TRIGONOMETRY REVIEW SHEET ___________________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________________ PLANE TRIANGLE RELATIONSHIPS
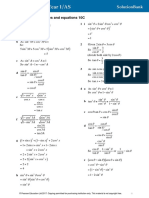
QUADRANTS & SIGNS OF FUNCTIONS a b c
Law of sines: ----------- = ----------- = ------------
sin A sin B sin C
sin & csc pos.
All positive c B Law of cosines: c 2 = a 2 + b 2 – 2ab cos C ,
others neg.
a
C = acos ---------------------------
II I a2 + b2 – c2
A 2ab
III IV C 1
tan --- ( A + B )
b
tan & cot pos. cos & sec pos . a+b 2
Law of tangents: ------------ = ------------------------------
a–b 1
others neg. others neg. tan --- ( A – B )
2
___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________
RIGHT-ANGLE TRIANGLE RELATIONSHIPS INVERSE TRIGONOMETRIC FUNCTIONS
a = opposite side
b = adjacent side Function Domain Range Quadrants
c = hypotenuse
c 90° - θ y = cos x
–1
–1 ≤ x ≤ 1 0≤y≤π I and II
side opposite θ a
a sin θ = ------------------------------------ = ---
hypotenuse c –1
–1 ≤ x ≤ 1 –π ⁄ 2 ≤ y ≤ π ⁄ 2 I and IV
y = sin x
side adjacent to θ b
θ 90° cos θ = ------------------------------------------ = ---
hypotenuse c y = tan x
–1 all reals –π ⁄ 2 < y < π ⁄ 2 I and IV
b side opposite θ a
tan θ = ------------------------------------------ = --- –1
x ≥ 1 or x ≤ – 1 0≤y≤π, y≠π⁄2 I and II
side adjacent to θ b y = sec x
Pythagorean theorem: c 2 = a 2 + b 2 y = csc x
–1
x ≥ 1 or x ≤ – 1 –π ⁄ 2 ≤ y ≤ π ⁄ 2 , y ≠ 0 I and IV
___________________________________________________________________________
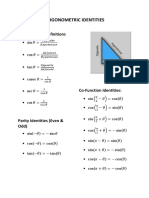
FUNDAMENTAL IDENTITIES y = cot x
–1 all reals 0<y<π I and II
sin x 1 1 1 cos x
1. tan x = ----------- 2. sec x = ----------- 3. csc x = ---------- 4. cot x = ----------- = -----------
cos x cos x sin x tan x sin x PRINCIPAL VALUES FOR INVERSE TRIGONOMETRIC FUNCTIONS
2 2 2 2 2 2
5. cos x + sin x = 1 6. 1 + tan x = sec x 7. cot x + 1 = csc x
Principal values for x ≥ 0 Principal values for x < 0
8a. cos ( π ⁄ 2 – x ) = sin x 8b. cos ( π ⁄ 2 + x ) = – sin x
9a. sin ( π ⁄ 2 – x ) = cos x 9b. sin ( π ⁄ 2 + x ) = cos x 0 ≤ sin x ≤ π ⁄ 2
–1
– π ⁄ 2 ≤ sin x < 0
–1
10. tan ( π ⁄ 2 – x ) = cot x
0 ≤ cos x ≤ π ⁄ 2 π ⁄ 2 < cos x ≤ π
–1 –1
OPPOSITE-ANGLE IDENTITIES
1. cos ( – x ) = cos x 2. sin ( – x ) = – sin x 3. tan ( – x ) = – tan x 0 ≤ tan x < π ⁄ 2
–1
– π ⁄ 2 < tan x < 0
–1
4. sec ( – x ) = sec x 5. csc ( – x ) = – csc x 6. cot ( – x ) = – cot x
0 < cot x ≤ π ⁄ 2 π ⁄ 2 < cot x < π
–1 –1
ADDITION LAWS
1. cos ( x ± y ) = cos x cos y + − sin x sin y 2. sin ( x ± y ) = sin x cos y ± cos x sin y 0 ≤ sec x < π ⁄ 2
–1
π ⁄ 2 < sec x ≤ π
–1
tan x ± tan y
3. tan ( x ± y ) = -------------------------------
0 < csc x ≤ π ⁄ 2 – π ⁄ 2 ≤ csc x < 0
1−
–1 –1
+ tan x tan y
DOUBLE-ANGLE IDENTITIES
2 2 2 2
INVERSE IDENTITIES (ASSUMING PRINCIPAL VALUES ARE USED)
1a. cos 2x = cos x – sin x 1b. cos 2 x = 2 cos x – 1 1c. cos 2 x = 1 – 2 sin x
1. sin x + cos x = π ⁄ 2 7. sin ( – x ) = – sin x
–1 –1 –1 –1
1 1
1d. sin x = --- ( 1 – cos 2x ) 1e. cos x = --- ( 1 + cos 2x )
2 2
2. tan x + cot x = π ⁄ 2 8. cos ( – x ) = π – cos x
–1 –1 –1 –1
2 2
2 tan x 3. sec x + csc x = π ⁄ 2
–1 –1
9. tan ( – x ) = – tan x
–1 –1
2. sin 2x = 2 sin x cos x 3. tan 2x = --------------------
2
-
1 – tan x
4. csc x = sin ( 1 ⁄ x ) 10. cot ( – x ) = π – cot x
–1 –1 –1 –1
HALF-ANGLE IDENTITIES
5. sec x = cos ( 1 ⁄ x ) 11. sec ( – x ) = π – sec x
–1 –1 –1 –1
x 1 + cos x + if x/2 is in quadrant I or IV 6. cot x = tan ( 1 ⁄ x )
–1 –1
12. csc ( – x ) = – csc x
–1 –1
1. cos --- = ± ---------------------
2 2 - if x/2 is in quadrant II or III
___________________________________________________________________________
x 1 – cos x + if x/2 is in quadrant I or II COMPLEX IDENTITIES
2. sin --- = ± --------------------
2 2 - if x/2 is in quadrant III or IV e iw + e –iw e iw – e –iw
cos w = --------------------- i sin w = -------------------- Euler Identity: e iw = cos w + i sin w
2 2
x 1 – cos x + if x/2 is in quadrant I or III
3a. tan --- = ± --------------------- ___________________________________________________________________________
2 1 + cos x - if x/2 is in quadrant II or IV
QUADRATIC FORMULA
x 1 – cos x sin x – b ± b 2 – 4ac
3b. tan --- = -------------------- = --------------------- = csc x – cot x x = --------------------------------------
Solution to ax 2 + bx + c = 0 :
2 sin x 1 + cos x 2a
PRODUCT IDENTITIES ___________________________________________________________________________
1. 2 cos x cos y = cos ( x – y ) + cos ( x + y ) 2. 2 sin x sin y = cos ( x – y ) – cos ( x + y ) EXACT VALUES
3. 2 sin x cos y = sin ( x + y ) + sin ( x – y ) 4. 2 cos x sin y = sin ( x + y ) – sin ( x – y )
Angle (deg) Angle (rad) cos(x) sin(x) tan(x)
5. cos mx cos nx = cos ( m + n )x + cos ( m – n )x
0° 0 1 0 0
SUM IDENTITIES
30 ° π⁄6 1⁄2
1. cos x + cos y = 2 cos ----------- cos ----------- 2. cos x – cos y = – 2 sin ----------- sin -----------
x+y x–y x+y x–y 3⁄2 3⁄3
2 2 2 2
45 ° π⁄4 2⁄2 2⁄2
1
3. sin x + sin y = 2 sin ----------- cos ----------- 4. sin x – sin y = 2 sin ----------- cos -----------
x+y x–y x–y x+y
2 2 2 2
60 ° π⁄3 1⁄2 3⁄2 3
___________________________________________________________________________
REDUCTION IDENTITY 90 ° π⁄2 0 1 ±∞
1. a sin x + b cos x = a 2 + b 2 sin ( x + y ) , where y is chosen so that 180 ° π -1 0 0
a b
cos y = -------------------- and sin y = -------------------- 270° 3π ⁄ 2 0 -1 ±∞
a2 + b2 a2 + b2