Professional Documents
Culture Documents
1a Syllabus Periodic Table Equations
1a Syllabus Periodic Table Equations
Uploaded by
Karina Leung0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views1 pageThis document outlines the syllabus for a chemistry course covering the periodic table and chemical equations. It lists 12 lessons that teach about physical and chemical changes, writing chemical equations, patterns in the periodic table including trends in groups 1 and 7, the composition of air and determining oxygen percentage, and the formation of carbon dioxide. The objectives are to understand key concepts about the periodic table, chemical reactions, and common substances like oxygen and carbon dioxide.
Original Description:
Original Title
1a Syllabus Periodic Table Equations
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document outlines the syllabus for a chemistry course covering the periodic table and chemical equations. It lists 12 lessons that teach about physical and chemical changes, writing chemical equations, patterns in the periodic table including trends in groups 1 and 7, the composition of air and determining oxygen percentage, and the formation of carbon dioxide. The objectives are to understand key concepts about the periodic table, chemical reactions, and common substances like oxygen and carbon dioxide.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views1 page1a Syllabus Periodic Table Equations
1a Syllabus Periodic Table Equations
Uploaded by
Karina LeungThis document outlines the syllabus for a chemistry course covering the periodic table and chemical equations. It lists 12 lessons that teach about physical and chemical changes, writing chemical equations, patterns in the periodic table including trends in groups 1 and 7, the composition of air and determining oxygen percentage, and the formation of carbon dioxide. The objectives are to understand key concepts about the periodic table, chemical reactions, and common substances like oxygen and carbon dioxide.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
Island School Chemistry PT & E 1a
IGCSE Chemistry : Periodic Table & Equations Syllabus
Statements with a ‘C’ are examined on Paper 2 only.
Lesson Teaching Objectives Refs.
1 Know the difference between physical and chemical changes Complete
Physical & Use observations to recognize physical and chemical changes Chemistry(CC)
Chemical Apply equation writing to practical situations p 47
Changes
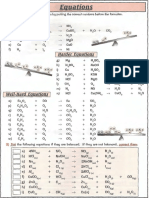
2&3 1.25 write word equations and balanced chemical equations (including CC
Equations state symbols) for reactions studied in this specification and for unfamiliar P68 - 69
reactions where suitable information is provided
4 1.23 understand why elements in the same group of the Periodic Table have CC
Patterns similar chemical properties P166 – 167,
1.24 understand why the noble gases (Group 0) do not readily react 172 – 173
5 1.20 understand how to use electrical conductivity and the acid-base CC
Metal & character of oxides to classify elements as metals or non-metals P174 – 177
Non 1.21 identify an element as a metal or a non-metal according to its position
Metal in the Periodic Table
6 2.1 understand how the similarities in the reactions of Group 1 elements CC
Alkali with water provide evidence for their recognition as a family of elements P168 – 169
Metals 2.2 understand how the differences between the reactions of these elements
with air and water provide evidence for the trend in reactivity in Group 1
2.3 use knowledge of trends in Group 1 to predict the properties of other
alkali metals
2.4C explain the trend in reactivity in Group 1 in terms of electronic
configuration
7&8 2.5 know the colours, physical states (at room temperature) and trends in CC
Halogens physical properties of the Halogens (F to I) P170 – 171
2.6 use knowledge of trends in Group 7 to predict the properties of other
halogens
2.7 understand how displacement reactions involving halogens and halides
provide evidence for the trend in reactivity in Group 7
2.8C explain the trend in reactivity in Group 7 in terms of electronic
configurations
9 & 10 2.9 know the approximate percentages by volume of the four most abundant CC
Air & gases in dry air P210 – 211
Oxygen 2.10 understand how to determine the percentage by volume of oxygen in 156 – 157
air using experiments involving the reactions of metals (e.g. iron) and non-
metals (e.g. phosphorus) with air.
2.14 practical: determine the approximate percentage by volume of oxygen
in air using a metal or a non-metal
2.11 describe the combustion of elements in oxygen, including magnesium,
hydrogen and sulfur
11 2.12 describe the formation of carbon dioxide from the thermal CC
Carbon decomposition of metal carbonates, including copper(II)carbonate P189, 238 – 239
Dioxide 2.13 know that carbon dioxide is a greenhouse gas and that increasing
amounts in the atmosphere may contribute to climate change
12 Test
You might also like
- Basics of Mining and Mineral Processing by W Scott Dunbar PDFDocument179 pagesBasics of Mining and Mineral Processing by W Scott Dunbar PDFFerudun Akyol100% (1)
- Aluminium PresentationDocument12 pagesAluminium PresentationDaniel McknightNo ratings yet
- Potline ProcessDocument12 pagesPotline ProcesssssduduNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2. Sophic Fire: (A) The Metals Necessary To Take in HandDocument3 pagesChapter 2. Sophic Fire: (A) The Metals Necessary To Take in HandtravellerfellowNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6. Nutrition.Document134 pagesChapter 6. Nutrition.myjesa07No ratings yet
- IGCSE Chemistry Revision ChecklistDocument10 pagesIGCSE Chemistry Revision ChecklistSadav ImtiazNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Chemistry Revision ChecklistDocument10 pagesIGCSE Chemistry Revision ChecklistAbdelmoneim Elmansy Igcse100% (1)
- Edexcel IGCSE ChemistryDocument11 pagesEdexcel IGCSE ChemistrySweetygirl_1650% (2)
- Chapter 9Document33 pagesChapter 9helloblarg100% (4)
- Organic ChemistryDocument39 pagesOrganic ChemistryAurora JimenezNo ratings yet
- RBI Damage Mechanism Potentials Rev-01 - 6-15-2016Document27 pagesRBI Damage Mechanism Potentials Rev-01 - 6-15-2016TommyNo ratings yet
- Chemical CharacterisationDocument66 pagesChemical Characterisationvenkatakrishna chalapaathiNo ratings yet
- Corrosion and Its Mitigation in The Oil and Gas Industry PDFDocument7 pagesCorrosion and Its Mitigation in The Oil and Gas Industry PDFArunachalam AvanashiNo ratings yet
- Principles of Geochemistry. G Ottonello 0231099843Document938 pagesPrinciples of Geochemistry. G Ottonello 0231099843Indra Gunawan100% (2)
- Chemistry Checklist For Y10 Autumn Exam (Y9 Material) : Topic 1 - Key Concepts in ChemistryDocument4 pagesChemistry Checklist For Y10 Autumn Exam (Y9 Material) : Topic 1 - Key Concepts in ChemistryJeffreyNo ratings yet
- GCSE 9-1 Chemistry Checklist - Y9 ExamDocument6 pagesGCSE 9-1 Chemistry Checklist - Y9 Examlewis112009No ratings yet
- Topic 3: Periodicity (6 Hours) : Assessment Statement Obj Teacher's NotesDocument2 pagesTopic 3: Periodicity (6 Hours) : Assessment Statement Obj Teacher's NotesAtharva SatputeNo ratings yet
- Edexcel GCSE (9-1) Chemistry Revision Checklist (Year 9) : Topic 1 - Key Concepts in ChemistryDocument6 pagesEdexcel GCSE (9-1) Chemistry Revision Checklist (Year 9) : Topic 1 - Key Concepts in ChemistryAshley Bissoondoyal (crypt1z)No ratings yet
- Topic 3 - Gases in The Air, Reactivity Series & Rusting, Periodic Table, Groups 1, 7 & 0Document2 pagesTopic 3 - Gases in The Air, Reactivity Series & Rusting, Periodic Table, Groups 1, 7 & 0stracklNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Year10 EoS1 LO BookletDocument62 pagesChemistry Year10 EoS1 LO Booklet29x4rk8pgfNo ratings yet
- Term 3 Checklist TRIPLEDocument8 pagesTerm 3 Checklist TRIPLELubzNo ratings yet
- Chemistry IGCSE SpecificationDocument14 pagesChemistry IGCSE SpecificationStudent Marc Sanchis VilaNo ratings yet
- 03 Periodic Trends NDocument16 pages03 Periodic Trends Nkhaled taseenNo ratings yet
- ManuscriptDocument8 pagesManuscriptbpxb5ms6w7No ratings yet
- GCSE 9-1 Chemistry Checklist - Paper 2Document8 pagesGCSE 9-1 Chemistry Checklist - Paper 2Arsh TewariNo ratings yet
- Edexcel IGCSE ChemistryDocument11 pagesEdexcel IGCSE ChemistrySamuel Muabia Plānet0% (1)
- Chem 2-4Document6 pagesChem 2-4stanleybaldwin28No ratings yet
- 3 Periodicity Assessment ChecklistDocument3 pages3 Periodicity Assessment ChecklistseyooraanpNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument2 pagesChemistryZyad MâğdyNo ratings yet
- Y10 PTB Self-AssessmentDocument2 pagesY10 PTB Self-AssessmentanythingNo ratings yet
- Theoretical Investigation of Regiodivergent AdditiDocument16 pagesTheoretical Investigation of Regiodivergent AdditiLavinia KassabNo ratings yet
- Theoretical Study of The Curu H Molecular Interaction: F. Colmenares, A. Ramõrez-Solõs, O. NovaroDocument7 pagesTheoretical Study of The Curu H Molecular Interaction: F. Colmenares, A. Ramõrez-Solõs, O. NovaroDiego Alejandro Hurtado BalcazarNo ratings yet
- 2021 DOUBLE Complete Checklist For 5th Form Trial ExamsDocument13 pages2021 DOUBLE Complete Checklist For 5th Form Trial ExamsLara SowandeNo ratings yet
- Assessment Statements Topic 3Document2 pagesAssessment Statements Topic 3Noreen ClarkNo ratings yet
- Guidelines See HighlightedDocument14 pagesGuidelines See HighlightedAlsid ZaimajNo ratings yet
- 220 ProjectDocument15 pages220 ProjectEcem ÇevikNo ratings yet
- Entrance Examination Syllabus 2021: ChemistryDocument46 pagesEntrance Examination Syllabus 2021: ChemistryFadhilah DefayanaNo ratings yet
- Sample Paper Xi ChemistryDocument4 pagesSample Paper Xi ChemistryYash BhagatNo ratings yet
- Y11 Electrolysis Assessment ChecklistDocument2 pagesY11 Electrolysis Assessment Checklistsanjay.vullisNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Year 8 Scheme 2012Document6 pagesChemistry Year 8 Scheme 2012Maoga2013No ratings yet
- Section: Site 2Document5 pagesSection: Site 2Hubbak KhanNo ratings yet
- Assessment Examples Chemistry July2012Document16 pagesAssessment Examples Chemistry July2012shoaibNo ratings yet
- Syllabus: Entrance TestDocument37 pagesSyllabus: Entrance TestJunaid AlamNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0009254102002632 MainDocument15 pages1 s2.0 S0009254102002632 MainAmanda AntunesNo ratings yet
- Syllabus & Model Paper: Entrance TestDocument60 pagesSyllabus & Model Paper: Entrance TestTanzil RahmanNo ratings yet
- Reactivity TrendsDocument3 pagesReactivity Trendsattiqueazan0No ratings yet
- 962 Chemistry (PPU) Semester 2 Topics-SyllabusDocument9 pages962 Chemistry (PPU) Semester 2 Topics-SyllabusJosh, LRT100% (1)
- ChemistryDocument28 pagesChemistrySanaina AhsanNo ratings yet
- Chemistry IGCSE Cambridge SyllabusDocument32 pagesChemistry IGCSE Cambridge SyllabusharshanvelNo ratings yet
- Y10 Chem Syllabus PointsDocument19 pagesY10 Chem Syllabus PointsLuis HuangNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry - Some Basic Principles and Techniques: Unit 12Document39 pagesOrganic Chemistry - Some Basic Principles and Techniques: Unit 12RosellaNo ratings yet
- 2018SU B.SC Chemistry SyllabusDocument22 pages2018SU B.SC Chemistry Syllabussachin81185No ratings yet
- 2004-Kinetics of The Absorption of Carbon Dioxide Into Mixed Aqueous Solutions in AMP+PZDocument14 pages2004-Kinetics of The Absorption of Carbon Dioxide Into Mixed Aqueous Solutions in AMP+PZbaohongqian2020No ratings yet
- SPM Chemistry Revision Module On The BasicsDocument64 pagesSPM Chemistry Revision Module On The Basicssuritanu96No ratings yet
- Promoting Biomass Electrooxidation Via ModulatingDocument11 pagesPromoting Biomass Electrooxidation Via ModulatingCB Dong SuwonNo ratings yet
- Chemistry QP in English Set 2Document4 pagesChemistry QP in English Set 2Annesha MondalNo ratings yet
- Reduccion de CO2Document10 pagesReduccion de CO2YovannyNo ratings yet
- Gr11 Phy P2 June 2017 Question PaperDocument16 pagesGr11 Phy P2 June 2017 Question Paperyoungmarley457No ratings yet
- Isotherm 1Document11 pagesIsotherm 1HemrajNo ratings yet
- Fuel Cell HandbookDocument18 pagesFuel Cell HandbookDiego AranibarNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Syllabus Class 9 2018 - 19 EoyDocument6 pagesChemistry Syllabus Class 9 2018 - 19 Eoyafzalakhtar370No ratings yet
- Course Compact STC 111Document6 pagesCourse Compact STC 111Benjamen FolarinNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 5070 Class 9Document9 pagesChemistry 5070 Class 9WaqarNo ratings yet
- 7670 PDFDocument12 pages7670 PDFDiogomussumNo ratings yet
- Handout - 2021 - CHEM F111Document2 pagesHandout - 2021 - CHEM F111vishnuNo ratings yet
- 1158 1 OnlineDocument10 pages1158 1 OnlineSebastián Alberto Campos MillaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13-15Document64 pagesChapter 13-15captain20119No ratings yet
- 1a Particles Bonding Syllabus (2017)Document2 pages1a Particles Bonding Syllabus (2017)Karina LeungNo ratings yet
- Electronic Charges of Bonds in Organic CompoundsFrom EverandElectronic Charges of Bonds in Organic CompoundsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- 1c Command WordsDocument2 pages1c Command WordsKarina LeungNo ratings yet
- 1b Glossary Particles and Bonding (2017)Document2 pages1b Glossary Particles and Bonding (2017)Karina LeungNo ratings yet
- 4a Periodic PatternsDocument2 pages4a Periodic PatternsKarina LeungNo ratings yet
- 4b ANSWERS Noble Gases (2017)Document1 page4b ANSWERS Noble Gases (2017)Karina LeungNo ratings yet
- 3c More EquationsDocument2 pages3c More EquationsKarina LeungNo ratings yet
- 3b Balancing Equations CGPDocument1 page3b Balancing Equations CGPKarina LeungNo ratings yet
- 2c ANSWERS Balancing Equations (2017)Document1 page2c ANSWERS Balancing Equations (2017)Karina LeungNo ratings yet
- Complete List of Inorganic AcidsDocument1 pageComplete List of Inorganic AcidsAlejandro VargasNo ratings yet
- Uranium InfoDocument1 pageUranium InfostefanNo ratings yet
- ACID BAse AssignmentDocument11 pagesACID BAse AssignmentMosfiqur Rahman100% (2)
- Chemical Stock UpdatedDocument21 pagesChemical Stock Updatedsivaraja kNo ratings yet
- Hydrogen - Mind MapDocument1 pageHydrogen - Mind Mapsarthakyedlawar04No ratings yet
- EASE SCI.I Module 6 Behavior of MatterDocument28 pagesEASE SCI.I Module 6 Behavior of MatterBoy SawagaNo ratings yet
- Gorni SFHTHandbookDocument83 pagesGorni SFHTHandbookapi-3762011No ratings yet
- NOx FormationDocument56 pagesNOx FormationYosita Dyah AninditaNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International AS & A Level: CHEMISTRY 9701/33Document8 pagesCambridge International AS & A Level: CHEMISTRY 9701/33higherlearningtutorshipNo ratings yet
- Laporan Praktikum Kimia Organik: Oleh: H-10 Nailal Mudliatunnur (110114452)Document16 pagesLaporan Praktikum Kimia Organik: Oleh: H-10 Nailal Mudliatunnur (110114452)SenopatiNo ratings yet
- Lithium Batteries - A Practical Application of Chemical Principles - TREPTOW - CHICAGO UDocument6 pagesLithium Batteries - A Practical Application of Chemical Principles - TREPTOW - CHICAGO Uabhik16No ratings yet
- Redox Chemistry: Background To Redox ReactionDocument4 pagesRedox Chemistry: Background To Redox ReactionAhmed Mohamed EwisNo ratings yet
- Hp02ver Endmember AbbreviationsDocument4 pagesHp02ver Endmember AbbreviationslinkyashuNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Module 3Document14 pagesChemistry Module 3MASHNo ratings yet
- Aluminium Bronze Valve Manufacturer - Shipham ValvesDocument2 pagesAluminium Bronze Valve Manufacturer - Shipham ValvesmohamedfirozNo ratings yet
- 201 L 4 Gravimetric AnalysisDocument24 pages201 L 4 Gravimetric AnalysisJawad AhmadNo ratings yet
- 9701 w06 QP 2Document12 pages9701 w06 QP 2Hubbak KhanNo ratings yet
- Efflorescence of Soluble Silicate Coatings 1991Document6 pagesEfflorescence of Soluble Silicate Coatings 1991Luis EnriqueNo ratings yet
- Speciality Graphite Materials: FOR Continuous CastingDocument6 pagesSpeciality Graphite Materials: FOR Continuous Castingramadan slimNo ratings yet