Professional Documents
Culture Documents
C3 C4 CAM Pathway P1
Uploaded by
gundappa bargalleCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
C3 C4 CAM Pathway P1
Uploaded by
gundappa bargalleCopyright:
Available Formats
Environment, Ecology and
Biodiversity Series – Simplifying for
Civil Services Exams P1
CONCEPTUALISED, COMPILED AND WRITTEN BY AKSHAY VRAT (TO BE SUPPLEMENTED WITH CLASS
DISCUSSIONS)
C3 C4 and CAM PATHWAY PHOTOSYNTHETIC ADAPTATIONS
• Photosynthesis is the most important chemical reaction on Earth. It sets the basis for all aerobic life of
Earth.
• The Photosynthesis process requires CO2 + H2O and Sunlight that is converted into Biomass in the form of
Glucose (Carbohydrate/ Biomass) and releases Oxygen as a residue.
• The process of photosynthesis is divided into two reactions i.e. Light Reaction and Dark Reaction.
• Light reaction happens in presence of Sunlight with the help of Chlorophyll pigment. Here Sun’s energy is
converted in to a chemical energy inside the leaves in the forms chemical compounds similar to ATP.
• Dark reaction also known as Calvin Cycle is triggered after the Light Reaction in which Biomass is
produced by absorption of CO2 and H2O. This reaction depends surrounding Temperature. Remember
the actual carbohydrate formation happens in the Dark reaction.
• Thus the photosynthetic process depends on surrounding temperature and humidity. This is due to varied
climatic regions on Earth. For e.g., the availability of water in Desert compared to Rainforest is different
thus plants found in these regions must adapt with certain changes in their photosynthetic processes.
• C3 C4 and CAM Pathways are different photosynthetic adaptations in plants depending on their climatic
conditions.
• Here the dark reaction happens during the day time.
• It is called C3 simply because it forms a 3 carbon compound first while making
Carbohydrates in the Dark reaction. But from Environmental Science (UPSC)
perspective it is not very relevant.
• Found in more than 90% plants on earth. Mostly prevalent in areas of low to high
temperature and wet conditions. Although its Photosynthetic efficiency decreases
with increase in temperature.
• Here the Stomata remains open throughout the Day. These plants observe an
C3 Pathway increase in productivity during an increase in Atmospheric CO2 concentrations.
• As the Stomata remains open, its photosynthetic efficiency is poor due to high rate
of photorespiration of Carbohydrates and it also keeps losing H2O through
transpiratory losses.
• E.g., of C3 Plants: Wheat, Rye, Oats, Rice, Cotton, Sunflower, Soybean.
• Impact of Climate change is evident on them due to increase in temperature and
decline in surface moisture levels.
• P.S.: from the context of Biological Sciences C3 Pathways shall require a detailed
discussion which may not be needed for the subject of Ecology. Also the Stomata
technically never fully closes.
GENERAL SCIENCE CONCEPTUALISED, COMPILED AND WRITTEN BY AKSHAY VRAT 1
ENVIRONMENT ECOLOGY AND BIODIVERSITY SERIES - SIMPLIFYING FOR CSE
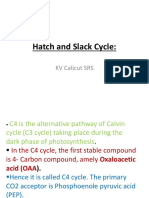
• It is another type of photosynthetic adaptation. Named C4 for the same reason i.e.
a 4 Carbon compound is formed during the Dark reaction.
• C4 plants are found in hot, dry conditions and can fix CO2 more efficiently than C3
plants under these conditions.
C4 Pathway • Here the Stomata opens in the day time but only for limited duration to absorb
CO2 which reduces the rate of photorespiration, increases their efficiency at fixing
CO2 and reduces transpiratory water loss.
• C4 plants are better tolerant to drought and high temperatures than C3 plants,
which allows them to grow well in hot, dry regions.
• E.g., Maize, Sorghum, Sugarcane, Millet.
• CAM or crassulacean acid metabolism (CAM) pathway is another specialised
Photosynthetic adaptation. Dark reaction happens at Night.
• CAM plants are adapted to arid conditions and can fix CO2 at night, when the
stomata are open and atmospheric CO2 concentrations are higher.
CAM Pathway
• It can conserve water by opening their stomata at night (Skotoactive) and closing
them during the day to reduce water loss through transpiration.
• It has better tolerance to dry and hot conditions than C3 and C4 plants.
• E.g. Pineapple, Pipal, Neem, Cactus, Areca palm.
GENERAL SCIENCE CONCEPTUALISED, COMPILED AND WRITTEN BY AKSHAY VRAT 2
You might also like
- C3, C4 and CAM PlantsDocument4 pagesC3, C4 and CAM PlantsJohn DavenportNo ratings yet
- Advantages and Disadvantages of C4 Plant PhotosynthesisDocument5 pagesAdvantages and Disadvantages of C4 Plant PhotosynthesisAhsan Raza100% (1)
- Chapter9 Photosynthesis Physiological and Ecological ConsiderationsDocument35 pagesChapter9 Photosynthesis Physiological and Ecological ConsiderationsLandau2016100% (1)
- Energy RevisionDocument28 pagesEnergy Revisionapi-407286530100% (2)
- AP Biology Chapter 8 Test ReviewDocument22 pagesAP Biology Chapter 8 Test ReviewMr. IntelNo ratings yet
- PhotosynthesisDocument5 pagesPhotosynthesisbluemonkeymei4921100% (1)
- C3 C4 CAM Photosynthesis VariationsDocument20 pagesC3 C4 CAM Photosynthesis VariationsKoons KoonsNo ratings yet
- Ecological SignificanceDocument19 pagesEcological SignificanceJauha HanafiNo ratings yet
- c4 and Cam PlantsDocument34 pagesc4 and Cam PlantsOxman BhattiNo ratings yet
- Cam PathwayDocument22 pagesCam PathwayRanu MondalNo ratings yet
- CAM Photosynthesis: How Plants Adapt to Arid ConditionsDocument9 pagesCAM Photosynthesis: How Plants Adapt to Arid ConditionsAtika ZulfiqarNo ratings yet
- Day 5 Cam, C3, C4Document50 pagesDay 5 Cam, C3, C4Bruh MomentNo ratings yet
- c3 and c4 PlantsDocument2 pagesc3 and c4 Plantsrexog51551No ratings yet
- Plant Biochemistry Presentation .... Asmat AraDocument12 pagesPlant Biochemistry Presentation .... Asmat Arachurail khanNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis C4 CAMDocument17 pagesPhotosynthesis C4 CAMDeborah EckhardtNo ratings yet
- C4 Photosynthesis: How It Works to Minimize PhotorespirationDocument5 pagesC4 Photosynthesis: How It Works to Minimize PhotorespirationErvin Ade PrasetyoNo ratings yet
- Carbon Fixation Teacher NotesDocument2 pagesCarbon Fixation Teacher NotesLesley BoultonNo ratings yet
- Andleeb DanishDocument11 pagesAndleeb DanishFareesa AmeerNo ratings yet
- Types of PhotosyntheseDocument6 pagesTypes of PhotosyntheseZain ul abdin QureshiNo ratings yet
- Photo Bio ChemDocument63 pagesPhoto Bio ChemJorge Munoz SotoNo ratings yet
- CAM Plants Fix CO2 at NightDocument22 pagesCAM Plants Fix CO2 at NightvijendNo ratings yet
- Energy Variations PracticeDocument3 pagesEnergy Variations Practiceapi-522847737No ratings yet
- BIF03 Satellite Tutorial WK 3Document33 pagesBIF03 Satellite Tutorial WK 3Benjamin SamaniNo ratings yet
- Alternative PathwaysDocument7 pagesAlternative PathwaysKHANSANo ratings yet
- Lesson+Check+Answer+Key PhotosynthesisDocument1 pageLesson+Check+Answer+Key PhotosynthesisZaina Nasser0% (1)
- Hatch-Slack Cycle: The C4 Pathway of PhotosynthesisDocument30 pagesHatch-Slack Cycle: The C4 Pathway of PhotosynthesisKalyani SreejithNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis: Alternative Methods of Carbon Fixation in Hot, Arid ClimatesDocument29 pagesPhotosynthesis: Alternative Methods of Carbon Fixation in Hot, Arid Climatessreetama100% (1)
- C4 and CAM Photosynthesis Adaptations Prevent PhotorespirationDocument2 pagesC4 and CAM Photosynthesis Adaptations Prevent PhotorespirationElijah IbsaNo ratings yet
- 6 Phys Ecol of c4 Vs c3Document11 pages6 Phys Ecol of c4 Vs c3Guddu MNo ratings yet
- PhotosynthesisDocument20 pagesPhotosynthesisVinch Samuel AchacosoNo ratings yet
- Photorespiration C3 PlantsDocument18 pagesPhotorespiration C3 Plantslady ann apple colipanoNo ratings yet
- Discussion of C3, C4, and CAM PhotosynthesisDocument2 pagesDiscussion of C3, C4, and CAM Photosynthesiswaqas bhatti00No ratings yet
- Comparing and Contrasting C3, C4, CAM - AP BiologyDocument1 pageComparing and Contrasting C3, C4, CAM - AP BiologyFVCproductionsNo ratings yet
- Alternative Pathways PowerpointDocument5 pagesAlternative Pathways Powerpointapi-418176886No ratings yet
- Photosynthetic Pathways 9Document8 pagesPhotosynthetic Pathways 9Nathaly Mendoza MorenoNo ratings yet
- PHOTOSYNTHESIS PATHWAYS - rePORTDocument22 pagesPHOTOSYNTHESIS PATHWAYS - rePORTGarry Michael Tarroma SarmientoNo ratings yet
- Climate Change ExplainedDocument74 pagesClimate Change ExplainedangelikaNo ratings yet
- Issues faced by environment and climate changeDocument23 pagesIssues faced by environment and climate changeM. Vadivel MURUGESANNo ratings yet
- Carbon Sequestration Methods Using Plants and MicroalgaeDocument15 pagesCarbon Sequestration Methods Using Plants and Microalgaesarathirv6No ratings yet
- CAM photosynthesis allows plants to thrive in arid conditionsDocument52 pagesCAM photosynthesis allows plants to thrive in arid conditionsBashiir NuurNo ratings yet
- c6 Abiotic ComponentsDocument37 pagesc6 Abiotic Componentsapi-386303659No ratings yet
- Carbonate FactoryDocument50 pagesCarbonate FactoryRizky Farlyan100% (3)
- Cam PathwayDocument7 pagesCam PathwayMelanie CabforoNo ratings yet
- Photorespiration: Bundle Sheath CellsDocument1 pagePhotorespiration: Bundle Sheath Cellsapi-296833859No ratings yet
- Carbon Assimilation: Sunidhi Verma Roll No.-607Document13 pagesCarbon Assimilation: Sunidhi Verma Roll No.-607sunidhi vermaNo ratings yet
- 7 Gr. 11 Life Sciences Remote Learning Booklet Term 4Document25 pages7 Gr. 11 Life Sciences Remote Learning Booklet Term 4popslilly41No ratings yet
- Royalbotanicgardensedinburghadaptationcasestudy PDFDocument2 pagesRoyalbotanicgardensedinburghadaptationcasestudy PDFPedro LuisNo ratings yet
- 2-Input Carbon Dalam PSFDocument23 pages2-Input Carbon Dalam PSFNahdiyaNo ratings yet
- Effects of Temperature On Photosynthesis Encyclopedie EnvironnementDocument15 pagesEffects of Temperature On Photosynthesis Encyclopedie EnvironnementCristina StanNo ratings yet
- BioGeoChemical CycleDocument35 pagesBioGeoChemical Cycleacheron_pNo ratings yet
- Week 16 17 Climate Change and Impacts To SocietyDocument59 pagesWeek 16 17 Climate Change and Impacts To SocietyLouise San BuenaventuraNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes 6Document38 pagesLecture Notes 6Marvin JeaNo ratings yet
- Hibernation EstivationDocument9 pagesHibernation EstivationSankar CobNo ratings yet
- R NaveDocument1 pageR NaveBereket YitayawNo ratings yet
- Class 5 Biological SequestrationDocument31 pagesClass 5 Biological SequestrationYash ChorariaNo ratings yet
- C3, C4, and CAM Plant CyclesDocument3 pagesC3, C4, and CAM Plant Cyclesf l o u n d e rNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis NotesDocument18 pagesPhotosynthesis NotesFranchez Cassandra EscanderNo ratings yet
- Xerophytic Plants and Their AdaptationsDocument56 pagesXerophytic Plants and Their AdaptationsMuzzAm Mil100% (1)
- EvsswagatDocument17 pagesEvsswagatSwagat LunawatNo ratings yet
- Crop Ecology - Productivity and Management in Agricultural Systems - (2011) Queensland Recomendation-275-295Document21 pagesCrop Ecology - Productivity and Management in Agricultural Systems - (2011) Queensland Recomendation-275-295CarolinaNo ratings yet
- Global Warming and the Power of Garbage - A Radical Concept for Cost-Effective CO2 ReductionFrom EverandGlobal Warming and the Power of Garbage - A Radical Concept for Cost-Effective CO2 ReductionNo ratings yet
- ChloroplastDocument3 pagesChloroplastdrug123addict25No ratings yet
- Photosynthesis CompressedDocument7 pagesPhotosynthesis Compressedsatwikdasmahapatra667No ratings yet
- Photosynthesis: Rafia Urooj Saman 2020-Ag-937Document18 pagesPhotosynthesis: Rafia Urooj Saman 2020-Ag-937Rafya ShabbirNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis Topic 13 A Level Biology Classified Past Papers 2010-2019Document88 pagesPhotosynthesis Topic 13 A Level Biology Classified Past Papers 2010-2019ADEEL AHMADNo ratings yet
- Light Reaction ReflectionDocument2 pagesLight Reaction ReflectionMARK BRIAN FLORESNo ratings yet
- 2 Semester Final Exam (2009A.Y.) Grade 11 Subject: Biology Time: 1:10 Mark: 40%Document5 pages2 Semester Final Exam (2009A.Y.) Grade 11 Subject: Biology Time: 1:10 Mark: 40%Nahom GarefoNo ratings yet
- Photosynthetic Processes: Chlorophyll and PigmentsDocument5 pagesPhotosynthetic Processes: Chlorophyll and PigmentsLyka LigsonNo ratings yet
- CALVIN CycleDocument13 pagesCALVIN CycleDaphne CuaresmaNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis in Higher Plants - Shobhit NirwanDocument21 pagesPhotosynthesis in Higher Plants - Shobhit NirwanVraj M Barot100% (1)
- Cell and Molecular Biology Concepts and Experiments 7th Edition Karp Test Bank DownloadDocument37 pagesCell and Molecular Biology Concepts and Experiments 7th Edition Karp Test Bank DownloadBen Flott100% (21)
- Chloroplasts and Chlorophyll T5-3Document4 pagesChloroplasts and Chlorophyll T5-3Kyile FernandoNo ratings yet
- The Hill RXN in Isolated Chloroplasts PostDocument12 pagesThe Hill RXN in Isolated Chloroplasts PostKarina Khan100% (12)
- Plastid SDocument15 pagesPlastid SkavithabommanaNo ratings yet
- HHMI Biointeractive Photosynthesis WSDocument7 pagesHHMI Biointeractive Photosynthesis WSJrNo ratings yet
- L8 9 PhotosynthesisDocument30 pagesL8 9 PhotosynthesisCheng FuNo ratings yet
- CELLULAR ENERGY-g9Document13 pagesCELLULAR ENERGY-g9Maria RosaNo ratings yet
- Calvin Cycle (Dark Reactions / Light Independent Reaction)Document47 pagesCalvin Cycle (Dark Reactions / Light Independent Reaction)L'ya Lieslotte100% (2)
- Chapter 23 - The Calvin Cycle (CO Fixation)Document13 pagesChapter 23 - The Calvin Cycle (CO Fixation)bukundadaNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis: Multiple ChoiceDocument23 pagesPhotosynthesis: Multiple ChoiceValentina RumhizhaNo ratings yet
- CalvinDocument4 pagesCalvinsenjicsNo ratings yet
- H3P2 - Nur Hanani - Lab Report SB025Document6 pagesH3P2 - Nur Hanani - Lab Report SB025Nur HananiNo ratings yet
- Calvin Cycle Reaction of Photosynthesis Reflection PaperDocument1 pageCalvin Cycle Reaction of Photosynthesis Reflection PaperMARK BRIAN FLORESNo ratings yet
- Importance of Hill Reaction in Elucidating Photosynthesis MechanismDocument2 pagesImportance of Hill Reaction in Elucidating Photosynthesis MechanismDarilyn AndresNo ratings yet
- C3 Carbon Fixation: Key Photosynthesis ProcessDocument8 pagesC3 Carbon Fixation: Key Photosynthesis ProcessBashiir NuurNo ratings yet
- The Hill Reaction in Isolated Chloroplasts (Prelab)Document5 pagesThe Hill Reaction in Isolated Chloroplasts (Prelab)viper121No ratings yet
- Photosynthesis Misconceptions Quiz - With AnswersDocument4 pagesPhotosynthesis Misconceptions Quiz - With AnswersJohn Kevin NocheNo ratings yet
- WORKSHEET 6.7 Photosynthesis - Leaf Structure (New)Document4 pagesWORKSHEET 6.7 Photosynthesis - Leaf Structure (New)netiiyah netiiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 Optional HomeworkDocument19 pagesChapter 10 Optional Homeworkcolahmundu100% (7)
- Cell Energy 2013 NotesDocument90 pagesCell Energy 2013 Notesapi-26963416No ratings yet