 Linkage&RecombinationDocument37 pagesSect 15 Linkage&RecombinationUsnia BaiqNo ratings yet
- LinkageDocument9 pagesLinkageHarshu JunghareNo ratings yet
- 2 GeneovrhDocument28 pages2 GeneovrhAndres ZabalaNo ratings yet
- Bio PopulationDocument7 pagesBio PopulationRamdhan HidayatNo ratings yet
- LKMM PhotoshopDocument57 pagesLKMM PhotoshopElsa DaraNo ratings yet
- The Theory ofDocument22 pagesThe Theory ofMelvin Earl AgdaNo ratings yet
- Chapter-5 Principles of Inheritance and VariationDocument9 pagesChapter-5 Principles of Inheritance and VariationbpmbhamoraNo ratings yet
- Linkage 1Document38 pagesLinkage 1fae-ar_raziNo ratings yet
- Answers: Activity 23.1 A Quick Review of Hardy-Weinberg Population GeneticsDocument6 pagesAnswers: Activity 23.1 A Quick Review of Hardy-Weinberg Population GeneticsR A Y S U N S H I N ENo ratings yet
- Linkage and Crossing OverDocument42 pagesLinkage and Crossing OverNaS raHNo ratings yet
- GeneticsDocument33 pagesGeneticsRalph Rezin MooreNo ratings yet
- Chromosomal CrossoverDocument4 pagesChromosomal CrossoverMitkoNo ratings yet
- Bio 93 Final Review BLANKDocument92 pagesBio 93 Final Review BLANKKenosNo ratings yet
- Homologous Chromosomes: Chromosome Centromere Genes Loci HomologousDocument3 pagesHomologous Chromosomes: Chromosome Centromere Genes Loci HomologousDharmendra SinghNo ratings yet
- Genetics From Genes To Genomes 5th Edition Solutions Manual 1Document36 pagesGenetics From Genes To Genomes 5th Edition Solutions Manual 1hollyclarkebfaoejwrny100% (23)
- Genetics From Genes To Genomes 5th Edition Hartwell Solutions Manual DownloadDocument53 pagesGenetics From Genes To Genomes 5th Edition Hartwell Solutions Manual DownloadFrederick Cannata100% (19)
- Genetics From Genes To Genomes 5Th Edition Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument36 pagesGenetics From Genes To Genomes 5Th Edition Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFmary.ratliff248100% (13)
- The Ethics of Respect For Nature - Paul W. Taylor PDFDocument22 pagesThe Ethics of Respect For Nature - Paul W. Taylor PDFArtur P. CoelhoNo ratings yet
- Clinical Biochemistry PDFDocument105 pagesClinical Biochemistry PDFJepri Purwanto67% (3)
- Cham PowerpointDocument19 pagesCham PowerpointElizabeth GenotivaNo ratings yet
- Biological Induced CorrosionDocument22 pagesBiological Induced CorrosionHemanth100% (1)
- EASL 2021 Version 4 NewDocument691 pagesEASL 2021 Version 4 NewGupse Köroğlu AdalıNo ratings yet
- Characterization of Tannia PlantDocument104 pagesCharacterization of Tannia PlantSolomon FantawNo ratings yet
- Social IntelligenceDocument10 pagesSocial IntelligencePeterMarquezNo ratings yet
- Syllabus CompletionDocument1 pageSyllabus CompletiongopimicroNo ratings yet
- OB Ultrasound Report Template 2Document1 pageOB Ultrasound Report Template 2PriyankaNo ratings yet
- 3 - Plasma Membrane and Transport MechanismsDocument67 pages3 - Plasma Membrane and Transport MechanismsThom PaglinawanNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S222541102200030X MainDocument11 pages1 s2.0 S222541102200030X Mainaman babuNo ratings yet
- CV Christopher Lean Jan 2024 Without ReferencesDocument5 pagesCV Christopher Lean Jan 2024 Without Referencesapi-399765628No ratings yet
- The Tai Chi Code - Martial Arts Ebook by Chris DavisDocument190 pagesThe Tai Chi Code - Martial Arts Ebook by Chris DavisTomas De Wael100% (2)
- Using STADEN For Sequence AssemblyDocument5 pagesUsing STADEN For Sequence AssemblyChristen Rune StensvoldNo ratings yet
- CROSS TREE - Sorte I Selekcije Voćaka I Vinove Loze Iz Severozapadne Srbije I Istočne Hrvatske PDFDocument153 pagesCROSS TREE - Sorte I Selekcije Voćaka I Vinove Loze Iz Severozapadne Srbije I Istočne Hrvatske PDFrraattaarrrraattaaNo ratings yet
- Cat ExamDocument25 pagesCat Examlahsivlahsiv684No ratings yet
- TGD FrameworkDocument10 pagesTGD FrameworkMatthew KleeNo ratings yet
- Social Institutions - Kinship, Family&Marriage PDFDocument47 pagesSocial Institutions - Kinship, Family&Marriage PDFAbhijith KNo ratings yet
- CV Monica Feliu-Mojer, Ph.D.Document13 pagesCV Monica Feliu-Mojer, Ph.D.moefeliuNo ratings yet
- Why Do Giraffes Have Long Necks?Document22 pagesWhy Do Giraffes Have Long Necks?johnosborneNo ratings yet
- Chest TubesDocument34 pagesChest TubesMuhd ShafiqNo ratings yet
- Recent DevelopmentsDocument295 pagesRecent DevelopmentsGabriel PinheiroNo ratings yet
- 19 - Lipid MetabolismDocument35 pages19 - Lipid MetabolismcheckmateNo ratings yet
- Published January 16, 2012 at In: 813 × 699 Block Diagram of Urea Production From NH3 and CO2Document9 pagesPublished January 16, 2012 at In: 813 × 699 Block Diagram of Urea Production From NH3 and CO2himanshuchawla654No ratings yet
- Kimia Daun PandanDocument4 pagesKimia Daun Pandanlutfi_alhayathullahNo ratings yet
- Gen. Zoo. Final ReviewerDocument34 pagesGen. Zoo. Final ReviewerAshley FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Psychophysics As New Priority in Modern Science - Physical Basics of Informational InteractionDocument15 pagesPsychophysics As New Priority in Modern Science - Physical Basics of Informational InteractionBoris PetrovicNo ratings yet
- Prelim QuizDocument3 pagesPrelim QuizXyriel MacoyNo ratings yet
- Skin and Body Membranes: EssentialsDocument43 pagesSkin and Body Membranes: EssentialsJohn Rex Lloyd TunaNo ratings yet
- CeropegiarevisionDocument116 pagesCeropegiarevisionVirgi CortésNo ratings yet