Professional Documents
Culture Documents
c3 and c4 Plants
Uploaded by
rexog51551Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
c3 and c4 Plants
Uploaded by
rexog51551Copyright:
Available Formats
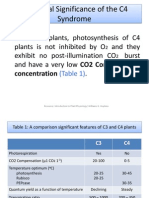
C3 and C4 plants are two distinct types of photosynthetic pathways found in plants:
1. C3 Plants:
o C3 plants include a wide variety of plant species, such as wheat, rice, and most
trees.
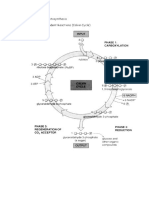
o They use a simple photosynthetic pathway known as the Calvin cycle, which
takes place in the mesophyll cells of the plant's leaves.
o C3 plants have a lower photosynthetic efficiency in high-temperature and high-
light conditions due to a process called photorespiration, which can reduce the
rate of carbon fixation.
2. C4 Plants:
o C4 plants are adapted to hot and arid environments and include species like
maize, sugarcane, and some grasses.
o They use a more complex photosynthetic pathway that involves both mesophyll
and bundle sheath cells, with an additional intermediate step before the Calvin
cycle.
o C4 plants have a higher photosynthetic efficiency and are better suited to high-
temperature and high-light conditions. They exhibit reduced photorespiration.
3. Differences Between C3 and C4 Plants:
a. Carbon Fixation:
o One of the fundamental differences between C3 and C4 plants is how they fix
carbon dioxide during photosynthesis. In C3 plants, carbon dioxide is initially
fixed into a three-carbon compound (3-phosphoglycerate) in the Calvin cycle. In
contrast, C4 plants initially fix carbon dioxide into a four-carbon compound
(oxaloacetate) in the mesophyll cells.
b. Leaf Anatomy:
o C3 plants typically have thinner leaves with a well-developed spongy mesophyll
layer. In contrast, C4 plants have thicker leaves with distinct mesophyll and
bundle sheath cells. This specialized leaf anatomy helps C4 plants optimize
carbon fixation and reduce photorespiration.
c. Photorespiration:
oPhotorespiration is a wasteful process where oxygen competes with carbon
dioxide in the Calvin cycle, leading to reduced photosynthetic efficiency. C4
plants have a mechanism to minimize photorespiration, making them more
efficient in conserving water and nutrients.
4. Advantages of C3 and C4 Pathways:
a. C3 Plant Advantages:
o C3 plants are well-suited to moderate temperature and light conditions.
o They are more widespread globally and include many important crop species.
b. C4 Plant Advantages:
o C4 plants are highly efficient in hot and dry environments, making them suitable
for regions with limited water availability.
o They exhibit higher rates of photosynthesis and biomass production in high-
temperature and high-light conditions.
5. Ecological Significance:
o The distribution of C3 and C4 plants can significantly impact ecosystems and
global carbon cycling. C3 plants are prevalent in temperate regions, while C4
plants dominate in tropical and subtropical areas. Understanding their distribution
helps in modeling the effects of climate change on vegetation patterns.
6. Agricultural Implications:
o Knowledge of C3 and C4 photosynthetic pathways is crucial in agriculture. Crops
like maize (C4) have a competitive advantage in hot climates, while wheat (C3)
thrives in cooler regions. This knowledge informs crop selection and breeding for
specific environments.
7. Conclusion:
o In conclusion, C3 and C4 plants represent two distinct photosynthetic pathways
with unique adaptations to different environmental conditions. Understanding
these pathways is vital for both ecological and agricultural research, as it helps us
comprehend the diverse plant responses to changing climate and optimize crop
production.
You might also like
- Advantages and Disadvantages of C4 Plant PhotosynthesisDocument5 pagesAdvantages and Disadvantages of C4 Plant PhotosynthesisAhsan Raza100% (1)
- Chapter9 Photosynthesis Physiological and Ecological ConsiderationsDocument35 pagesChapter9 Photosynthesis Physiological and Ecological ConsiderationsLandau2016100% (1)
- Andleeb DanishDocument11 pagesAndleeb DanishFareesa AmeerNo ratings yet
- C4 Photosynthesis: How It Works to Minimize PhotorespirationDocument5 pagesC4 Photosynthesis: How It Works to Minimize PhotorespirationErvin Ade PrasetyoNo ratings yet
- Fotosintesis en Especies C4 No TipicasDocument31 pagesFotosintesis en Especies C4 No TipicasFelipe MontejoNo ratings yet
- Content Paper For C3 and C4 PlantsDocument3 pagesContent Paper For C3 and C4 PlantsHazel Love AlforqueNo ratings yet
- Fotosintesis en Diferentes Partes de La PlantaDocument20 pagesFotosintesis en Diferentes Partes de La PlantaFelipe MontejoNo ratings yet
- C4 PlantsDocument4 pagesC4 PlantsIsidro ChanNo ratings yet
- Types of PhotosyntheseDocument6 pagesTypes of PhotosyntheseZain ul abdin QureshiNo ratings yet
- C3 C4 CAM Pathway P1Document2 pagesC3 C4 CAM Pathway P1gundappa bargalleNo ratings yet
- R NaveDocument1 pageR NaveBereket YitayawNo ratings yet
- Carbon Fixation Teacher NotesDocument2 pagesCarbon Fixation Teacher NotesLesley BoultonNo ratings yet
- Energy Variations PracticeDocument3 pagesEnergy Variations Practiceapi-522847737No ratings yet
- c3 and c4 PlantDocument13 pagesc3 and c4 PlantWaseem HaiderNo ratings yet
- Cam PathwayDocument22 pagesCam PathwayRanu MondalNo ratings yet
- CRPSCI 1100-Module5Document14 pagesCRPSCI 1100-Module5carbonel.carlaNo ratings yet
- Photorespiration: Bundle Sheath CellsDocument1 pagePhotorespiration: Bundle Sheath Cellsapi-296833859No ratings yet
- How Plants Respond to Environmental FactorsDocument33 pagesHow Plants Respond to Environmental FactorsnuningNo ratings yet
- Coping With Environmental Variation: EnergyDocument4 pagesCoping With Environmental Variation: EnergyKim CaelianNo ratings yet
- Photosynthetic Pathways 9Document8 pagesPhotosynthetic Pathways 9Nathaly Mendoza MorenoNo ratings yet
- Exercise Questions Page Number - 224-225: NCERT Solution For Class 11 Biology Chapter 13 Photosynthesis in Higher PlantsDocument4 pagesExercise Questions Page Number - 224-225: NCERT Solution For Class 11 Biology Chapter 13 Photosynthesis in Higher PlantsGuni GuptaNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis: Light to Chemical EnergyDocument3 pagesPhotosynthesis: Light to Chemical EnergyLiquartervoisNo ratings yet
- c4 and Cam PlantsDocument34 pagesc4 and Cam PlantsOxman BhattiNo ratings yet
- Punam Jaiswal Sem-IV Primary Production Process in c3, c4 and Cam Plants (Part C) - Organized - RepairedDocument2 pagesPunam Jaiswal Sem-IV Primary Production Process in c3, c4 and Cam Plants (Part C) - Organized - Repairedمحمد الجبوريNo ratings yet
- Day 5 Cam, C3, C4Document50 pagesDay 5 Cam, C3, C4Bruh MomentNo ratings yet
- Ecological SignificanceDocument19 pagesEcological SignificanceJauha HanafiNo ratings yet
- A Better Quality Forage To The 1972) .: 811I1TlcliDocument55 pagesA Better Quality Forage To The 1972) .: 811I1TlcliWalen JosefNo ratings yet
- Biology 3460 - Plant Physiology - Lab Exercise 4 Leaf Structure: Comparison of C & C Plants and Sun-& Shade-Grown Plants ObjectivesDocument4 pagesBiology 3460 - Plant Physiology - Lab Exercise 4 Leaf Structure: Comparison of C & C Plants and Sun-& Shade-Grown Plants ObjectivesMalik TAHIRNo ratings yet
- 6 Phys Ecol of c4 Vs c3Document11 pages6 Phys Ecol of c4 Vs c3Guddu MNo ratings yet
- Biology Group WorkDocument3 pagesBiology Group WorkbluejackbroNo ratings yet
- Hatch-Slack Cycle: The C4 Pathway of PhotosynthesisDocument30 pagesHatch-Slack Cycle: The C4 Pathway of PhotosynthesisKalyani SreejithNo ratings yet
- CRSC 1 GUIDE QUESTIONS FOR CHAPTER 4Document5 pagesCRSC 1 GUIDE QUESTIONS FOR CHAPTER 4RanielJohn CollantesNo ratings yet
- C3 Carbon Fixation: Key Photosynthesis ProcessDocument8 pagesC3 Carbon Fixation: Key Photosynthesis ProcessBashiir NuurNo ratings yet
- Crop Ecology - Productivity and Management in Agricultural Systems - (2011) Queensland Recomendation-275-295Document21 pagesCrop Ecology - Productivity and Management in Agricultural Systems - (2011) Queensland Recomendation-275-295CarolinaNo ratings yet
- Revision Chapter 6 Photosynthesis (Calvin Cycle)Document6 pagesRevision Chapter 6 Photosynthesis (Calvin Cycle)MOHAMAD SAHIMI BIN MAHAT MoeNo ratings yet
- C3 C4 CAM Photosynthesis VariationsDocument20 pagesC3 C4 CAM Photosynthesis VariationsKoons KoonsNo ratings yet
- Plants and Environment Factors - The PlantDocument33 pagesPlants and Environment Factors - The PlantRania PrastiwiNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis Study Material C4 Cycle OnwardsDocument6 pagesPhotosynthesis Study Material C4 Cycle OnwardsmoonyNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis (KEY)Document6 pagesPhotosynthesis (KEY)kylevNo ratings yet
- PhotosynthesisDocument5 pagesPhotosynthesisbluemonkeymei4921100% (1)
- Carbon Fixation Activity SheetDocument2 pagesCarbon Fixation Activity SheetLesley BoultonNo ratings yet
- Chloroplast: Structure, Function and InhibitorsDocument83 pagesChloroplast: Structure, Function and InhibitorsRaissa P. RebatoNo ratings yet
- SBC Chap 7.4 - 7.5Document21 pagesSBC Chap 7.4 - 7.5Salwa ZakariaNo ratings yet
- CO2 Concentrating MechanismDocument2 pagesCO2 Concentrating MechanismAzhar Ud Din AzadNo ratings yet
- B4 Respiration LessonDocument28 pagesB4 Respiration LessonHai Anh LeNo ratings yet
- What Is The Difference Between C3 Plants and C4 PlantsDocument1 pageWhat Is The Difference Between C3 Plants and C4 PlantsANGGI RINTA APRILIANDININo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis Types C3 C4 CAMDocument2 pagesPhotosynthesis Types C3 C4 CAMRicardo Manuel Ventura Tito AstoNo ratings yet
- Plant Photosynthesis and Symbiotic AdaptationsDocument21 pagesPlant Photosynthesis and Symbiotic AdaptationsSheelendra Mangal BhattNo ratings yet
- Factors Affecting Photosynthesis in CropsDocument26 pagesFactors Affecting Photosynthesis in CropsAlthea DoradoNo ratings yet
- Sweet Sorghum ( Sorghum Bicolor (L.) Moench) Bioenergy Value - Importance For PortugalDocument8 pagesSweet Sorghum ( Sorghum Bicolor (L.) Moench) Bioenergy Value - Importance For PortugalMaryam AsdNo ratings yet
- Full Stress Froid RubiscoDocument12 pagesFull Stress Froid RubiscoQuentin MauriceNo ratings yet
- Energy in The Biosphere: Photosynthesis (& Respiration)Document22 pagesEnergy in The Biosphere: Photosynthesis (& Respiration)Prikshit HoodaNo ratings yet
- AQA GCSE Biology - Unit 2 Summary NotesDocument5 pagesAQA GCSE Biology - Unit 2 Summary NotesRajashree MuNo ratings yet
- Comparing and Contrasting C3, C4, CAM - AP BiologyDocument1 pageComparing and Contrasting C3, C4, CAM - AP BiologyFVCproductionsNo ratings yet
- 4.4 How Do Plants Produce Food ReadingDocument2 pages4.4 How Do Plants Produce Food ReadingDanica FelicesNo ratings yet
- PhotosynthesisDocument37 pagesPhotosynthesisibrahimgrewallNo ratings yet
- RENEWABLE ENERGY CROP SPECIESDocument6 pagesRENEWABLE ENERGY CROP SPECIESyemresimsekNo ratings yet
- 9B Quiz ANSDocument3 pages9B Quiz ANScalebNo ratings yet
- Photorespiration C3 PlantsDocument18 pagesPhotorespiration C3 Plantslady ann apple colipanoNo ratings yet
- Progress in Phytochemistry: Volume 6From EverandProgress in Phytochemistry: Volume 6L. ReinholdNo ratings yet
- Uncorrected Manuscript: Efficacy and Safety of COVID-19 Vaccines in Older PeopleDocument9 pagesUncorrected Manuscript: Efficacy and Safety of COVID-19 Vaccines in Older PeopleKiky HaryantariNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Cells Development Biodiversity and ConservationDocument47 pagesUnit 2 Cells Development Biodiversity and ConservationKevir Man100% (1)
- BUITEMS Sensation and Perception DocumentDocument6 pagesBUITEMS Sensation and Perception DocumentAleksandarNo ratings yet
- Anatomy CheckpointDocument8 pagesAnatomy CheckpointPrinces Jecyvhel De LeonNo ratings yet
- Enzyme Activity Lab Report - IB BiologyDocument15 pagesEnzyme Activity Lab Report - IB BiologyNada SalmanNo ratings yet
- Package: Catalog No. SizeDocument3 pagesPackage: Catalog No. SizeHairul IslamNo ratings yet
- Osmosis Virtual LabDocument2 pagesOsmosis Virtual Labapi-33857887483% (6)
- Pex 03 03Document7 pagesPex 03 03Jila Hafizi100% (1)
- BCH 5425 Molecular Biology and Biotechnology Exam QuestionsDocument11 pagesBCH 5425 Molecular Biology and Biotechnology Exam QuestionsAniruddha RoyNo ratings yet
- Geneva College Beaver Falls, PA Lesson Plan TemplateDocument3 pagesGeneva College Beaver Falls, PA Lesson Plan Templateapi-545176468No ratings yet
- Daftar Pustaka PDFDocument5 pagesDaftar Pustaka PDFNeneng AlifiaNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic ModelingDocument33 pagesIntroduction to Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic ModelingDrAmit VermaNo ratings yet
- Biology 1sec SB E 2014 PDFDocument156 pagesBiology 1sec SB E 2014 PDFAnonymous tdtTl8KypNo ratings yet
- Gene Regulation in Prokaryotes-1Document17 pagesGene Regulation in Prokaryotes-1Fasiha Mushadi100% (1)
- Alcoholic Liver Disease: Pathogenesis and Current ManagementDocument15 pagesAlcoholic Liver Disease: Pathogenesis and Current ManagementRahelin KidoNo ratings yet
- GPAT Past Paper 2007Document10 pagesGPAT Past Paper 2007Cosmic CreatureNo ratings yet
- Practice Worksheet: Fundamental Unit of LifeDocument2 pagesPractice Worksheet: Fundamental Unit of LifeDharmendra SinghNo ratings yet
- General Pharmacology) 343 (Document28 pagesGeneral Pharmacology) 343 (ALNAKI100% (1)
- Rattan 2010Document8 pagesRattan 2010Bere GarcíaNo ratings yet
- BMC Evol BiolDocument17 pagesBMC Evol BiolStacy JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Lab 4 Protein SolubilityDocument9 pagesLab 4 Protein Solubilityapi-249635202No ratings yet
- Cell Processes and MaintenanceDocument9 pagesCell Processes and MaintenanceJennifer ShabaNo ratings yet
- Investigating conditions for producing nata-de-coco bacterial celluloseDocument6 pagesInvestigating conditions for producing nata-de-coco bacterial celluloseMAE ANGELESNo ratings yet
- Cell Membrane TransportDocument3 pagesCell Membrane TransportHarry TeasdaleNo ratings yet
- LO: To Understand The Use of Genetic Screening and The Issues RelatedDocument22 pagesLO: To Understand The Use of Genetic Screening and The Issues RelatedKevir ManNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Vert Phys Students)Document76 pagesChapter 5 Vert Phys Students)Kertayvia Yepwekan HarrisNo ratings yet
- Parent: Biological vs. Non-Biological ParentageDocument3 pagesParent: Biological vs. Non-Biological ParentagekarthikeyanNo ratings yet
- Hydropericardium SyndromeDocument22 pagesHydropericardium SyndromeSumit JyotiNo ratings yet
- The Effects of Cell Structure On Function Lab ExperimentDocument3 pagesThe Effects of Cell Structure On Function Lab ExperimentRio Ruby LloviaNo ratings yet
- The Fundamental Unit of LifeDocument137 pagesThe Fundamental Unit of LifeSudarshan S KNo ratings yet