Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Jncm2e Ws 3b07b Sol e
Uploaded by
Chan Wai KuenCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Jncm2e Ws 3b07b Sol e
Uploaded by
Chan Wai KuenCopyright:
Available Formats
New Century Mathematics (2nd Edition)
Chapter 7 Quadrilaterals In △BCD,
∵ BCD = 90 (proved)
Lesson Worksheet 7B Solutions ∴ BC + DC = BD
2 2 2
(Pyth. theorem)
Instant Drill 1
BC = √ BD −DC 2
2
m = 56 (property of rhombus) z= √( y+5)2−6 2
= √ (5+5) −6
∵ RT = PT (property of rhombus) 2 2
∴ n=4 =8
Instant Drill 2 4. In △HGK,
SRQ = 90 (property of rectangle) ∵ HK = GK (property of rectangle)
35 + m = 90 ∴ m=n (base s, isos. △)
m = 55 m + n = 136 (ext. of △)
∵ ST = PT (property of rectangle) m + m = 136
∴ n=7 2m = 136
m = 68
Instant Drill 3 n = m = 68
∵ PS = SR (by definition)
∴ 4p = p + 9 5. ∵ ACD = 45 (property of square)
3p = 9 ∴ x + 30 = 45
p=3 x = 15
∵ SQ PR (property of square) CDA = 90 (property of square)
∴ n = 90 In △CDE,
y = x + CDA (ext. of △)
Exercise = 15 + 90
1. ∵ PQ = PS (by definition) = 105
∴ m=5
∵ PT = RT (property of rhombus) 6. n = 45 (property of square)
∴ n=4 ∵ PQRS is a square. (given)
∴ PQRS is also a parallelogram.
2. ∵ DB AC (property of rhombus) PS // QR (by definition)
∴ x = 90 m = 64 (alt. s, PS // QR)
y = 52 (property of rhombus) In △PTW,
n + m + k = 180 ( sum of △)
3. x = 90 (property of rectangle)
45 + 64 + k = 180
∵ BE = DE (property of rectangle)
k = 71
∴ y=5
7. P + Q = 180 (int. s, PS // QR)
m + 78 = 180
m = 102
∵ PQRS is an isosceles trapezium.
(given)
© Oxford University Press 2017 Book 3B Lesson Worksheet Solutions 7B-1
New Century Mathematics (2nd Edition)
∴ R = Q ‘Explain Your Answer’ Question
k = 78 13. (a) BCD + 90 = 180 (adj. s on st. line)
S = P BCD = 90
n=m (b) ABC = DCE (corr. s, BA // CD)
= 102 = 90
CDA = DCE (alt. s, AD // BE)
8. ∵ ABCD is an isosceles trapezium. = 90
(given) DAB = BCD (opp. s of //gram)
∴ BD = CA = 90 (proved in (a))
x=2+4 ∵ ABC = BCD = CDA = DAB
=6 = 90
AB = DC (by definition) ∴ ABCD is a rectangle.
y=5 (by definition)
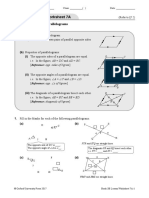
9. OB = OD (property of kite) Level Up Question
m=4 14. Draw a perpendicular line from D to meet BC
DAC = BAC (property of kite) at E.
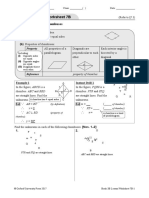
n = 21 A 15 cm D
12 cm
10. ∵ BD AC (property of kite) C
B E
∴ m = 90 50 cm
BCD = BAD (property of kite) ∵ DE BC (by construction)
41 + n = 103 ∴ DEB = DEC = 90
n = 62 ADE = DEC = 90 (alt. s, AD // BC)
∵ DAB = ABE = DEB = ADE = 90
11. PSR = PQR (property of kite) ∴ ABED is a rectangle. (by definition)
x = 110 ∴ DE = AB = 12 cm (property of rectangle)
54 + 110 + y + x = (4 2) 180 BE = AD = 15 cm (property of rectangle)
( sum of polygon) EC = BC BE
54 + 110 + y + 110 = 360
= (50 15) cm
274 + y = 360
= 35 cm
y = 86
In △DEC,
∵ DEC = 90 (proved)
12. SPR = QPR (property of kite)
∴ DC = DE + EC
2 2 2
(Pyth. theorem)
x = 48
PQR = PSR = 95 (property of kite) DC = √ DE +EC 2 2
= √ 12 +35 cm
2 2
(48 + x) + PQR + y + 95 = (4 2) 180
( sum of polygon) = 37 cm
(48 + 48) + 95 + y + 95 = 360
286 + y = 360
y = 74
© Oxford University Press 2017 Book 3B Lesson Worksheet Solutions 7B-2
You might also like
- Answers to Selected Problems in Multivariable Calculus with Linear Algebra and SeriesFrom EverandAnswers to Selected Problems in Multivariable Calculus with Linear Algebra and SeriesRating: 1.5 out of 5 stars1.5/5 (2)
- 02 - Mathematics - Part - II-AP - PDF (SHARED) PDFDocument11 pages02 - Mathematics - Part - II-AP - PDF (SHARED) PDFKamrunissa ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Allen RMO 2018 - Solutions PDFDocument6 pagesAllen RMO 2018 - Solutions PDFnavin guptaNo ratings yet
- Nodia and Company: Gate Solved Paper Mechanical Engineering 2004Document52 pagesNodia and Company: Gate Solved Paper Mechanical Engineering 2004murugeshmech22No ratings yet
- Pre Final Exam Nov. 17 2018 AnswerDocument4 pagesPre Final Exam Nov. 17 2018 AnswerJovy OpenianoNo ratings yet
- Pre Final Exam Nov. 17 2018 AnswerDocument4 pagesPre Final Exam Nov. 17 2018 AnswerJovy OpenianoNo ratings yet
- Act-Sat Formulas NotesDocument3 pagesAct-Sat Formulas Notesapi-372775136No ratings yet
- Gong Show San PedroDocument12 pagesGong Show San PedroEpilef ZaidNo ratings yet
- Geometry MasterkeyDocument5 pagesGeometry MasterkeyPoonam MishraNo ratings yet
- 2015 BoS Trials Mathematics Extension 1 SolutionsDocument22 pages2015 BoS Trials Mathematics Extension 1 SolutionsKowsik LakshmananNo ratings yet
- KVPY SA Hints and Solutions for Model Test Paper 1Document65 pagesKVPY SA Hints and Solutions for Model Test Paper 1VamsiMadupuNo ratings yet
- GATE ME 2004 Solved PaperDocument51 pagesGATE ME 2004 Solved PaperMayur MandrekarNo ratings yet
- 2020 Canadian Mathematical Olympiad Official SolutionsDocument6 pages2020 Canadian Mathematical Olympiad Official SolutionspaovueyongpaoNo ratings yet
- QuadrilateralDocument18 pagesQuadrilateralviralroshNo ratings yet
- I SucceedMath10thStandardSP 11Document9 pagesI SucceedMath10thStandardSP 11samridhahuja8No ratings yet
- Subject: MATHEMATICS (Code No.041) - SET 1 - Answer Key Section ADocument10 pagesSubject: MATHEMATICS (Code No.041) - SET 1 - Answer Key Section ARifatNo ratings yet
- KVPY SA 2018 Maths Question Answerkey SolutionsDocument1 pageKVPY SA 2018 Maths Question Answerkey SolutionsSaloni KumariNo ratings yet
- Model Answer Sheet Maths-2Document6 pagesModel Answer Sheet Maths-2Pratik KambleNo ratings yet
- Option Pricing: A Simplified Approach: John C. Cox, Stephen A. Ross and Mark RubinsteinDocument19 pagesOption Pricing: A Simplified Approach: John C. Cox, Stephen A. Ross and Mark Rubinsteinsophisticated321No ratings yet
- New A Level Formula SheetDocument2 pagesNew A Level Formula Sheetr8jrqkhzwgNo ratings yet
- 1.Basic Maths for PhysicsDocument4 pages1.Basic Maths for Physicsupanshupandit3No ratings yet
- Differential Calculus Formulas and ConceptsDocument5 pagesDifferential Calculus Formulas and ConceptsDroffilc Nav Cm MulihamNo ratings yet
- SSLC Model Exam 2020 MATHS (EM) Answer Key by Sibi Sir & Prathap SirDocument5 pagesSSLC Model Exam 2020 MATHS (EM) Answer Key by Sibi Sir & Prathap SirAKHILNo ratings yet
- 2013 Physics Trial Exam Solutions: SECTION A - Core StudiesDocument4 pages2013 Physics Trial Exam Solutions: SECTION A - Core StudiesorhanaliuNo ratings yet
- Test 1 Spring 2013Document2 pagesTest 1 Spring 2013Ali BakhsasNo ratings yet
- Solutions AIATS JEE (Adv) - 2021 Test-1A (Paper-1) (Code-E & F) 17-11-2019Document22 pagesSolutions AIATS JEE (Adv) - 2021 Test-1A (Paper-1) (Code-E & F) 17-11-2019Amman ChopadiyaNo ratings yet
- Algebra: X y NC X y N (n+1) A+ BDocument11 pagesAlgebra: X y NC X y N (n+1) A+ BLaissa SerranoNo ratings yet
- Class 9 E Unit T-1 Math-2 QDocument4 pagesClass 9 E Unit T-1 Math-2 QSayli shelkarNo ratings yet
- AddMath Formula SheetDocument5 pagesAddMath Formula SheetHidayah TeacherNo ratings yet
- Cartography FormulaDocument2 pagesCartography FormulaConcepcion Arreza SalupadoNo ratings yet
- Mathematics 1Document22 pagesMathematics 1RubyJanePartosa100% (1)
- Mathematics in Real Life-6: Answer Keys Chapter 10: AnglesDocument7 pagesMathematics in Real Life-6: Answer Keys Chapter 10: AnglesAshish ThapliyalNo ratings yet
- 2007 2008S6HyearlyPmath 1Document2 pages2007 2008S6HyearlyPmath 1api-3742735No ratings yet
- Question Bank - Brain Books An E Learning PlatformDocument3 pagesQuestion Bank - Brain Books An E Learning PlatformBabri masjid Ghistosof Babrii masjadNo ratings yet
- End of Stage 1/AS Mathematics:: Mathematics A (H230, H240) Paper 2: Pure Mathematics and MechanicsDocument21 pagesEnd of Stage 1/AS Mathematics:: Mathematics A (H230, H240) Paper 2: Pure Mathematics and MechanicsrebeccaNo ratings yet
- Finanzas Free Boundary Value ProblesDocument30 pagesFinanzas Free Boundary Value ProblesMauro SalinasNo ratings yet
- Section - D: Matrix-Match Type: Length ForceDocument13 pagesSection - D: Matrix-Match Type: Length Forcesarthakyedlawar04No ratings yet
- Rational Factoradimals TerminateDocument3 pagesRational Factoradimals TerminateTed BaggNo ratings yet
- Bézier CurveDocument3 pagesBézier CurvexunrageNo ratings yet
- Uconn ECE6439 Final 2014Document3 pagesUconn ECE6439 Final 2014Nemo OutisNo ratings yet
- ملخص لشابتر9.5 to 9.9 PDFDocument13 pagesملخص لشابتر9.5 to 9.9 PDFBalqees AlriyamiNo ratings yet
- Cal1 HW6 Fall 2013Document2 pagesCal1 HW6 Fall 2013KensleyTsangNo ratings yet
- 2ND W3W4 Precalculus Las 1Document12 pages2ND W3W4 Precalculus Las 1gfam59552No ratings yet
- Paper Solutions PDFDocument4 pagesPaper Solutions PDFSunil SinghNo ratings yet
- Algebra Worksheet 3 - InequalitiesDocument3 pagesAlgebra Worksheet 3 - InequalitiesJane ChangNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Mathematics Formula SheetDocument7 pagesIGCSE Mathematics Formula Sheetburner bNo ratings yet
- Ib Math Applications and Interpretations Summer PacketDocument21 pagesIb Math Applications and Interpretations Summer Packetapi-327140356No ratings yet
- Solving Quadratic Equations and InequalitiesDocument25 pagesSolving Quadratic Equations and InequalitiesSiddhantNo ratings yet
- Basic Mathematics Used in PhysicsDocument3 pagesBasic Mathematics Used in PhysicsEternalChronosNo ratings yet
- Ancment638232159769852432 (1)Document21 pagesAncment638232159769852432 (1)suhaas.s.sanshiNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 10 Mathematics Sample Paper 1 Solutions PDFDocument7 pagesCBSE Class 10 Mathematics Sample Paper 1 Solutions PDFShona KhattarNo ratings yet
- Article Theorem Proof Polynomial DivisionDocument2 pagesArticle Theorem Proof Polynomial Divisionminuch00newsNo ratings yet
- Important Formulae For CAT: Ratio, Proportion, VariationDocument10 pagesImportant Formulae For CAT: Ratio, Proportion, Variationvenkatakrishnan srinivasanNo ratings yet
- Math 2250 Homework 5 Model SolutionDocument2 pagesMath 2250 Homework 5 Model SolutionUmair MalikNo ratings yet
- RakeshYQ QuadDocument1 pageRakeshYQ QuadAvinash KumarNo ratings yet
- Constants and Key Equations in Chemicall ReactionDocument5 pagesConstants and Key Equations in Chemicall ReactionFrancisca BrazNo ratings yet
- Disc Math Lecture 09Document19 pagesDisc Math Lecture 09अभिषेक मानNo ratings yet
- Ps3 SolutionDocument4 pagesPs3 SolutionBruno OliveiraNo ratings yet
- Unified Council Unified Council: National Level Science Talent Search ExaminationDocument8 pagesUnified Council Unified Council: National Level Science Talent Search ExaminationNeha RapartiwarNo ratings yet
- BEM theory for calculating wind turbine performanceDocument6 pagesBEM theory for calculating wind turbine performanceDanial KhanNo ratings yet
- Jncm2e Ws 3b07a eDocument8 pagesJncm2e Ws 3b07a eChan Wai KuenNo ratings yet
- Jncm2e Ws 3b07b eDocument7 pagesJncm2e Ws 3b07b eChan Wai KuenNo ratings yet
- Jncm2e Ws 3b07a Sol eDocument3 pagesJncm2e Ws 3b07a Sol eChan Wai KuenNo ratings yet
- Directed Numbers and The Number LineDocument3 pagesDirected Numbers and The Number LineChan Wai KuenNo ratings yet
- Mark Dyczkowski and Trika Journal March 2015 Vol.1.No.1.Document10 pagesMark Dyczkowski and Trika Journal March 2015 Vol.1.No.1.Mark Dyczkoswki and Trika Journal100% (2)
- T2-1 MS PDFDocument27 pagesT2-1 MS PDFManav NairNo ratings yet
- G.raju Reddy Resume (PDF1) PDFDocument3 pagesG.raju Reddy Resume (PDF1) PDFanon_708469687No ratings yet
- Acrogym: by Ahana AnandDocument9 pagesAcrogym: by Ahana AnandAhana AnandNo ratings yet
- Signals and Systems Analysis: NET 351 Instructor: Dr. Amer El-Khairy يريخلا &رماع .دDocument44 pagesSignals and Systems Analysis: NET 351 Instructor: Dr. Amer El-Khairy يريخلا &رماع .دمصعب جاسمNo ratings yet
- The Dogon Tribe of The Sirius MysteryDocument5 pagesThe Dogon Tribe of The Sirius MysteryLaron Clark100% (1)
- Price Action - Japanese Candlestick Patterns SheetDocument4 pagesPrice Action - Japanese Candlestick Patterns SheetVicaas VSNo ratings yet
- Mental Status Examination FormatDocument7 pagesMental Status Examination FormatMala Rasaily100% (3)
- F2 IS Exam 1 (15-16)Document10 pagesF2 IS Exam 1 (15-16)羅天佑No ratings yet
- LogDocument15 pagesLogandrew_hm925635No ratings yet
- A Rite of SpringDocument10 pagesA Rite of SpringLucius Gregory MeredithNo ratings yet
- 02.casebook - BLDG Repairs & Maint - Chapter 1 - 2011 (Water Seepage)Document13 pages02.casebook - BLDG Repairs & Maint - Chapter 1 - 2011 (Water Seepage)Hang kong TseNo ratings yet
- Pcit Brochure TemplateDocument2 pagesPcit Brochure Templateapi-370829251No ratings yet
- Omega: Mahdi Alinaghian, Nadia ShokouhiDocument15 pagesOmega: Mahdi Alinaghian, Nadia ShokouhiMohcine ES-SADQINo ratings yet
- Multicolor Fluorochrome Laser Chart PDFDocument1 pageMulticolor Fluorochrome Laser Chart PDFSathish KumarNo ratings yet
- Carbon Disulfide: Hazard SummaryDocument5 pagesCarbon Disulfide: Hazard SummaryAlyssa ZerlinaNo ratings yet
- Boston Globe Article - Jonnie Williams & Frank O'DonnellDocument3 pagesBoston Globe Article - Jonnie Williams & Frank O'DonnellFuzzy PandaNo ratings yet
- Economics of Power GenerationDocument32 pagesEconomics of Power GenerationKimberly Jade VillaganasNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9: Operating SystemsDocument166 pagesChapter 9: Operating SystemsGazzzeeNo ratings yet
- Chapter (3) Simple Stresses in Machine Parts: Design of Machine Elements I (ME-41031)Document80 pagesChapter (3) Simple Stresses in Machine Parts: Design of Machine Elements I (ME-41031)Dr. Aung Ko LattNo ratings yet
- ĐỀ THI HSGDocument13 pagesĐỀ THI HSGahmad amdaNo ratings yet
- S1.4.5.) Datasheet PRESSURE GAUGEDocument3 pagesS1.4.5.) Datasheet PRESSURE GAUGEEkoNo ratings yet
- IM PS Fashion-Business-Digital-Communication-And-Media 3Y Course Pathway MI 04Document7 pagesIM PS Fashion-Business-Digital-Communication-And-Media 3Y Course Pathway MI 04oliwia bujalskaNo ratings yet
- Unit 5: Structural Modelling: Block II: From Analysis To DesignDocument76 pagesUnit 5: Structural Modelling: Block II: From Analysis To DesignPatrick FarahNo ratings yet
- Yingli CS Centrale-Poggiorsini EN 062011-1 PDFDocument2 pagesYingli CS Centrale-Poggiorsini EN 062011-1 PDFZvonko Trajkov100% (1)
- Remote Control Panel (RCP) User'S GuideDocument13 pagesRemote Control Panel (RCP) User'S GuideAdrian PuscasNo ratings yet
- Edited Hydraulics Lecture - Part 2 - OrificesDocument36 pagesEdited Hydraulics Lecture - Part 2 - OrificesVincentNo ratings yet
- Strawberry GenerationDocument2 pagesStrawberry GenerationImat12No ratings yet
- PTR01 21050 90inst PDFDocument40 pagesPTR01 21050 90inst PDFЯн ПавловецNo ratings yet
- Vici Line Card 2015Document14 pagesVici Line Card 2015Argel Linard Francisco MabagaNo ratings yet