Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Science Pre Finals
Uploaded by
MONICA DELIMA0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views2 pagesThis document contains a science exam for grade 8 with multiple choice and true/false questions testing knowledge of various science topics including:
- Biodiversity, genetics, species, ecosystems, and ecology
- Classification of organisms and examples like prokaryotes, vertebrates, invertebrates, and consumers
- Systems of the human body like the digestive system and its organs/functions
- Food chains and consumer levels showing producer, primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary consumers
The exam covers a wide range of essential science concepts and vocabulary for an 8th grade level.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document contains a science exam for grade 8 with multiple choice and true/false questions testing knowledge of various science topics including:
- Biodiversity, genetics, species, ecosystems, and ecology
- Classification of organisms and examples like prokaryotes, vertebrates, invertebrates, and consumers
- Systems of the human body like the digestive system and its organs/functions
- Food chains and consumer levels showing producer, primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary consumers
The exam covers a wide range of essential science concepts and vocabulary for an 8th grade level.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views2 pagesScience Pre Finals
Uploaded by
MONICA DELIMAThis document contains a science exam for grade 8 with multiple choice and true/false questions testing knowledge of various science topics including:
- Biodiversity, genetics, species, ecosystems, and ecology
- Classification of organisms and examples like prokaryotes, vertebrates, invertebrates, and consumers
- Systems of the human body like the digestive system and its organs/functions
- Food chains and consumer levels showing producer, primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary consumers
The exam covers a wide range of essential science concepts and vocabulary for an 8th grade level.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
Science 8 Pre-Finals
SHADE THE LETTER OF THE CORRECT ANSWER. PRAY BEFORE ANSWERING.
1. It refers to the variety of organism (plants,animals and micro-organism) found in a particular
area or habitat.
a. Biology b. Chemistry C. Biodiversity d. Ecology
2. It refers to genetic information that organisms contain.
a. Ecosystem diversity b. Genetic diversity c. Species diversity d. Ecology
3. It refers to the different kinds of organisms.
a. Ecosystem diversity b. Genetic diversity c. Species diversity d. Ecology
4. It refers to the different kinds of places where organisms live and interconnections that bind
these organisms together.
a. Ecosystem diversity b. Genetic diversity c. Species diversity d. Ecology
5. Most prokaryotes are tiny and unicellular, thus, are referred to as _______________.
a. Microorganisms b. Macroorganisms c. Multicellular d. None of the Above
6. For any organisim identified, a ________________ is given.
a. Classification B. Kingdom c. Scientific Name d. Class
7. Methanogens can survive in places where there is no ___________.
a. Light b. Oxygen c. Water d. Air
8. Biogas is utilized by the production of ____________.
a. Salt b. Water c. Oxygen d. Methane
9. ______________ can live in places with high temperatures including volcanic hot springs.
a. Methanogens b. Fish c. Thermophiles d. Halophiles
10. ____________ can live in the Dead Sea and the Great Salt Lake of Utah because it is salty.
a. Methanogens b. Fish c. Thermophiles d. Halophiles
11. Which of the following is not an example of a Eubacteria?
a. Cocci b. Bacilli c. Spirilla d. Animalia
12. Which is an example of a vertebrate?
a. cat b. worm c. bacteria d. carrot
13. Which is an example of an invertebrate?
a. cat b. worm c. bacteria d. carrot
14. Which is an example of a microscopic organisim?
a. cat b. worm c. bacteria d. carrot
15. Which is an example of a consumer?
a. cat b. worm c. bacteria d. plant
FOR ITEMS 16-25 - SHADE “A” IF TRUE AND “B” IF FALSE.
16. Amphibian: Frog
17. Reptile: Cat
18. Vertebrate: Dog
19. Invertibrate: Jellyfish
20. Amphibian: Snake
21. Reptile: Rabbit
22. Fish: Shark
23. Vertibrate: Horse
24. Reptile: Seahorse
25. Bird: Philippine Eagle
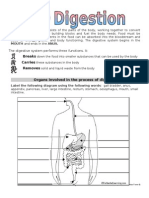
FOR ITEMS 26-30 DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
26. The ___________ is the beginning of the digestive tract
a. mouth b. stomach c. esophagus d. anus
27. Located in your throat near your trachea (windpipe), the ___________ receives food from your mouth when you
swallow.
a. mouth b. stomach c. esophagus d. anus
28. The _________ is a hollow organ, or "container," that holds food while it is being mixed with stomach enzymes.
a. mouth b. stomach c. esophagus d. anus
29. The ________ secretes digestive enzymes into the duodenum that break down protein, fats and carbohydrates.
a. liver b. stomach c. pancreas d. anus
30. The ______ has many functions, but its main job within the digestive system is to process the nutrients absorbed
from the small intestine.
a. liver b. stomach c. pancreas d. anus
FOR ITEMS 31-40 SHADE “A” IF TRUE AND “B” IF FALSE.
31. The anus is the last part of the digestive tract.
32. The colon is responsible for processing waste so that emptying your bowels is easy and convenient.
33. The gallbladder stores and concentrates bile from the liver, and then releases it into the duodenum in the small
intestine to help absorb and digest fats.
34. The liver is your body's chemical "factory." It takes the raw materials absorbed by the intestine and makes all the
various chemicals your body needs to function.
35. The food you eat takes an incredible journey through your body, from top (your mouth) to bottom (your anus).
36. Digestion is important because your body needs nutrients from the food you eat and the liquids you drink in order to
stay healthy and function properly. Nutrients include carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins, minerals and water.
37. Your digestive system is uniquely constructed to do its job of turning your food into the nutrients and energy you
need to survive.
38. The organs that make up your Gastrointestinal tract, in the order that they are connected, include your mouth,
esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine and anus.
39. Stool, or waste left over from the digestive process, is passed through the colon by means of peristalsis, first in a
liquid state and ultimately in a solid form.
40. It normally takes about 36 hours for stool to get through the colon. The stool itself is mostly food debris and bacteria.
REFER TO THE IMAGE, TRUE OR FALSE
SHADE “C” IF TRUE AND “D” IF FALSE
41. Producer: Eagle
42. Primary Consumer: Caterpillar
43. Primary Consumer: Squirrel
44. Secondary Consumer: Bird
45. Tertiary Consumer: Butterfly
46. Secondary Consumer: Snakes
47. Secondary Consumer: Plants
48. Quaternary Consumer: Eagle
49. Producer: Frog
50. Secondary Consumer: Fox
You might also like
- 2ND QUARTER 4th SUMMATIVE TEST EARTH AND LIFE SCIENCE.Document5 pages2ND QUARTER 4th SUMMATIVE TEST EARTH AND LIFE SCIENCE.Jed Jimenez-SinsuanNo ratings yet
- EcosystemDocument5 pagesEcosystemCharlieNo ratings yet
- 2nd Quarter FINAL EXAM Earth and Life ScienceDocument3 pages2nd Quarter FINAL EXAM Earth and Life ScienceCherrina Aguila100% (1)
- Grade 8 Science 4th Quarter ExamDocument7 pagesGrade 8 Science 4th Quarter ExamMARIA THERESA TULALINo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Sample Test Living ThingsDocument13 pagesChapter 1 Sample Test Living ThingsyasinalifNo ratings yet
- Microbiology A Systems Approach Cowan 4th Edition Test BankDocument10 pagesMicrobiology A Systems Approach Cowan 4th Edition Test BankKathy Gasiewski100% (41)
- Physics Republic of The PhilippinesDocument13 pagesPhysics Republic of The PhilippinesGlenda AstodilloNo ratings yet
- 4TH Quarter Examination in Science 8Document3 pages4TH Quarter Examination in Science 8Zooey LucenarioNo ratings yet
- EALS - Test-A-Key Akle HSDocument7 pagesEALS - Test-A-Key Akle HSERICA DE GUZMAN100% (1)
- 4th QUARTER TEST SCIENCE 8Document5 pages4th QUARTER TEST SCIENCE 8Lecille Concepcion PriaNo ratings yet
- 4TH Quarter Science Grade 8Document7 pages4TH Quarter Science Grade 8Alessa Lames100% (2)
- 50 Items Multiple ChoiceDocument8 pages50 Items Multiple ChoiceJueren MaciaNo ratings yet
- Ungulate Taxonomy 2011Document322 pagesUngulate Taxonomy 2011Gestión Documental BioApNo ratings yet
- Sumative Test (4TH Quarter) Science 8Document4 pagesSumative Test (4TH Quarter) Science 8Jonel Rule100% (2)
- Ecology PracticeTest 1Document3 pagesEcology PracticeTest 1h8alfredNo ratings yet
- Placenta and TrophoblastDocument490 pagesPlacenta and Trophoblastalex100% (1)
- Marulas Christian School Third Periodical Exam Science-6Document4 pagesMarulas Christian School Third Periodical Exam Science-6iyaNo ratings yet
- Quiz - EcosystemDocument2 pagesQuiz - Ecosystemnathan casinaoNo ratings yet
- Science Quiz 8Document14 pagesScience Quiz 8VanLinzCastilloNo ratings yet
- Genbio 2 ExamDocument9 pagesGenbio 2 ExamRaisa Louise Gamiao TattaoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 TestDocument9 pagesChapter 1 TestShivali PatelNo ratings yet
- Importance of Environmental Education at Secondary School LevelDocument4 pagesImportance of Environmental Education at Secondary School LevelImpact JournalsNo ratings yet
- LIFE SCIENCE SECOND QUARTER EXAMDocument3 pagesLIFE SCIENCE SECOND QUARTER EXAMVinz AlilingNo ratings yet
- Summative TestDocument29 pagesSummative TestGinielle Gem Atim BelarminoNo ratings yet
- SchoolDocument4 pagesSchoolAbegail ReyesNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 2. NutritionDocument6 pagesWorksheet 2. NutritionrosaronceroNo ratings yet
- Assessment of LearningDocument5 pagesAssessment of LearningJan Lloyd OdruniaNo ratings yet
- Let Review MajorDocument14 pagesLet Review MajorLeah PerezNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGY LET ReviewDocument4 pagesBIOLOGY LET ReviewLili PinkNo ratings yet
- Science 6Document4 pagesScience 6Rosalie Flores ClavioNo ratings yet
- Earth ScienceDocument3 pagesEarth Sciencechulnayeon0No ratings yet
- 2nd-Quarter-Final-Exam-Earth-And-Life-Science (2) .FinalDocument3 pages2nd-Quarter-Final-Exam-Earth-And-Life-Science (2) .FinalNiño BelanoNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGY ReviewDocument4 pagesBIOLOGY ReviewLili PinkNo ratings yet
- Earth-and-Life-Science-Q2 2023 FINALDocument4 pagesEarth-and-Life-Science-Q2 2023 FINALISAGANINo ratings yet
- BiologyDocument4 pagesBiologyLili PinkNo ratings yet
- 2nd Periodical Test in Science VI Jerrianne Tique QuestionsDocument8 pages2nd Periodical Test in Science VI Jerrianne Tique QuestionstiquejerrianneaubreyNo ratings yet
- For Each Question On The Questionnaire, Using A Dark PencilDocument4 pagesFor Each Question On The Questionnaire, Using A Dark PencilRainer FlormataNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGY SASE REVIEW Answer KeyDocument2 pagesBIOLOGY SASE REVIEW Answer KeyTasnimah Moh. IsmaelNo ratings yet
- TQ ELS 2ndquarterDocument10 pagesTQ ELS 2ndquarterHyacinth RaeNo ratings yet
- TQ ELS 2ndquarterDocument9 pagesTQ ELS 2ndquarterHyacinth RaeNo ratings yet
- Els Q2Document4 pagesEls Q2Irish John GulmaticoNo ratings yet
- SJTRC BioDocument11 pagesSJTRC BioRaeh YooNo ratings yet
- 1Document20 pages1yaj8cruzadaNo ratings yet
- TTS Multiple ChoiceDocument8 pagesTTS Multiple ChoiceJueren MaciaNo ratings yet
- Periodical Assessment in Science Q4Document2 pagesPeriodical Assessment in Science Q4Arlyn BarlosoNo ratings yet
- 2nd Periodical Test in Science 6Document6 pages2nd Periodical Test in Science 6Jonniza AlbitNo ratings yet
- Bio QuestionsDocument7 pagesBio Questionsjohn carlo rollonNo ratings yet
- Science VDocument1 pageScience Ve_geanga100% (1)
- Mock Drill Bio Set BDocument25 pagesMock Drill Bio Set BIrene Miranda FloresNo ratings yet
- Prelims Envi SciDocument5 pagesPrelims Envi SciCyndi SamaniegoNo ratings yet
- Envi Sci QuestionsDocument3 pagesEnvi Sci Questionsaya keleovNo ratings yet
- Envi Sci Questions - Ver2Document5 pagesEnvi Sci Questions - Ver2aya keleov100% (1)
- Biology SASE ReviewDocument2 pagesBiology SASE ReviewTasnimah Moh. IsmaelNo ratings yet
- Bonifacio Summative Test With Key AnswersDocument2 pagesBonifacio Summative Test With Key AnswersSein Borongan VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Biologija TestDocument4 pagesBiologija TestEldin Hajric100% (1)
- Worksheet - Fifth Grade - EnergyDocument13 pagesWorksheet - Fifth Grade - EnergyMaricel SalazarNo ratings yet
- NYA Practice Questions BiodiversityDocument7 pagesNYA Practice Questions Biodiversitymartin.kv4No ratings yet
- SCIENCEDocument12 pagesSCIENCELeah PerezNo ratings yet
- First Periodical Test in Science and Health VDocument4 pagesFirst Periodical Test in Science and Health Vrubieann_danzalanNo ratings yet
- Biological Science ReviewDocument14 pagesBiological Science ReviewMarjenneilNo ratings yet
- C-7 (ch-1 and 2)Document4 pagesC-7 (ch-1 and 2)shweta srivastavaNo ratings yet
- Qe2 ElsDocument7 pagesQe2 Elsjulieann.capalNo ratings yet
- Are All Bacteria Dangerous? Biology Book for Kids | Children's Biology BooksFrom EverandAre All Bacteria Dangerous? Biology Book for Kids | Children's Biology BooksNo ratings yet
- A Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia Patient With Progressive Multifocal Leukoencephalopathy Caused by John Cunningham VirusDocument8 pagesA Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia Patient With Progressive Multifocal Leukoencephalopathy Caused by John Cunningham VirusYtyNo ratings yet
- Genbio 2 Mod13 Gas Exchange 1 Converted 2Document33 pagesGenbio 2 Mod13 Gas Exchange 1 Converted 2acebealsabasNo ratings yet
- Section 1: Cellular AdaptationsDocument30 pagesSection 1: Cellular Adaptationshaddi awanNo ratings yet
- Effect of Adjunctive Use of Local Simvastatin and Chitosan Based Simvastatin On GCF Levels of Netrin-1 and Its Receptor Unc5b in PeriodontitisDocument10 pagesEffect of Adjunctive Use of Local Simvastatin and Chitosan Based Simvastatin On GCF Levels of Netrin-1 and Its Receptor Unc5b in PeriodontitisIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- What Is General EntomologyDocument3 pagesWhat Is General EntomologySiraw tadesseNo ratings yet
- The Learners Demonstrate Understandin G Of... The Learners Should Be Able To..Document3 pagesThe Learners Demonstrate Understandin G Of... The Learners Should Be Able To..Sab Ibarreta100% (2)
- Poster PresentationDocument4 pagesPoster Presentationapi-586722985No ratings yet
- BIOL GEN 313 Vollbrecht Lhhoward 4.28.14 KEYDocument3 pagesBIOL GEN 313 Vollbrecht Lhhoward 4.28.14 KEYNgoc-Le DuongNo ratings yet
- Aniket Sengupta CV 2022 JanDocument8 pagesAniket Sengupta CV 2022 Janapi-343430641No ratings yet
- Nares or NostrilsDocument17 pagesNares or NostrilsMelody EncinasNo ratings yet
- Mattu Gulla BrinjalDocument2 pagesMattu Gulla BrinjalronNo ratings yet
- 3 Principios de Biofarmacia PDFDocument96 pages3 Principios de Biofarmacia PDFAnonymous Se5IdneSpNo ratings yet
- The Neuron: Published Reviewed Author SourceDocument10 pagesThe Neuron: Published Reviewed Author SourceJennie KimNo ratings yet
- Childrens Books About BrainsSDocument4 pagesChildrens Books About BrainsSSorin HotnogNo ratings yet
- Noncanonical Transnitrosylation Network Contributes To Synapse Loss in Alzheimer's DiseaseDocument18 pagesNoncanonical Transnitrosylation Network Contributes To Synapse Loss in Alzheimer's DiseasedmitworNo ratings yet
- Books To DownloadDocument2 pagesBooks To Downloadmohityahoo0% (1)
- Tutorial PDFDocument339 pagesTutorial PDFJeanneth MosqueraNo ratings yet
- PapadogiannisDocument10 pagesPapadogiannisjhupressNo ratings yet
- MicrobiologyDocument2 pagesMicrobiologyIrfan SalimNo ratings yet
- 31 - Grade 8 Reading ComprehensionDocument4 pages31 - Grade 8 Reading ComprehensionLolo ElsaiedNo ratings yet
- HIV-1 Viral Load ENGLISH Package Insert 301-3068, Rev. HDocument24 pagesHIV-1 Viral Load ENGLISH Package Insert 301-3068, Rev. HHidanti KarlinaNo ratings yet
- Gene Splicing FinDocument18 pagesGene Splicing FinNoellah Jeannica MacamNo ratings yet
- Digestive System 3 HistologyDocument29 pagesDigestive System 3 HistologyshmirtbNo ratings yet
- Günter Kampf - Antiseptic Stewardship - Biocide Resistance and Clinical Implications-Springer International Publishing (2018)Document722 pagesGünter Kampf - Antiseptic Stewardship - Biocide Resistance and Clinical Implications-Springer International Publishing (2018)Nguyên NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Cells Genes and Stories by Priscilla WaldDocument19 pagesCells Genes and Stories by Priscilla WaldClarissa WorcesterNo ratings yet
- Digestion HandoutDocument4 pagesDigestion HandoutStephanie ZammitNo ratings yet