Professional Documents
Culture Documents
1b Glossary Particles and Bonding (2017)
Uploaded by
Karina LeungCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
1b Glossary Particles and Bonding (2017)
Uploaded by
Karina LeungCopyright:
Available Formats
Island School Chemistry P&B 1b
Glossary for Particles & Bonding Topic
Atom The smallest part of an element that can exist.
Particles Extremely small pieces of matter, for example, atoms, molecules and
ions.
Molecule A molecule usually consists of a small number of atoms joined
together covalently
Element A single pure substance that cannot be split up into anything
simpler.
Symbols Chemists use symbols to represent atoms. Every element has a
different symbol. For example, the symbol for carbon is C.
Diffusion Gaseous/liquid particles spread out/mix.
Dissolving Solid particles break apart and exist in the gaps between the liquid
particles.
Simple A separation technique that allows a pure liquid to be separated
distillation from a mixture. Involves the liquid boiling and then condensing.
Filtration A separation technique that allows an insoluble solid to be
separated from a mixture in a liquid. The liquid passes through the
filter paper but the solid does not.
Crystallisation A separation technique that allows a soluble solid to be separated
from a dissolved mixture in a liquid. The mixture is heated and the
liquid partially evaporates. As the mixture cools, the solid starts to
appear. This is called crystallisation.
Paper A technique that allows a complex mixture of substances to be
chromatography separated and identified. Each pure substance rises up the filter
paper by different distances.
Retention factor Used to identify the substances used in paper chromatography.
(Rf value). The distance moved by the substance / distance moved by the
solvent (liquid).
Solute Solid particles that you are trying to dissolve.
Solvent Liquid that you are using to dissolve the solid. Water is the most
common solvent, but there are others such as propanone is used
to dissolve nail polish.
Solution When the solid has dissolved in the liquid, we call this a solution.
Saturated This is the maximum amount of solute that a solvent can dissolve
solution at a given temperature.
Solubility This is a measure of how much solute has been dissolved in the
solvent. It is often measured in g of solute per 100g of solvent.
Periodic Table A table of elements arranged in order of increasing atomic number
to show the similarities of the chemical elements. The elements are
arranged in vertical groups and horizontal periods.
Period A horizontal row of the Periodic Table.
Island School Chemistry P&B 1b
Proton number The number of protons in the nucleus of an atom. It is also the
(atomic number) number of electrons present in an atom and the position of the
element within the Periodic Table
Nucleon number the total number of protons and neutrons present in the nucleus
(mass number) of an atom.
Sub-atomic Very small particles - protons, neutrons, and electrons - from
particles which all atoms are built
Proton A sub-atomic particle with a relative mass of 1 a relative charge
of +1 found in the nucleus of all atoms
Electron A sub-atomic particle with negligible mass and a relative charge of -
1; electrons are present in all atoms, located in shells outside the
nucleus.
Neutron An uncharged sub-atomic particle present in the nuclei of atoms.
A neutron has a mass of 1 relative to a proton.
Electron Arrangement of electrons in shells/orbitals around nucleus.
Configuration
Ion Charged particles made from an atom, or groups of atoms
(polyatomic ions), by the loss or gain of electrons - the gain of
electrons produces negative ions; the loss of electrons produces
positive ions.
Ionic Bond A chemical bond formed between metals and non metal
elements. Involves the attraction between oppositely charged
ions.
Covalent bond A chemical bond formed by the sharing of one or more pairs of
electrons between two atoms - such bonds are present in
compounds involving non-metals. In addition to single covalent
bonds, double and triple bonds can also exist in some elements
and compounds.
The atoms are held by the mutual attraction of the shared pair of
electrons for both nuclei
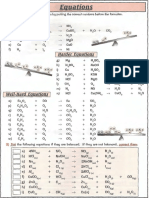
Formulae Formulae are written for compounds. The formula of a
compound consists of the symbols of the elements present and
some numbers. The numbers show the ratio in which the atoms
are present. The compound carbon dioxide has the formula
CO2
Valency The combining power of an atom or group of atoms
You might also like
- GCSE Chemistry Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandGCSE Chemistry Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Flashcards - Topic 01 Atomic Structure and The Periodic Table - AQA Chemistry GCSEDocument137 pagesFlashcards - Topic 01 Atomic Structure and The Periodic Table - AQA Chemistry GCSEEva xuNo ratings yet
- HTTPSBMC - unideb.hupublicdocuments2022!09!132BMCI Lecture Week2 Compounds Mixtures PDFDocument82 pagesHTTPSBMC - unideb.hupublicdocuments2022!09!132BMCI Lecture Week2 Compounds Mixtures PDFayoubNo ratings yet
- Chemistry NotesDocument70 pagesChemistry NotesAngelina SandifordNo ratings yet
- Welcome To Ap Chemistry: Mahua ChakrabortyDocument33 pagesWelcome To Ap Chemistry: Mahua ChakrabortyKahfiantoroNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument39 pagesChemistrysiennakransiqiNo ratings yet
- Atomic Theory and Atomic Structure 1Document25 pagesAtomic Theory and Atomic Structure 1Mohamed YahiaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry: Presented By: Mrs. Marie Nella T. VictoriaDocument75 pagesChemistry: Presented By: Mrs. Marie Nella T. VictoriaJESPHER GARCIANo ratings yet
- Chemistry Polaris LectureDocument80 pagesChemistry Polaris LectureDonn SabalNo ratings yet
- Science 20 Unit ADocument133 pagesScience 20 Unit Aapi-2079572300% (1)
- Atoms and Molecules Class 9 Notes Chapter 3Document7 pagesAtoms and Molecules Class 9 Notes Chapter 3ANAYA SHARANNo ratings yet
- Atoms and MoleculesDocument4 pagesAtoms and MoleculesHitesh kalraNo ratings yet
- CHEMISTRY NOTES Class 9 CBSEDocument13 pagesCHEMISTRY NOTES Class 9 CBSERamRakh YadavNo ratings yet
- Presentation C.elementsDocument17 pagesPresentation C.elementsEsterkaKraljikNo ratings yet
- Kanav 9a 90040 CH 3 Chem.Document6 pagesKanav 9a 90040 CH 3 Chem.Kanav WallechaNo ratings yet
- RVCDocument48 pagesRVCfluronineNo ratings yet
- Science Reviewer V2Document33 pagesScience Reviewer V2eliotrichard570No ratings yet
- Atoms and Bohr Model of AtomsDocument31 pagesAtoms and Bohr Model of Atomsogedengbed28No ratings yet
- Short Notes (Chemistry)Document8 pagesShort Notes (Chemistry)ninaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: The Chemical Context of LifeDocument35 pagesChapter 2: The Chemical Context of LifeJustin RobenyNo ratings yet
- Campbell Lecture Notes Chemistry of LifeDocument42 pagesCampbell Lecture Notes Chemistry of LifeSophia Andrei VillalunaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Notes English Medium by Goswami SirDocument20 pagesChemistry Notes English Medium by Goswami SirManoj GoswamiNo ratings yet
- Official Biology 102 Course Package (2011) by Tyler Vance and Megan Valencia PDFDocument88 pagesOfficial Biology 102 Course Package (2011) by Tyler Vance and Megan Valencia PDFreadingisgudNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Ch. 2 NotesDocument10 pagesUnit 1 Ch. 2 Notesanthony.brown2No ratings yet
- Meera Class 9 Chemistry NotesDocument11 pagesMeera Class 9 Chemistry Noteslalitha muraliNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Definitions Form 4 GuideDocument8 pagesChemistry Definitions Form 4 GuideWaggle The GreatNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Basic ChemistryDocument22 pagesChapter 2 - Basic ChemistryHannah Lee LumosbogNo ratings yet
- Physical Science Sci - 102Document16 pagesPhysical Science Sci - 102Jay MabiniNo ratings yet
- Chemistry and Engineering: Big Stuff (Objects, Etc.)Document27 pagesChemistry and Engineering: Big Stuff (Objects, Etc.)Madhav MakkarNo ratings yet
- CLASSIFICATION OF MATTER RevisedDocument42 pagesCLASSIFICATION OF MATTER RevisedBoni Almueda Valdez Jr.No ratings yet
- Chemistry Notes Year10Document6 pagesChemistry Notes Year10CubicatNo ratings yet
- AP Bio Study Guide Topics Chemistry Elements CompoundsDocument33 pagesAP Bio Study Guide Topics Chemistry Elements CompoundsHayden CaseyNo ratings yet
- VolcanoDocument2 pagesVolcanoJhaynnon AniezNo ratings yet
- Chemistry ReviewerDocument14 pagesChemistry ReviewerZildjian ApudNo ratings yet
- The Chemical Earth-Ahmad ShahDocument46 pagesThe Chemical Earth-Ahmad ShahYouseffNo ratings yet
- Chem ReviewerDocument8 pagesChem ReviewerRhea Marielle EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- 01-02. The Chemical Context of LifeDocument4 pages01-02. The Chemical Context of LifeDaniel Angelo MiradorNo ratings yet
- Classification of Matter RevisedDocument42 pagesClassification of Matter Revisedyazan alsoradiNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Periodic TableDocument23 pagesIntroduction To Periodic TableMa. Oliva Diana CastroNo ratings yet
- Gen. Chem. (Group Activity)Document5 pagesGen. Chem. (Group Activity)jaishenneNo ratings yet
- Chemistry IGCSE Rev PackDocument39 pagesChemistry IGCSE Rev Packرهام کاظمیNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - ChemistryDocument9 pagesChapter 4 - ChemistryHakim Abbas Ali PhalasiyaNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 9 Atoms Molecules NotesDocument5 pagesCBSE Class 9 Atoms Molecules NotesManjot kaurNo ratings yet
- Chem NotesDocument51 pagesChem NotesHannah RossNo ratings yet
- Basic Chemistry ReviewDocument5 pagesBasic Chemistry ReviewArman Neil J. BudogNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure & the Periodic Table ExplainedDocument19 pagesAtomic Structure & the Periodic Table ExplainedAiza ImranNo ratings yet
- Important DefinitionsDocument6 pagesImportant DefinitionsicedgoblinNo ratings yet
- GED Chemistry Note1 (Atoms, Molecules and Their Properties)Document6 pagesGED Chemistry Note1 (Atoms, Molecules and Their Properties)Shahadat Hussain Parvez100% (1)
- Chemistry Form 4 KSSM Definition GuideDocument4 pagesChemistry Form 4 KSSM Definition Guideprebasubah100% (1)
- EASA Module 2 Questions and ExplanationsDocument6 pagesEASA Module 2 Questions and ExplanationsSteven J. SelcukNo ratings yet
- Science Reviewer A. Phase Change in MatterDocument6 pagesScience Reviewer A. Phase Change in MatterNicole VictorinoNo ratings yet
- Physical Science 2nd QuarterDocument6 pagesPhysical Science 2nd QuarterAngelica C. BramajeNo ratings yet
- Preliminary Chemistry NotesDocument33 pagesPreliminary Chemistry NotesStacey100% (1)
- Elements, Compounds and Mixtures: - Year 9, Week 3Document37 pagesElements, Compounds and Mixtures: - Year 9, Week 3Agim OnyekaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 WorkbookDocument12 pagesChapter 2 WorkbookChantelle LemieuxNo ratings yet
- Chap 4 BIOLOGY BIODocument82 pagesChap 4 BIOLOGY BIOsarah575No ratings yet
- EASA Module 2 - NotesDocument24 pagesEASA Module 2 - NotesSteven J. SelcukNo ratings yet
- Chemistry: Role of Chemistry in Modern LifeDocument7 pagesChemistry: Role of Chemistry in Modern LifeLoLo AlobaidyNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 Atoms and Molecules NotesDocument7 pagesGrade 9 Atoms and Molecules NotesAujasvi JainNo ratings yet
- 4b ANSWERS Noble Gases (2017)Document1 page4b ANSWERS Noble Gases (2017)Karina LeungNo ratings yet
- Periodic TableDocument1 pagePeriodic TableSubbash EkambaramNo ratings yet
- 4a Periodic PatternsDocument2 pages4a Periodic PatternsKarina LeungNo ratings yet
- 3c More EquationsDocument2 pages3c More EquationsKarina LeungNo ratings yet
- 3b Balancing Equations CGPDocument1 page3b Balancing Equations CGPKarina LeungNo ratings yet
- 2c ANSWERS Balancing Equations (2017)Document1 page2c ANSWERS Balancing Equations (2017)Karina LeungNo ratings yet
- Mean Sea Level, GPS, and The GeoidDocument3 pagesMean Sea Level, GPS, and The Geoidamungme_amungme100% (1)
- B31.3 2016 Acc TableDocument3 pagesB31.3 2016 Acc TablePrasan SJNo ratings yet
- Tekla Tedds 2020 Engineering LibraryDocument55 pagesTekla Tedds 2020 Engineering LibraryCSEC Uganda Ltd.No ratings yet
- Cheat Sheet SurfaceDocument2 pagesCheat Sheet SurfaceArchita VNo ratings yet
- CES SEC Mid Term ExamDocument1 pageCES SEC Mid Term ExamxlorenNo ratings yet
- Massachusetts Institute of Technology Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer ScienceDocument3 pagesMassachusetts Institute of Technology Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer ScienceKrishna GNo ratings yet
- Toaz - Info Astm d4543 Preparing Rock Core Specimens PRDocument4 pagesToaz - Info Astm d4543 Preparing Rock Core Specimens PRSajaNaimatNo ratings yet
- ... Go To Air Volume Calculation Prepared by MD - Zafar ... Go To Strength & Leak TestDocument5 pages... Go To Air Volume Calculation Prepared by MD - Zafar ... Go To Strength & Leak Testmahesh100% (1)
- A - 3 - 6 - 10 Beam ReportDocument5 pagesA - 3 - 6 - 10 Beam ReportChanna SamarasingheNo ratings yet
- IbrDocument5 pagesIbrSuresh Ram RNo ratings yet
- Exxon Mobil Matls Lab A105N Vs A350LF2 GrainSize PDFDocument5 pagesExxon Mobil Matls Lab A105N Vs A350LF2 GrainSize PDFAnonymous nw5AXJqjdNo ratings yet
- Engineering Metallurgy Course OverviewDocument86 pagesEngineering Metallurgy Course OverviewDKNo ratings yet
- ASME & AWS Welding Codes-Similarities and DifferencesDocument7 pagesASME & AWS Welding Codes-Similarities and DifferencesMnttoMecNo ratings yet
- RF4 PK PDFDocument2 pagesRF4 PK PDFMuhammad WaseemNo ratings yet
- Lab Report Exp 5 Redox ReactionDocument4 pagesLab Report Exp 5 Redox ReactionAqirah FadzNo ratings yet
- Statistical PhysicsDocument112 pagesStatistical PhysicsSharon Di SpenaNo ratings yet
- Spe 191575 PaDocument14 pagesSpe 191575 PaNavneet SinghNo ratings yet
- Astm A53 Elongation SpecificationDocument3 pagesAstm A53 Elongation SpecificationHéctor AtzinNo ratings yet
- TMD 07Document3 pagesTMD 07Hemanth KumarNo ratings yet
- As Competition Paper 2007 Solutions: Section A: Multiple ChoiceDocument8 pagesAs Competition Paper 2007 Solutions: Section A: Multiple ChoiceAhmad HaikalNo ratings yet
- AIAA EbooksDocument9 pagesAIAA Ebookssarah86304325No ratings yet
- Acceleration: Graphs and ProblemsDocument11 pagesAcceleration: Graphs and ProblemsMithilesh BiswasNo ratings yet
- Bubble Cap DesignDocument18 pagesBubble Cap Designsanjuct0686% (7)
- Module 8.1 - B1B2 - Rev 00 (Full Permission)Document24 pagesModule 8.1 - B1B2 - Rev 00 (Full Permission)Ahsan MalikNo ratings yet
- Acoustics: Course No. Arch5251 Instructors: Dawit Melaku (Msc. in Advanced Architecture)Document21 pagesAcoustics: Course No. Arch5251 Instructors: Dawit Melaku (Msc. in Advanced Architecture)ዮናታን ኦርቶዶክስNo ratings yet
- Practice Test Questions - Fluid MechanicsDocument25 pagesPractice Test Questions - Fluid MechanicsMehrozNo ratings yet
- Pripol Dimer Acids: Flexibility and HydrophobicityDocument4 pagesPripol Dimer Acids: Flexibility and Hydrophobicitymaged_abdnaghoNo ratings yet
- Units Measurements MCQ PDFDocument9 pagesUnits Measurements MCQ PDFkathyayaniNo ratings yet
- Tugas Mekanika Tanah IIDocument10 pagesTugas Mekanika Tanah IIAriNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document45 pagesUnit 1C.HarshithaNo ratings yet